Characteristic analysis of friction additive assisted Ti/Al friction stir lap welding
-
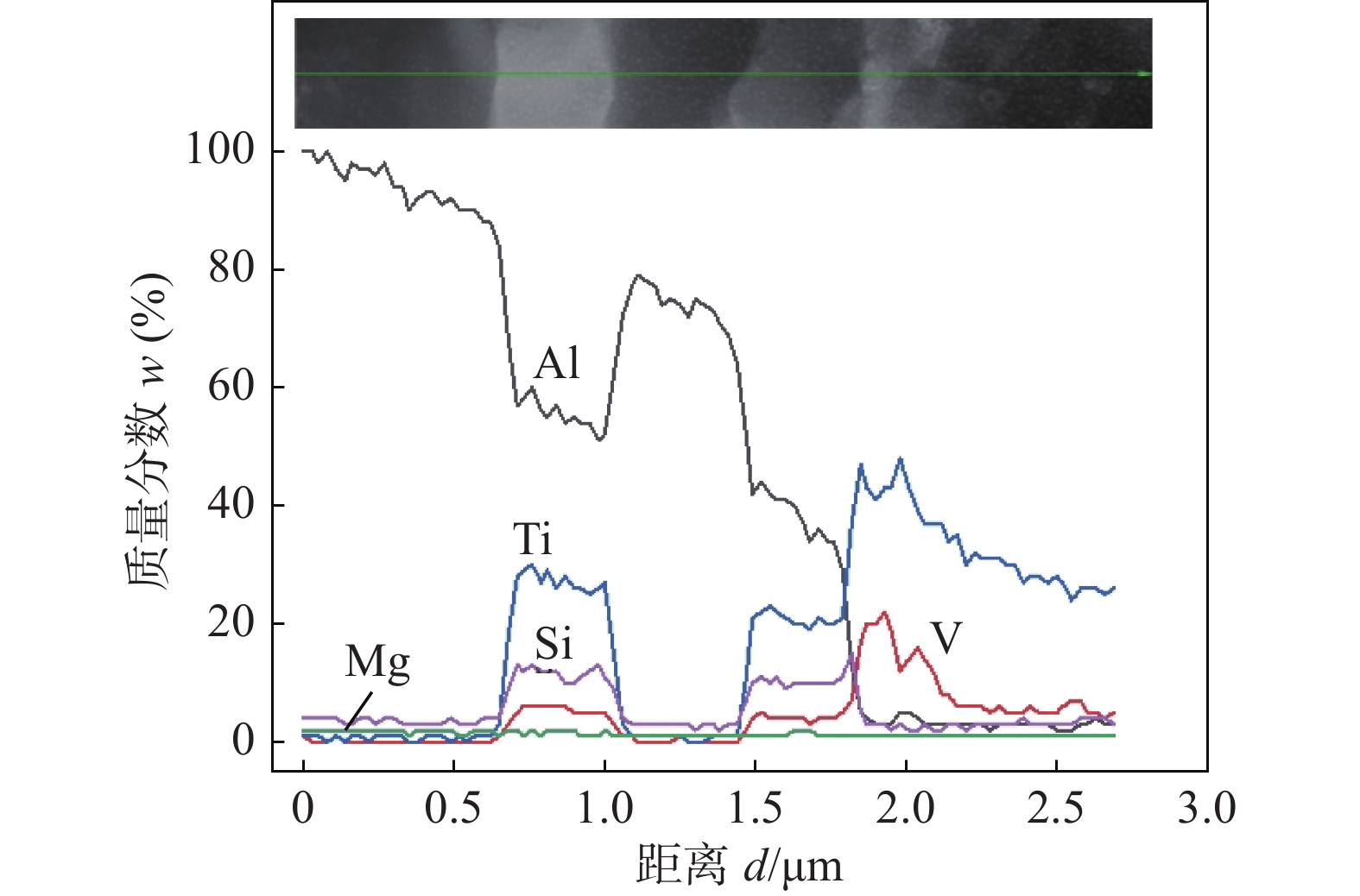
摘要: 为解决Ti/Al异种材料搅拌摩擦焊接接头强度低、搅拌针磨损等问题,提出一种摩擦增材辅助搅拌摩擦搭接焊(friction addition-friction stir lap welding, FA-FSLW)技术. 该新工艺延续了固相连接的优势,具有热输入量低、界面金属间化合物薄等特点.文中研究了以6082铝合金作预沉积层辅助实现3 mm厚2A12铝合金板与4 mm厚TC4钛合金板之间的连接,焊接过程中搅拌头扎入铝沉积层而不接触钛表面,得到抗拉载荷最大为12.2 kN的接头.结果表明, FA-FSLW复合焊接头的界面迁移越大,接头承载越小.同时,发现界面处的Ti, Al元素发生了明显互扩散,Si元素在界面偏聚,与Ti, Al元素发生冶金反应后形成层状纳米级Ti-Al-Si金属间化合物,为提高接头强度奠定基础.Abstract: Friction stir lap welding assisted by friction additive (FA-FSLW) was proposed to solve the following problems during Ti/Al dissimilar friction stir welding process: low joint strength and wear of tool. This new technology contains the advantages of solid state welding, such as low heat input, thinner intermetallic compounds layer. This study selected 6082 aluminum alloys as the pre-deposition layer to assist the bonding between 3 mm thick 2A12 aluminum alloy and 4 mm thick TC4 titanium alloy plates. The tool was set into the 6082 deposition without touching the titanium surface. The joint with the maximum tensile load of 12.2 kN was obtained. The study found that the larger the interface offset, the lower the load bearing. The Ti and Al elements have undergone significant inter-diffusion during FA-FSLW process. The element of Si was segregated at the interface, and then metallurgical reacted with Ti and Al, to form a Ti-Al-Si intermetallic compound layered of nano-level, which established the foundation for high load-bearing of the joint.
-
-
-
[1] Liu H J, Zhou L, Liu Q W. Microstructural characteristics and mechanical properties of friction stir welded joints of Ti–6Al–4V titanium alloy[J]. Materials and Design, 2010, 31: 1650 − 1655. doi: 10.1016/j.matdes.2009.08.025
[2] 黄永宪, 吕宗亮, 万龙, 等. 钛/铝异质金属搅拌摩擦焊技术研究进展[J]. 航空学报, 2018, 39(11): 1 − 12. Huang Yongxian, Lv Zongliang, Wan Long, et al. Research progress of friction stir welding technology for Ti/Al dissimilar metals[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2018, 39(11): 1 − 12.
[3] Fujii H, Sun Y F, Kato H, Nakata K. Investigation of welding parameter dependent microstructure and mechanical properties in friction stir welded pure Ti joints[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2010, 527: 3386 − 3391. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2010.02.023
[4] Huang Y X, Lv Z L, Wan L, et al. A new method of hybrid friction stir welding assisted by friction surfacing for joining dissimilar Ti/Al alloy[J]. Materials Letters, 2017, 207(15): 172 − 175.
[5] 李 梁, 孙建科, 孟祥军. 钛合金的应用现状及发展前景[J]. 钛工业进展, 2004, 21(5): 19 − 24. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-9964.2004.05.005 Li Liang, Sun Jianke, Meng Xiangjun. Application status and development prospect of titanium alloy[J]. Titanium Industry Progress, 2004, 21(5): 19 − 24. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-9964.2004.05.005
[6] Chen Y C, Quan N, Ke L M. Interface characteristic of friction stir welding lap joints of Ti/Al dissimilar alloys[J]. Transations Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2012, 22: 299 − 304.
[7] 陈玉华, 董春林, 倪泉, 等. 钛合金/铝合金搅拌摩擦焊接头的显微组织[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2010, 20: s211 − s214. doi: 10.1016/S1003-6326(10)60041-6 Chen Yuhua, Dong Chunlin, Ni Quan, et al. Microstructure of friction stir welded joint of Ti/Al alloys[J]. The Chinses Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2010, 20: s211 − s214. doi: 10.1016/S1003-6326(10)60041-6
[8] Chen Y C, Nakata K. Microstructural characterization and mechanical properties in friction stir welding of aluminum and titanium dissimilar alloys[J]. Materials and Design, 2009, 30: 469 − 474. doi: 10.1016/j.matdes.2008.06.008
[9] Bang H S, Bang H S, Song H J, et al. Joint properties of dissimilar Al6061-T6 aluminum alloy/Ti-6%Al-4%V titanium alloy by gas tungsten arc welding assisted hybrid friction stir welding[J]. Materials and Design, 2013, 51: 544 − 551. doi: 10.1016/j.matdes.2013.04.057
[10] Li B, Zhang Z H, Shen Y F, et al. Dissimilar friction stir welding of Ti-6Al-4V alloy and aluminum alloy employing a modified butt joint configuration: Influences of process variables on the weld interfaces and tensile properties[J]. Materials and Design, 2014, 53: 838 − 848. doi: 10.1016/j.matdes.2013.07.019
[11] Meng X C, Huang Y X, Cao J, et al. Recent progress on control strategies for inherent issues in friction stir welding[J]. Progress in Materials Science, 2021, 115: 100706. doi: 10.1016/j.pmatsci.2020.100706
[12] Mishra R S, Ma Z Y. Friction stir welding and processing[J]. Materials Science and Engineering:R, 2010, 50(1): 1 − 78.
[13] K V, Semiatin S L. Continuous dynamic recrystallization during friction stir welding of high strength aluminum alloys[J]. Scripta Materialia, 2000, 43(8): 743 − 749. doi: 10.1016/S1359-6462(00)00480-2
[14] Lv Z L, Han Z Y, Zhu D, et al. Enlarged-end tool for friction stir lap welding towards hook defect controlling[J]. China Welding, 2020, 29(1): 1 − 7.
[15] Prado R A, Murr L E, Shindo D J, et al. Tool wear in the friction-stir welding of aluminum alloy 6061 + 20%Al2O3: a preliminary study[J]. Scripta Materialia, 2001, 45(1): 75 − 80. doi: 10.1016/S1359-6462(01)00994-0
[16] 孙天娇. Ti-6Al-4V/Al-12Si界面金属间化合物生长规律及转变机制研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2011. Sun Tianjiao. Growth and Transformation Mechanism of Intermetallic Compounds at the Interface of Ti-6Al-4V/Al-12Si[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2011.
[17] Luo J G, Acoff V L. Using cold roll bonding and annealing toprocess Ti/Al multi-layered composites from elemental foils[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2004, 379: 164 − 172. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2004.01.021
-
期刊类型引用(4)
1. 金玉花,周子正,邢逸初,吴博. 滚动轧制对7050铝合金FSW接头组织的影响. 兰州理工大学学报. 2023(04): 30-34 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 贺地求,刘朋,王海军,王东曜,赖瑞林. 2219-T6静轴肩辅助搅拌摩擦焊组织与性能分析. 湖南大学学报(自然科学版). 2021(08): 11-18 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 徐韬,周灿丰. 一种液压摩擦焊机电液系统研究与试验. 液压气动与密封. 2020(03): 32-35 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 赵惠. 成型工艺对钨基复合材料界面组织和性能的影响. 材料导报. 2020(S2): 1351-1355 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(3)




 下载:
下载: