Study on grain size and microstructure of TC4 titanium alloy TIG and laser welding joint
-
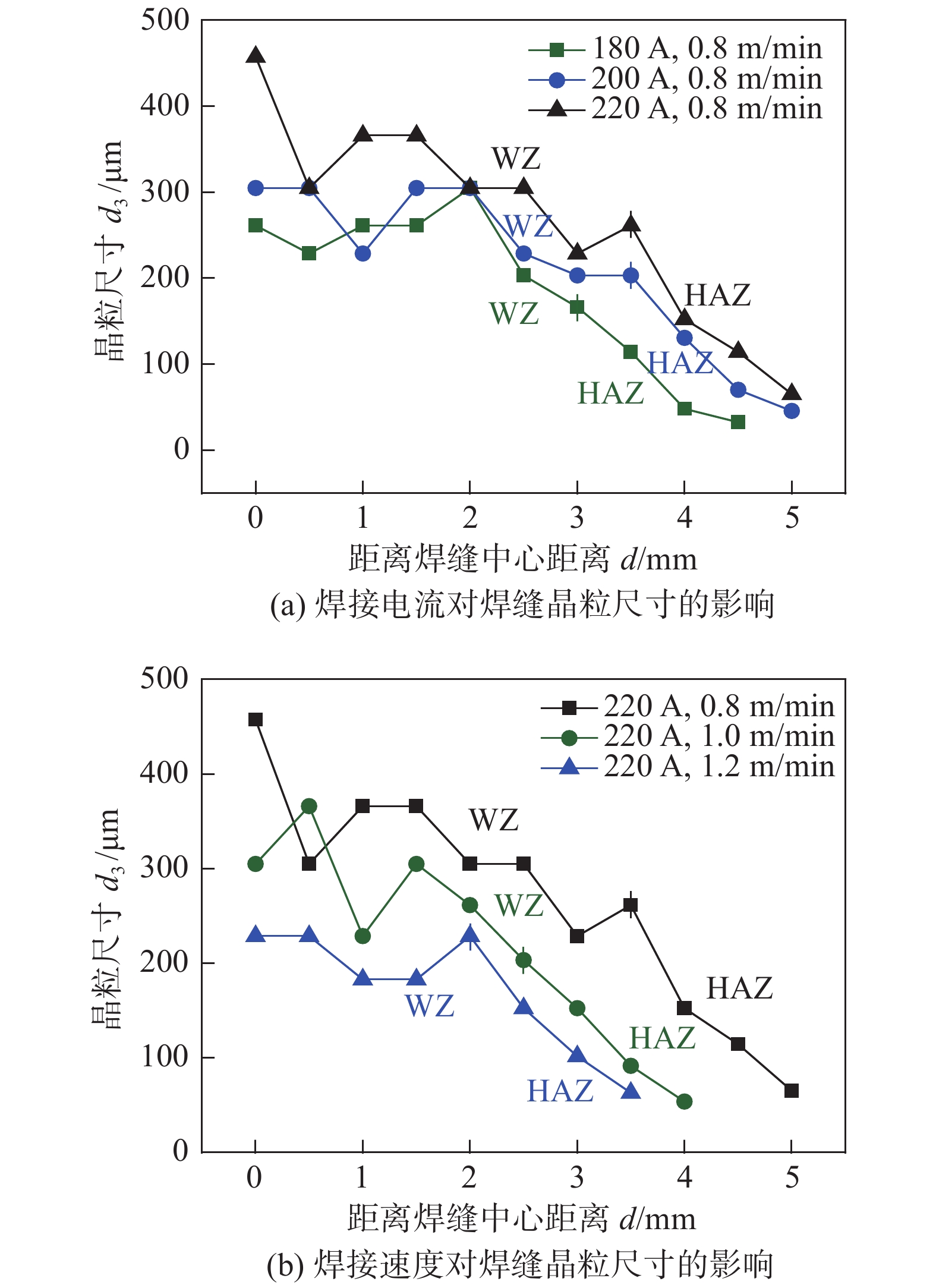
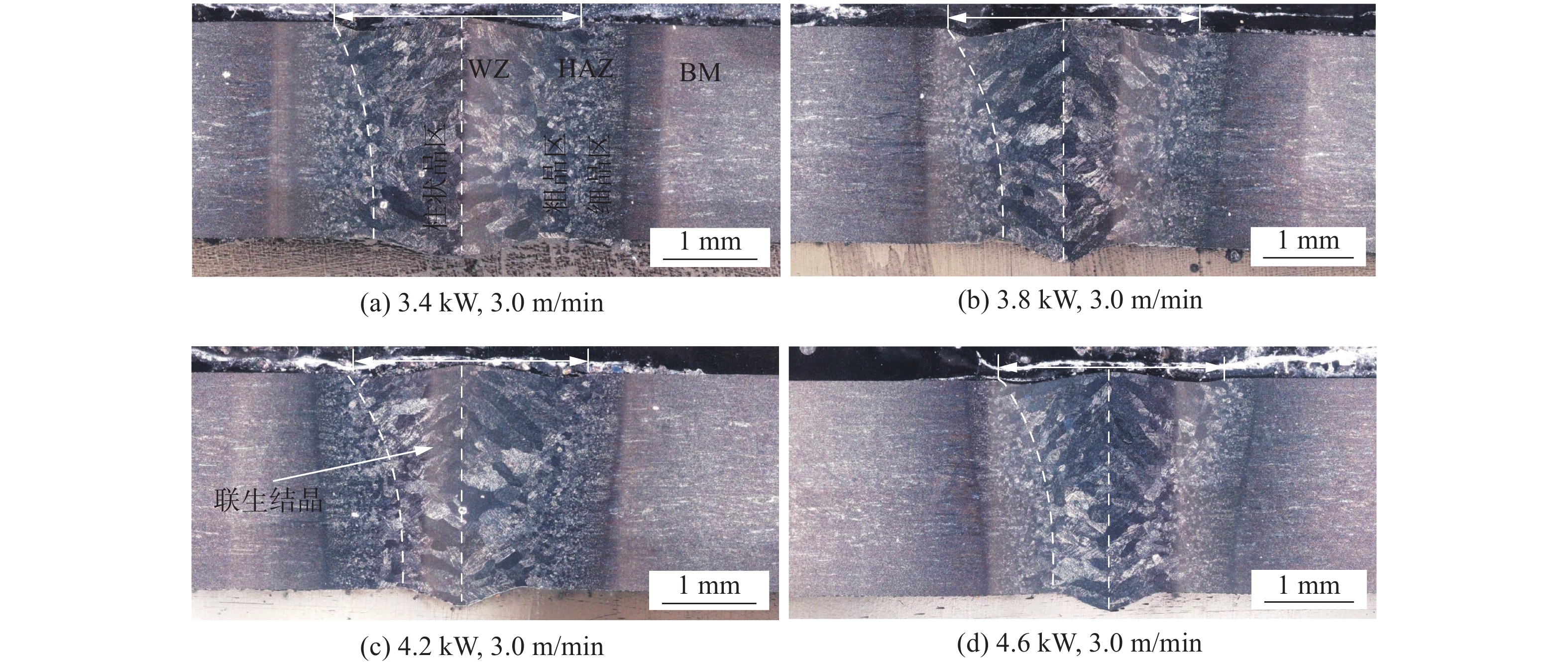
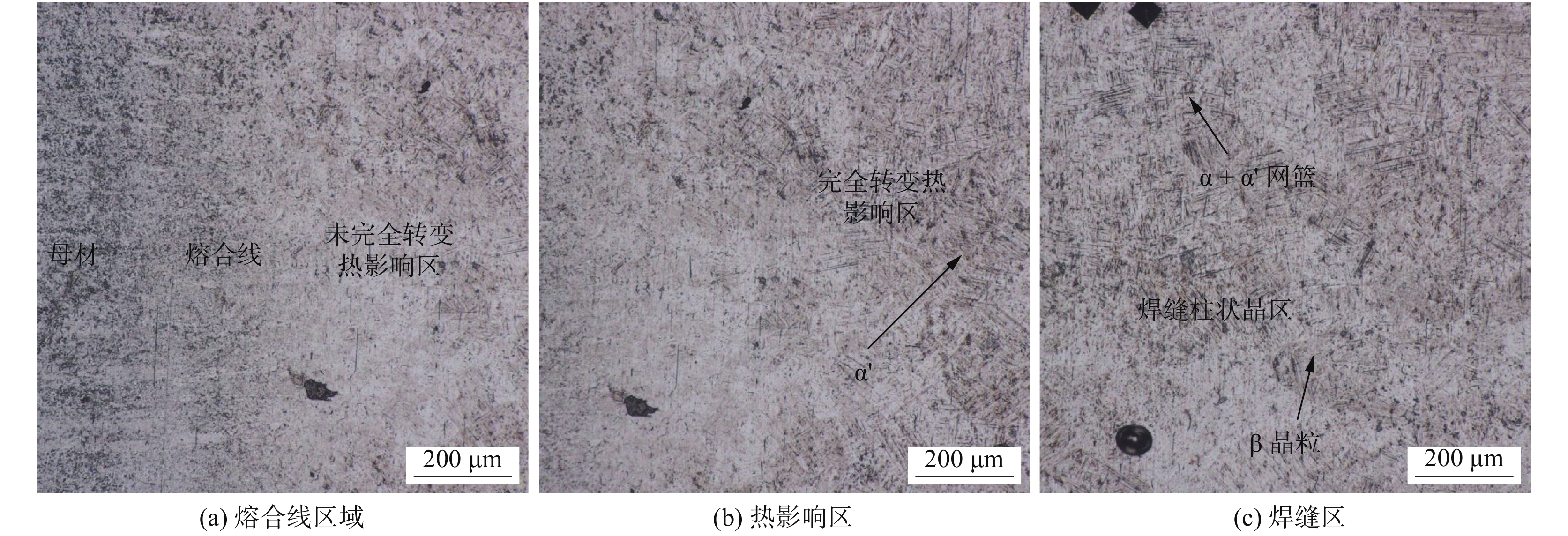
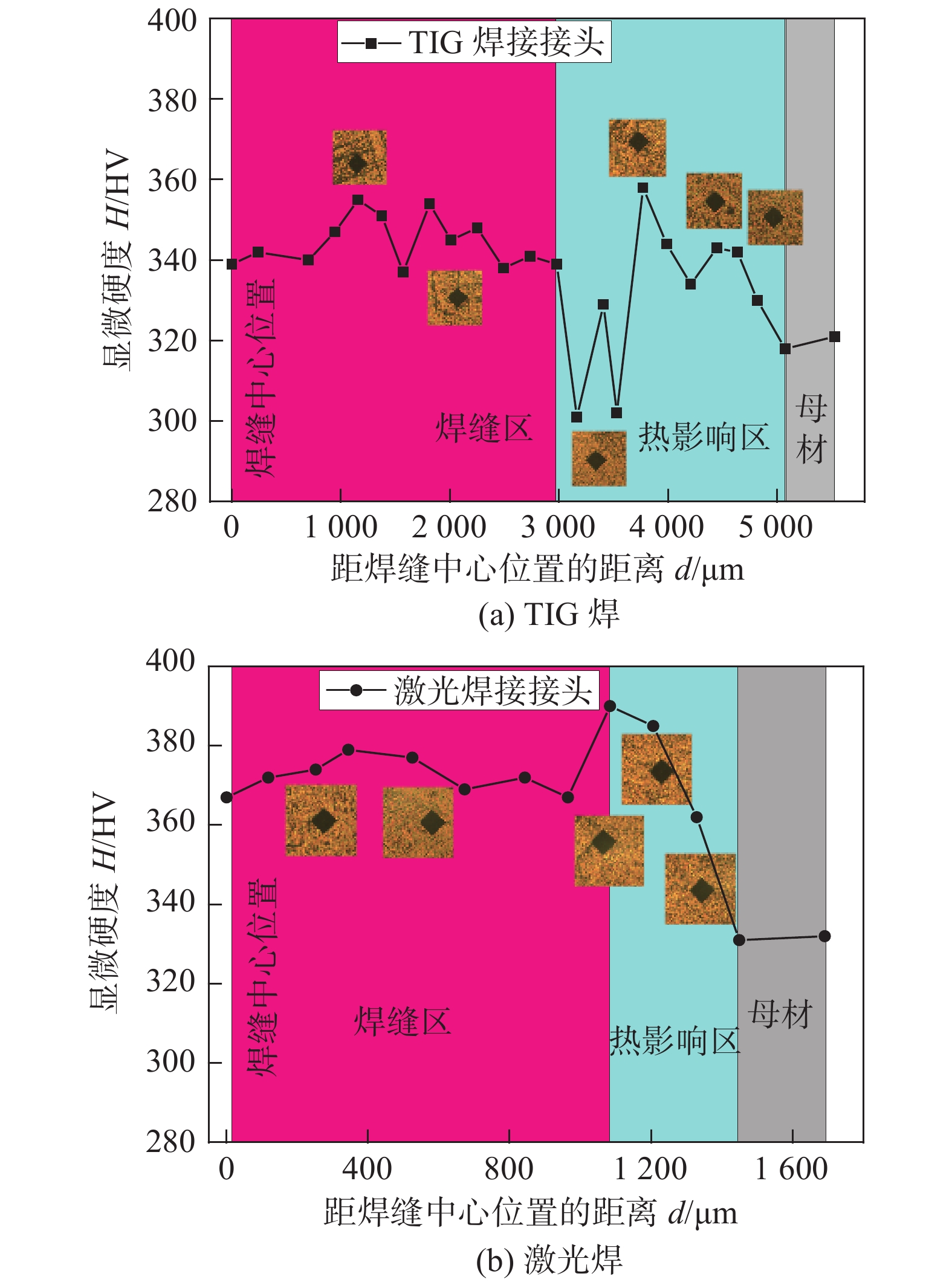
摘要: 对薄板TC4钛合金进行TIG电弧和激光焊接技术研究,重点分析了TIG焊接电流、焊接速度和激光输出功率对TC4钛合金焊接接头晶粒尺寸、微观组织和显微硬度的影响规律. 试验结果表明,在实现薄板TC4钛合金完全熔透的条件下,激光焊接具有更小热输入,接头焊缝区和热影响区宽度也显著降低. TIG焊接接头晶粒尺寸随热输入增加,呈现增加趋势. 随距焊缝中心位置增加,焊接接头晶粒尺寸均逐渐降低. TC4钛合金激光焊接接头焊缝区呈现魏氏组织特征,针状α'马氏体细小. 近缝热影响区组织为网篮状α'马氏体,而近母材热影响区为未转变α相和针状α'马氏体的双相组织. 随距焊缝中心位置增加,马氏体生成量逐渐减少,焊缝显微硬度值呈现降低趋势;同时相比于TIG焊接,TC4激光焊接接头具有更高的显微硬度.Abstract: The TC4 sheet was welded by TIG and laser welding technology. The effects of TIG welding current, welding speed and laser output power on the grain size, microstructure and microhardness of TC4 titanium alloy welded joint were analyzed. The experimental results show that laser welding had a lower heat input, and the width of weld zone and heat-affected zone was significantly reduced under the condition of complete penetration of TC4 titanium alloy sheet. The grain size of TIG welded joint increased with the increase of heat input. The grain size of welded joint decreased gradually with the increase of distance from the center of weld. The laser welded joint showed the characteristics of widmanstatten structure with the finer acicular martensite α' phase. The microstructure of martensite α' near the heat-affected zone was basket shaped, while the microstructure of martensite α' near the base metal was double phase of untransformed α phase and needle shaped martensite α'. With the increase of the distance from the weld centerline, the martensite content decreased gradually, and the weld microhardness decreased. At the same time, compared with TIG welding, TC4 laser welded joint had higher microhardness.
-
Keywords:
- TC4 titanium alloy /
- TIG welding /
- laser welding /
- microstructure /
- grain size
-
-
表 1 TC4钛合金主要化学成分(质量分数, %)
Table 1 Chemical composition of TC4 alloy
Al V Fe Si C N H O Ti 5.5 ~ 6.8 3.5 ~ 4.5 0.30 0.15 0.10 0.05 0.015 0.15 余量 表 2 不同TIG焊接参数下的焊缝横截面形状参数
Table 2 The shape parameters of TIG weld cross sections with various parameters
序号 焊接电流I/A 焊接电压U/V 焊接速度 v/(m·min−1) 热输入Q/(J·mm−1) 焊缝宽度d1/mm 单侧热影响区宽度d2/mm 1 180 14.3 0.8 116 5.81 1.57 2 200 14.8 0.8 133 6.50 1.71 3 220 15.4 0.8 152 7.04 1.80 4 220 15.2 1.0 120 5.69 1.58 5 220 15.2 1.2 100 5.11 1.36 表 3 不同激光焊接参数下的焊缝横截面形状参数
Table 3 The shape parameters of laser weld cross sections with various parameters
序号 激光功率P/kW 焊接速度v /(m·min−1) 离焦量dF /mm 热输入Q /(J·mm−1) 焊缝宽度d1 /mm 单侧热影响区宽度d2 /mm 1 3.4 3.0 0 68 2.61 0.53 2 3.8 3.0 0 76 2.77 0.35 3 4.2 3.0 0 84 2.49 0.38 4 4.6 3.0 0 92 2.50 0.40 -
[1] 孙文君, 王善林, 陈玉华, 等. 钛合金先进焊接技术研究现状[J]. 航空制造技术, 2019, 62(18): 63 − 72. doi: 10.16080/j.issn1671-833x.2019.18.063 Sun Wenjun, Wang Shanlin, Chen Yuhua, wt al. Development of advanced welding technologies for titanium alloys[J]. Aeronautical Manufacturing Technology, 2019, 62(18): 63 − 72. doi: 10.16080/j.issn1671-833x.2019.18.063
[2] 张颖云, 陈素明, 李波. 激光焊接参数对1.2mm TC4钛合金薄板焊缝的影响[J]. 焊管, 2019, 42(9): 26 − 31. Zhang Yinyun, Chen Suming, Li Bo. Influence of laser welding parameters on the weld of TC4 titanium alloy with 1.2 mm thickness[J]. Welded Pipe and Tube, 2019, 42(9): 26 − 31.
[3] 马忠贤, 冯军宁, 胡志杰. 钛及钛合金型材研究进展[J]. 世界有色金属, 2016, 24: 52 − 53. Ma Zhongxian, Feng Junning, Hu Zhijie. Research and development of titanium and titanium alloys shapes[J]. World Nonferrous Metals, 2016, 24: 52 − 53.
[4] 吴巍, 程广福, 高洪明, 等. TC4合金TIG焊接头组织转变与力学性能分析[J]. 焊接学报, 2009, 30(7): 81 − 84,117. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-360X.2009.07.021 Wu Wei, Cheng Guangfu, Gao Hongming, et al. Microstructure transformation and mechanical properties of TC4 alloy joints welded by TIG[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2009, 30(7): 81 − 84,117. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-360X.2009.07.021
[5] 吴健文, 徐孟嘉, 范文艳, 等. 钛合金快频脉冲柔性波形调制TIG焊接工艺[J]. 机械工程学报, 2020, 56(6): 102 − 109. doi: 10.3901/JME.2020.06.102 Wu Jianwen, Xu Mengjia, Fan Wenyan, et al. Flexible waveform interpulse TIG welding for titanium alloy[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2020, 56(6): 102 − 109. doi: 10.3901/JME.2020.06.102
[6] 杨烁, 宋文清, 曲伸, 等. 薄壁TC4钛合金激光焊缝成形试验研究[J]. 焊接, 2019(1): 5 − 11, 65. Yang Shuo, Song Wenqing, Qu Shen, et al. Experimental study on laser weld appearance of thin-walled TC4 titanium alloy[J]. Welding & Joining, 2019(1): 5 − 11, 65.
[7] Baruah M, Bag S. Influence of pulsation in thermo-mechanical analysis on laser micro-welding of Ti6Al4V alloy[J]. Optics and Laser Technology, 2017, 90: 40 − 51. doi: 10.1016/j.optlastec.2016.11.006
[8] 段爱琴, 王振苏, 彭欢, 等. 咬边缺陷对TC4钛合金激光焊接头静力拉伸形变特征的影响[J]. 焊接学报, 2019, 40(11): 54 − 60, 163. doi: 10.12073/j.hjxb.2019400288 Duan Aiqin, Wang Zhensu, Peng Huan, et al. Effect of undercut defect on deformation behavior TC4 titanium alloy laser welded butt joint under static tensile loading[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2019, 40(11): 54 − 60, 163. doi: 10.12073/j.hjxb.2019400288
[9] 黄炜, 王少刚, 李立泽, 等. 钛合金激光焊及其接头的显微组织与力学性能[J]. 材料开发与应用, 2019, 34(2): 20 − 27. Huang Wei, Wang Shaogang, Li Lize, et al. Laser beam welding of titanium alloy and microstructure and mechanical properties of welded joint[J]. Development and Application of Materials, 2019, 34(2): 20 − 27.
[10] Liu H, Nakata K, Yamamoto N, et al. Microstructural characteristics and mechanical properties in laser beam welds of Ti6Al4V alloy[J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2012, 47(3): 1460 − 1470. doi: 10.1007/s10853-011-5931-8
[11] Xu Z Z, Dong Z Q, Yu Z H, et al. Relationships between microhardness, microstructure, and grain orientation in laser-welded joints with different welding speeds for Ti6Al4V titanium alloy[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2020, 30(5): 1277 − 1289. doi: 10.1016/S1003-6326(20)65295-5




 下载:
下载: