Microstructure and property of flash welded joint of FeCrAl alloy tube
-
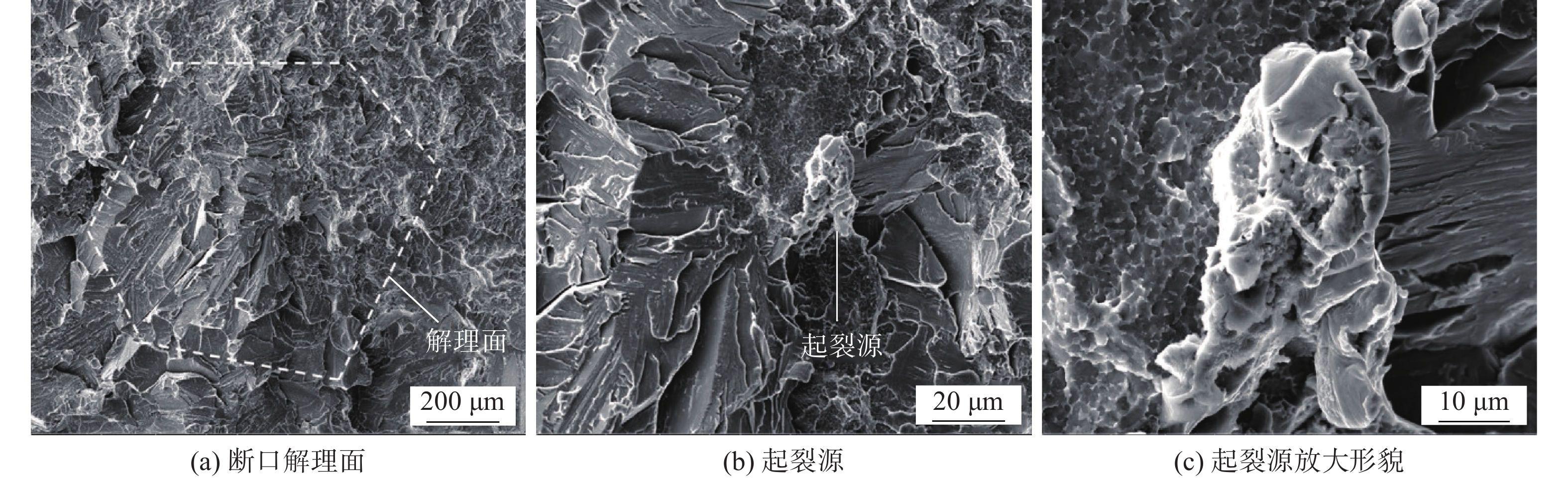
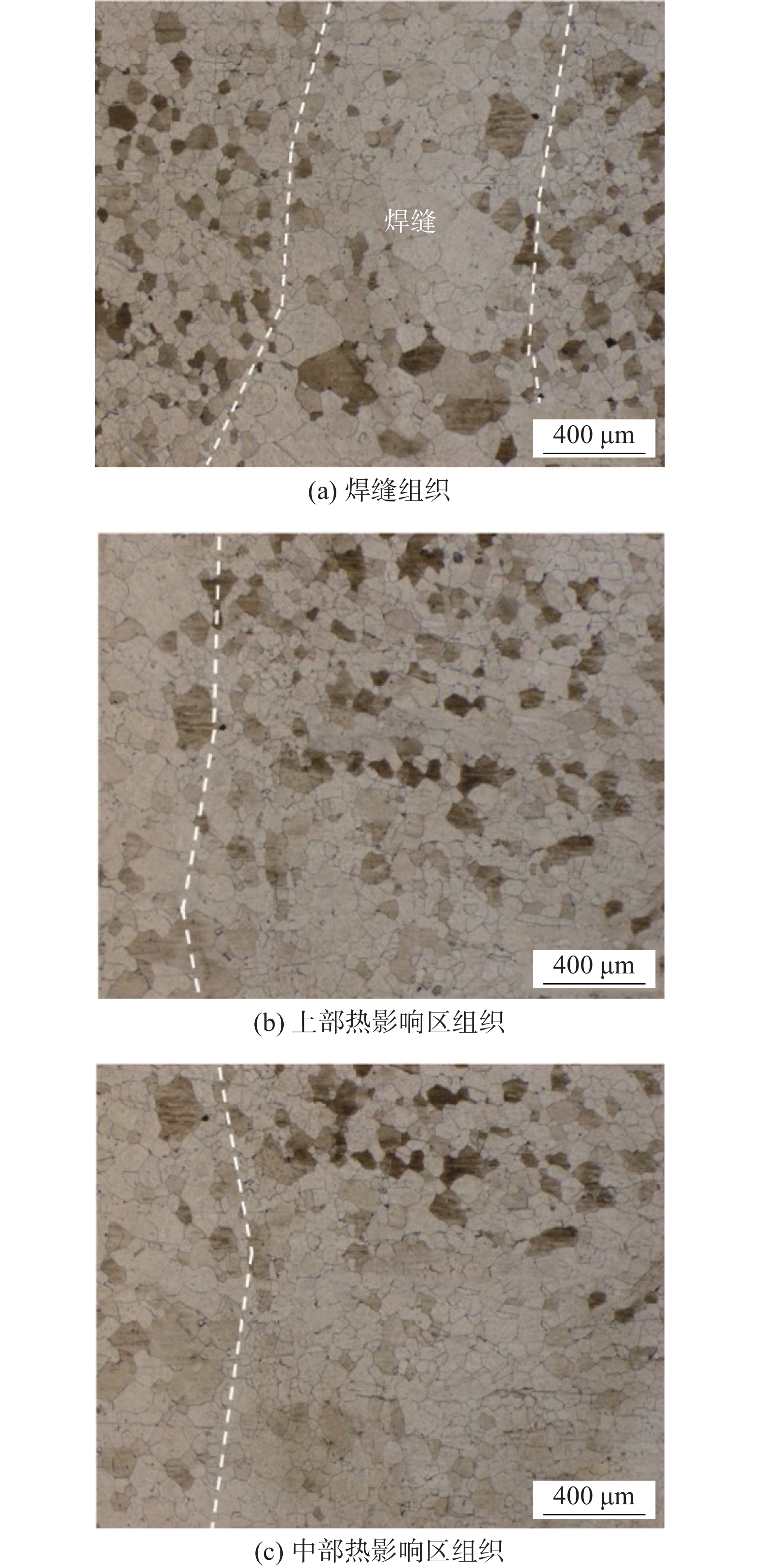
摘要: 采用闪光焊对FeCrAl合金进行对接接头焊接,通过扫描电子显微镜及能谱仪等手段研究了焊接接头的显微组织特征、不同区域氧化物颗粒的分布情况及力学性能. 结果表明,闪光焊焊接FeCrAl合金所得焊接接头显微组织主要为等轴晶,在焊缝和热影响区氧化物未出现明显聚集及向晶界偏聚的现象,且在晶内和晶界都可以呈现弥散分布的特征;焊接接头抗拉强度值达到594 MPa,为母材强度的90.5%;接头断裂在焊缝区,整体呈现脆性断裂模式;焊缝晶粒的粗化导致焊缝区硬度降低,最终引起焊接接头出现软化.Abstract: The butt joints of FeCrAl alloy were welded by flash light welding. The microstructure, distribution of oxide particles and mechanical properties of the welded joints were investigated by scanning electron microscope and energy dispersive spectrometer. The results show that: the microstructure of FeCrAl alloy welded by flash light welding is mainly equiaxed grain. No obvious oxides are aggregated and segregated in the grain boundary of weld metal and heat-affected zone. Most oxides are dispersed in the grain and grain boundary. The tensile strength of the welded joint reaches 594 MPa, which is 90.5% of the strength of the base metal. The joint is fractured in the weld zone and presents the brittle fracture mode as a whole. The grain coarsening of the weld metal makes the hardness decrease, which leads to the softening of the welded joint.
-
Keywords:
- FeCrAl alloy /
- flash light welding /
- nanoscale oxide particles /
- tensile properties
-
-
图 2 母材组织及晶界析出相
Figure 2. Microstructure of base metal and precipitated phase at grain boundary. (a) microstructure of the base metal; (b) distribution of oxides in the base metal; (c) distribution of oxides in the base metal grain boundary; (d) types of oxides and grain boundary precipitate in the base metal
表 1 FeCrAl合金管材的主要化学成分(质量分数, %)
Table 1 Main chemical compositions of FeCrAl alloy tube base material
C Si Cr Al Ni Y Hf Ti Zr Fe 0.028 0.29 20 ~ 23 4 ~ 5 0.11 0.16 0.06 0.009 0.06 余量 表 2 闪光焊FeCrAl合金管材的焊接工艺参数
Table 2 Welding parameters of FeCrAl alloy tube by flash welding
焊接电流
I/A顶锻留量
Su/mm闪光时间
t/s顶锻时间
t0/s550 15 10 7 表 3 图2d中氧化物颗粒的化学成分(质量分数, %)
Table 3 Chemical compositions of oxide particles in Fig. 2d
位置 Fe Cr Al Hf Zr 1 44 16.7 3.5 13.5 8.7 2 66.1 22.2 5.1 0 0.7 3 44.0 40.3 3.4 0.5 0.3 4 63.2 23.0 5.8 0 0 位置 Y Ti O 可能氧化物及
析出相类型1 1.1 0.8 1.1 Y-M-O 2 0.5 0.1 2.5 Y2O3 3 0.2 0 3.9 富Cr析出相 4 0 0.1 2.3 — -
[1] Yamamoto Y, Pint A, Terrani K A, et al. Development and property evaluation of nuclear grade wrought FeCrAl fuel cladding for light water reactors[J]. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 2015, 467(2): 703 − 716.
[2] 张静. 核聚变用材料的辐照效应和焊接行为研究[D]. 北京: 北京科技大学, 2016. Zhang Jing. Irradiation effects and welding behavior of materials for nuclaer fusion reactor[D]. Beijing: Univerisity of Science and Technology Beijing, 2016.
[3] Gussev M N, Field K G, Yamamoto Y. Design, properties, and weldability of advanced oxidation-resistant FeCrAl alloys[J]. Materials & Design, 2017, 129(5): 227 − 238.
[4] Kevin G, Field K, Samuel A. Mechanical properties of neutron-irradiated model and commercial FeCrAl alloys[J]. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 2017, 489(8): 118 − 128.
[5] 吕铮. 聚变堆第一壁用纳米结构ODS钢的发展与前瞻[J]. 原子能科学技术, 2011, 45(9): 1105 − 1111. Lü Zheng. Development and prospect of nanostructured ODS steel for first wall of fusion reactor[J]. Atomic Energy Science and Technology, 2011, 45(9): 1105 − 1111.
[6] 王铁军, 秦巍, 陈永庆,等. Al和 Mo含量对热等静压制备的 FeCrAlMo 合金组织及拉伸性能的影响[J]. 材料导报, 2020, 34(6): 12105 − 12108. Wang Tiejun, Qin Wei, Chen Yongqing, et al. Effect of Al and Mo content on the microstructures and tensile property of FeCrAlMo alloys[J]. Materials Reports, 2020, 34(6): 12105 − 12108.
[7] Lin Zhang, Shigeharu Ukai, Takeshi Hoshino, et al. Y2O3 evolution and dispersion refinement in Co-base ODS alloys[J]. Acta Materialia, 2009, 57(3): 3671 − 3682.
[8] 谢锐, 吕铮, 徐长伟, 等. 钛元素对9Cr 氧化物弥散强化钢微观组织和拉伸性能的影响[J]. 材料导报, 2020, 34(11): 22111 − 22117. Xie Rui, Lü Zheng, Xu Changwei, et al. Effect of Ti element on the microstructures and tensile properties of 9Cr oxides dispersion strengthened steels[J]. Materials Reports, 2020, 34(11): 22111 − 22117.
[9] Dawson H, Serrano M, Cater S, et al. Residual stress distribution in friction stir welded ODS steel measured by neutron diffraction[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2017, 246(9): 305 − 312.
[10] 雷玉成, 任闻杰, 谢伟峰. 氧化物弥散强化MGH956合金TIG焊缝气孔问题分析[J]. 焊接学报, 2011, 32(11): 1 − 4. Lei Yucheng, Ren Weijie, Xie Weifeng. Study on pores in TIG welding of oxide dispersion strengthened(ODS) alloys MGH956[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2011, 32(11): 1 − 4.
[11] Kiyohiro Yabuuchi, Naoto Tsuda, Akihiko Kimura, et al. Effects of tool rotation speed on the mechanical properties and microstructure of friction stir welded ODS steel[J]. Materials Science & Engineering A, 2014, 596(10): 291 − 296.
[12] Han Wentuo, Liu Pingping, Yi Xiaoou, et al. Impact of friction stir welding on recrystallization of oxide dispersion strengthened ferritic steel[J]. Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 2018, 34(1): 209 − 213.
[13] 高世一, 刘正林. 闪光对焊技术及应用[M]. 北京: 机械工业出版社, 2015. Gao Shiyi, Liu Zhenglin. Flash butt welding technology and application[M]. Beijing: China Machine Press, 2015.
[14] Seki M, Hirako K, Kono S. Pressurized resistance welding technology development in 9Cr-ODS martensitic steels[J]. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 2004, 329(1): 1534 − 1538.
[15] Olivier Doyen, Brendan Le Gloannec, Alexis Deschamps. Ferritic and martensitic ODS steel resistance upset welding of fuel claddings: Weldability assessment and metallurgical effects[J]. Journal of Nuclear Materials 2019, 518(5): 326 − 333.
[16] Jerred N D, Charit I, Zirker L R. Pressure resistance welding of MA-957 to HT-9 for advanced reactor applications[J]. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 2019, 508(9): 265 − 277.
[17] Wang Jiye, Yuan Wei, Rajiv S, et al. Microstructural evolution and mechanical properties of friction stir welded ODS alloy MA754[J]. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 2013, 442(3): 1 − 6.
[18] 雷玉成, 梁申勇, 赵凯, 等. 在TIG粉末焊接中Y2O3对ODS合金焊接接头组织和性能的影响[J]. 材料科学与工程, 2013, 21(5): 20 − 24. Lei Yucheng, Liang Shenyong, Zhao Kai, et al. Effect of Y2O3 on microstructure and properties of ODS alloy welded joints in TIG powder welding[J]. Materials Science and Engineering, 2013, 21(5): 20 − 24.
[19] Nerea Ordas, Emma Gil, Arturs Cintins. The role of yttrium and titanium during the development of ODS ferritic steels obtained through the STARS route: TEM and XAS study[J]. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 2018, 504(2): 8 − 22.
[20] 周磊磊, 余腾义. 380CL 钢闪光对焊接头组织及冲击性能的研究[J]. 热加工工艺, 2017, 46(17): 210 − 212. Zhou Leilei, Yu Tengyi. Study on microstructure and impact properties of 380CL steel flash butt welding joint[J]. Hot Working Technology, 2017, 46(17): 210 − 212.
[21] 高杰. 高强度环链对焊接头组织与性能的研究[D]. 济南: 山东大学, 2020. Gao Jie. Microstructure and properties of butt welding joints of high strength chain[D]. Jinan: Shandong University, 2020.
[22] 潘华, 丁凯, 霍世宗. DP540双相钢闪光对焊接头的组织与硬度研究[J]. 上海金属, 2018, 40(6): 60 − 65. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7208.2018.06.012 Pan Hua, Ding Kai, Huo Shizong. Microstructure and hardness of flush-butt welded DP540 dual-phase steel joints[J]. Shanghai Metals, 2018, 40(6): 60 − 65. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7208.2018.06.012
[23] 王振伟, 许鸿吉, 王赫. 高温电加热处理对贝氏体钢与U75V钢闪光对焊接头组织与性能的影响[J]. 铁道建筑, 2019, 59(4): 144 − 147. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-1995.2019.04.32 Wang Zhenwei, Xu Hongji, Wang He. Influences of high temperature electric heating on constitutions and properties of bainite steel and U75V steel flash butt-welded joints[J]. Railway Engineering, 2019, 59(4): 144 − 147. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-1995.2019.04.32
[24] 王铁军, 杨博, 梁晨, 等. 退火温度对热轧态M390 组织与性能的影响[J]. 材料导报, 2020, 34(6): 12122 − 12126. Wang Tiejun, Yang Bo, Liang Chen, et al. Effect of annealing temperature on microstructure and mechanical property of hot-rolled M390[J]. Materials Reports, 2020, 34(6): 12122 − 12126.
-
期刊类型引用(0)
其他类型引用(4)




 下载:
下载: