Effect of pre-weld heat treatment on the microstructure and mechanical properties of electron beam welded 440C stainless steel joint
-
摘要: 研究了焊前退火和调质2种热处理工艺对440C不锈钢电子束焊接接头的组织和力学性能的影响,分析了2种状态下的组织演变规律、接头拉伸力学性能和硬度分布特点. 结果表明:2种热处理状态的板材经过电子束焊接后,焊缝成形良好,焊缝区域均为马氏体和残留奥氏体组织,呈现出非平衡凝固组织,碳及合金元素以固溶形式存在于马氏体及残余奥氏体中,焊缝区域硬度达到398 HV. 焊前经调质热处理后,母材基体由铁素体转变成回火马氏体和残余奥氏体混合组织,同时部分碳化物固溶在基体组织中,使基体组织硬度提高了60%. 与焊前退火态相比,焊前调质热处理板材经电子束焊接后,可使焊接接头抗拉强度提高20%,焊接热影响区硬度提高35%,但接头的塑性变形能力有所下降,断裂均发生在热影响区.Abstract: The effects of pre-weld heat treatment on microstructure and mechanical properties of electron beam welded 440C stainless steel joint were observed and studied, including annealing as well as quenching and tempering. The characteristics of structure change, joint tension and hardness distribution in the two states are analyzed. The results show that the electron beam weld has a good shape without any microcracks. The microstructure located at the weld consists of martensite and retained austenite, showing a non-equilibrium solidification microstructure, carbon and alloying elements exist in the weld structure in solid solution, and the hardness reaches 398 HV. After quenching and tempering heat treatment before welding, the base metal matrix transforms from ferrite into tempered martensite and retained austenite, and at the same time the carbide part is solid-dissolved into the matrix structure, which increases the matrix structure hardness by 60%. Compared with the annealed state before welding, after electron beam welding, the tensile strength of the welded joint is increased by 20%, and the hardness of the welded heat-affected zone is increased by 35%, but the plastic deformation ability of the joint is reduced, and the fracture occurs in the heat-affected zone.
-
Keywords:
- 440C stainless steel /
- EBW /
- pre-weld heat treatment /
- microstructures /
- mechanical properties
-
0. 序言
440C不锈钢是一种高碳高铬型马氏体不锈钢,含有Cr,Mo,Ni等多种合金元素,在马氏体不锈钢中具有较高的机械强度,广泛的应用于船舶、建筑、电力等诸多工业领域[1-5]. 然而,440C不锈钢的供货状态通常为退火状态,在实际应用中需要先通过调质热处理硬化,然后再焊接形成结构件,以满足使用性能要求[6-8],因此,要求焊接后接头不再进行大量机加工,仍然能满足装配要求. 电子束焊接作为一种高能束焊接方法,具有能量密度高、焊接变形小、可控精度高等优势,在精密构件焊接中获得广泛应用[9-11].
鉴于440C不锈钢含有较高的碳元素与合金元素,碳化物是其中重要的第二相. 碳化物的种类、数量、尺寸、形态和分布对钢的性能有重要影响[12]. 焊前调质热处理的方式可以改变碳化物的溶解和沉淀,达到固溶强化和沉淀强化的效果[13-16],同时,碳化物中的合金元素分布也影响热处理过程中马氏体转变温度[17],因此调质态的440C母材与退火态母材具有截然不同的组织和性能,其焊接性如何变化,尚未见到相关报道. 通过对退火和调质2种焊前热处理状态的440C不锈钢进行电子束焊接,揭示2种热处理状态下,母材、焊缝区和热影响区的组织特征,并且进一步分析不同热处理工艺的母材对于焊接接头硬度、抗拉强度的影响,为440C不锈钢电子束焊接加工提供参考.
1. 试验方法
试验材料采用尺寸为150 mm × 100 mm × 5 mm的440C不锈钢板材,化学成分组成如表1所示. 对440C不锈钢板材进行不同的焊前热处理,其中退火工艺(板材供货时的状态)为899 ℃下保温1 h,炉冷至593 ℃,随后空冷;调质热处理工艺为退火后的板材加热到1 020 ℃保温1.3 h,深冷处理2 h,随后进行590 ℃的高温回火处理. 板材经消磁处理后采用360目SiC砂纸研磨并用酒精清理表面污染物,然后采用真空电子束焊机对板材进行对接焊接. 焊接工艺参数为:加速电压150 kV,电子束流17 mA,焊接速度850 mm/min,采用表面聚焦,同时添加三角波扫描焊接以较少咬边. 在焊接过程中,没有填充金属或预热处理.
表 1 440C不锈钢化学成分 (质量分数,%)Table 1. Chemical composition of 440C stainless steelC Cr Mo Mn Si Ni Cu P S Fe 1.04 16.3 0.48 0.75 0.32 0.11 0.06 0.016 0.002 余量 用于微观组织观察的试样使用SiC 砂纸研磨和金刚石膏抛光后使用王水(浓盐酸与浓硝酸体积比3∶1)进行腐蚀. 通过蔡司Axio Imager M2m光学显微镜和Quanta 250钨灯丝扫描电子显微镜(SEM)和附带能谱分析(EDS)观察母材、热影响区(HAZ)、熔合线(FL)和焊缝(FZ)区域的微观结构与成分变化. 使用透射电子显微镜(TEM, Tecnai G2 F20 S-TWIN 200kv)观察其热影响区微观结构. 采用FISCHIONE双射流电解抛光装置,在室温下以35 mA电流,用10%高氯酸在冰醋酸中组成的溶液制备TEM箔片. 用Image-Pro-plus6.0分析了碳化物的特征. 显微硬度测试在美国威尔逊Wilson公司BUEHLER VH1202 维氏显微硬度上进行,负载500 g,持续10 s. 根据GB/T 228.1—2010《焊接接头拉伸测试方法》标准,在室温下使用GP-TS2000 M/300 KN试验机测试了接头的拉伸性能,拉伸试样的尺寸如图1所示.
2. 结果与分析
2.1 热处理对母材和焊缝金属组织的影响
图2a和图2b分别为退火热处理及调质热处理后母材的扫描电镜图片,从图中可以看出两种热处理状态的基体上均匀分布着两种类型的碳化物,即粗大不规则形状的一次碳化物,及细小的球状碳化物(也被称为二次碳化物). 根据Jalaja等的研究可知,440C不锈钢在淬火和回火条件下存在的一次和二次碳化物,分别为正交结构的M7C3碳化物和面心立方结构的M23C6碳化物[18]. Puli等人[19]在对440C马氏体不锈钢表面涂层组织与性能的研究过程中,检测得出退火状态下基体为铁素体,经1050℃奥氏体化,油淬后又经200℃回火,空冷至室温,基体由回火马氏体和残留奥氏体组成. 对不同热处理试样碳化物的统计与拟合结果如图2c所示,定量分析结果如表2所示,退火母材中碳化物的尺寸主要分布在0.8 ~ 1.0 μm,分布频率约为27%,平均尺寸为(0.86 ± 0.03)μm;调质母材碳化物的颗粒尺寸主要分布在0.8 ~ 1.0 μm,分布频率约为31%,平均尺寸为(0.94 ± 0.02)μm. 在退火母材中,碳化物体积分数约为27%;而调质态母材中碳化物体积分数约为20%.
表 2 母材中碳化物颗粒定量分析Table 2. Quantitative analysis of carbide particles in base materials母材 颗粒尺寸主要分布d/μm 分布频率A(%) 平均尺寸d1/μm 标准误差d2/μm 体积分数B(%) 退火态母材 0.8 ~ 1.0 27 0.86 0.03 27 调质态母材 0.8 ~ 1.0 31 0.94 0.02 20 上述结果表明退火母材经调质热处理后,碳化物颗粒部分固溶在马氏体基体中,同时,未溶解的碳化物颗粒由于热激活作用有所长大. 440C钢的力学性能取决于基体强度与碳化物沉淀强化共同作用:基体强度则取决于过饱和固溶的C含量;碳化物沉淀强化效果与其体积分数成正比,与平均尺寸成反比. 退火态母材在淬火热处理过程中,碳化物颗粒逐渐发生溶解,使基体中碳含量增加,达到固溶强化的效果,而未溶解的碳化物颗粒阻碍了奥氏体晶粒的生长[20]. 在440C回火过程中,过饱和固溶在马氏体基体中的碳化物析出并长大[21].
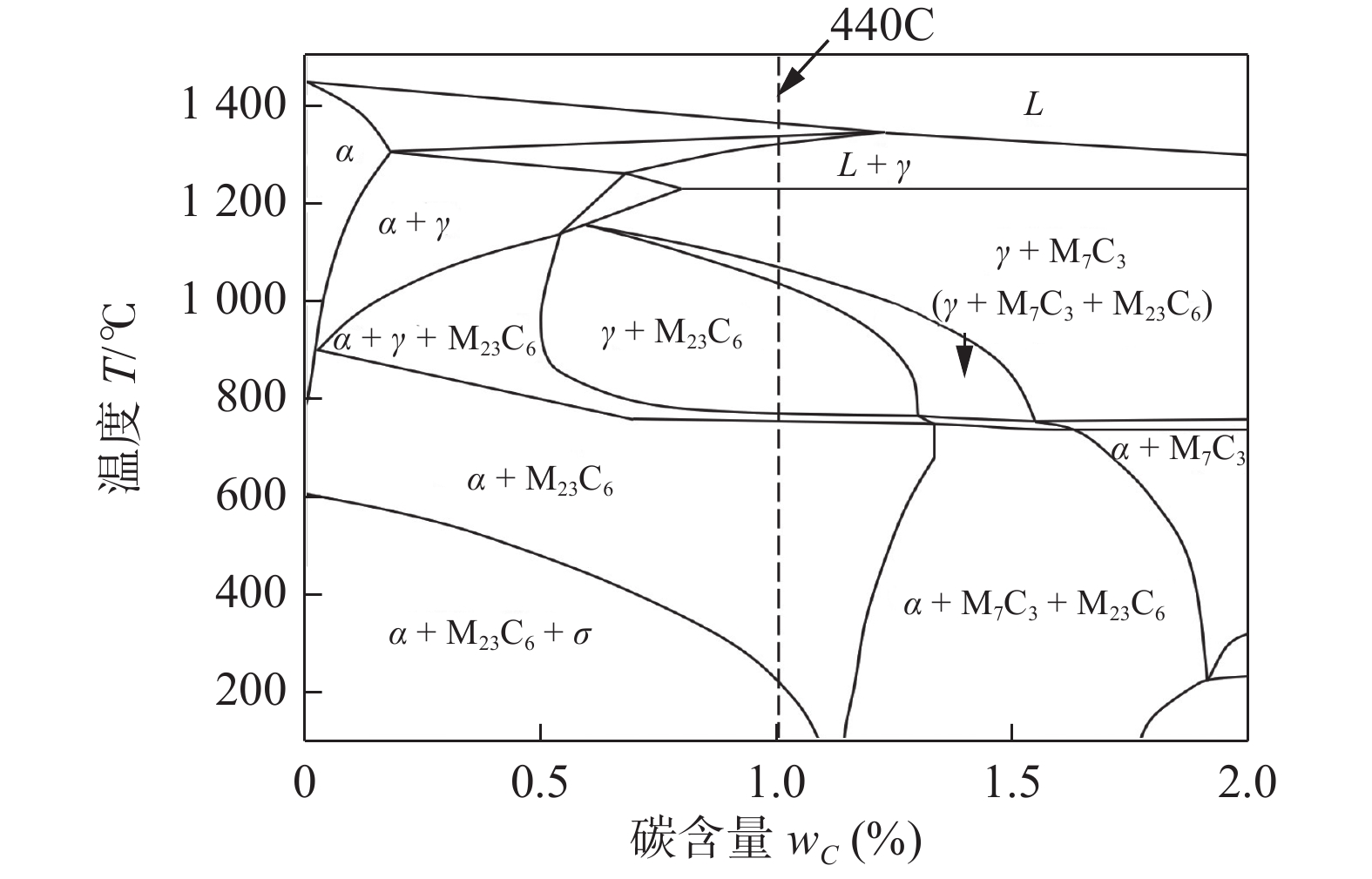
图3显示了一个典型的真空电子束焊接接头在显微镜下焊缝形貌的图片,焊缝成形良好,形成典型钟罩形电子束焊缝形状,焊缝表面较为平整,焊缝熔融金属在重力作用下自然下沉,焊缝背部形成一定的余高,3条白线为硬度测试位置. 无论焊前状态如何,焊缝区域的金属都会经历熔化和凝固的过程,因此焊缝金属的金相组织与焊前状态无关. 图4为碳含量为1%的Fe-C-Cr三元合金相图,焊接过程中,焊缝区域金属经历快速加热而熔化,在随后的冷却过程中,由于存在较大的过冷度,焊缝区域金属快速冷却,转化形成马氏体组织. 在含碳量为1%的440C不锈钢中,固溶在基体中的Cr、Mo、Mn元素均使马氏体开始转变温度Ms和马氏体终止转变温度Mf降低,并且使Mf低于室温,导致马氏体转变并不能完全进行,部分未能发生转变的奥氏体将保留下来,形成残留奥氏体[22]. 如图5所示,焊缝区域分布着长条状的一次枝晶和二次枝晶,最终在焊缝区域形成马氏体和残余奥氏体组织[23]. 在含碳量为0.1% ~ 0.6%的钢中,马氏体是呈板条状,高于0.6%的钢中,马氏体则呈现针状(见图5). 而碳化物颗粒熔解后,在快速冷却的条件下来不及析出,过饱和的固溶在了马氏体和残留奥氏体中.
2.2 热处理对热影响区组织的影响
在焊接热循环作用下,焊缝两侧母材中碳化物颗粒和基体组织发生变化,形成焊接热影响区. 不同焊前热处理条件下样品热影响区组织SEM图片如图6a与图6b所示. 对焊接热影响区碳化物颗粒的统计与拟合结果如图6c所示,定量分析结果如表3所示,退火态焊接HAZ中碳化物尺寸主要分布在0.8 ~ 1.0 μm,分布频率约为20%,平均尺寸为1.07 ± 0.06 μm;调质焊缝HAZ碳化物颗粒尺寸主要分布在0.7 ~ 0.9 μm,分布频率约为29%,平均尺寸为0.92 ± 0.04 μm. 这表明,熔合线附近的热影响区中,焊接热影响区碳化物颗粒在焊接热循环的作用下发生溶解并长大,基体中的Cr,Mo,Mn等合金元素也随着碳化物颗粒的析出而减少. 由Capdevila等人[24]研究合金元素对钢的马氏体起始温度的影响可知,合金元素的含量对于马氏体起始转变温度Ms有着重要的影响,在基体中Cr,Mo,Mn元素析出时,会提高马氏体起始转变温度Ms,促使奥氏体向马氏体转变,导致焊接热影响区中的残留奥氏体在焊接热循环作用下进一步转变成为马氏体.
![]() 图 6 不同热处理状态下HAZ的SEM图片Figure 6. SEM pictures of metallographic structure in different heat treatment states. (a) microstructure of HAZ in base metal annealed; (b) microstructure of HAZ in base metal quenched and tempered; (c) distribution of carbide particles in HAZ with different heat treatment states表 3 HAZ中碳化物颗粒定量分析Table 3. Quantitative analysis of carbide particles in HAZ
图 6 不同热处理状态下HAZ的SEM图片Figure 6. SEM pictures of metallographic structure in different heat treatment states. (a) microstructure of HAZ in base metal annealed; (b) microstructure of HAZ in base metal quenched and tempered; (c) distribution of carbide particles in HAZ with different heat treatment states表 3 HAZ中碳化物颗粒定量分析Table 3. Quantitative analysis of carbide particles in HAZ母材 颗粒尺寸主要分布d/μm 分布频率A(%) 平均尺寸d1/μm 标准误差d2/μm 退火态母材 0.8 ~ 1.0 20 1.07 0.06 调质态母材 0.7 ~ 0.9 29 0.92 0.04 图7为调质态焊缝HAZ的TEM图,并对该区域进行选区电子衍射分析,结果如图8所示. 由明场和暗场下的TEM图和基体的多晶环衍射结果(图8c)可以得出基体为马氏体和残余奥氏体的混合组织. 图8b为对碳化物颗粒的电子衍射结果,并对碳化物颗粒进行线扫描,如图9所示,由图可知,碳化物颗粒的化学成分为Cr49.2Mn7.22Fe33.8Mo0.714C9.13(原子分数,%),因此也可说明为M23C6型碳化物.
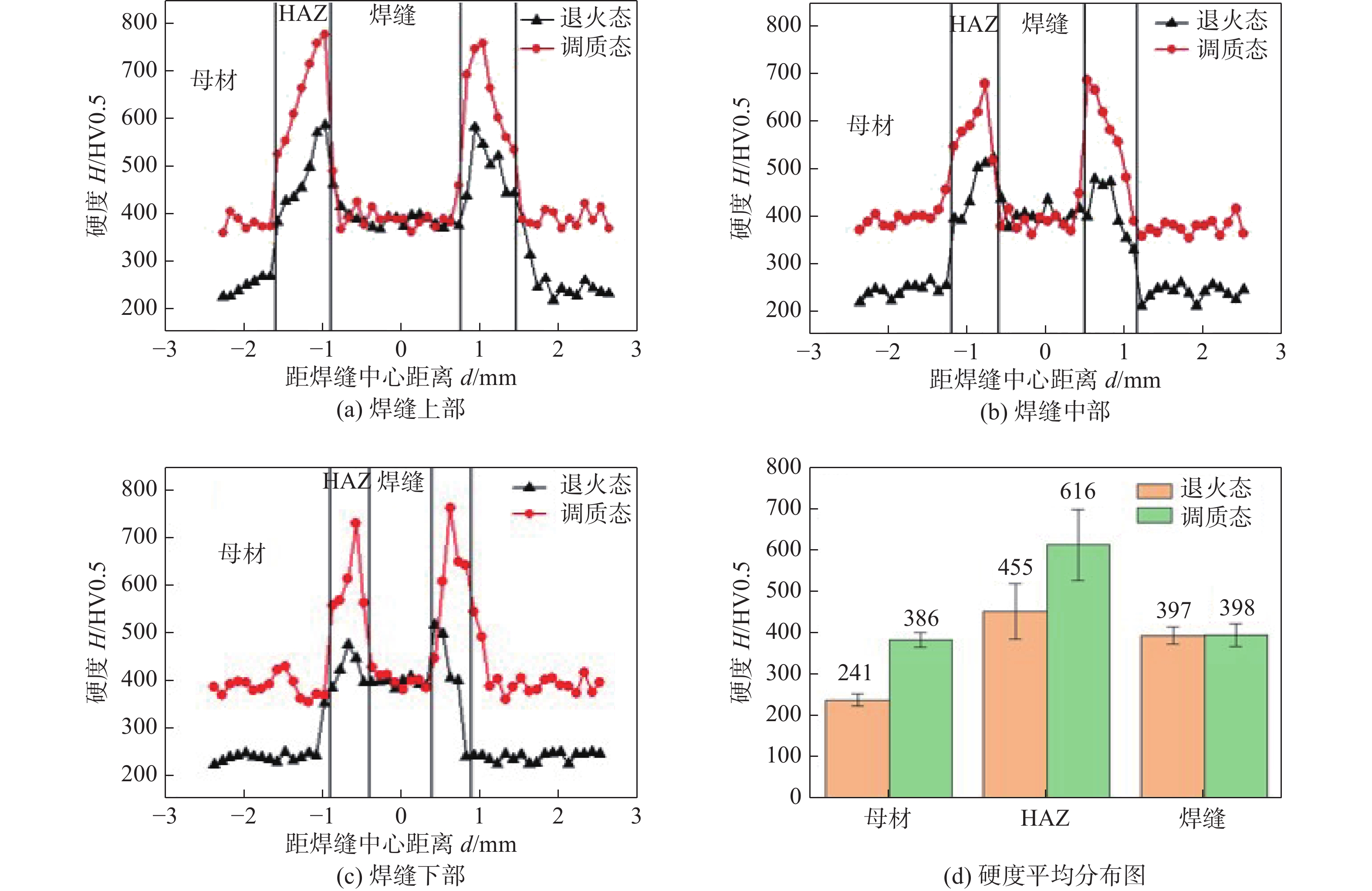
两种不同焊前热处理条件下试样的硬度分布曲线如图10所示,图10a、10b、10c分别代表焊缝上、中、下3个位置的硬度分布,图10d表示硬度分布的平均值. 3个位置上硬度分布整体上呈“M”型分布,焊接热影响区的硬度最高. 在退火态焊接接头上,焊接热影响区硬度为(455 ± 67) HV,最高可达588 HV;在调质态焊接接头上,焊接热影响区熔合线附近的硬度为(616 ± 86) HV,最高可达780 HV,比退火态下提高了35%. 2种热处理状态下,在热影响区随着离熔合线距离的增加,都呈现出硬度逐渐减小现象,这是由于在靠近熔合线的地方,在焊接热循环的作用下碳化物发生了明显的溶解和长大. 如图10d所示,两种热处理状态下的焊缝区域硬度和调质母材硬度相当,这是由于焊缝区域组织和调质态下的母材均由马氏体和残留奥氏体组成. 退火态母材的硬度最低,平均为(241 ± 15) HV,经调质热处理后,母材硬度提高了60%,达到(386 ± 17) HV,这是由于退火态的铁素体组织经调质处理后转变成回火马氏体和少量的残余奥氏体,硬度得到很大的提高.
2.3 拉伸性能和断口形貌
两种焊接接头与母材的抗拉强度和伸长率如图11所示. 退火态母材和调质态母材抗拉强度分别为718 MPa和1268 MPa,退火态焊接接头和调质态焊接接头的抗拉强度分别为698 MPa和839 MPa,焊接接头的抗拉强度均不如母材高,但是调质态下的焊接接头抗拉强度比退火态下焊接接头提高20%. 对于退火态母材,在进行电子束焊接后,为母材(强度系数)的97%,断后伸长率由焊前的18%降到5%,为脆性断裂. 调质态母材电子束焊接后,强度系数为66%,断后伸长率由母材的2%降低到完全脆性断裂.
结合“热处理对母材和焊缝金属组织的影响”与“热处理对热影响区组织的影响”部分的组织分析可知,焊缝金属熔化过程中,碳化物溶解到基体,在快速冷却的条件下,焊缝区域的组织由铁素体转变成马氏体,快速冷却导致碳化物不能从马氏体中析出,进一步强化了焊缝的硬度,使焊缝的塑性变形能力下降. 试样断口的位置在热影响区,这是因为焊接热影响区在焊接热循环的作用下,碳化物从基体上析出并聚集长大,使碳化物的弥散强化作用减弱,距离熔合线越近,这种影响越明显,所以断裂发生在热影响区. 焊接接头的脆性断裂,这是由于调质后的母材和焊缝区域组织都为马氏体和残余奥氏体的混合组织,可以有效的提高材料的抗拉强度,但是会大大降低材料的塑性. 在焊接热循环的作用下,焊接热影响区分布的小颗粒碳化物发生溶解,并且会聚集在块状的碳化物上,使热影响区的塑性变形能力下降,导致脆性断裂的发生.
图12为扫描电镜下2种焊接接头试样拉伸断口的微观形貌,均为脆性断裂. 在退火态拉伸试样断口上,可以看到大量由拉伸形成的小型孔洞,碳化物颗粒分布在孔洞中,并且存在少量的解理断裂面. 这些小型孔洞是由小而分布的碳化物颗粒从基体中分离而形成的[25]. 调质态拉伸试样上呈现出少量由碳化物颗粒形成的孔洞,形成明显的解理断裂面,在解理断裂面和碳化物的界面上有明显的裂纹. 根据Manwatkar等人[26]研究可知,解理断裂面为碳化物与基体结合较弱的界面,拉伸过程中,这些弱界面在应力的作用下易导致裂纹的萌生和扩展. 在HAZ的断口处观察到碳化物颗粒数量减少,碳化物固溶到基体组织中,使基体中碳元素含量升高,导致调质态焊接接头塑性严重下降.
3. 结 论
(1) 焊前经过退火和调质热处理的440C板材均可以进行电子束焊接,焊缝成形良好,无明显缺陷,可以获得典型钟罩形电子束接头形状.
(2) 退火和调质2种不同的焊前热处理工艺对440C不锈钢电子束焊接焊缝显微组织没有明显影响. 母材在退火态下,组织为铁素体基体上弥散分布碳化物颗粒;经调质处理后,基体由回火马氏体及残留奥氏体组成,碳化物颗粒发生部分的固溶,颗粒数量减少,但尺寸增大,硬度也由退火态的241 HV提高了60%,达到了386 HV. 经过电子束焊接后,焊缝区域组织均由马氏体与残留奥氏体构成,碳及合金元素以过饱和固溶的形式存在于焊缝组织中,硬度达到398 HV.
(3) 2种不同的焊前热处理工艺对焊接热影响区的显微组织和力学性能产生了明显影响. 在经历焊接热循环后,HAZ部分碳化物颗粒发生溶解,固溶到基体组织中,引起组织的固溶强化,未溶解碳化物颗粒分布在基体上并且尺寸得到进一步的长大,固溶强化与弥散强化的综合效果使焊接接头的强度和硬度都有所提高. 与退火态相比,采用焊前调质热处理可以使焊缝接头热影响区硬度由588 HV提高到 780 HV,提高了35%,接头抗拉强度由698 MPa提高到了839 MPa,提高了20%.
-
图 6 不同热处理状态下HAZ的SEM图片
Figure 6. SEM pictures of metallographic structure in different heat treatment states. (a) microstructure of HAZ in base metal annealed; (b) microstructure of HAZ in base metal quenched and tempered; (c) distribution of carbide particles in HAZ with different heat treatment states
表 1 440C不锈钢化学成分 (质量分数,%)
Table 1 Chemical composition of 440C stainless steel
C Cr Mo Mn Si Ni Cu P S Fe 1.04 16.3 0.48 0.75 0.32 0.11 0.06 0.016 0.002 余量 表 2 母材中碳化物颗粒定量分析
Table 2 Quantitative analysis of carbide particles in base materials
母材 颗粒尺寸主要分布d/μm 分布频率A(%) 平均尺寸d1/μm 标准误差d2/μm 体积分数B(%) 退火态母材 0.8 ~ 1.0 27 0.86 0.03 27 调质态母材 0.8 ~ 1.0 31 0.94 0.02 20 表 3 HAZ中碳化物颗粒定量分析
Table 3 Quantitative analysis of carbide particles in HAZ
母材 颗粒尺寸主要分布d/μm 分布频率A(%) 平均尺寸d1/μm 标准误差d2/μm 退火态母材 0.8 ~ 1.0 20 1.07 0.06 调质态母材 0.7 ~ 0.9 29 0.92 0.04 -
[1] Bush R, Gill J, Teakell J. Heat treatment optimization and fabrication of a 440C stainless steel knife[J]. JOM, 2016, 68(12): 3167 − 3173. doi: 10.1007/s11837-016-2117-5
[2] Prieto G, Mandri A, Rabbia G, et al. Rolling contact fatigue resistance of cryogenically treated AISI 440C steel[J]. Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance, 2020, 29(11): 2216 − 2226.
[3] 季文彬. 梯度功能金属陶瓷复合刀具的扩散烧结制备及其切削性能研究[D]. 济南, 山东大学, 2017. Ji Wenbin. Diffusion sintering fabrication and cutting performance functional gradient cermet composite cutting tools[D].Jinan, Shandong University, 2017.
[4] 康超, 郭秀乔, 唐雪明, 等. 冷处理温度对440C不锈钢组织和硬度的影响[J]. 热加工工艺, 2017(24): 211 − 212. Kang Chao, Guo Xiuqiao, Tang Xueming, et al. Effects of cold treatment temperature on microstructure and hardness of 440C stainless steel[J]. Hot Working Technology, 2017(24): 211 − 212.
[5] 胡飞, 刘利国, 陈未来, 等. AISI440C不锈钢QPQ盐浴复合表面处理及其耐磨性研究[J]. 热加工工艺, 2021(18): 107 − 110. Hu Fei, Liu Liguo, Chen Weilai, et al. Study on QPQ salt bath composite surface treatment and wear resistance of AISI440C stainless steel[J]. Hot Working Technology, 2021(18): 107 − 110.
[6] Yang J R, Yu T H, Wang C H. Martensitic transformations in AISI 440C stainless steel[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2006, 438(11): 276 − 280.
[7] Salleh S H, Omar M Z, Syarif J, et al. Investigation of microstructures and properties of 440C martensitic stainless steel[J]. International Journal of Mechanical and Materials Engineering, 2009, 4(2): 123 − 126.
[8] Hetzner D W, Geertruyden W V. Crystallography and metallography of carbides in high alloy steels[J]. Materials Characterization, 2008, 59(7): 825 − 841. doi: 10.1016/j.matchar.2007.07.005
[9] Sokkalingam R, Mastanaiah P, Muthupandi V, et al. Electron-beam welding of high-entropy alloy and stainless steel: microstructure and mechanical properties[J]. Materials and Manufacturing Processes, 2020, 35(16): 1885 − 1894. doi: 10.1080/10426914.2020.1802045
[10] Chen G, Yin Q, Zhang G, et al. Underlying causes of strength weakening of electron beam welded joints of high-speed steels[J]. Journal of Manufacturing Processes, 2019, 39: 250 − 258. doi: 10.1016/j.jmapro.2019.01.047
[11] Jin J, Gao R, Peng H, et al. Rapid solidification microstructure and carbide precipitation behavior in electron beam melted high-speed steel[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2020, 51: 2411 − 2429. doi: 10.1007/s11661-020-05661-z
[12] Wang H, Li J, Shi C B, et al. Evolution of carbides in H13 steel in heat treatment process[J]. Materials Transactions, 2017, 58(2): 152 − 156. doi: 10.2320/matertrans.M2016268
[13] Jin J, Liu F B, Chen Y B, et al. Surface carbon chemical states of ion implanted AISI 440C martensitic stainless steel[J]. Journal of Iron & Steel Research International, 2015, 22(6): 513 − 518.
[14] Lin Y T, Wang D P, Wang M C, et al. Effect of different pre-and post-weld heat treatments on microstructures and mechanical properties of variable polarity TIG welded AA2219 joints[J]. Science & Technology of Welding & Joining, 2015, 21(3): 234 − 241.
[15] 张敏, 贾芳, 程康康, 等. 调质处理对G520钢焊接接头组织及性能的影响[J]. 金属学报, 2019, 55(11): 1379 − 1387. Zhang Min, Jia Fang, Cheng Kangkang, et al. Influence of quenching and tempering on microstructure and properties of welded joints of G520 martensitic steel[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2019, 55(11): 1379 − 1387.
[16] 张敏, 仝雄伟, 李洁, 等. 焊前和焊后调质处理下25Cr2Ni4MoV钢焊接接头的组织及性能[J]. 机械工程材料, 2021, 45(1): 34 − 40. Zhang Min, Tong Xiongwei, Li Jie, et al. Microstructure and properties of 25Cr2Ni4MoV steel welded joint under pre-welding and post-welding quenching and tempering treatment[J]. Materials For Mechanical Engineering, 2021, 45(1): 34 − 40.
[17] Huang K T, Chang S H, Hsieh P C. Microstructure, mechanical properties and corrosion behavior of NbC modified AISI 440C stainless steel by vacuum sintering and heat treatments[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2017, 712: 760 − 767. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2017.04.125
[18] Jalaja K, Manwatkar S K, Anand P, et al. Metallurgical analysis of surface distress on balls during the operation of AISI 440C ball bearings for satellite applications[J]. Engineering Failure Analysis, 2021, 124: 105376. doi: 10.1016/j.engfailanal.2021.105376
[19] Puli R, Ram G. Microstructures and properties of friction surfaced coatings in AISI 440C martensitic stainless steel[J]. Surface & Coatings Technology, 2012, 207: 310 − 318.
[20] Veerababu R, Prasad K S, Balamuralikrishnan R, et al. Austenite stability and M2C carbide decomposition in experimental secondary hardening ultra-high strength steels during high temperature austenitizing treatments[J]. Materials Characterization, 2018, 144: 191 − 204. doi: 10.1016/j.matchar.2018.07.013
[21] Krishna S C, Tharian K T, Chakravarthi K V A, et al. Heat treatment and thermo-mechanical treatment to modify carbide banding in AISI 440C steel: a case study[J]. Metallography, Microstructure, and Analysis, 2016, 5(2): 108 − 115. doi: 10.1007/s13632-016-0266-0
[22] Kawata H, Hayashi K, Wakabayashi C, et al. Martensite transformation start temperature during quench and austempering in Fe-8Ni-0.2 C alloys[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2021, 52(4): 1395 − 1408. doi: 10.1007/s11661-021-06167-y
[23] Lo K H, Cheng F T, Kwok C T, et al. Effects of laser treatments on cavitation erosion and corrosion of AISI 440C martensitic stainless steel[J]. Materials Letters, 2004, 58(1-2): 88 − 93. doi: 10.1016/S0167-577X(03)00421-X
[24] Capdevila C, Caballero F G, García de Andrés C. Analysis of effect of alloying elements on martensite start temperature of steels[J]. Materials science and technology, 2003, 19(5): 581 − 586. doi: 10.1179/026708303225001902
[25] Syarif J, Yousuf M H, Sajuri Z, et al. Effect of partial solution treatment temperature on microstructure and tensile properties of 440C martensitic stainless steel[J]. Metals - Open Access Metallurgy Journal, 2020, 10(5): 1 − 14.
[26] Manwatkar S K, Bahrudheen A, Tiwari S B, et al. Failure analysis of AISI 440C steel ball screws used in the actuator system of a satellite launch vehicle[J]. Journal of Failure Analysis and Prevention, 2017, 17(3): 505 − 512. doi: 10.1007/s11668-017-0268-5
-
期刊类型引用(5)
1. 袁明新,戴现令,刘超,孙宏伟,王磊. 基于空间位置和轮廓线距离的船舶焊缝特征参数提取. 焊接学报. 2023(01): 84-92+133-134 .  本站查看
本站查看
2. 陈兵,贺晟,刘坚,陈圣峰,路恩会. 基于轻量化DeepLab v3+网络的焊缝结构光图像分割. 中国激光. 2023(08): 49-58 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 张开放,刘蔓,陈欢群,柴绪彬. 基于电容式传感器的焊缝特征检测技术. 自动化与仪表. 2023(06): 81-84+90 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 祖海英,卢兴宇,宋玉杰,李大奇. 基于激光熔覆再制造PDC钻头的机器人仿真分析. 焊接学报. 2022(10): 71-76+117-118 .  本站查看
本站查看
5. 夏卫生,方向瑶,杨帅,林富明,杨云珍. 基于频率调谐的焊缝红外图像显著性检测算法. 焊接. 2021(04): 8-12+62 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(9)



 下载:
下载: