Effect of heat treatment on microstructure evolution and mechanical properties of 2219 aluminum alloy joint as fabricated by double-pulsed TIG welding
-
摘要: 系统对比研究了直接时效处理和固溶时效处理对2219-T6铝合金双频复合脉冲TIG焊接头强化的影响. 分析了焊后热处理工艺对α-Al晶粒、共晶组织及时效析出行为的影响,讨论了接头组织不均匀性对塑性变形行为的影响机制. 结果表明,直接时效处理对α-Al晶粒和共晶组织影响较小,在焊缝区引入低密度粗大θ'-Al2Cu析出相,对接头强化效果有限,且对塑性有损害;而固溶时效处理导致α-Al晶粒粗化、共晶组织含量降低且尺寸细化,在焊缝区引入高密度细小θ''-Al3Cu析出相(平均直径22 nm),并显著提升接头强度和塑性,使得接头强度系数达到0.84,断后伸长率升高至7.0%. 固溶时效处理导致的接头强塑化源于焊缝区内高密度纳米θ''-Al3Cu相所产生的析出强化效应,使得接头强度匹配更加均衡,促进了接头均匀塑性变形,并提升了接头抗拉强度.Abstract: In the present study, the effects of typical post-welding heat treatments, including direct aging treatment (AT) and solution treatment + aging treatment (STAT), on the strengthening effect of 2219-T6 joint fabricated by double-pulsed variable polarity tungsten inert gas welding were investigated comparatively. The evolution of α-Al grain, eutectic structure and precipitations during different post-welding heat treatments were investigated. Moreover, the influence mechanism of microstructure heterogeneity on the plastic deformation behavior of the joint was discussed. Obtained results show that AT affected slightly α-Al grain and eutectic structure, and introduced low-density coarse θ'-Al2Cu precipitation into the welding seam. AT has a limited strengthening effect on 2219-T6 aluminum alloy joint and a damage to plasticity. While, STAT lead to coarsening of α-Al grain and decrease in the content and size of eutectic structure. Meanwhile, a high-density fine θ''-Al3Cu particles with a mean diameter of 22 nm was introduced by STAT into the welding seam. STAT can significantly improve the strength and plasticity of the joint, make the strength coefficient of the joint reach up to 0.84 and the elongation increase to 7.0%. The strengthening and plasticizing effect of the joint caused by STAT result from a more homogeneous strength matching among each region of the joint, due to the significant precipitation strengthening of nano θ'' particles in welding seam. That promoted a more uniform overall plastic deformation and lead to the increase in ultimate tensile strength.
-
Keywords:
- heat treatment /
- aluminum alloy /
- pulsed welding /
- microstructure /
- mechanical property
-
0. 序言
在动力软包电池中,极耳通常由铝或铜制成,以并联或串联形式连接到汇流排,铜是动力电池中的主要导电材料,据统计,一辆新能源汽车中铜的使用量可达83 kg[1],在新能源汽车电池系统中,电池模块之间的连接质量直接影响到整车的动力性能[2],电池系统中的接头须满足低电阻、高强度、高抗疲劳性和耐腐蚀等特性[3],1050 Al是动力电池中的常见材料,具有轻质、廉价且导电性强等优点[4-5]. 铝与铜焊接时会形成脆性金属间化合物,导致焊点电阻率增加、裂纹敏感性提高、力学性能下降[6],研究表明,异种金属焊缝中金属间化合物(intermetallic compound,IMC)厚度大于5 μm将显著降低接头抗拉性能[7],因此控制接头中脆性IMC的生成及分布,成为新能源电池中铝/铜异质金属,高质高效可靠连接的关键.
与电阻焊和超声波焊相比,激光焊的产品具有更低的接触电阻和更高的接头强度[8],然而,铝和铜之间物化性能差异较大,铝/铜异质金属接头中极易生成脆硬的IMC和较高的残余焊接应力,制约了铝/铜异质金属焊接结构的应用[9]. 铝/铜激光焊主要研究提高金属对激光的吸收率以及抑制液态金属的流动,包括预热和焊后缓冷处理、材料表面处理、采用短波长激光、电弧激光复合和添加中间过渡层等[10]. Schmalen等人[11]通过调节激光功率和摆动幅度实现了0.2 mm厚铝与0.5 mm 铜的可靠连接;Yan等人[12]研究了铝/铜激光接头的微观组织,焊缝金属主要由Al固溶体和Al-Cu共晶相组成,铜基体与熔合区之间的界面区主要由Cu固溶体、锯齿状Al2Cu相和蠕虫状Al-Cu合金相组成,接头的剪切强度最大约为99.8 MPa,接头断裂于Al-Cu共晶区,呈脆性断裂特征. Solchenbach等人[13]采用铝上铜下的搭接形式,研究了SF-Cu/AA1050 Al焊缝中IMC分布规律及其对接头性能的影响;Lee等人[14]比较了装配方式对铝/铜激光搭接接头熔池流动和焊缝金属间化合物的影响,研究表明,铝在上时,铝元素主要聚集在熔池上方,界面附近生成厚度约5 µm的Al2Cu化合物层;铝在下时,熔融的铜在重力和激光搅拌下沉入熔池底部,焊缝中生成大量Al2Cu和Al4Cu9相;Zuo等人[15]研究发现,θ-Al2Cu与铝基体之间结合较弱,导致接头断裂于此;Dimatteo等人[16]研究了光斑直径对铝/铜异质材料激光搭接焊的影响,较小的光斑直径可有效控制熔深和母材稀释率,减少了基体金属熔化和富铜相的形成,形成良好的焊缝;Pérez等人[6]指出激光能量输入的升高导致焊缝中硬脆金属间化合物增多、尺寸增大,进而提高了铝、铜二者之间的接触电阻.
综上可知,对焊缝中IMC的生成及分布的调控是实现铝/铜高质量激光焊的关键. 此外,影响热输入特性的另一难点在于铝、铜合金对激光的反射率高,铜在室温下对1 070 nm波长激光反射率高达95%[17],导致作用于焊缝区域的激光能量非常有限,提高了该类材料激光焊接的最低功率,进一步增加了异质金属焊接时金属间化合物的控制难度.
新型激光器能在铜和铝等有色高反金属表面实现更高的能量吸收率[18]. Hess和Das等人[19-20]使用低功率绿色激光(532 nm)和红外激光(1 064 nm)复合技术提高了铜合金焊接过程中对激光的吸收率,使熔深易于控制,并可以显著改善焊缝几何形状和接头强度,但蓝光激光技术目前最大的局限在于激光器功率较低,难以满足对较大熔深的焊接需求,因此,文中采用蓝-红复合激光焊接铝/铜异质材料,研究红光功率对铝/铜异质材料复合激光焊接头组织性能的影响规律.
1. 试验方法
试验材料为150 mm × 50 mm × 0.5 mm的1050 铝板和150 mm × 50 mm × 1 mm T2 铜板,化学成分见表1. 焊前采用细砂纸打磨待焊试件表面,并用无水乙醇清洗去除表面氧化膜和油污,打磨试件表面以提高母材对激光的吸收率.
表 1 母材的化学成分(质量分数,%)Table 1. Chemical compositions of base materialsAA1050铝 Cu Zn Fe Si Ti Al 0.05 0.07 0.2 0.17 0.05 余量 T2纯铜 S Bi Pb As Fe Cu 0.005 0.001 0.002 0.002 0.005 余量 铝/铜复合激光焊接试验采用UW1000-455型蓝光激光器与UW-S3000-UM光纤激光器通过复合激光出射头复合而成,准直镜焦距90 mm,聚焦镜焦距180 mm,其中,蓝光激光器功率范围10 ~ 1 000 W,光纤芯径50 μm;红外激光功率10 ~ 3 000 W,光纤芯径100 μm. 红、蓝光斑直径分别为500 μm和1 mm,离焦量为 + 2 mm,保护气为99.99%的高纯氩气,气流量15 L/min. 接头装配采用铝上铜下的搭接形式,搭接宽度20 mm,如图1所示. 激光焊接试验参数见表2.
表 2 试验工艺参数Table 2. Experimental process parameters编号 红光功率
PR /W蓝光功率
PB /W焊接速度
v /(mm·min−1)离焦量
f /mm1 600 300 60 +2 2 700 300 60 +2 3 800 300 60 +2 4 900 300 60 +2 5 1 000 300 60 +2 6 1 100 300 60 +2 7 1 200 300 60 +2 8 1 300 300 60 +2 9 1 400 300 60 +2 对焊接试样取样后镶嵌在环氧树脂内,使用SiC砂纸打磨,抛光后进行金相观察,使用SEM和EDS显微组织及IMC化学成分分析,每个参数试样取3个拉伸试样进行拉伸试验,结果取平均值,并对断口形貌及显微组织进行分析,试样的接触电阻采用开尔文四线检测法测量.
2. 结果和讨论
2.1 焊缝形貌分析
当PB = 300 W,通过改变PR值,获得各工艺条件下铝/铜搭接接头焊缝横截面及焊缝表面形貌如图2所示. 当PR = 600 W时,能量过低,未能实现铝铜之间的有效连接. 由试样表面形貌可知,PR处于700 ~ 800 W时,焊缝表面连续平整,未观察到气孔和裂纹等缺陷;PR处于900 ~ 1000 W时,焊缝表面光整度下降,并可观察到飞溅缺陷;PR处于1100 ~ 1400 W后,焊缝表面出现尺寸不等、断续分布的焊穿孔洞,且该孔洞缺陷随红光激光功率升高而增多.
从焊缝横截面可看出,横截面总体呈现T形. 如图3所示,随红外激光功率增加,T2铜板的熔深和熔宽逐步增加,当PR = 1 000 W时,可观察到明显匙孔,由热导焊转变为深熔焊;当PR = 1 400 W时,铜板被完全熔透; 当PR = 700 W时,试件结合良好,未发现未熔合、裂纹和气孔等缺陷;当PR = 800 W时,焊缝颈部出现小范围未熔合缺陷. 当PR增加至900 ~ 1400 W时,焊缝均出现了气孔、未熔合等缺陷.
随着激光功率增加,熔池温度随之升高,且液态熔池下方的铜板开始熔化,导致焊缝中Al-Cu脆性金属间化合物数量增加. 气体元素在以金属间化合物为主的焊缝中的溶解量低于固溶体焊缝(PR = 700,800 W),导致焊缝中气孔增多,同时,高温作用下铜板表面吸附的水分形成蒸汽,在熔池与上下两层板之间的间隙阻碍液态金属的铺展润湿,从而形成未熔合型孔洞缺陷. 裂纹主要存在于熔池底部,即脆性金属间化合物聚集的位置,铝板、铜板之间线膨胀系数差异较大,熔化焊接时接头中存在较大焊接应力,在应力与脆性相的共同作用下易形成伴随金属间化合物的微裂纹,与Dimatteo所述结论一致.
2.2 焊缝的微观组织分析
图4为PR = 800 W时铝/铜异种金属激光焊接接头的微观组织及图中位置元素分析见表3. 图4(a)中焊缝靠近铝板的一侧,微观组织分布均匀,主要为Al固溶体,在较低的激光功率下,铜板的熔化量较少,并且铜的密度大于铝,铜不容易向熔池上方扩散,因此焊缝上方仅有少量Al-Cu化合物固溶在铝中. 通过图4(b)的微观组织分析,图4(b)中Ⅰ区域和Ⅱ区域都是由Al-Cu共晶合金组成,但组织形貌不同,根据Al-Cu二元相图和EDS结果分析可知,焊缝Ⅰ区域发生了Al-Cu过共晶反应,而在下部(Ⅱ区)则发生了亚共晶反应. 在亚共晶反应过程中,α-Al为初生相,θ-Al2Cu为次生相,结晶析出温度较低,Al2Cu在α-Al晶界处形核,形成小颗粒;过共晶反应是θ-Al2Cu金属间化合物为初生相,α-Al为次生相. 由液相中直接析出的θ-Al2Cu相晶粒比较粗大,表现为树枝晶. 在铜侧界面处铝/铜原子比接近2∶1,由相图可知此处发生匀晶反应形成了短棒状的Al2Cu金属间化合物层,并且Al2Cu的生长垂直于熔合线向焊缝中心生长,化合物层厚度为4 μm. 在图4(d)中d3区域铜元素偏聚生成放射状Al2Cu金属间化合物. 紧邻棒状Al2Cu生成厚度约为8 μm的Al-Cu共晶化合物层,铜元素含量达到20%,呈蠕虫状分布.
表 3 图4标记区域化学元素及相组成(质量分数,%)Table 3. Chemical elements and phase composition of labeled regions in Fig. 4位置 元素 相组成 Al Cu b1 85.37 14.63 Al-Cu共晶 b2 92.18 7.82 Al-Cu共晶 c1 97.34 2.66 α-Al固溶体 c2 95.82 4.18 α-Al固溶体 d1 70.22 29.78 Al2Cu d2 81.56 18.44 Al-Cu共晶 d3 65.68 34.32 Al2Cu d4 93.54 6.46 Al-Cu共晶 e1 68.74 31.26 Al2Cu e2 79.44 20.56 Al2Cu e3 95.21 4.79 α-Al固溶体 图5为PR = 1 000 W时铝/铜异种金属搭接焊缝界面微观组织. 焊缝可分为如图5(a)中Ⅰ、Ⅱ两个区域,结合表4的EDS结果分析:I区域组织为主要为α-Al固溶体;Ⅱ区域中存在大量的Al-Cu共晶相,在局部铜元素偏聚的区域,生成少量Al4Cu9相,围绕Al4Cu9相生成一周羽毛状Al2Cu相,Al固溶体相主要位于铝侧焊缝边缘;在铜侧焊缝中,主要由Al2Cu相、Al-Cu共晶相和Al4Cu9组成,且在焊缝底部交界处,出现了多个层状组织(AlCu, Al4Cu9和AlCu3),Al2Cu金属间化合物层厚度由800 W时的4 μm增长至29 μm.
表 4 图5标记区域化学元素及相组成(质量分数,%)Table 4. chemical elements and phase composition of labeled regions in Fig. 5位置 元素 相组成 Al Cu b1 80.51 19.49 Al-Cu共晶 b2 69.25 30.75 Al2Cu b3 34.66 65.34 Al4Cu9 c1 92.32 7.68 Al-Cu共晶 c2 81.47 18.53 Al-Cu共晶 c3 96.41 3.59 α-Al固溶体 d1 66.13 33.87 Al2Cu d2 80.38 19.62 Al-Cu共晶 d3 34.11 65.89 Al4Cu9 e1 66.08 33.92 Al2Cu e2 57.89 42.11 AlCu e3 33.67 66.33 Al4Cu9 e4 24.56 75.44 AlCu3 2.3 力学性能
不同激光功率下的铝/铜异种金属激光搭接焊焊接接头拉伸剪切强度如图6所示. 当激光功率PR = 800 W与PB = 300 W复合时,铝/铜搭接接头的拉剪强度最大达108.6 MPa,随着激光功率的增加,接头的抗剪强度先增加后减少;当PR处于700 ~ 800 W范围内增加时,接头有效连接面积起主导作用;而当PR处于800 ~ 1400 W范围内增加时,界面处Al2Cu金属间化合物和Al-Cu共晶相增多增厚,焊缝的连接强度快速下降. 此外气孔等缺陷的存在,也是导致焊缝强度下降的另一个重要原因.
铝/铜复合激光焊接头断裂位置如图7所示. 当PR处于700 ~ 1 000 W时,焊缝沿铜侧焊缝中心底部断裂;PR增加至1 400 W时,接头沿铝侧焊缝边缘断裂. 图8为PR = 800 W时铝/铜接头铝侧断口形貌,从图8(a) 中观察到铝/铜焊缝接头可分为3个区域:即位于焊缝两侧相对光滑平坦的Ⅰ、Ⅲ区域和焊缝中心部位较为粗糙的Ⅱ区域,Ⅱ区断口处主要为台阶状形貌,判断断裂特征为脆性断裂. 断口EDS结果见表5,接头在受到拉力的作用时,裂纹沿着两侧Al2Cu共晶合金扩展,并扩展到了Al + Al-Cu共晶区,Al2Cu金属间化合物在室温下呈现硬脆特性,在受到拉伸力作用下,焊缝边缘位置的Al2Cu相先产生裂纹,裂纹沿着熔池边缘Al2Cu与Al-Cu共晶界面扩展,最终在熔池底部的Al + Al-Cu共晶相部位断裂. 在图8(d)放大的图中观察到台阶状的断裂面和微小的河流状结构,结合EDS结果分析,断裂的主要形式为解理断裂.
表 5 图8标记区域化学元素及相组成(质量分数,%)Table 5. Chemical elements and phase composition of labeled regions in Fig. 8位置 元素 相组成 Al Cu b1 70.66 29.34 Al2Cu b2 68.01 31.99 Al2Cu b3 70.99 29.01 Al2Cu b4 86.34 13.66 Al + Al-Cu共晶 c1 92.71 7.29 Al + Al-Cu共晶 c2 90.49 9.51 Al + Al-Cu共晶 c3 86.03 13.97 Al + Al-Cu共晶 2.4 导电性能
不同红光功率的接头电阻值如图9所示,从图中可观察到,PR = 700,800 W时的电阻最小,达到了94 μΩ,功率增加到900 ~ 1 400 W时,电阻由94 μΩ增加到130 μΩ. 主要是由于IMC的电阻率较高,随功率增长,化合物层厚度增加,从而导致电阻增加[21],结合2.3力学性能的分析,可以在同一工艺下获得最大拉剪强度与最小接触电阻.
3. 结论
(1) 采用蓝-红复合激光热源实现了1050 Al和T2 Cu的激光焊接. PR在800 W时可获得表面平整、连接质量良好的铝/铜接头;PR超过1 100 W后,焊缝表面形成熔穿孔洞,无法实现铝铜之间的有效焊接.
(2)焊缝组织分布从上至下为Al固溶体,Al固溶体 + Al-Cu共晶,Al2Cu相,且Al2Cu相和Al-Cu共晶化合物层厚度随PR增加而增加.
(3)复合激光功率PR = 800 W和PB = 300 W时,铝/铜接头拉剪强度最高达108.6 MPa,接头断裂过程中裂纹自焊缝颈部Al2Cu相萌生,沿Al-Cu共晶相向底部扩展,最终延伸到底部Al固溶体区域,断裂形式为解理断裂.
(4)复合激光功率PR = 800 W和PB = 300 W时,铝/铜接触电阻最小达到94 μΩ.
-
图 3 不同热处理状态接头不同区域金相组织
Figure 3. Metallography of different regions of the joints under different heat treatment conditions. (a) as-welded HAZ; (b) directly aging-treated HAZ; (c) solution and aging treated HAZ; (d) FZ line of the as-welded joint; (e) FZ line of the directly aging-treated joint; (f) FZ line of the solution and aging treated joint; (g) WS of the as-welded joint; (h) WS of the directly aging-treated joint; (i) WS of the solution and aging treated joint; (j) BM of the as-welded joint; (k) BM of the directly aging-treated joint; (l) BM of the solution and aging treated joint
表 1 焊接工艺参数
Table 1 Welding parameters
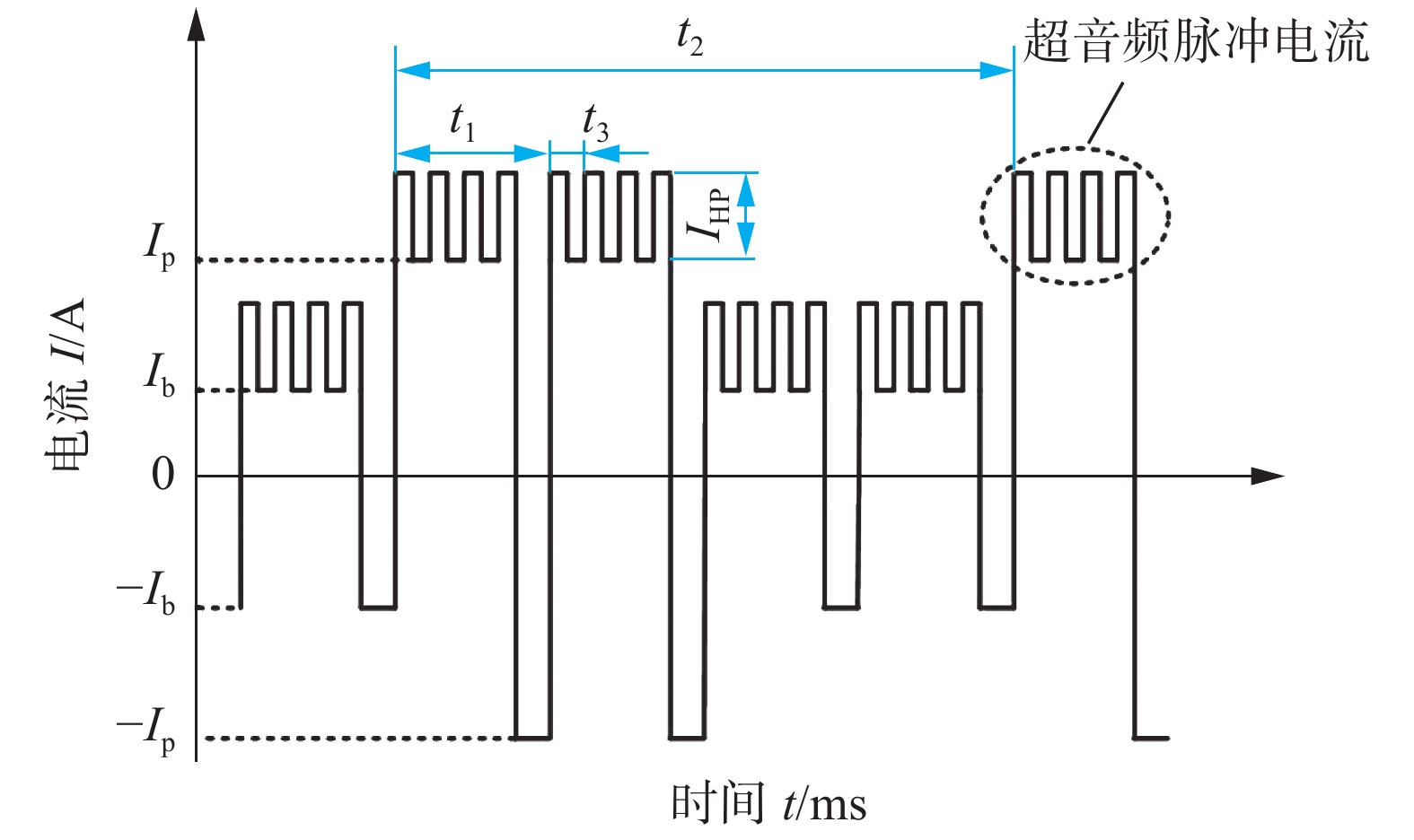
基值电流Ib/A 峰值电流IP/A 超音频脉冲
电流IHP/A低频脉冲
周期t2/ms超音频脉冲
周期t3/ms变极性电流
周期t1/ms送丝速度vs/(m·min−1) 焊接速度v/(m·min−1) 氩气流量Q/(L·min−1) 110 220 80 500 0.05 10 1.5 20 20 表 2 不同热处理焊缝区第二相特征尺寸定量统计结果
Table 2 Characteristic sizes of second phases in the welding seams under different heat treatment conditions
热处理状态 α + θ共晶组织 析出相 面积分数f(%) 周长l/μm 直径D/nm 厚度δ/nm 数量密度dn/nm−3 焊态 5.1 12.3 — — — 直接时效 4.7 11.2 106 5.4 11.7 固溶时效 2.5 1.8 22 0.6 68.5 表 3 不同热处理状态2219铝合金接头显微硬度(HV0.2)
Table 3 Microhardness of 2219 aluminum alloy joints under different heat treatment conditions
热处理状态 热影响区 熔合区 焊缝 母材 焊态 104 112 76 134 直接时效处理 117 141 89 140 固溶时效处理 144 155 148 156 表 4 不同热处理状态2219铝合金接头拉伸性能
Table 4 Tensile properties of 2219 aluminum alloy joints under different heat treatment conditions
热处理状态 抗拉强度
Rm/MPa断后伸长率
A(%)强度系数
φ2219-T6母材 439 12.5 — 焊态 253 5.5 0.57 直接时效处理 264 2.0 0.60 固溶时效处理 371 7.0 0.84 -
[1] 从保强, 樊弢, 齐铂金, 等. 2219铝合金双脉冲VP-GTAW接头组织与性能[J]. 航空制造技术, 2018, 61(20): 16 − 21. Cong Baoqiang, Fan Tao, Qi Bojin, et al. Microstructure and properties of 2219 aluminum alloy welded joint produced by double-pulsed VP-GTAW process[J]. Aeronautical Manufacturing Technology, 2018, 61(20): 16 − 21.
[2] Wang Y P, Cong B Q, Qi B J, et al. Process characteristics and properties of AA2219 aluminum alloy welded by double pulsed VPTIG welding[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2019, 266: 255 − 263. doi: 10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2018.11.015
[3] Wang Y P, Qi B J, Cong B Q, et al. Keyhole welding of aa2219 aluminum alloy with double-pulsed variable polarity gas tungsten arc welding[J]. Journal of Manufacturing Processes, 2018, 34: 179 − 186. doi: 10.1016/j.jmapro.2018.06.006
[4] Wang S C, Starink M J, Precipitates and intermetallic phases in precipitation hardening Al-Cu-Mg-(Li) based alloys [J], International materials reviews, 2005, 50(4): 193–215.
[5] Ding J K, Wang D P, Wang Y, et al. Effect of post weld heat treatment on properties of variable polarity TIG welded AA2219 aluminium alloy joints[J]. Transaction of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2014, 24: 1307 − 1316. doi: 10.1016/S1003-6326(14)63193-9
[6] Zhu Z Y, Deng C Y, Wang Y, et al. Effect of post weld heat treatment on the microstructure and corrosion behavior of AA2219 aluminum alloy joints welded by variable polarity tungsten inert gas welding[J]. Materials & Design, 2015, 65: 1075 − 1082.
[7] Lü Zongliang, Li Chong, Wan Long, et al. The influence of gradient mismatches on mechanical properties and microstructure of 2219-T6 aluminum alloy VP-TIG joints[J]. China Welding, 2017, 26(4): 20 − 28.
[8] 周政, 王国庆, 宋建岭, 等. 2219铝合金不同气氛下TIG焊焊接接头组织性能[J]. 焊接学报, 2018, 39(7): 47 − 50,131. Zhou Zheng, Wang Guoqing, Song Jianling, et al. Microstructure and mechanical properties of 2219 aluminum alloys TIG welding welded joints in different shielding gases[J]. Transactions of the China welding institution, 2018, 39(7): 47 − 50,131.
[9] 王富鑫, 骆良顺, 王亮, 等. 合金成分和冷却速率对Al-Cu合金凝固过程中初生Al2Cu相生长形貌的影响[J]. 金属学报, 2016, 52(3): 361 − 368. doi: 10.11900/0412.1961.2015.00326 Wang Fuxin, Luo Liangshun, Wang Liang, et al. , Effect of alloy composition and cooling rate on the growth morphology of primary Al2Cu phase in Al-Cu alloy during solidification[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2016, 52(3): 361 − 368. doi: 10.11900/0412.1961.2015.00326
[10] Gao L, Li K, Ni S, et al. The growth mechanisms of θ' precipitate phase in an Al-Cu alloy during aging treatment[J]. Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 2021, 61: 25 − 32.
[11] Fu S h, Yi D Q, Liu H Q, et al. Effects of external stress aging on morphology and precipitation behavior of θ'' phase in Al-Cu alloy[J]. Transaction of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2014, 24: 2282−2288.
[12] Bahl S, Xiong L H, Allard L F, et al. Aging behavior and strengthening mechanisms of coarsening resistant metastable θ' precipitates in an Al-Cu alloy[J]. Materials & Design, 2021, 198: 109378.
[13] Bellón B, Haouala S, Lorca J. An analysis of the influence of the precipitate type on the mechanical behavior of Al-Cu alloys by means of micropillar compression tests[J]. Acta Materialia, 2020, 194: 207 − 223. doi: 10.1016/j.actamat.2020.05.040
[14] Zhang P, Bian J J, Zhang J Y, et al. Plate-like precipitate effects on plasticity of Al-Cu alloys at micrometer to sub-micrometer scales[J]. Materials & Design, 2020, 188: 108444.



 下载:
下载: