Effect of element distribution on the microstructure of FeCoCrNi high entropy alloy coating
-
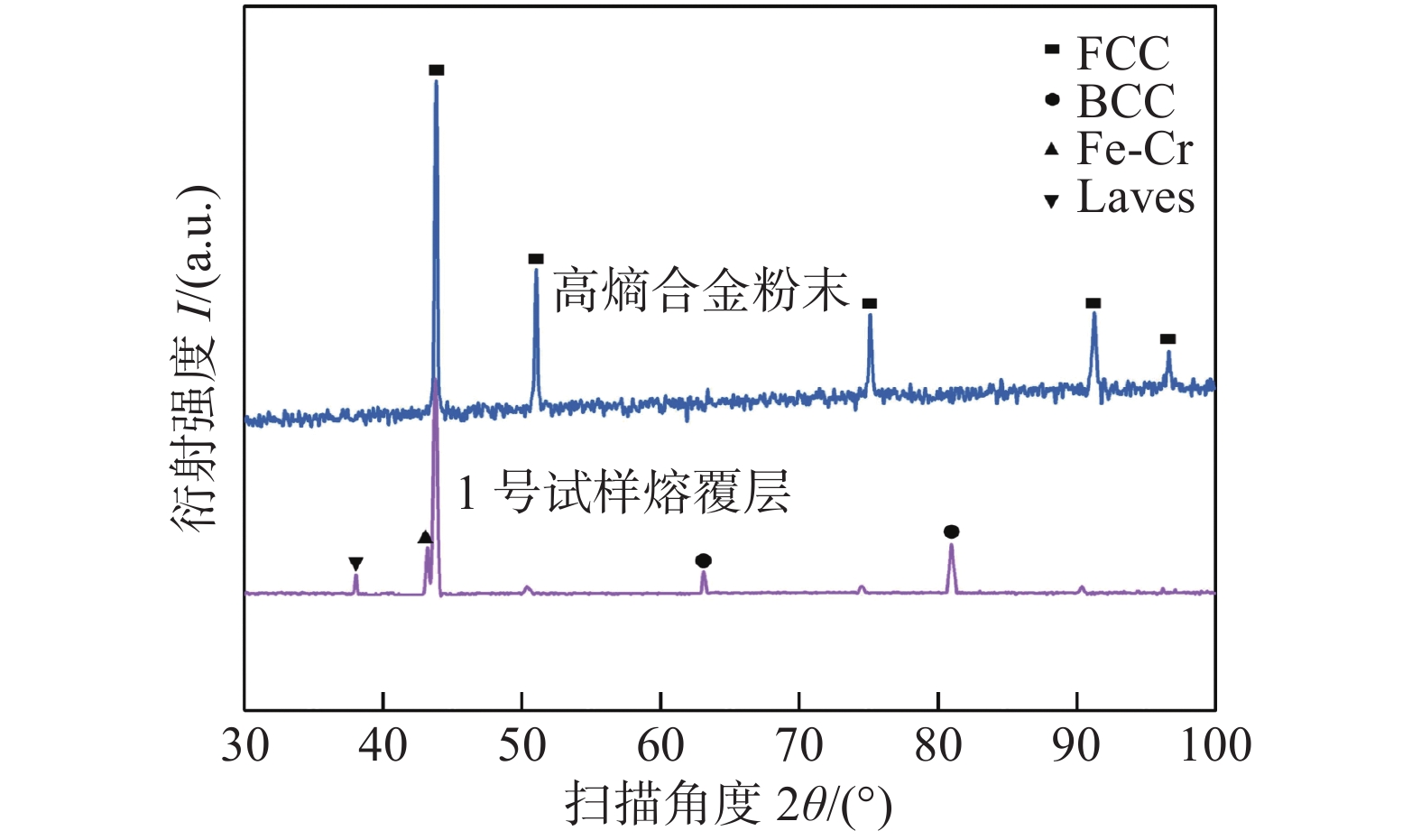
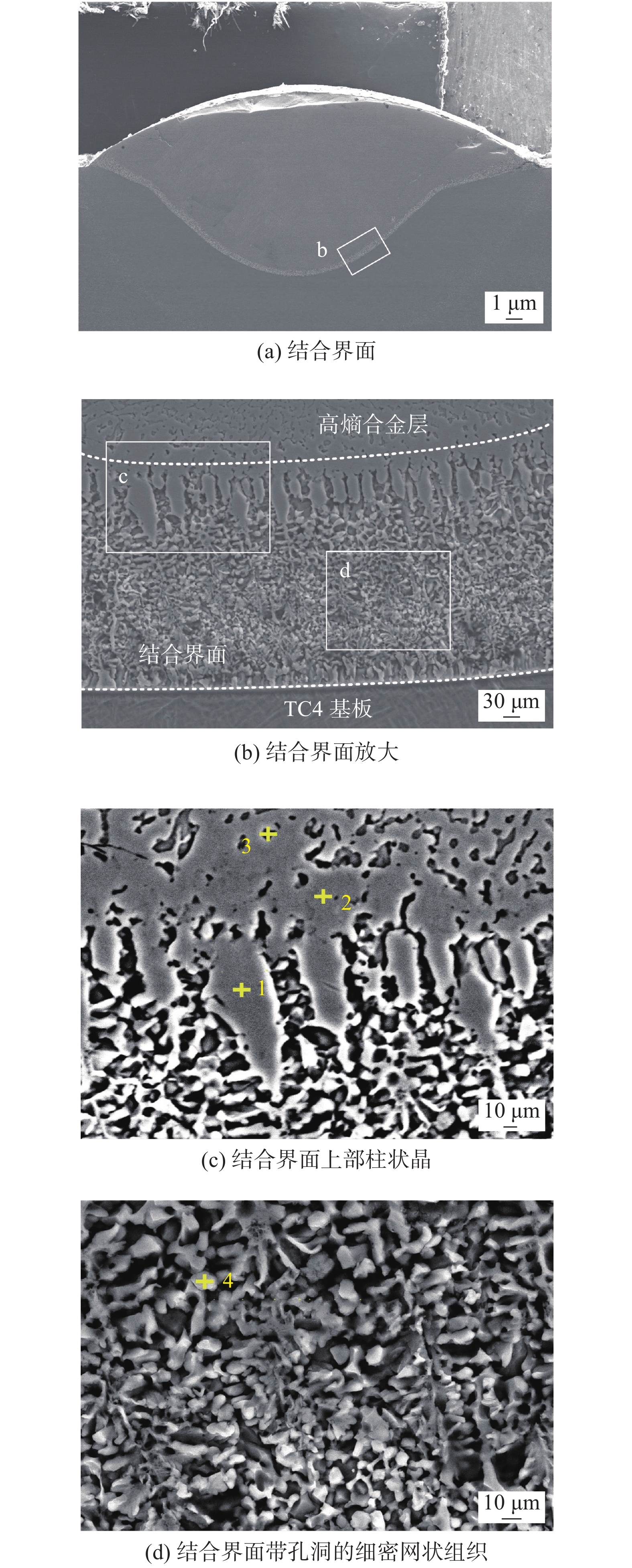
摘要: 聚焦于激光熔覆高熵合金表面强化技术,开展了6 mm厚TC4钛合金板材表面激光熔覆FeCoCrNi高熵合金涂层的研究. 首先通过X射线衍射(XRD)对FeCoCrNi高熵合金熔覆层进行物相分析,探究其相组成. 随后,利用金相显微镜和场发射扫描电子显微镜表征手段,探究了熔覆层以及其与TC4基体结合界面处的微观组织形态及物相分布. 结果表明,Ti,Ni组合和Ti,Co组合具有最大的负混合焓(∆Hmix),因此易造成部分物相中(Ti,Ni,Co)的富集,而其周围相中则会呈现出(Fe,Cr)的富集. 结合界面上部和下部主要由灰色的柱状晶组成,中部区域主要由白色网状组织和灰色收缩孔洞组成.Abstract: Laser cladding of FeCoCrNi high entropy alloy coating on the surface of 6 mm thick TC4 titanium plate was studied by focusing on the surface strengthening technology of laser cladding high entropy alloy. Firstly, the phase analysis of the FeCoCrNi high entropy alloy cladding layer was carried out by X-ray diffraction to explore its phase composition. Then, the microstructure and phase distribution of the cladding layer and its interface with TC4 substrate were investigated by metallographical microscope and field emission scanning electron microscope. The results show that Ti and Ni, Ti and Co have the most significant negative mixing enthalpy (∆Hmix), so it is easy to cause the enrichment of (Ti, Ni, Co) in some phases, and the enrichment of (Fe, Cr) in the surrounding phases. The upper and lower part of the bonding interface is mainly composed of gray columnar grains, and the middle part is mainly composed of white reticulum structure and gray shrinkage cavity.
-
Keywords:
- TC4 titanium alloy /
- high entropy alloy /
- laser cladding /
- element distribution /
- microstructure
-
0. 序言
机器人电弧焊(robotic arc welding , AW)技术,以其高效、成型快、成本低等优势,在航空航天、汽车制造等多个领域获得广泛应用[1].
焊缝尺寸是评价焊接质量的重要指标,准确预测焊缝尺寸,有助于提高机器人电弧焊智能化程度和控制性能. 焊接工作者对焊缝尺寸特征预测进行了大量研究.柏久阳等人[2]建立了基于二次回归方程的工艺参数与焊缝宽度预测模型;Xiong等人[3]提出了基于单变量阶跃响应传递函数的增材层尺寸动态预测模型;周春东等人[4]通过回归分析,揭示工艺参数对焊缝表面特征纹路及成形尺寸的影响. 早期的预测研究多依赖于经验公式和简单数学模型,由于焊接过程的复杂性和非线性特性,这些方法往往难以实现对多因素作用下焊缝尺寸的准确预测.
人工神经网络作为一种非线性建模工具,在焊缝尺寸预测研究中得到广泛应用[5]. 赵鹏等人[6]利用GA-BP神经网络,研究了单焊缝尺寸预测及工艺参数对形貌的影响;孙家豪等人[7]采用Hermite插值和最小二乘拟合方法,构建了广义回归神经网络焊缝二维形貌预测模型;上述研究搭建网络实现了对焊缝尺寸的预测,但其浅层结构限制了特征提取能力,影响了焊缝尺寸预测精度.
深度信念网络(deep belief network, DBN)作为一种深度学习算法,在大数据预测、分类等领域展现出巨大潜力,与传统方法和浅层神经网络相比,DBN通过无监督预训练方法显著提升了数据挖掘能力和预测精度. 据此文中提出了一种基于鲸鱼优化算法(whale optimization algorithm, WOA)和深度信念网络的机器人电弧焊焊缝尺寸预测方法,构建了多输入工艺参数与焊缝尺寸之间的非线性映射模型,并通过实验验证了模型的有效性.
1. 试验方法
试验平台由FANUC工业机器人(M-10iA),工控机(R-30iB A plus),MIG焊机(S5-Ro boMIG)和工作台等组成.试验参数如下:焊丝高度15 mm,焊丝伸出长度12 mm,焊道长度150 mm,保护气体为98%Ar + 2%CO2,气体流量15L/min,试件为100 mm × 50 mm的316L不锈钢.
根据团队前期研究基础[8-9],选取电流、频率、占空比和焊接速度这4个对焊缝熔宽和余高影响最大的因素进行研究,每个因素选择10个水平值,设计L100(104)正交试验方案,因素水平如表1所示.
表 1 试验因素水平表Table 1. Experimental factors and levels table因素 焊接电流
I/A频率
f/Hz占空比
D(%)焊接速度
v/(cm·min−1)水平 53 0.5 28 25 60 1 30 30 68 1.5 32 35 75 2 35 40 83 2.5 38 45 90 3 40 50 98 3.5 42 55 105 4 45 60 113 4.5 48 65 120 5 50 70 选取焊缝中段间隔2 cm的连续三个位置用游标卡尺进行测量,取3次平均值作为焊缝的熔宽(w)、余高(h)数据,测量焊缝尺寸位置示意图见图1.
2. 基本原理
2.1 深度信念网络
DBN是由多层限制玻尔兹曼机(RBM)堆叠而成的深度学习模型, 用于焊缝尺寸预测可有效捕捉复杂焊接数据中的层级特征,通过逐层贪婪预训练提升对焊缝结构的抽象表示,提高预测性能.DBN模型参数θ = (W,a,b)通常随机生成,并可能采用特定的初始化策略来设定其他参数,之后进入阶段学习.
(1)前向训练阶段:采用无监督学习方法逐层训练网络,通过计算隐藏层输出、可见层和隐藏层重构输出以及权重、可见层偏置和隐藏层偏置更新值,来更新DBN的模型参数.
(2)反向微调阶段:通过反向传播和梯度下降算法训练DBN网络,计算顶层的均方误差(以下缩写为MSE),并逐层向后传播MSE. 通过梯度下降法更新连接权值和偏差,调整学习率步长,优化DBN模型参数,实现模型优化.
2.2 鲸鱼优化算法
鲸鱼优化算法(whale optimization algorithm,WOA)是一种新型智能优化算法.通过鲸鱼觅食行为中的个体协作和追踪目标的策略实现鲸鱼全局搜索能力和自适应性的平衡,算法简单高效.过程如下:
首先确定鲸鱼的初始位置为
$$ {{\boldsymbol{X}}} _{ {i} } { = } \mathrm{(} {x} _{ {i} }^{ {1} } {,x} _{ {i} }^{ {2} } {,\cdots ,x} _{ {i} }^{ {D} } \mathrm{),}\;\; {i = 1,2,\cdots ,N} $$ (1) 式中:i代表鲸鱼种群大小,D代表搜索维度,Xi代表鲸鱼随机初始位置.
评估鲸鱼个体的环境适应度,记录猎物位置为
$$ {{\boldsymbol{X}}} ^{ * } { = } \mathrm{(} {x} _{ {i} }^{ {1} } {,x} _{ {i} }^{ {2} } {,\cdots,x} _{ {i} }^{ {D} } \mathrm{)} $$ (2) 式中:i和D代表鲸鱼种群大小和搜索维度,$ {{{\boldsymbol{X}}^*}} $是猎物位置.搜索猎物时,随机分配概率p和系数向量r,搜索向量A的自适应变化和概率p来更新鲸鱼的位置,从而实现三种不同情况下的位置更新.
(1)当p<50%和A<1时,通过收缩包围机制更新鲸鱼的位置,即
$$ {{\boldsymbol{X}}} \mathrm{(} {t} \mathrm{ + 1) = } {{\boldsymbol{X}}} ^{ {*} } \mathrm{(} {t} \mathrm{)-} {{\boldsymbol{A}}} \mathrm{\times } {D} $$ (3) $$ {D} { = } \mathbf{|} {{\boldsymbol{C}}\times } {{\boldsymbol{X}}} ^{ * } {(} {t} {)-} {{\boldsymbol{X}}} {(} {t} {)} \mathbf{|} $$ (4) $$ {{\boldsymbol{A}}} \mathrm{ = 2} {{\boldsymbol{a}}} \mathrm{\times } {{\boldsymbol{r}}} \mathrm- {{\boldsymbol{a}}} $$ (5) $$ {{\boldsymbol{C}}} \mathrm{ = 2} {{\boldsymbol{r}}} $$ (6) 式中:t表示当前迭代次数,X(t)和X(t + 1)表示当前和下一位置向量,${{\boldsymbol{X}}} ^{ {*} }(t) $表示当前最优位置向量,A和C是两个系数向量,r是在[0,1]范围内的随机向量, a是计算过程期间从2减小到0的向量.
(2)当p<50%和A≥1时,鲸鱼位置更新为
$$ {{\boldsymbol{X}}} {(} {t} { + 1) = } {{\boldsymbol{X}}} _{ {rand} } {-{\boldsymbol{A}}} {\times } {|{\boldsymbol{C}}} {\times } {{\boldsymbol{X}}} _{ {rand} } - {{\boldsymbol{X}}} {(} {t} {)} {|} $$ (7) 式中:Xrand是随机位置向量.
(3)当p≥50%时,鲸鱼螺旋向上位置更新为
$$ {{\boldsymbol{X}}} \mathrm{(} {t} \mathrm{ + 1) = } {{\boldsymbol{X}}} ^{ {*} } {(t) + } {D^{\prime}\times e} ^{ {bl} } \mathrm{\times } {\cos(2\text{π} l)} $$ (8) $$ {D^ {\prime}} \mathrm{ = } {|{\boldsymbol{X}}} ^{ {*} } \mathrm{(} {t} \mathrm{)-} {{\boldsymbol{X}}} \mathrm{(} {t} \mathrm{)} {|} $$ (9) 式中:b表示固定的螺旋尺寸,l是[−1,1]内的随机数.
3. 焊缝尺寸预测
3.1 WOA-DBN预测模型
由于各因素的数值单位和量级不一致,进行归一化处理后再将数据集划分为80组训练集,20组测试集.算法参数确定过程如下:
首先确定DBN超参数的搜索范围:隐藏层层数K∈[0,8],各层隐元数nk∈[0,40],学习速率$ \eta $∈[0.01,0.05],预训练和反向微调的最大迭代次数T1∈[1,100],T2∈[1,100];同时设定鲸鱼参数,包括最大迭代数Tmax = 10、鲸鱼种群大小N = 6和螺旋大小参数b = 2.其中隐藏层层数和各层隐元数对预测精度的影响如图2所示,可见最佳隐藏层为4,每层隐元分别为10,25,20,15.最后,根据WOA-DBN模型得到预测值,结合真实值数据,确定适应度函数为
$$ f = \left(\frac{{{{\displaystyle\sum\limits_{i = 1}^M {({y_{1i}} - y_{1i}^{'})^2} }}}}{M}\right) + \left(\frac{{{{\displaystyle\sum\limits_{i = 1}^M {({y_{2i}} - y_{2i}^{'})^2} }}}}{M}\right) $$ (10) 式中:$y_{1i} $和$y_{2i} $分别为第i个样本熔宽和余高的输出值,$y_{1i}^{'} $和$y_{2i}^{'} $为对应样本的真实值,M为样本数.
优化超参数见表2:隐层层数K、隐层神经元数nk(表中n1-n4)、学习速率$ \eta $、预训练最大迭代次数T1和反向微调最大迭代次数T2.可见WOA- DBN模型最佳结构为4-10-25-20-15-2,模型预测流程见如图3所示.
表 2 WOA-DBN的超参数Table 2. Hyperparameters of WOA-DBN隐层层数
K/层隐层神经元数 学习速率 预训练最大迭代次数
T1/次反向微调最大迭代次数
T2/次n1 n2 n3 n4 $ \eta $ 4 10 25 20 15 0.03 5 32 3.2 对比分析
为验证WOA-DBN模型的有效性,将文献[10]提出的PSO- DBN、SSA-DBN模型和DBN,CNN,BP模型作为对比算法,计算预测结果,对比见图4.
从图4可以看出BP、CNN模型预测偏差较大;DBN模型局部效果良好,整体预测效果欠佳;SSA -DBN、PSO-DBN、WOA-DBN模型预测效果相对更优,其中WOA -DBN模型预测整体和局部更近真实值,稳定性和重合度高于其他几种模型.
进一步分析各模型预测误差3D曲面图(颜色越红误差越大),结果见图5. 图中BP模型因其浅层结构导致误差较大,误差峰值明显;CNN和DBN模型优于BP模型,但局部误差较大;SSA-DBN、PSO-DBN、WOA-DBN模型误差分布较为均匀,稳定性好,其中WOA-DBN模型误差波动范围最小,具有更高的预测精度.
3.3 改进AAMCWOA-DBN预测模型
从前述分析可以看出,WOA-DBN模型展示了较好的预测性能,但同样也存在搜索效率不高、收敛能力欠缺、陷入局部最优等不足.因此,提出一种改进鲸鱼优化方法用于优化DBN网络,即融合模拟退火和自适应变异的混沌鲸鱼优化算法优化DBN网络模型,即AAMCWOA-DBN模型(以下简称优化WOA模型).
采用混沌反向学习初始化种群:WOA-DBN模型(简称原WOA模型)收敛能力不足可能是因为模型初始化参数随机产生导致,故采用结构简单、遍历性均匀和搜索速度更佳的Tent混沌映射和反向学习的种群初始化方法,通过在Tent映射中添加随机数$ rand(0,1)/N $.避免了迭代时落入小周期点和不稳定周期点,生成初始种群,随机数为
$$x_{i+1}=\left\{\begin{array}{l} 2 x_i+{rand}(0,1) \times \dfrac{1}{N},\quad 0 \leqslant x \leqslant \dfrac{1}{2} ; \\ 2\left(1-x_i\right)+{rand}(0,1) \times \dfrac{1}{N},\quad \dfrac{1}{2} < x \leqslant 1 . \end{array}\right. $$ (11) 式中:N是序列内粒子的个数.
再利用该混沌序列Zkj生成对应的初始种群xij,即
$$ {x_{ij}} = {x_{\min j}} + {Z_{kj}}({x_{\max j}} - {x_{\min j}}) $$ (12) 然后,生成反向种群$ x_{ij}^* $,即
$$ x_{ij}^* = {x_{\min j}} + {x_{\max j}} - {x_{ij}} $$ (13) 最后,比较初始和反向种群,选择适应度最优的N个个体组成初始群.
再增加非线性收敛因子a:由式(5)和式(6)重新提出了一个非线性收敛因子a,代替从2到0的线性递减策略,前后期兼顾了全局和局部勘探能力,以改善算法逃逸出局部最优的能力,即
$$ a = {a_0} \cdot {e^{ - \left(\tan {{\left(1.2\times\tfrac{t}{T}\right)}^2}\right)}} $$ (14) 最后增加模拟退火操作及自适应变异扰动以增加种群多样性,避免局部最优解,以解决迭代后期种群多样性降低和早熟收敛的问题,即
$$ {X}_{b\_new}^{t} = \frac{t}{Maxiter}{X}_{b\_gaussian}^{t} + \left(1-\frac{t}{Maxiter}\right){X}_{b\_cauchy}^{t}(15) $$ 式中:gaussian为高斯变异,cauchy为柯西变异,Maxiter为最大迭代次数.
随着t值变化,柯西变异获得较大步长,高斯变异获得较大权值,利于局部精确搜索.
3.4 试验验证
将AAMCWOA与WOA、GWO、PSO、GA算法对比并在CEC2005测试函数集上检验模型的性能,如图6所示,可见AAMCWOA模型的收敛速度和精度都更好.
优化WOA模型的预测性能与原WOA模型性能指标对比分析见表3,优化WOA模型的运行时间相对原模型大幅降低,平均误差值θ降低至原模型一半以下,指标平均绝对百分比误差(mean abso- lute percentage error,MAPE)、平均绝对误差(mean absolute deviation,MAE)均大幅小于原模型,性能指标表明优化WOA模型收敛速度更快、优化效率更高、预测更具优越性.
表 3 性能指标对比分析Table 3. Performance Metrics Comparative Analysis预测模型 指标 性能指标 时间t/s 平均绝对百分比误差εMAPE(%) 平均绝对误差εMAE 平均绝对误差值θ AAMCWOA-DBN 熔宽 1.62 1.85 0.13 0.1255 WOA-DBN 2.93 3.96 0.47 0.3335 AAMCWOA-DBN 余高 1.145 0.47 0.08 0.0765 WOA-DBN 1.985 1.28 0.17 0.2025 进一步对预测精度ε进行对比分析,结果见表4. 表中,优化WOA模型预测精度ε大幅高于原WOA模型,熔宽预测中最高精度ε达99.6%,且预测精度ε≥95%和≥98%的分布各占比100%、70%:余高预测中最高精度ε达99.6%,且预测精度ε≥95%和≥98%的分布各占比100%、20%,无论是预测精度ε区间和高精度分布占比均远优于原WOA模型.
表 4 预测精度分析Table 4. Prediction Accuracy Analysis指标 预测模型 最低精度ε(%) 最高精度ε(%) 分布占比δ(%) ≥95% ≥98% 熔宽 WOA-DBN 92.1 99.4 65 5 AAMCWOA-DBN 96.4 99.6 100 70 余高 WOA-DBN 87.6 99.1 20 10 AAMCWOA-DBN 94.8 99.6 100 20 验证结果表明,优化WOA模型无论性能指标还是预测精度均优于原模型,具有更精确效果.
4. 结论
(1)提出了一种融合模拟退火和自适应变异的混沌鲸鱼优化算法,通过混沌反向学习初始化、非线性收敛因子等策略,有效提升了算法的全局搜索能力和局部搜索精度,解决了传统WOA-DBN算法在收敛能力和局部最优问题上的不足.
(2)通过与WOA-DBN、PSO-DBN、SSA-DBN、DBN、CNN、BP等多种预测模型进行对比试验,结果表明优化后模型实现了对电弧焊焊缝尺寸高精度预测,熔宽预测的MAPE仅1.85%,余高预测的MAPE仅0.47%,验证了模型的优越性和稳定性.
(3)进行了L100(104)正交试验,分析了电流、频率、占空比和焊接速度四个关键工艺参数对电弧焊焊缝尺寸的影响,验证了所提出模型有效性,为焊缝尺寸预测提供了新方法,为焊接过程智能化控制提供了新思路.
-
表 1 TC4基体的化学成分(质量分数,%)
Table 1 Chemical compositions of TC4 substrate
Fe Ti Al V $\leqslant $ 0.15余量 6.04 3.71 表 2 FeCoCrNi高熵合金粉末的化学成分(质量分数,%)
Table 2 Chemical compositions of FeCoCrNi high entropy alloy
Fe Co Cr Ni 24.44 26.18 22.43 余量 表 3 FeCoCrNi高熵合金激光熔覆试验工艺参数
Table 3 Experimental process parameters of FeCoCrNi high entropy alloy during laser cladding
试样
编号激光功率
P/W扫描速度
V/(mm·s−1)热输入
E/(J·mm−2)预铺层厚度
D(mm)1 800 10 40 0.5 2 900 12 37.5 1 3 900 10 45 1 表 4 熔覆层与TC4基体结合界面微观组织的元素分布(质量分数,%)
Table 4 Elements distribution of microstructure at the bonding interface of cladding layer and TC4 substrate
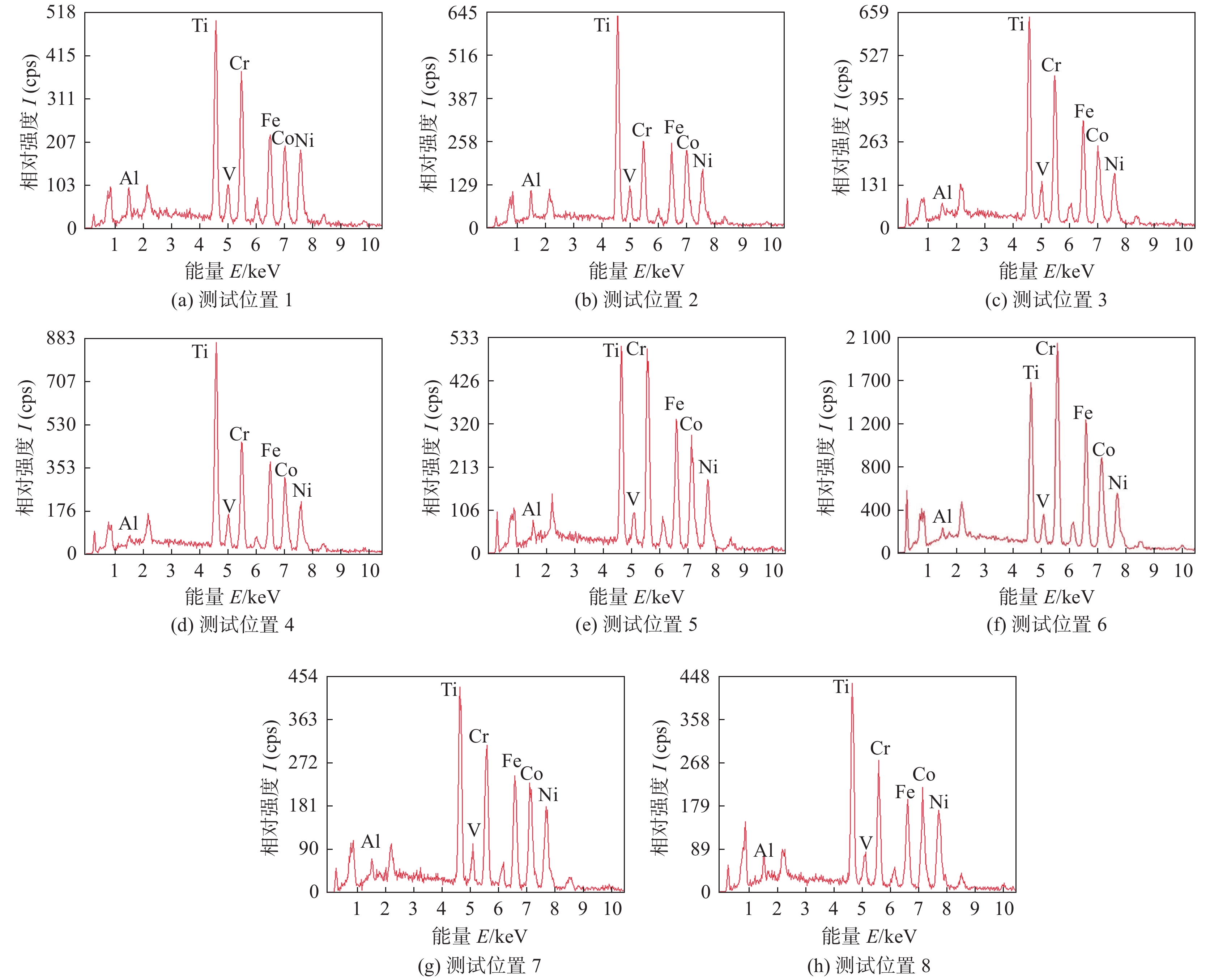
测试位置 Fe Co Cr Ni Ti Al V 1 11.61 11.43 10.57 9.36 50.63 3.52 2.85 2 9.09 12.59 8.49 11.86 52.44 3.06 2.46 3 13.96 10.07 20.11 6.78 43.09 2.56 3.42 4 3.68 3.20 53.88 5.31 30.29 2.18 1.95 -
[1] 刘世锋, 宋玺, 薛彤, 等. 钛合金及钛基复合材料在航空航天的应用和发展[J]. 航空材料学报, 2020, 40(3): 77 − 94. doi: 10.11868/j.issn.1005-5053.2020.000061 Liu Shifeng, Song Xi, Xue Tong, et al. Application and development of titanium alloy and titanium matrix composites in aerospace field[J]. Journal of Aeronautical Materials, 2020, 40(3): 77 − 94. doi: 10.11868/j.issn.1005-5053.2020.000061
[2] 张天刚, 孙荣禄. Ti811 合金表面 TC4 激光熔覆层微观组织及性能[J]. 焊接学报, 2019, 40(4): 41 − 45. doi: 10.12073/j.hjxb.2019400097 Zhang Tiangang, Sun Ronglu. Microstructure and properties of TC4 laser cladding coating on Ti811 titanium alloy surface[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2019, 40(4): 41 − 45. doi: 10.12073/j.hjxb.2019400097
[3] Yeh J, Chen S, Lin S, et al. Nanostructured high-entropy alloys with multiple principal elements: novel alloy design concepts and outcomes[J]. Advanced Engineering Materials, 2004, 6(5): 299 − 303. doi: 10.1002/adem.200300567
[4] Chookajorn T, Murdoch H A, Schuh C A. Design of stable nanocrystalline alloys[J]. Science, 2012, 337(6097): 951 − 954. doi: 10.1126/science.1224737
[5] Ma Y, Wang Q, Jiang B, et al. Controlled formation of coherent cuboidal nanoprecipitates in body-centered cubic high-entropy alloys based on Al2(Ni, Co, Fe, Cr)14 compositions[J]. Acta Materialia, 2018, 147: 213 − 225. doi: 10.1016/j.actamat.2018.01.050
[6] 赵盛举, 祁文军, 黄艳华, 等. TC4激光熔覆NiCrCoAlY热循环特性及组织性能[J]. 焊接学报, 2020, 41(9): 89 − 96. doi: 10.12073/j.hjxb.20200521001 Zhao Shengju, Qi Wenjun, Huang Yanhua, et al. Research on thermal cycle characteristics and microstructure performance of TC4 laser cladding NiCrCoAlY[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2020, 41(9): 89 − 96. doi: 10.12073/j.hjxb.20200521001
[7] Guo S, Hu Q, Ng C, et al. More than entropy in high-entropy alloys: Forming solid solutions or amorphous phase[J]. Intermetallics, 2013, 41: 96 − 103. doi: 10.1016/j.intermet.2013.05.002
[8] Cai Y, Chen Y, Manladan S M, et al. Influence of dilution rate on the microstructure and properties of FeCrCoNi high-entropy alloy coating[J]. Materials & Design, 2018, 142: 124 − 137.
[9] Guo S, Ng C, Lu J, et al. Effect of valence electron concentration on stability of fcc or bcc phase in high entropy alloys[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2011, 109(10): 103505. doi: 10.1063/1.3587228
[10] Kube S A, Sohn S, Uhl D, et al. Phase selection motifs in High Entropy Alloys revealed through combinatorial methods: Large atomic size difference favors BCC over FCC[J]. Acta Materialia, 2019, 166: 677 − 686. doi: 10.1016/j.actamat.2019.01.023
[11] Cieslak J, Tobola J, Berent K, et al. Phase composition of AlxFeNiCrCo high entropy alloys prepared by sintering and arc-melting methods[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2018, 740: 264 − 272. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2017.12.333
[12] 齐超琪. TC4表面激光熔覆FeCoCrNi高熵合金组织与性能研究[D]. 南京: 南京航空航天大学, 2020. Qi, Chaoqi. Microstructure and Properties of Laser Cladded FeCoCrNi High-entropy Alloy on TC4 Surface[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2020.
-
期刊类型引用(2)
1. 王新宇,周惦武,赵蕾,邓乔,贺赵国. 基于DBO-RF的磁场辅助镁/铝异种金属激光焊工艺. 焊接学报. 2025(02): 72-79 .  本站查看
本站查看
2. 盖胜男,王玉,许斌,王凯,肖珺,陈树君. 基于被动视觉的铝合金TIG焊缝成形监测. 焊接学报. 2025(04): 32-40 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(0)



 下载:
下载: