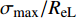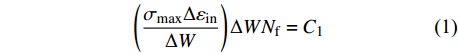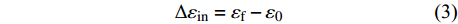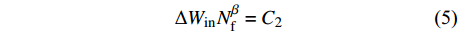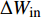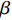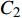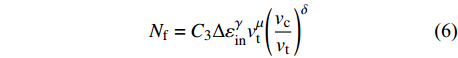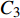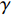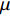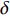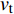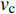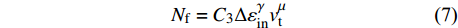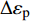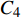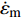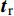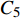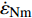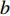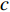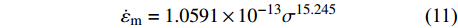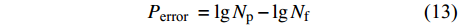Creep-fatigue properties and life prediction method of new martensitic heat resistant steel
-
摘要: 针对P92和G115新型马氏体耐热钢进行了应力控制下蠕变-疲劳性能研究,分析了保载时间和峰值应力对应力控制下蠕变-疲劳性能的影响规律. 结果表明,应力控制下蠕变-疲劳过程中蠕变变形和损伤主导了蠕变-疲劳寿命. 蠕变-疲劳寿命随峰值应力和保载时间的增加而下降,同时相同峰值应力下,G115钢的蠕变-疲劳寿命约是P92钢的8~10倍,但G115钢对峰值应力与保载时间的交互作用更为敏感. 材料高温强度的变化导致G115钢的蠕变-疲劳性能优于P92钢. 针对应力控制下蠕变-疲劳寿命预测,研究了能量法、应变能密度耗竭法、频率分离法和回线能量法等. 并基于应力控制蠕变-疲劳非弹性应变损伤机制,提出了最小循环蠕变速率法和基于纯蠕变的最小蠕变速率法. 结果表明:最小循环蠕变速率法预测精度最高,而基于纯蠕变的最小蠕变速率法对高寿命区预测良好,而低寿命区误差偏大.Abstract: In this paper, the creep-fatigue properties of P92 and G115 new martensitic heat-resistant steels under load control are studied. Influence of dwell time and peak stress on the creep-fatigue properties under load control is analyzed. The results show that the creep-fatigue life decrease with the increase of peak stress and dwell time, and the creep-fatigue life of G115 steel is about 8-10 times that of P92 steel under the same peak stress, but G115 steel is more sensitive to the interaction between peak stress and dwell time. Changes in high temperature strength of materials lead to better creep-fatigue properties of G115 steel than P92 steel. Creep deformation and damage dominate creep-fatigue life during creep-fatigue under load control. For the creep-fatigue life prediction method under load control, the energy method, toughness exhaustion method, frequency separation method and frequency modified tensile hysteresis energy model are studied. Furthermore, based on the mechanism of load controlled creep-fatigue inelastic strain damage, the minimum cyclic creep rate method and the minimum creep rate method based on pure creep are proposed. The results show that the minimum cyclic creep rate model exhibited the highest prediction accuracy, and the method based on the minimum creep rate under pure creep predicts the high-life zone well, but the error in the low-life zone is relatively large.
-
Keywords:
- heat-resistant steel /
- load control /
- creep fatigue /
- life prediction
-
0. 序言
随着绿色能源的发展,火电机组承担调峰任务将成为必然趋势. 现代机组主要采用变负荷运行的方式,可使机组具有深度调峰能力,如两班制运行、频繁启停和变负荷的能力[1]. 深度调峰使得机组关键部件长期在交变载荷和静载荷的共同作用下服役,同时高参数下也会导致锅炉及蒸气管道等部件产生蠕变、疲劳以及两者交互作用下的损伤[2]. 常用蠕变-疲劳测试方法分为应变控制、应力控制和混合控制. 目前多数进行的是应变控制下蠕变-疲劳性能的研究,然而应变控制模式保载期间,由于应力松弛,无法反映蠕变损伤主导下的蠕变-疲劳行为[3]. 混合控制和应力控制下的情况较为复杂,相对研究较少. Tahir和Zhang等人[3-4]研究了在混合控制下的蠕变-疲劳性能,发现在实际运行期间,高温部件可能受到稳定的应力控制或应力-应变混合控制下的蠕变-疲劳载荷. 混合控制中,应力保持的时间依赖损伤比应变保持更具有破坏性. 因此研究应力控制下蠕变-疲劳对高温部件性能以及寿命预测具有重要作用.
蠕变-疲劳寿命预测常用方法有线性累积损伤法、延性耗竭法、能量守恒法、应变能密度耗竭法、应变范围划分法、频率修正法、频率分离法、回线能量法等. 这些方法多数在应变控制模式下被提出,对应变控制下的蠕变-疲劳试验具有较好的适应性,但对应力控制下的蠕变-疲劳寿命预测适用性仍需要进一步的验证和分析[5].
Zhao等人[6]研究发现常规的线性累积损伤准则不能准确评价9%~12% Cr铁素体钢应力控制的蠕变-疲劳寿命. Riedel等人[7]基于晶界空化和微裂纹扩展提出一种适用于任意载荷和温度循环的演化方程模型. 该类方法虽直接与微观机理相连,但应用困难. 郝玉龙[8]根据延性耗竭法,考虑疲劳对蠕变的影响建立寿命预测方程,发现疲劳对蠕变的影响在应力、温度一定的工况下,仅与保载时间有关,且呈二次多项式关系,但该方法仅讨论了保载时间变化所引起的寿命变化关系. Chen等人[9]根据能量动量守恒,提出一种寿命预测模型,对应力控制的1.25Cr0.5Mo钢蠕变-疲劳寿命预测良好. 张力文等人[10]通过试验发现延性耗竭法适用于应力控制的寿命预测,但该方法需要获取循环强度系数、循环应变硬化指数等参数,较为复杂.
以上蠕变-疲劳寿命预测方法对温度和材料特性具有依赖性,通常只适用于特定试验条件与特定材料. 文中研究了新型马氏体耐热钢P92钢和G115钢应力控制下蠕变-疲劳性能,并基于试验结果对不同模型蠕变-疲劳寿命预测可靠性进行了分析;在此基础上,发展了基于耐热钢蠕变性能的蠕变-疲劳寿命预测模型,为高温结构蠕变-疲劳寿命预测提供了新的解决思路.
1. 蠕变-疲劳试验方案
文中研究了应力控制下保载时间和峰值应力对P92 钢和 G115 钢两种马氏体耐热钢蠕变-疲劳性能的影响规律,并对其进行了寿命预测研究. 这两种材料均为高参数超超临界机组和第四代核电候选材料. P92钢主要用于630 ℃以下高温部件,G115钢主要应用于650 ℃以上高温部件[4, 11]. P92钢和G115钢650 ℃下高温拉伸性能测试结果如表1所示,可以看出G115钢高温拉伸性能优于P92钢.
表 1 P92和G115高温拉伸性能Table 1. Tensile properties of P92 and G115 at high temperature材料 温度 T/℃ 屈服强度ReL/MPa 抗拉强度Rm/MPa P92 650 240 261 G115 650 275 288 蠕变-疲劳试样根据标准ASTM E2714-13《Standard Test Method for Creep-Fatigue Testing》设计,采用圆棒试样,直径6 mm,标距20 mm. 蠕变-疲劳试验采用RPL50蠕变-疲劳试验机,试验载荷采用梯形波,在峰值应力添加保载时间模拟蠕变-疲劳载荷工况,应力比固定为R = 0,加载速率恒定为90 kN/min,试验温度为650 ℃ ± 2 ℃. 基于两种材料屈服强度差异,设定了P92钢和G115蠕变-疲劳的试验载荷. 其中P92峰值应力分别为160,180,200,220,240,260 MPa,保载时间为30,60,600,1800,3 600 s;G115峰值应力分别为180,190,210,230,250,270 MPa,保载时间为30,60,600,3 600 s.
2. P92钢和G115钢应力控制蠕变-疲劳性能
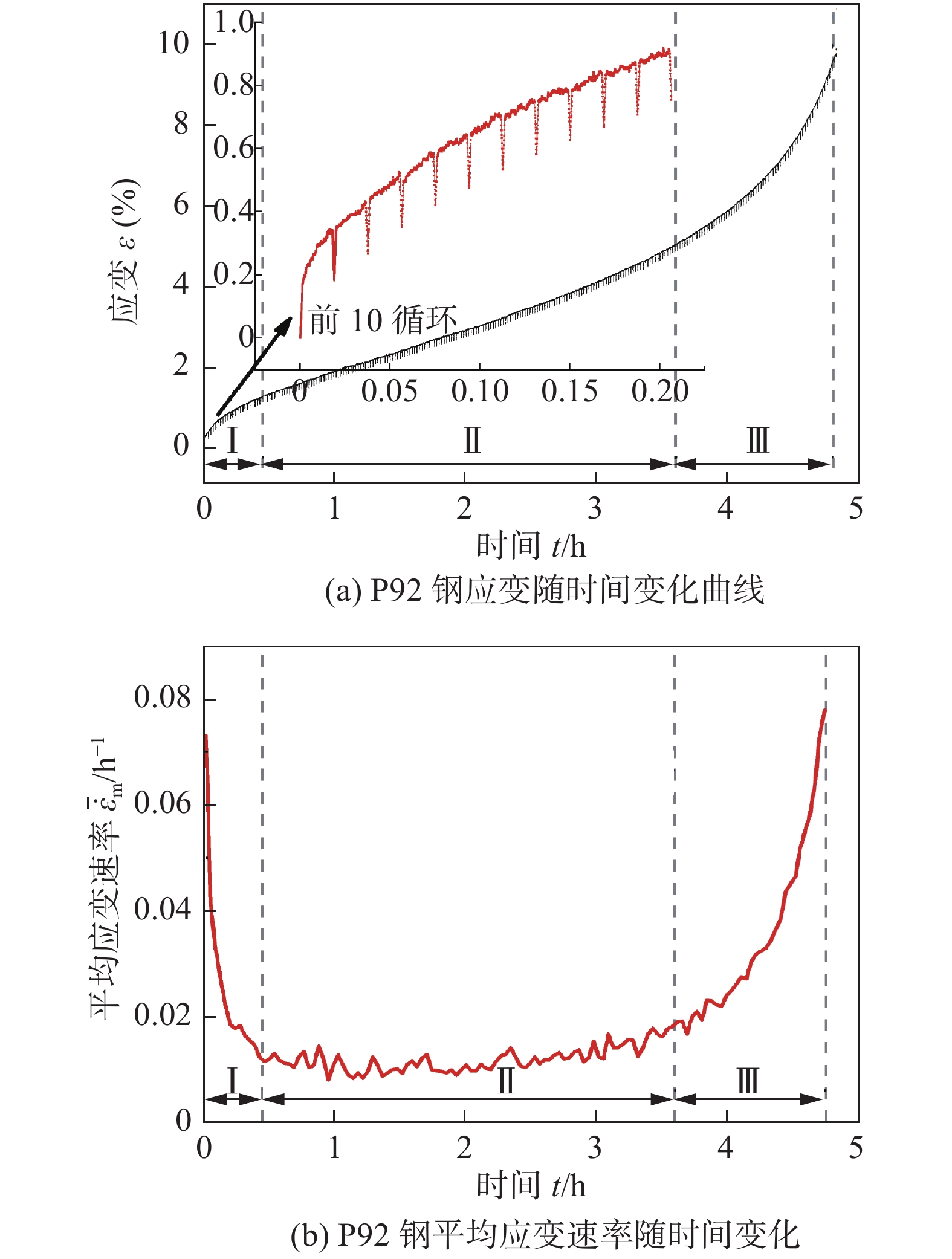
图1a为P92钢蠕变-疲劳前10个循环的应力—应变曲线,图1b为整个蠕变-疲劳过程的有代表性循环的应力—应变关系. 图中试验温度为650 ℃,峰值应力为200 MPa,保载时间60 s. 可以发现加载阶段主要是弹性变形,应变较小;卸载阶段会发生少量的变形回复,变形主要是保载阶段产生的非弹性变形. 随着循环次数增加,非弹性应变先减小随后趋于稳定,再急剧增加,与单轴蠕变下蠕变应变变化趋势相同[12],表明应力控制蠕变-疲劳试验主要由循环蠕变变形主导非弹性应变. 不同于应变控制下保载阶段会发生应力松弛,非弹性应变主要受疲劳循环硬化/软化影响[13]. 此外应力控制下蠕变-疲劳应力应变滞回曲线不稳定、不封闭,循环蠕变现象明显. 这也是现有蠕变-疲劳寿命预测模型无法很好适用于应力控制下蠕变-疲劳模式的原因之一.
图2a为P92钢应力控制下蠕变-疲劳过程中累积应变随时间变化曲线. 在应力控制下蠕变-疲劳过程中应变的增加主要发生在载荷保持阶段(图2a中局部放大图),进一步表明主要是由于循环蠕变变形产生非弹性应变. 应力控制下蠕变-疲劳平均应变速率随时间的变化情况如图2b所示,主要分为3个阶段,与典型蠕变曲线三阶段划分方法一致[12]. 第Ⅰ阶段,非弹性应变速率逐渐降低,由于热激活而立刻产生非弹性应变,并随时间推移,非弹性应变速率逐渐降低;第Ⅱ阶段,非弹性应变速率基本保持恒定,即变形速率稳定阶段,主要是材料加工硬化与原子扩散、析出强化、位错和晶界强化等和损伤累积引起的软化相互作用下的平衡状态;第Ⅲ阶段,非弹性应变速率急剧增大,由于材料开裂或产生内部空洞等,导致应力集中及试样颈缩直至断裂.
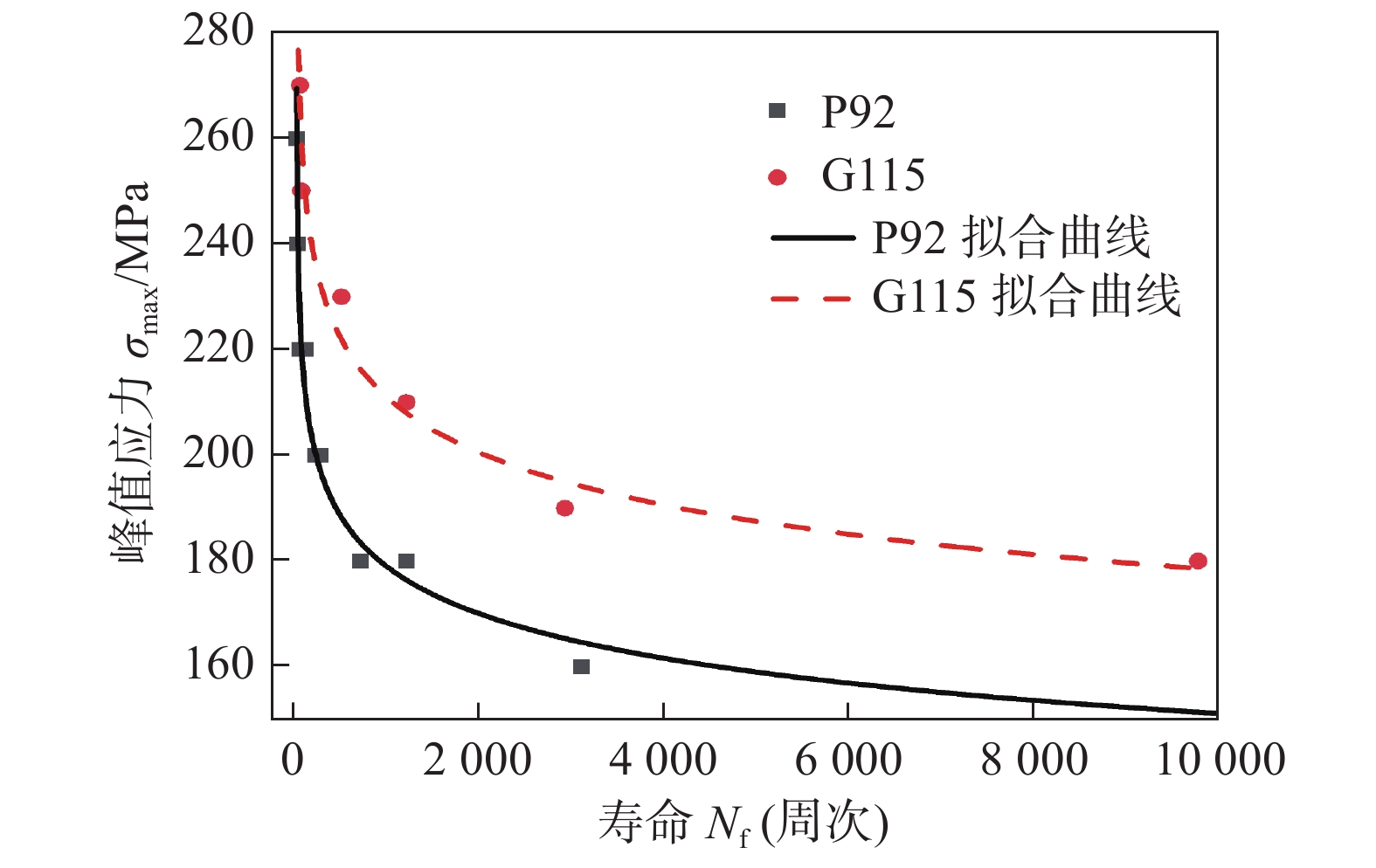
图3对比分析了P92和G115钢不同峰值应力下蠕变-疲劳性能. 随着峰值应力增加,循环断裂寿命Nf呈指数下降趋势,当峰值应力高于一定应力后,寿命大幅降低. 此外G115钢性能明显优于P92钢,在相同峰值应力下,G115钢的蠕变-疲劳寿命约是P92钢的8~10倍.
图4分析了归一化应力下P92钢和G115钢蠕变-疲劳性能. 归一化应力定义为峰值应力与材料屈服强度的比值
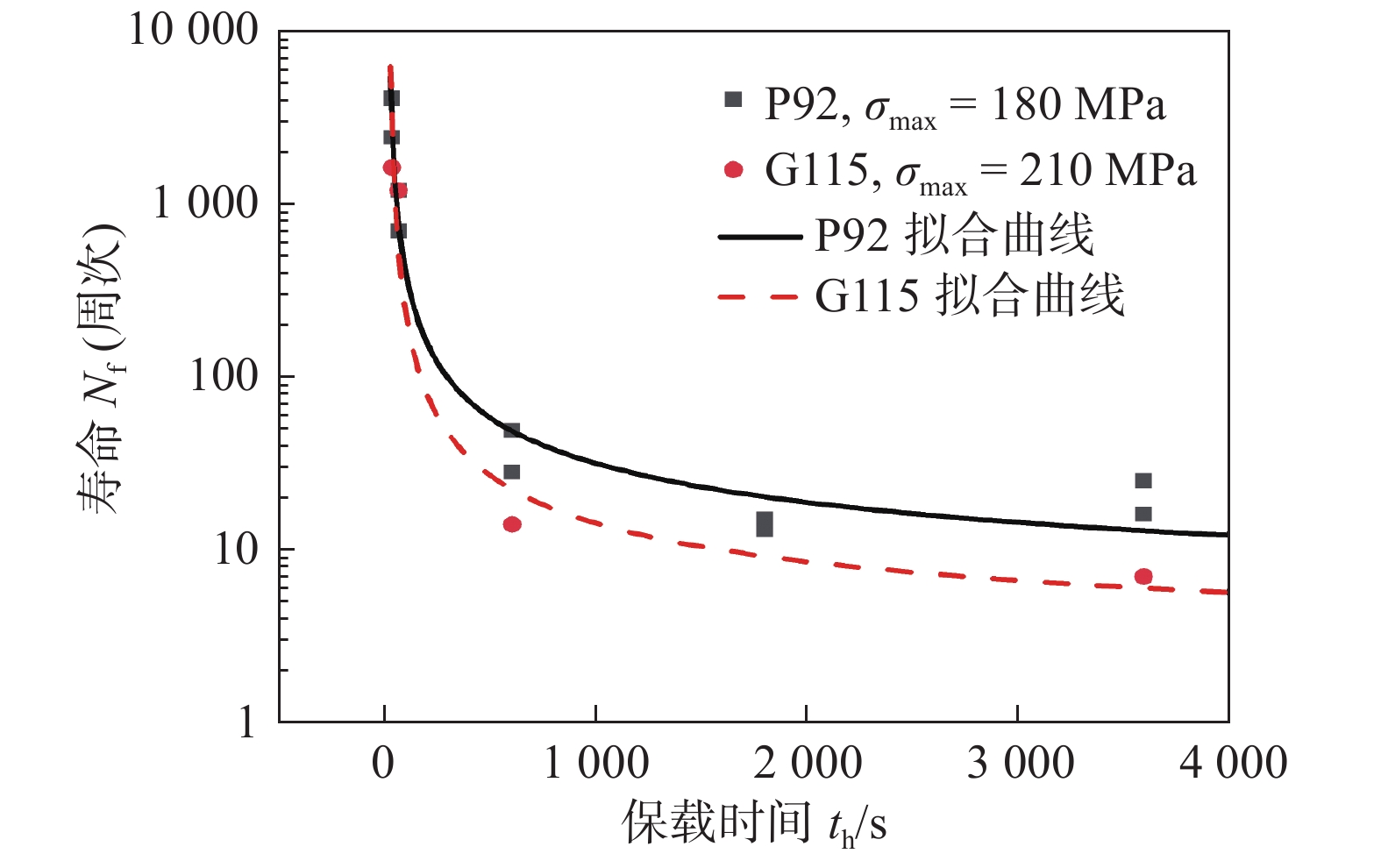
${\sigma }_{\mathrm{m}\mathrm{a}\mathrm{x}}/R_{{\rm{eL}}}$ . 可以发现在不同归一化应力下,P92和G115钢蠕变-疲劳循环断裂寿命的变化趋势基本相同,表明P92和G115钢应力控制下蠕变-疲劳变形机制相同,性能差距主要是由于屈服强度差异引起的. G115钢屈服强度是P92钢的1.15倍,屈服强度越高,蠕变-疲劳性能越好.在相同归一化应力下,研究了不同保载时间对蠕变-疲劳寿命的影响,如图5所示. 对于P92和G115钢,随保载时间的增加,循环断裂寿命Nf逐渐减小;然后当保载时间高于一定水平后,循环断裂寿命减小趋势变缓,保载时间对蠕变-疲劳寿命的影响逐渐达到饱和.
保载时间和峰值应力都是影响应力控制下蠕变-疲劳寿命的关键因素. 峰值应力增加或保载时间增加都会加剧保载阶段的循环蠕变损伤以及蠕变-疲劳交互作用,以致寿命大幅降低. 同时从图5发现相同保载时间下G115钢寿命低于P92钢,表明相同归一化应力下,G115钢对峰值应力与保载时间的交互作用更为敏感.
3. P92钢和G115钢蠕变-疲劳寿命预测
3.1 不同蠕变-疲劳寿命预测方法对比分析
分别采用能量法、应变能密度耗竭法、频率分离法、回线能量法[5, 9]对P92和G115钢蠕变-疲劳寿命进行预测,不同寿命预测模型如下.
(1)能量法.
$$\left(\frac{\sigma_{\max } \Delta \varepsilon_{{\rm{in}}}}{\Delta W}\right) \Delta W N_{{\rm{f}}}=C_{1} $$ (1) 式中:
$\Delta \varepsilon_{\text {in }} $ 为非弹性应变;$ \Delta W $ 为应变能;$ C_{1} $ 为常数.$$ \Delta W=\int_{\varepsilon_{{\rm{f}}}}^{\varepsilon_{0}} \sigma \approx \sigma \Delta \varepsilon_{{\rm{in}}} $$ (2) $$ \Delta \varepsilon_{\mathrm{in}}=\varepsilon_{{\rm{f}}}-\varepsilon_{0} $$ (3) 式中:
$ \varepsilon_{0} $ 和$\varepsilon_{{\rm{f}}}$ 分别为一个循环中的初始应变和最终应变. 因此对于应力控制蠕变-疲劳,能量法寿命预测模型简化为$$ \Delta W N_{{\rm{f}}}=C_{1} $$ (4) (2)应变能密度耗竭法.
$$ \Delta {W_{{\rm{in}}}}N_{\rm{f}}^\beta = {C_2} $$ (5) 式中:
$\Delta {W_{{\rm{in}}}}$ 为非弹性应变能密度,即应力-应变曲线所围面积;$ \beta $ 为参数;$ {C_2} $ 为常数.(3)频率分离法.
$$ {N_{\rm{f}}} = {C_3}\Delta \varepsilon _{{\rm{in}}}^\gamma v_{\rm{t}}^\mu {\left( {\frac{{{v_{\rm{c}}}}}{{{v_{\rm{t}}}}}} \right)^\delta } $$ (6) 式中:
$ {C_3} $ ,$ \gamma $ ,$ \mu $ ,$ \delta $ 是与时间、温度和材料有关的参数;${v_{\rm{t}}}$ 和${v_{\rm{c}}}$ 分别为拉伸和压缩保载频率. 对于无压缩保载的应力控制下蠕变-疲劳试验可简化为$$ {N_{\rm{f}}} = {C_3}\Delta \varepsilon _{{\rm{in}}}^\gamma v_{\rm{t}}^\mu $$ (7) (4)回线能量法.
$$ {\sigma _{\max }}\Delta {\varepsilon _{\rm{p}}}{\left( {{N_{\rm{f}}}{v^{k - 1}}} \right)^\theta } = {C_4} $$ (8) 式中:
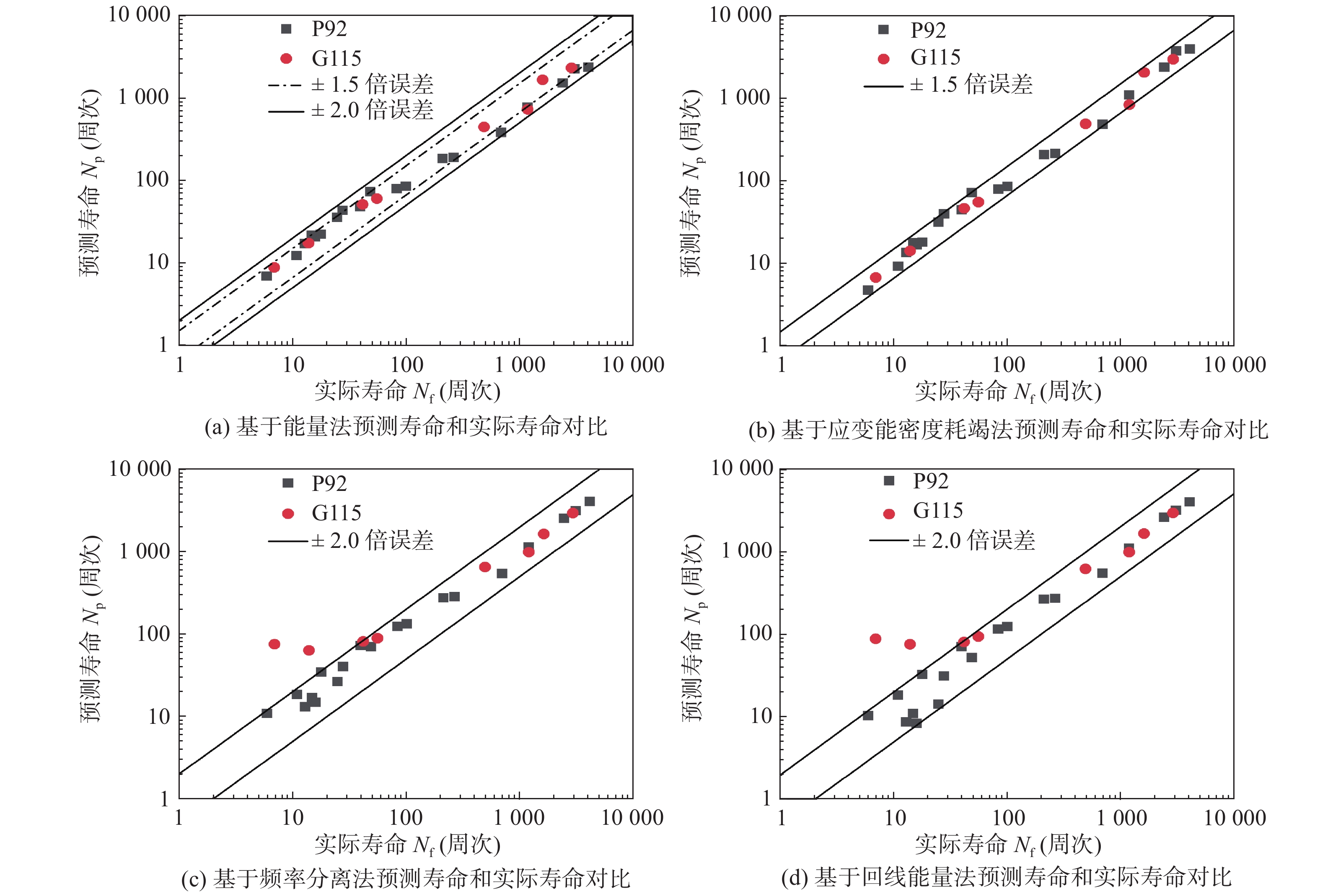
$\Delta {\varepsilon _{\rm{p}}}$ 为非弹性应变;v为频率;k和θ为参数;$ {C_4} $ 为常数.能量法寿命预测结果如图6a所示,虽然对P92和G115两种材料预测精度整体在2倍误差内,且多数落点在1.5倍误差内,但对两种材料的预测均呈现高寿命区偏小、低寿命区偏大的现象,且对P92材料该现象更为明显. 应变能密度耗竭法寿命预测结果如图6b所示,对P92和G115钢应力控制下蠕变-疲劳寿命预测具有较好的适用性,预测寿命都在1.5倍误差以内. 应变能密度耗竭法可看作是对能量法将应变能近似处理的一个修正,因为存在试样制作误差,且即使是在弹性段,也存在静蠕变、蠕变-疲劳交互作用等导致的应力-应变曲线过渡问题. 频率分离法和回线能量法寿命预测如图6c, 6d所示,发现这两种寿命预测方法预测精度远低于能量法和应变能密度耗竭法,对应力控制下的蠕变-疲劳寿命预测效果不好且并不完全适用. 这两种方法可以反映P92钢,但无法很好评价G115钢应力控制下蠕变-疲劳寿命变化规律. 同时频率分离法和回线能量法均会高估长时保载和高应力下低寿命区的蠕变-疲劳寿命,使得寿命预测结果在2倍误差带的边界上,回线能量法略有改善,但改善效果不明显. 此现象说明不同的寿命预测方法并不是对所有材料和情况都适用.
![]() 图 6 P92和G115钢不同寿命预测模型对比分析Figure 6. Comparison of different life prediction models for P92 and G115 steel. (a) comparison of predicted life and actual life based on the energy method; (b) comparison of predicted life and actual life based on strain energy density depletion method; (c) comparison of predicted life and actual life based on frequency separation method; (d) comparison of predicted life and actual life based on frequency modified tensile hysteresis energy model
图 6 P92和G115钢不同寿命预测模型对比分析Figure 6. Comparison of different life prediction models for P92 and G115 steel. (a) comparison of predicted life and actual life based on the energy method; (b) comparison of predicted life and actual life based on strain energy density depletion method; (c) comparison of predicted life and actual life based on frequency separation method; (d) comparison of predicted life and actual life based on frequency modified tensile hysteresis energy model3.2 改进的蠕变-疲劳寿命预测方法
通过对P92钢和G115钢应力控制下蠕变-疲劳寿命以及变形曲线分析,发现主要是由蠕变变形主导了循环断裂寿命;而应变控制下主要是由疲劳变形主导循环断裂寿命,断裂机制与疲劳也较为接近[13]. 因此文中提出基于蠕变应变的应力控制下蠕变-疲劳寿命预测.
(1)基于最小循环蠕变速率的蠕变-疲劳寿命预测法. 最小蠕变速率和蠕变断裂时间之间满足Monkman–Grant (MG)关系[14],即
$$ \dot{\varepsilon}_{{\rm{m}}}^{a} t_{{\rm{r}}}=C_{5} $$ (9) 式中:
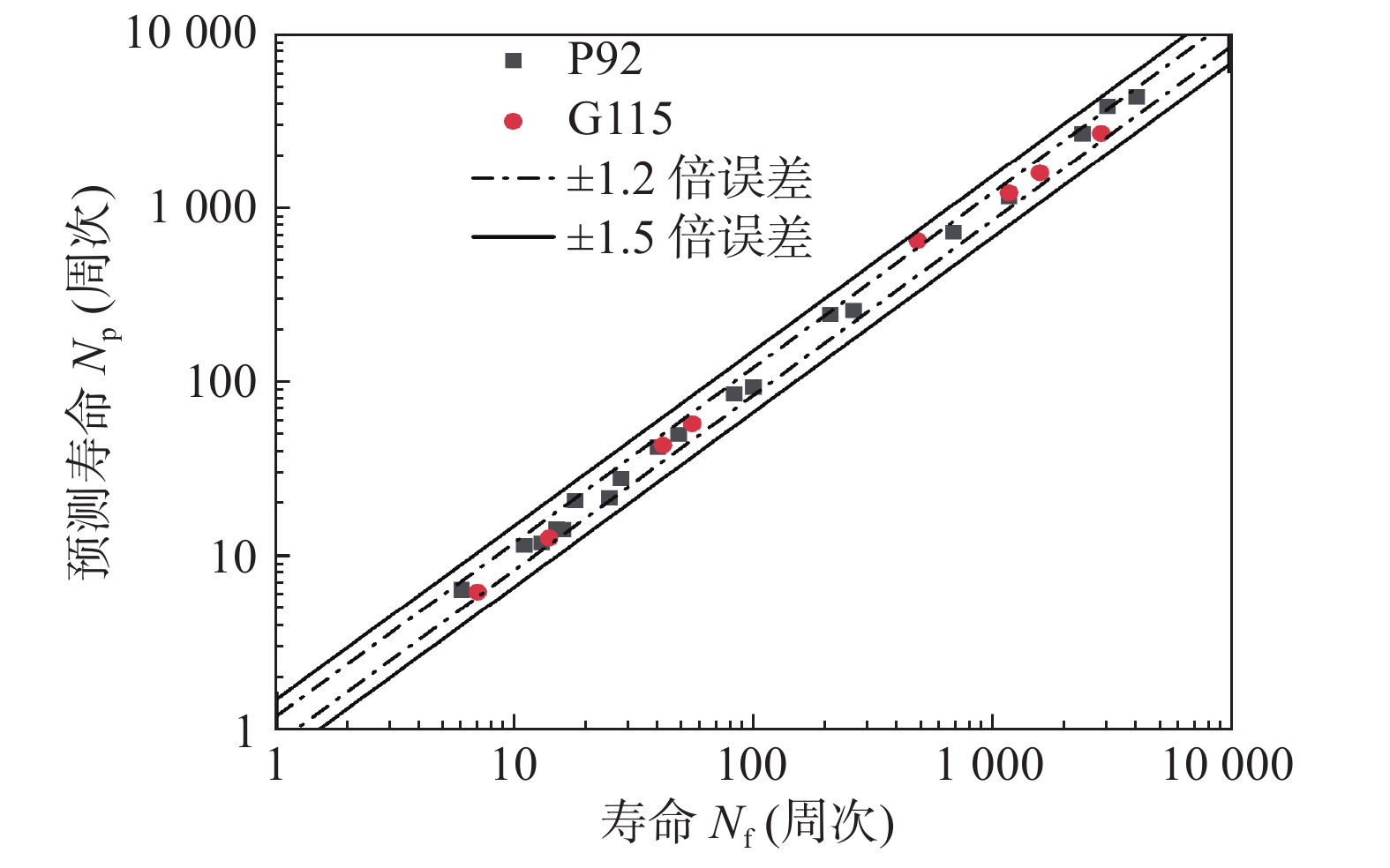
$\dot{\varepsilon}_{{\rm{m}}}$ 为最小蠕变速率;$\boldsymbol{t}_{{\rm{r}}}$ 为蠕变断裂时间;$a$ 为参数;$ C_{5} $ 为常数.应力控制下蠕变-疲劳变形主要是由保载阶段的蠕变变形引起的,如图2a所示,故可利用最小循环蠕变速率
${\dot{\varepsilon }}_{{\rm{Nm}}}$ 预测蠕变-疲劳寿命. 最小循环蠕变速率通过计算蠕变-疲劳第二阶段每循环的峰值应变获得.图7是基于最小循环蠕变速率的蠕变-疲劳寿命预测结果,发现对P92和G115钢寿命预测精度非常高,预测精度由1.5倍误差带缩小至1.2倍误差带,同时这种方法计算也更为简单,也符合应力控制下蠕变-疲劳变形机制.(2)基于纯蠕变的蠕变-疲劳寿命预测. 应力控制下蠕变-疲劳寿命受峰值应力和载荷保持时间影响,损伤主要由蠕变损伤主导. 结合最小循环蠕变速率法,考虑能否基于纯蠕变参数来进行蠕变-疲劳寿命评估. 对于不方便或无法获得蠕变-疲劳下参数的高温部件,可以利用纯蠕变下获得的最小蠕变速率进行寿命预测,提出寿命预测模型为
$$ N_{{\rm{f}}}=A \dot{\varepsilon}_{{\rm{m}}}^{b}\left(\ln t_{{\rm{h}}}\right)^{c} $$ (10) 式中:
$\dot \varepsilon_{{\rm{m}}}$ 为最小蠕变速率;${t}_{{\rm{h}}}$ 为峰值保载时间;A,$ b $ ,$c$ 为参数.基于纯蠕变最小蠕变速率的蠕变-疲劳寿命预测结果如图8所示. 由于未找到G115钢相同温度条件下蠕变数据,只分析了P92钢蠕变-疲劳寿命预测结果,P92纯蠕变数据来自文献[15].
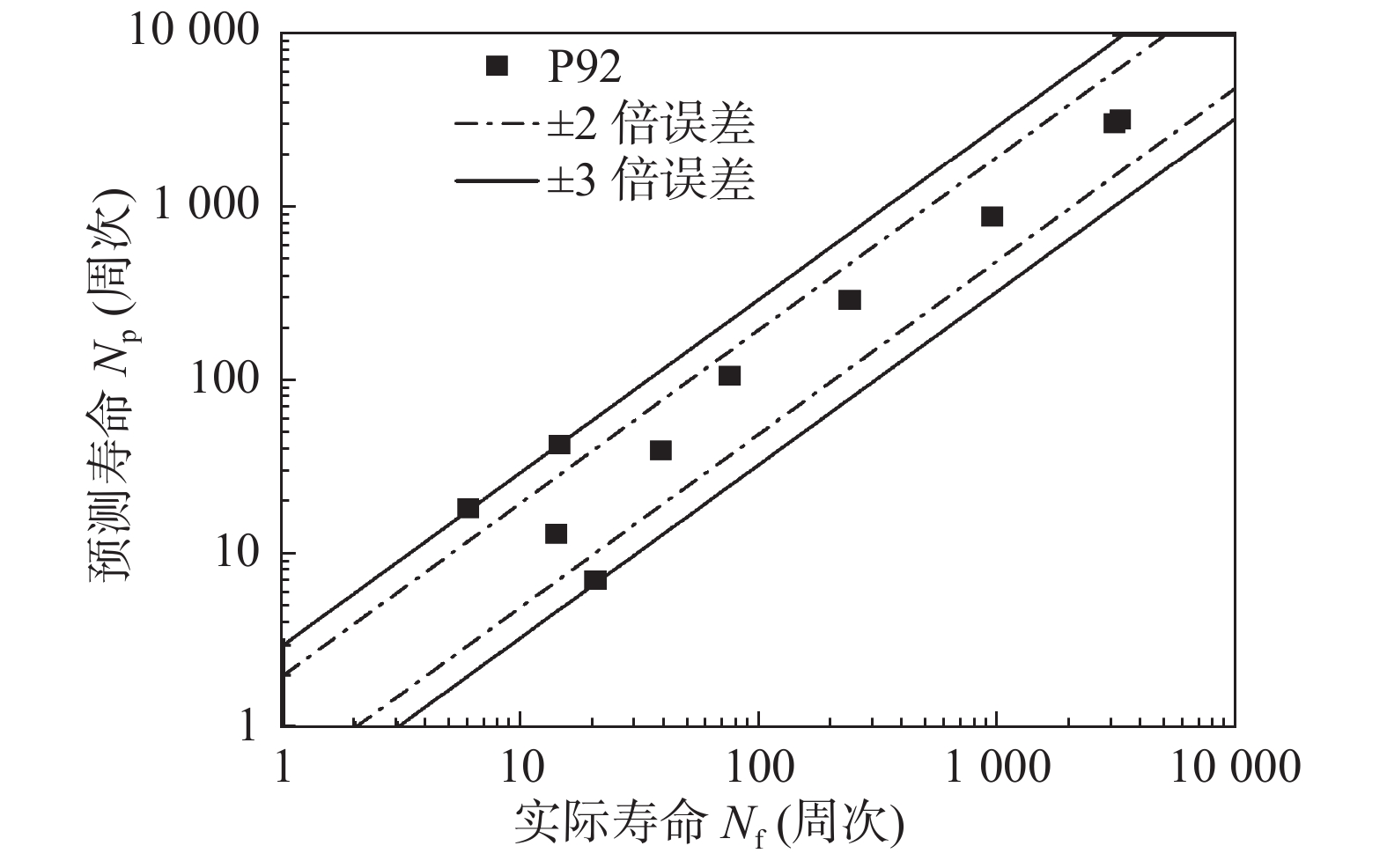
P92在650 ℃下,应力与最小蠕变速率之间关系为
$$ \dot \varepsilon_{{\rm{m}}}=1.0591 \times 10^{-13} \sigma^{15.245} $$ (11) 蠕变-疲劳寿命与相同温度下最小蠕变速率关系可以表示为
$$ N_{{\rm{f}}}=373\;259 \dot{\varepsilon}_{{\rm{m}}}^{-0.67}\left(\ln t_{{\rm{h}}}\right)^{-6.978} $$ (12) 从图8可以看出,最小蠕变速率法能很好反映短时保载或者低峰值应力下高寿命区蠕变-疲劳寿命,对于长时保载或高峰值应力下低寿命区蠕变-疲劳寿命预测精度较差,寿命预测精度扩大到3倍误差带. 尽管该方法对低寿命区的预测需要进一步研究,但仍较好反映了应力控制下蠕变-疲劳寿命,尤其适用于实际工程条件下较长寿命状态的部件寿命评估.
3.3 不同蠕变-疲劳寿命预测方法误差分析
为了对比分析不同蠕变-疲劳寿命预测方法的精度,利用正态分布概率密度函数(PDF)直观地量化分析不同蠕变-疲劳寿命预测方法的误差大小.
$$ P_{\text {error }}=\lg{N_{{\rm{p}}}}-\lg{N_{{\rm{f}}}}$$ (14) 式中:
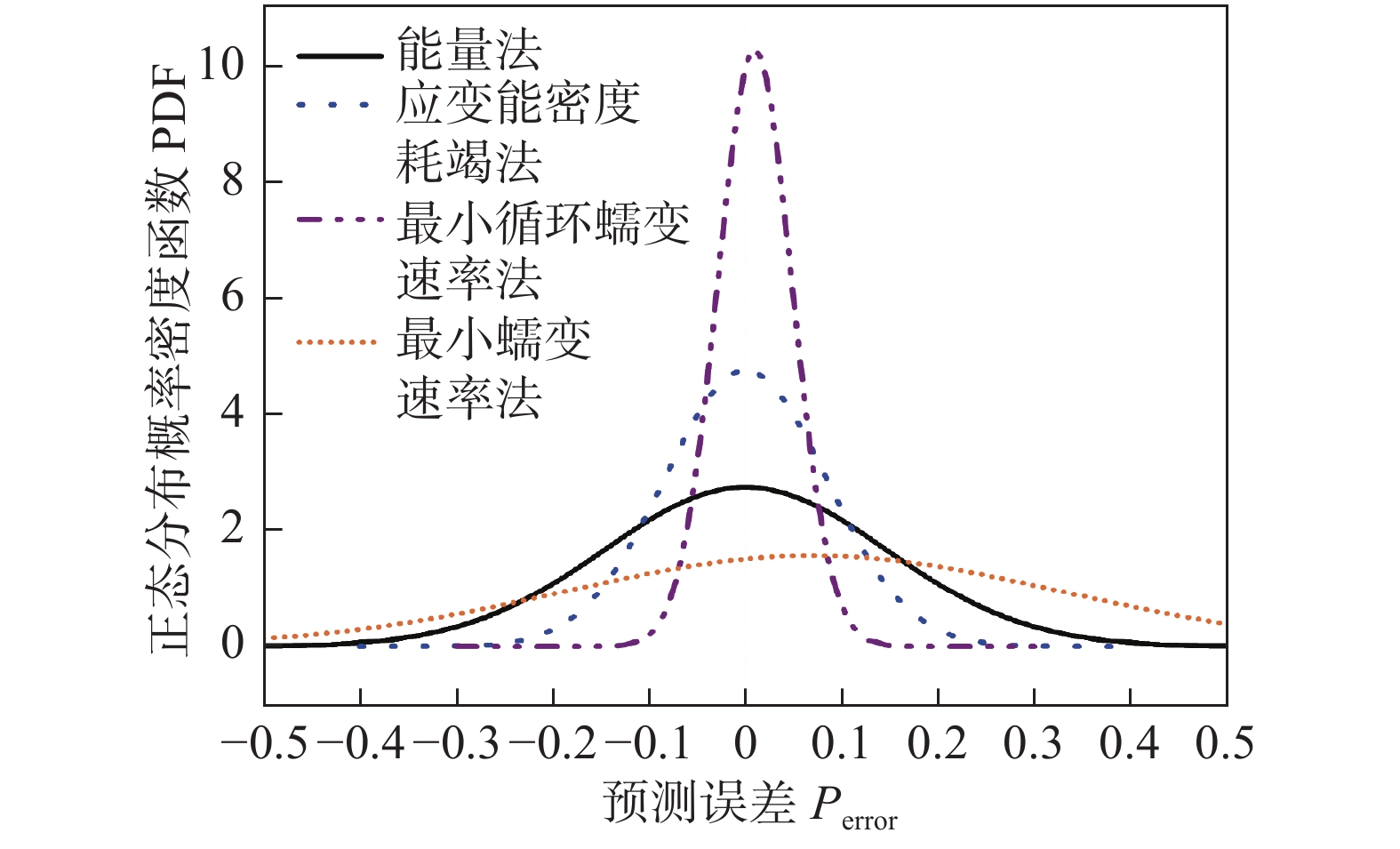
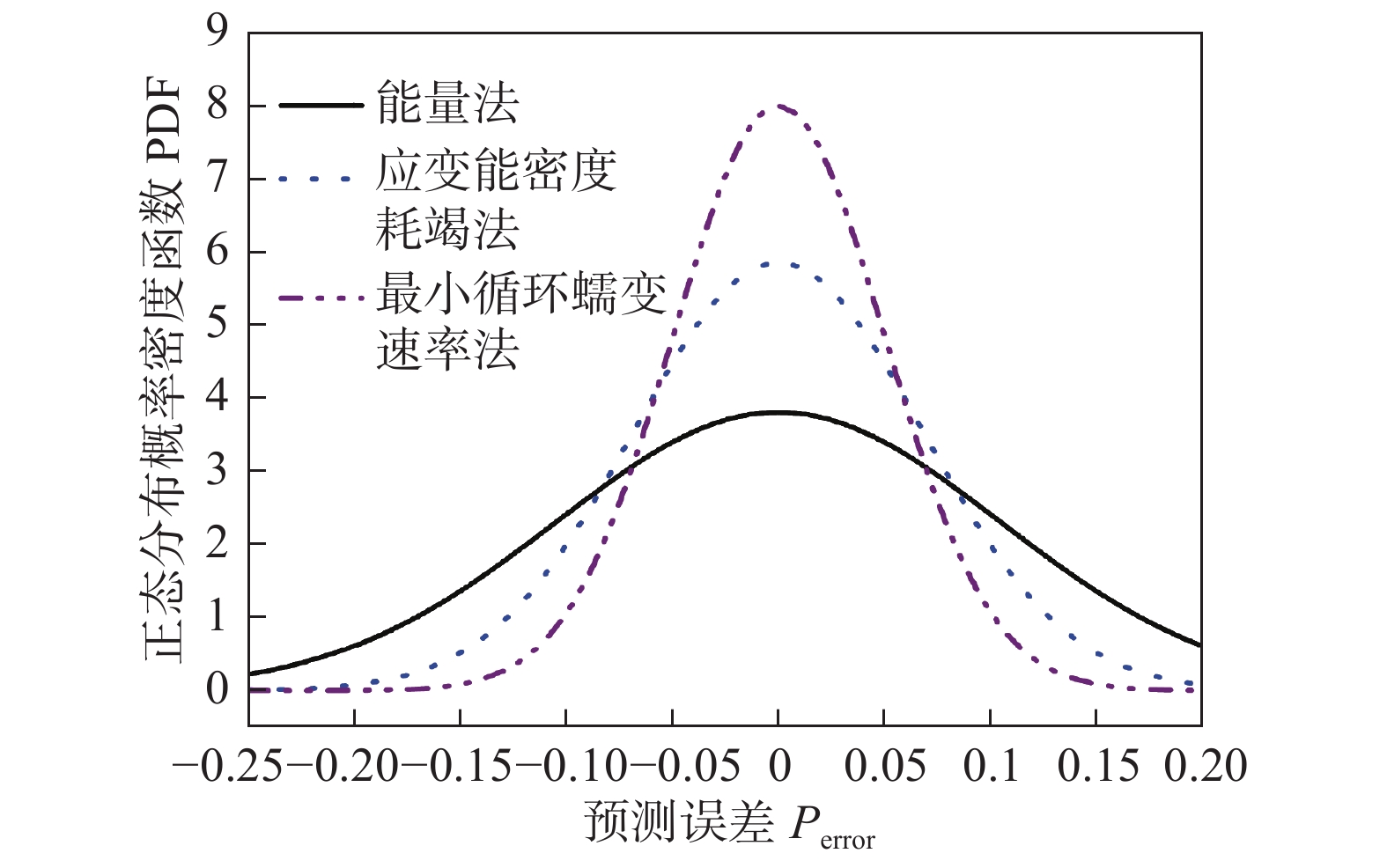
$N_{{\rm{p}}}$ 为预测寿命;$N_{{\rm{f}}}$ 为试验寿命.图9和图10分别对比了P92钢和G115钢不同蠕变-疲劳寿命预测模型误差. 根据正态分布规律,曲线越细高,则误差越小,误差分散度越低. P92钢不同方法寿命预测精度由大到小依次为最小循环蠕变速率法—应变能密度耗竭法—能量法—基于纯蠕变的最小蠕变速率法. 而对于G115钢,由大到小依次为最小循环蠕变速率法—应变能密度耗竭法—能量法.
能量法和基于纯蠕变的最小蠕变速率法的寿命预测精度最差,无法很好反映应力控制下蠕变-疲劳寿命变化规律,可能需要考虑蠕变和疲劳非线性交互作用的影响. 而文中提出的基于最小循环蠕变速率的寿命预测方法预测精度最高,可很好反映应力控制蠕变-疲劳寿命的变形和损伤影响机制. 这也说明了在基本不超屈服的应力控制下的蠕变-疲劳试验中蠕变特征明显,可以利用蠕变-疲劳第二阶段的最小循环蠕变速率实现蠕变-疲劳寿命的精准预测.
4. 结论
(1) 峰值应力和峰值保载时间均为影响蠕变-疲劳寿命的关键因素,且材料屈服强度也为影响蠕变-疲劳性能的一个因素. 蠕变-疲劳寿命随峰值应力增加呈指数减小趋势,随保载时间增加先呈减小趋势,当保载时间达到一定值后,蠕变-疲劳寿命随保载时间变化不大. G115钢蠕变-疲劳性能优于P92钢,相同峰值应力下,G115钢的蠕变-疲劳寿命约是P92钢的8~10倍;但G115钢对峰值应力与保载时间的交互作用更为敏感.
(2) 对应力控制下P92钢和G115钢的蠕变-疲劳寿命预测,应变能密度耗竭法表现出很好的预测效果,能量法预测效果较差;频率分离法以及回线能量法对P92钢应力控制下蠕变-疲劳寿命预测效果一般,且无法反映G115钢应力控制下蠕变-疲劳寿命变化.
(3) 基于最小循环蠕变速率法的寿命预测精度最高,对P92钢和G115钢应力控制下蠕变-疲劳寿命均具有很好的适应性,且该方法表征了应力控制下蠕变-疲劳的非弹性应变和损伤累积过程的蠕变主导作用.
(4) 基于纯蠕变最小蠕变速率法的蠕变-疲劳寿命预测方法虽然对低寿命区预测误差偏大,但对高寿命区预测良好,且该方法可利用纯蠕变最小蠕变速率和保载时间直接预测应力控制下蠕变-疲劳寿命,但可能需要考虑蠕变-疲劳交互作用对蠕变应变累积的影响与低寿命区的适用性.
-
图 6 P92和G115钢不同寿命预测模型对比分析
Figure 6. Comparison of different life prediction models for P92 and G115 steel. (a) comparison of predicted life and actual life based on the energy method; (b) comparison of predicted life and actual life based on strain energy density depletion method; (c) comparison of predicted life and actual life based on frequency separation method; (d) comparison of predicted life and actual life based on frequency modified tensile hysteresis energy model
表 1 P92和G115高温拉伸性能
Table 1 Tensile properties of P92 and G115 at high temperature
材料 温度 T/℃ 屈服强度ReL/MPa 抗拉强度Rm/MPa P92 650 240 261 G115 650 275 288 -
[1] Zhou Y. Optimal scheduling for power system peak load regulation considering short-time startup and shutdown operations of thermal power unit[J]. International Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems, 2021, 131(11): 107012.
[2] Gopinath K, Gupta R K, Sahu J K, et al. Designing P92 grade martensitic steel header pipes against creep-fatigue interaction loading condition: Damage micromechanisms[J]. Materials & Design, 2015, 86: 411 − 420.
[3] Tahir F, Liu Y. A new experimental testing method for investigation of creep-dominant creep-fatigue interaction in alloy 617 at 950 °C[J]. International Journal of Pressure Vessels & Piping, 2017, 154: 75 − 82.
[4] Zhang T, Wang X, Ji Y, et al. P92 steel creep-fatigue interaction responses under hybrid stress-strain controlled loading and a life prediction model[J]. International Journal of Fatigue, 2020, 140: 105837. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfatigue.2020.105837
[5] 葛仁跃. 基于损伤演化机理的P92钢蠕变-疲劳试验研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江工业大学, 2020. Ge Renyue. Microstructure and high-temperature creep analysis of P92 steel[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University of Technology, 2020.
[6] Zhao P, Xuan F. Study on creep-fatigue damage evaluation for advanced 9%-12% chromium steels under stress controlled cycling[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica (English Letters), 2011, 24(2): 148 − 154.
[7] Riedel H, Maier G, Oesterlin H. A lifetime model for creep-fatigue interaction with applications to the creep resistant steel P92[J]. International Journal of Fatigue, 2021, 150: 106308.
[8] 郝玉龙. P91钢蠕变特性及蠕变疲劳交互作用研究[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2005. Hao Yulong. Study on creep characteristics and creep fatigue interaction of P91 steel[D]. Chengdu: Southwest Jiaotong University, 2005.
[9] Chen L, Jiang J, Fan Z, et al. A new model for life prediction of fatigue-creep interaction[J]. International Journal of Fatigue, 2007, 29(4): 615 − 619. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfatigue.2006.07.009
[10] 张力文, 钟玉平, 李世乾, 等. 304H 焊接接头蠕变疲劳寿命预测[J]. 焊接学报, 2019, 40(1): 156 − 160. doi: 10.12073/j.hjxb.2019400031 Zhang Liwen, Zhong Yuping, Li Shiqian, et al. Life prediction of creep-fatigue for 304H with welded joints[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2019, 40(1): 156 − 160. doi: 10.12073/j.hjxb.2019400031
[11] 徐连勇, 庞红宁, 赵雷, 等. G115钢CMT + P焊接工艺及组织和性能[J]. 焊接学报, 2020, 41(8): 1 − 5. Xu Lianyong, Pang Hongning, Zhao Lei, et al. CMT+P welding process, microstructure and properties of G115 steel[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2020, 41(8): 1 − 5.
[12] 胡苏阳. P92钢微观结构与高温蠕变分析[D]. 北京: 华北电力大学, 2013. Hu Suyang. Microstructure and high-temperature creep analysis of P92 steel[D]. Beijing: North China Electric Power University, 2013.
[13] Fournier B, Sauzay M, Caees C, et al. Creep-fatigue-oxidation interactions in a 9Cr-1Mo martensitic steel. Part I: Effect of tensile holding period on fatigue life time[J]. International Journal of Fatigue, 2008, 30(4): 649 − 662. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfatigue.2007.05.007
[14] Maruyama K, Sekido N, Yoshimi K. Changes in Monkman-Grant relation among four creep regions of modified 9Cr-1Mo steel[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2019, 749(3): 223 − 234.
[15] 赵雷. P92钢焊接接头的蠕变损伤机理研究[D]. 天津: 天津大学, 2009. Zhao Lei. Research on creep damage mechanism of welded joints of P92 steel[D]. Tianjin: Tianjin University, 2009.
-
期刊类型引用(5)
1. 龚凌诸,朱猛,蔡宝杰,徐火力,伏喜斌. P92钢锅炉管道焊接组织分析与残余应力模拟. 压力容器. 2023(02): 1-10 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 杨二娟,李勇,米紫昊,刘福广,刘刚,石岩松,赵雷. 蒸汽发生器焊接堵管残余应力数值模拟及寿命预测. 电焊机. 2023(05): 12-20 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 杨二娟,刘福广,李勇,米紫昊,刘刚,赵雷,王栋. 高温气冷堆蒸汽发生器机械式胀焊堵管接头残余应力计算及寿命预测. 焊接技术. 2023(07): 23-27 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 王宇冬,尚建路,孙斌,杨佳,王妍. 不同焊接工艺对P92钢焊接接头组织性能的影响. 钢铁研究学报. 2023(09): 1152-1160 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 肖晖,马风辉. 9%Cr马氏体耐热钢C9MVW和5Co1焊条的研制. 机械制造文摘(焊接分册). 2022(06): 34-39 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)



 下载:
下载: