Analysis of reheat embrittlement and softening of coarse-grained zone of Q960E welding joint
-
摘要: 为了精确获得不同温度梯度条件下焊接热影响区的组织和性能,采用焊接热模拟的方式对一种低碳当量Q960E及其对比钢进行了两次模拟热循环试验,并获得了一次热模拟后的CGHAZ,以及二次热模拟后的未变粗晶热影响区(UA CGHAZ)、过临界粗晶热影响区(SCR CGHAZ)、临界粗晶热影响区(ICR CGHAZ)和亚临界粗晶热影响区(SR CGHAZ)的显微组织,开展了组织分析、冲击韧性测试和硬度表征.结果表明,低碳当量Q960E和高碳当量对比钢的ICR CGHAZ和SR CGHAZ均有再热脆化敏感性,在−40 ℃下对比钢的SR CGHAZ的冲击韧性低至9 J,其晶界点状和条状碳化物分布是再热脆化的主要原因;低碳当量Q960E的SR CGHAZ软化最为严重,其原因是细晶强化、位错强化和析出强化联合丧失造成的.Abstract: In order to accurately obtain the microstructure and properties of the welding heat affected zone under different temperature gradient conditions, two simulated thermal cycle tests were carried out on a low carbon equivalent Q960E and its comparative steel by using the welding thermal simulation method. And the microstructures of CGHAZ after the first thermal simulation, and UA CGHAZ, SCR CGHAZ, ICR CGHAZ and SR CGHAZ after the second thermal simulation were obtained. Microstructures were analyzed, impact toughness test and hardness characterization were carried out in this paper. Results showed that both ICR CGHAZ and SR CGHAZ of Q960E and comparative steel had reheat embrittlement sensitivity. The impact toughness of SR CGHAZ of comparative steel was as low as 9 J at −40 ℃. And the distribution of point-type and strip-type carbides formed at the grain boundary was the main reason for reheating embrittlement. The softening of SR CGHAZ with low carbon equivalent Q960E is the most serious, which is caused by the combined loss of fine-grain strengthening, dislocation strengthening and precipitation strengthening.
-
Keywords:
- CGHAZ /
- reheat embrittlement /
- softening /
- thermal simulation
-
0. 序言
近年来,商用车轻量化进程带动了大梁钢向着高强度、薄规格的方向发展[1].Q960E作为重型商用车大梁应用的最高强度级别材料,具有高强度、高硬度和高碳当量(Ceq)的特点[2],在焊接热循环作用下不可避免的出现热影响粗晶区(CGHAZ)脆化和热影响区(HAZ)局部软化问题,严重制约Q960E焊接梁架结构的使役安全性. Zhou等人[3]研究发现,随着焊接热输入的增加,CGHAZ组织由板条马氏体向粒状贝氏体转变,且基体上分布大量M/A组元,并在冲击作用下易与基体剥离;Lambert和Davis等人[4-5]进一步研究证明了在高碳当量材料中,CGHAZ热影响区组织中的M/A组元会恶化材料韧性,其研究结果被Wang等人[6]进一步利用透射电镜所证实. 张楠等人[7]在针对700 MPa级大梁钢也开展了单道次焊接接头软化行为分析,并在此基础上进一步研究了1 500 MPa高强钢HAZ析出相尺寸、数量、分布和形态对不同t8/5下的CGHAZ软化的影响[8]. 以上研究仅对单次热循环HAZ的脆化研究相对比较系统,但考虑到采用Q960E高强钢制造轻量化商用车工字梁结构,其腹板因焊接形成的HAZ会受到二次热循环的作用.根据二次峰值温度(tp2)的不同,将再热CGHAZ进一步细分为未变粗晶热影响区(位置A,UA CGHAZ,tp2≥1 200 ℃),过临界粗晶热影响区(位置B,SCR CGHAZ,Ac3≤tp2<1 200 ℃),临界粗晶热影响区(位置C,ICR CGHAZ,Ac1≤tp2<Ac3)和亚临界粗晶热影响区(位置D,SR CGHAZ,tp2<Ac1),进而针对Q960E大梁钢开展焊后CGHAZ区再热组织脆化[9-11]和软化[12-14],原因分析研究尚未见公开报道.通过前期研究[15],开发了一种低碳当量Q960E大梁钢. 在前期研究的基础上,通过焊接热模拟手段,对比分析了两种碳当量Q960E再热CGHAZ组织的形貌、冲击吸收能量和硬度分布特征,进一步揭示了脆化薄弱区和软化区的原因,为低碳当量Q960E大梁钢在轻量化商用车制造领域的应用提供前期研究基础.
1. 试验方法
试验用6.5 mm厚低碳当量设计的Q960E钢板及其对比钢的化学成分见表1,两种材料经900 ℃ + 15 min高温感应淬火后,连续完成550 ℃ + 15 min高频感应回火,得到表2所示力学性能.
表 1 Q960E和对比钢的化学成分(质量分数,%)Table 1. Chemical composition of Q960E and its comparative steel材料 C Si Mn P S Cu Ni Cr Mo B V Ceq Q960E 0.12 0.23 1.30 ≤0.02 ≤0.002 — — 0.50 0.50 0.001 2 0.1 0.395 对比钢 0.14 0.40 1.0 ≤0.02 ≤0.002 0.1 2.2 0.50 0.50 0.001 1 — 0.546 注:Ceq= C + ( Mn + Si )/6 + ( Ni + Cu )/15 + ( Cr + Mo + V )/50 表 2 Q960E和对比钢的典型力学性能Table 2. Typical mechanical properties of Q960E and its comparative steel材料 屈服强度ReL/MPa 抗拉强度Rm/MPa 断后伸长率A50(%) −40 ℃冲击吸收能量AKV(%) Q960E 990 1 020 13.5 43, 40, 49 对比钢 1 000 1 080 13.0 45, 47, 43 1.1 试验方法
对Q960E及对比钢加工6 mm (板厚) × 11 mm (板纵向) × 90 mm (板横向)的焊接热模拟试样. 通过测定两种材料在焊接热循环t8/5 = 7 s条件下的相变温度Ac1分别为705和691 ℃,Ac3分别为825和810 ℃,由此制定表3焊接热模拟工艺.
表 3 CGHAZ热模拟工艺Table 3. Thermal simulation process of CGHAZ工艺
编号一次热循环 二次热循环 预热温度
T0/℃升温速率
v /(℃·s−1)峰值温度
Tc/℃保温时间
ts/s热循环时间
t8/5/ s升温速率
v /(℃·s−1)峰值温度
Tc/℃保温时间
ts/s热循环时间
t8/5/s1 25 150 1 250 2 7 — — — — 1A 25 150 1 250 2 7 150 1 250 2 7 1B 25 150 1 250 2 7 150 950 2 10 1C 25 150 1 250 2 7 150 750 2 12 1D 25 150 1 250 2 7 150 600 2 15 将试样沿着热模拟热电偶点位置为中心加工55 mm × 10 mm × 5 mm的冲击试样,加工深度2 mm的V形缺口,并根据国家标准GB/T 2650,采用ZBC2452-3型冲击试验机测试缺口位置−40 ℃下的冲击吸收能量.
根据国家标准GB/T 2654制样,并采用HVS-10Z型维氏硬度计测试热电偶点位置的硬度,加载载荷为19.6 N,加载时间15 s,测试3个值后取均值.
对热电偶区域截取金相试样,经研磨、抛光后,用3%硝酸酒精进行侵蚀,利用BX35型光学显微镜和Libra120型场发射扫描电镜(SEM)观察其显微组织形态;利用电解双喷技术,获得热电偶区金属薄片,并在JEM-2100F透射电镜(TEM)上观察微区组织及第二相粒子形态,EDS分析其成分.
2. 试验结果
2.1 显微组织
当采用热模拟1工艺进行第一次模拟热循环(t8/5 = 7 s)后,两种成分钢在不同tp2条件下进行二次热循环,其室温下再热粗晶热影响区的SEM像如图1所示. UA CGHAZ的组织形态为板条马氏体,经过两次热循环后的Q960E和对比钢的UA CGHAZ位置的马氏体packet和block尺寸相差不大. 经二次正火处理的SCR CGHAZ可见等轴态晶界,组织以马氏体 + 贝氏体为主. 经模拟两相区短暂热处理获得的ICR CGHAZ得到马氏体 + 残余奥氏体的混合组织,组织均匀性恶化.SR CGHAZ的组织基本保持了CGHAZ粗大的晶粒特征,但经模拟短暂高温回火后的组织边界相对模糊,而观察到对比钢SR CGHAZ板条束间存在大量“白亮带”组织.
![]() 图 1 不同tp2温度下再热CGHAZ的SEM像Figure 1. SEM images of reheated CGHAZ under different tp2 temperatures. (a) UA CGHAZ of Q960E; (b) UA CGHAZ of comparative steel; (c) SCR CGHAZ of Q960E; (d) SCR CGHAZ of comparative steel; (e) ICR CGHAZ of Q960E; (f) ICR CGHAZ of comparative steel; (g) SR CGHAZ of Q960E; (h) SR CGHAZ of comparative steel
图 1 不同tp2温度下再热CGHAZ的SEM像Figure 1. SEM images of reheated CGHAZ under different tp2 temperatures. (a) UA CGHAZ of Q960E; (b) UA CGHAZ of comparative steel; (c) SCR CGHAZ of Q960E; (d) SCR CGHAZ of comparative steel; (e) ICR CGHAZ of Q960E; (f) ICR CGHAZ of comparative steel; (g) SR CGHAZ of Q960E; (h) SR CGHAZ of comparative steel2.2 力学性能
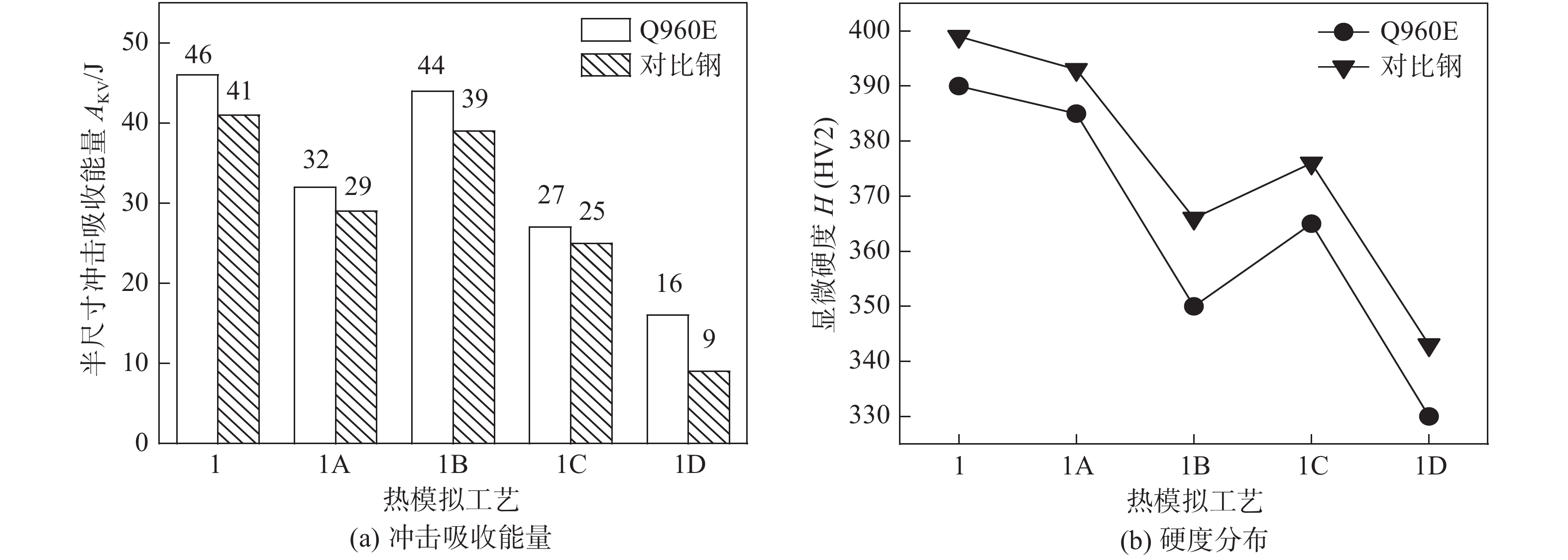
Q960E和对比钢经不同热模拟工艺下−40 ℃冲击吸收能量和显微硬度值如图2所示. 由图2a可知,Q960E热模拟CGHAZ,UA CGHAZ,SCR CGHAZ,ICR CGHAZ和SR CGHAZ的−40 ℃冲击吸收能量优于对比钢,分别为46,32,44,27和16 J,二次热循环和一次热循环的冲击吸收能量相差较为明显,SR CGHAZ的冲击吸收能量最低,对比钢的SR CGHAZ脆化最为严重,冲击吸收能量仅9 J. 图2b所示SR CGHAZ为硬度低谷值,发生软化.
3. 试验结果分析
Q960E大梁钢在商用车使役条件下可能承受着瞬态高应力负载.Q960E焊接接头热影响区的韧性改善有助于抑制疲劳裂纹扩展速率,提高焊接梁架的疲劳耐久性. C作为有效提高淬透性,提升热影响区强度和硬度的基本元素,可显著提高Ceq值,对焊接性不利. V作为一种微合金化元素,在550 ~ 600 ℃下驰豫可显著提升钢材的屈服强度[16],但对Ceq的增加并不显著. 由此,文中给出了表1所示低Ceq设计的Q960E成分,通过降C、去Cu-Ni、加V处理,得到与传统成分体系不同的低碳当量、高强度Q960E大梁钢[15],旨在焊后通过损失一定的HAZ硬度(图2b)来换取低碳当量Q960E大梁钢HAZ韧性的改善,从而提升商用车梁架的疲劳寿命[2]. 由于HAZ较窄,通过热模拟过程获得可供分析的热影响区域,重点讨论两种成分钢焊后脆化最严重的ICR CGHAZ和SR CGHAZ脆化原因,以及低碳当量Q960E焊接热模拟SR CGHAZ硬度低于对比钢的主要原因.
3.1 ICR CGHAZ和SR CGHAZ的脆化
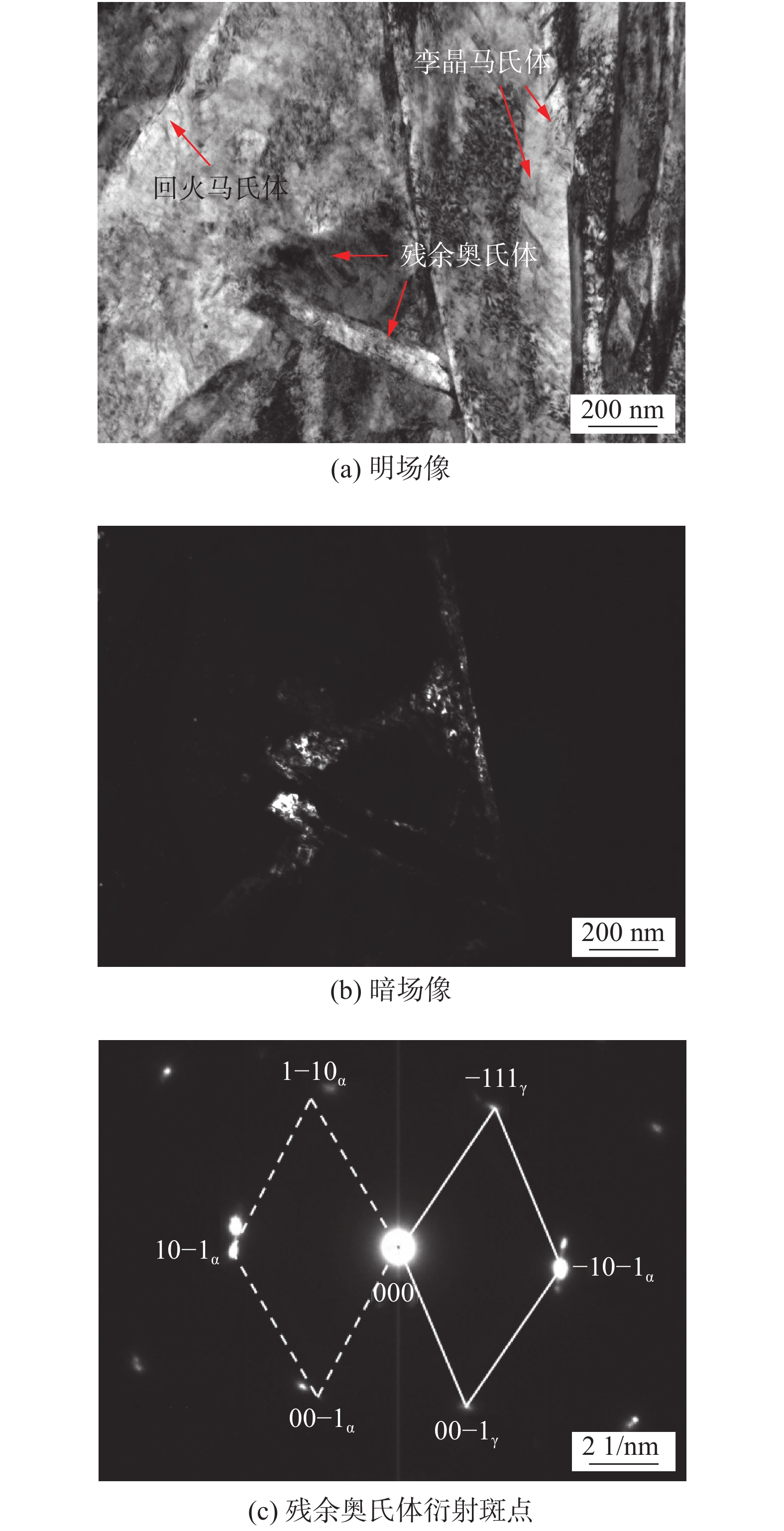
根据试验结果可见,Q960E和对比钢经二次热循环后,显著发生脆化的区域是ICR CGHAZ和SR CGHAZ. 图3为Q960E大梁钢的ICR CGHAZ的TEM像,该区组织可进一步细分为回火马氏体 + 短片状的孪晶马氏体 + 残余奥氏体组成.在二次热循环作用下,部分一次热循环的马氏体板条边界重新生成了奥氏体,由于奥氏体溶C能力强,马氏体中的C原子经短距扩散进入边界位置的奥氏体,使得奥氏体稳定性和体积增加.在随后冷却过程中,一部分不稳定的奥氏体转化为孪晶马氏体,溶C较多的奥氏体随之冷却至室温,同时,末奥氏体化的一次热循环马氏体经二次“回火”,板条组织略有长大,位错密度降低. 由于回火马氏体C元素含量相对孪晶马氏体较低,属于软相;而孪晶马氏体通过原奥氏体溶C变得脆硬,韧性极差. 残余奥氏体中C元素含量最高,稳定到室温后易夹在回火马氏体与孪晶马氏体中间,同样属于脆硬相[17-18]. 在冲击载荷作用下极易发生脆断,这也是该区发生再热脆化的原因.
SR CGHAZ是在一次CGHAZ组织的基础上再经短暂的“高温回火”后形成的,Q960E和对比钢在该区的冲击韧性最低. 通过图4的TEM像可见,Q960E由于Ceq较对比钢低,在一次热循环后的CGHAZ的马氏体组织中位错密度较高,但未发现影响韧性的孪晶马氏体存在,经二次“高温回火”后,马氏体板条界呈现点状析出碳化物;而对比钢在一次热循环CGHAZ的组织中呈现大量孪晶马氏体,经二次“高温回火”后在晶界发现点状和条状碳化物,这是该区韧性最低的主要原因.
3.2 SR CGHAZ的软化
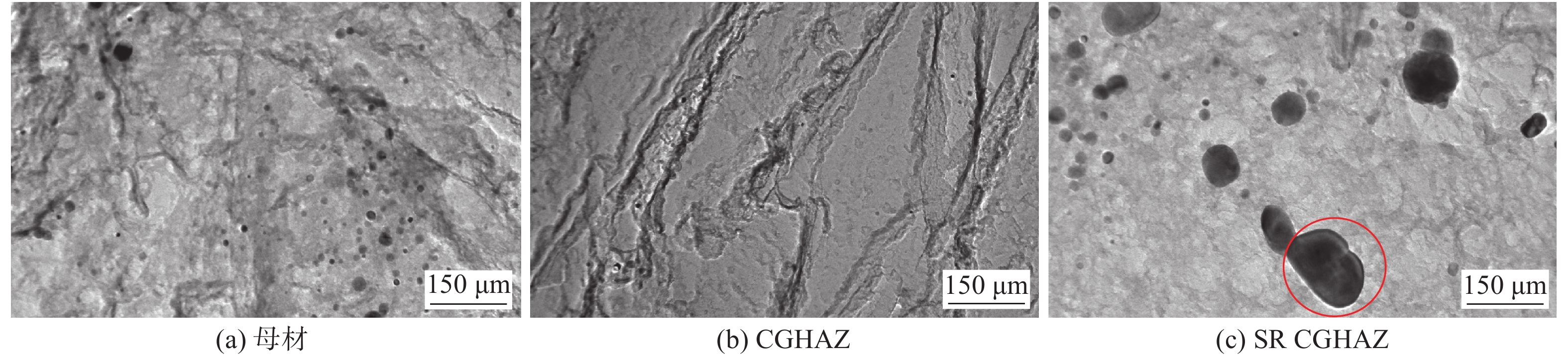
由于焊接特有的热循环过程使得Q960E的CGHAZ组织发生了与母材不同的组织形貌.图5为母材经15 min短暂的感应淬火 + 感应回火热处理后,晶粒尺寸均匀细小,约8 ~ 10 μm.经焊接热循环后,该区瞬时峰值温度接近1 300 ℃[7],焊接空冷条件下得到板条状马氏体组织,并可见原高温下等轴奥氏体晶粒,尺寸约为50 ~ 100 μm. 可见,粗晶区晶粒长大显著,成为CGHAZ软化的原因之一.
变形强化丧失是SR CGHAZ软化的内在原因. 利用TEM对低碳当量Q960E母材、CGHAZ和SR CGHAZ进行了微区分析. 图6为母材中相对均匀析出的50 nm及以下尺度析出相周围密集缠绕着高密度位错;而CGHAZ与母材形成显著差异的是其组织形貌可见马氏体板条结构,结构内部位错密度显著降低;经过二次“高温回火”后的SR CGHAZ内部位错密度进一步降低,这说明SR CGHAZ位错强化效果经二次热循环后发生弱化.
另注意到,图6c中析出相尺寸较母材50 nm以下尺度含V析出相发生明显粗化行为. 为此,图7通过碳膜复形的方法清晰地表征了析出相形貌. 相关研究表明[19],母材基体中50 nm以下均匀细小的析出相对材料的强度提升贡献较大. 在经一次热循环后,图7b所示CGHAZ中大部分细小弥散的析出相消失,这是因为细小的析出相比表面能较低,属于亚稳态相,易受升温环境影响而发生回溶基体的现象,使原母材中析出强化的贡献效果丧失,但参考图2b的硬度数据可见,CGHAZ并未因析出强化效果丧失而发生软化,这主要是该区有一定的淬硬性,组织强化效果弥补了析出强化的不足. CGHAZ在经过短暂的二次“高温回火”热循环后,基体中的析出相反而粗化,这主要是因为CGHAZ基体中残留的第二相粒子本身也会随二次热循环过程发生Ostwald机制长大[20],其微观表现为:二次“高温回火”热循环峰值温度越高,停留时间越长,回溶的第二相粒子经元素短距扩散,可依附原未溶第二相粒子表面,并随之长大,最终形成粒径较大的近圆形富V第二相粒子(图8),且粒子尺度显著大于50 nm,数量显著降低. 因此,SR CGHAZ的软化最为严重,除图6中位错强化效果的丧失外,还有伴随该区析出强化效果的弱化.
4. 结论
(1) 低碳当量Q960E和对比钢的ICR CGHAZ和SR CGHAZ均有再热脆化敏感性. 对比钢的再热脆化倾向更大,在−40 ℃下SR CGHAZ的冲击韧性低至9 J.
(2) 低碳当量Q960E的ICR CGHAZ组织由回火马氏体 + 短片状孪晶马氏体 + 残余奥氏体组成,组织均匀性差是该区脆化的因素.
(3) 低碳当量Q960E和对比钢的CGHAZ经二次“高温回火”后得到SR CGHAZ,其晶界点状和条状碳化物分布是韧性最低的主要原因.
(4) 低碳当量Q960E的SR CGHAZ软化原因是细晶强化、位错强化和析出强化联合丧失造成的.
-
图 1 不同tp2温度下再热CGHAZ的SEM像
Figure 1. SEM images of reheated CGHAZ under different tp2 temperatures. (a) UA CGHAZ of Q960E; (b) UA CGHAZ of comparative steel; (c) SCR CGHAZ of Q960E; (d) SCR CGHAZ of comparative steel; (e) ICR CGHAZ of Q960E; (f) ICR CGHAZ of comparative steel; (g) SR CGHAZ of Q960E; (h) SR CGHAZ of comparative steel
表 1 Q960E和对比钢的化学成分(质量分数,%)
Table 1 Chemical composition of Q960E and its comparative steel
材料 C Si Mn P S Cu Ni Cr Mo B V Ceq Q960E 0.12 0.23 1.30 ≤0.02 ≤0.002 — — 0.50 0.50 0.001 2 0.1 0.395 对比钢 0.14 0.40 1.0 ≤0.02 ≤0.002 0.1 2.2 0.50 0.50 0.001 1 — 0.546 注:Ceq= C + ( Mn + Si )/6 + ( Ni + Cu )/15 + ( Cr + Mo + V )/50 表 2 Q960E和对比钢的典型力学性能
Table 2 Typical mechanical properties of Q960E and its comparative steel
材料 屈服强度ReL/MPa 抗拉强度Rm/MPa 断后伸长率A50(%) −40 ℃冲击吸收能量AKV(%) Q960E 990 1 020 13.5 43, 40, 49 对比钢 1 000 1 080 13.0 45, 47, 43 表 3 CGHAZ热模拟工艺
Table 3 Thermal simulation process of CGHAZ
工艺
编号一次热循环 二次热循环 预热温度
T0/℃升温速率
v /(℃·s−1)峰值温度
Tc/℃保温时间
ts/s热循环时间
t8/5/ s升温速率
v /(℃·s−1)峰值温度
Tc/℃保温时间
ts/s热循环时间
t8/5/s1 25 150 1 250 2 7 — — — — 1A 25 150 1 250 2 7 150 1 250 2 7 1B 25 150 1 250 2 7 150 950 2 10 1C 25 150 1 250 2 7 150 750 2 12 1D 25 150 1 250 2 7 150 600 2 15 -
[1] Joseph C, Benedyk. Light metal in automotive applications[J]. Light Metal Age, 2000, 58(10): 34 − 35.
[2] 张楠, 田志凌, 董现春, 等. Q960E热影响粗晶区疲劳寿命与ΔKth值的关系分析[J]. 焊接学报, 2018, 39(7): 106 − 110. Zhang Nan, Tian Zhiling, Dong Xianchun, et al. Research on relationship between ΔKth and fatigue life of heat-affected coarse grain zone in Q960E[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2018, 39(7): 106 − 110.
[3] Zhou Y L, Jia T, Zhang X J, et al. Microstructure and toughness of the CGHAZ of an offshore platform steel[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2015, 219: 314 − 320.
[4] Lambert A, Drillet J, Gourgues A F, et al. Microstructure of mattensite-austensite constituents in heat affected zones of high strength low alloy steel welds in relation to toughness properties[J]. Science and Technology of Welding and Joining, 2000, 5(3): 168 − 173.
[5] Davis C L, King J E. Cleavage initiation in the intercritically reheated coarse-grained heat-affected zone: Part I. fractographiv evidence[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 1994, 25(3): 563 − 573.
[6] Wang C M, Wu X F, Liu J, et al. Transmission electron microscopy of martensite/austensite islands in pipeline steel X70[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2006, 438(25): 257 − 271.
[7] 张楠, 田志凌, 张书彦, 等. 700MPa微合金高强钢焊接软化机理及解决方案[J]. 钢铁研究学报, 2019, 31(3): 318 − 326. Zhang Nan, Tian Zhiling, Zhang Shuyan, et al. Mechanism and solution of welding softening for 700MPa microalloyed high strength steel[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, 2019, 31(3): 318 − 326.
[8] 董现春, 潘辉, 赵阳, 等. 仿弹钢板激光焊接接头的组织和性能[J]. 材料热处理学报, 2019, 40(9): 163 − 168. Dong Xianchun, Pan Hui, Zhao Yang, et al. Microstructure and properties of laser welded joint of bulletproof steel plant[J]. Transactions of Materials and Heat Treatment, 2019, 40(9): 163 − 168.
[9] 王学, 常建伟, 黄关政, 等. WB36钢临界再热粗晶区组织和性能[J]. 焊接学报, 2008, 29(10): 29 − 32. Wang Xue, Chang Jianwei, Huang Guanzheng, et al. Study on microstructure and properties of IRCGHAZ in WB36 steel[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2008, 29(10): 29 − 32.
[10] 姚钦. HQ-80钢再热裂纹机理[J]. 焊接学报, 2004, 25(6): 77 − 81. Yao Qin. Mechanism of HQ-80 steel reheat crack[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2004, 25(6): 77 − 81.
[11] Hu J, Du L X, Wang J J, et al. High toughness in the intercritically reheated coarse-grained (ICRCG) heat-affected zone (HAZ) of low carbon microalloyed steel[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2014, 590: 323 − 328.
[12] 张楠, 董现春, 张熹, 等. 钛微合金化SQ700MCD高强钢粗晶热影响区软化的原因[J]. 机械工程材料, 2012, 36(4): 88 − 92. Zhang Nan, Dong Xianchun, Zhang Xi, et al. The softening analysis of CGHAZ in Ti microalloyed SQ700MCD steel[J]. Materials for Mechanical Engineering, 2012, 36(4): 88 − 92.
[13] 张楠, 董现春, 徐晓宁, 等. Ti-Nb微合金化高强钢的焊接接头组织和性能[J]. 材料热处理学报, 2014, 35(6): 115 − 120. Zhang Nan, Dong Xianchun, Xu Xiaoning, et al. Microstructure and property of welding joint with Ti-Nb microalloyed high-strength steel[J]. Transactions of Materials and Heat Treatment, 2014, 35(6): 115 − 120.
[14] 张楠, 董现春, 潘辉, 等. 高Ti-Nb系高强钢焊接接头回火前后的力学行为[J]. 焊接学报, 2015, 36(5): 93 − 98. Zhang Nan, Dong Xianchun, Pan Hui, et al. Mechanical behavior of welded joint of a high Ti-Nb content microalloyed high-strength steel before and after drawing temper treatment[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2015, 36(5): 93 − 98.
[15] 张楠, 田志凌, 张书彦, 等. 感应回火对含钒900MPa级高强钢组织与性能的影响[J/OL]. 热加工工艺: 1-5[2020-11-11]. https://doi.org/10.14158/j.cnki.1001-3814.20193019. Zhang Nan, Tian Zhiling, Zhang Shuyan, et al. Effects of induction tempering on microstructure and properties of 900 MPa grade high strength steel containing vanadium[J/OL]. Hot Working Technology: 1-5 [2020-11-11]. https://doi.org/10.14158/j.cnki.1001-3814.20193019.
[16] 李晓林, 崔阳, 肖宝亮, 等. V-N微合金钢在线快速感应回火工艺中V(C, N)析出强化机制[J]. 金属学报, 2018, 54(10): 1368 − 1376. doi: 10.11900/0412.1961.2018.00119 Li Xiaolin, Cui Yang, Xiao Baoliang, et al. Effect of on-line rapid induction tempering on precipitation strengthening mechanism of V(C, N) in V-N microalloyed steel[J]. ACTA Metallurgica Sinica, 2018, 54(10): 1368 − 1376. doi: 10.11900/0412.1961.2018.00119
[17] Mohseni P, Solberg J K, Karlsen M, et al. Investigation of mechanism of cleavage fracture initiation in intercritically coarse grained heat affected zone of HSLA steel[J]. Materials Science and Technology, 2012, 28(11): 1261 − 1268.
[18] Moeinifar S, Kokabi A H, Hosseini H R M. Influence of peak temperature during simulation and real thermal cycles on microstructure and fracture properties of the reheated zones[J]. Materials and Design, 2010, 31(6): 2948 − 2955.
[19] 李永亮. 700 MPa级高强度汽车大梁钢成分设计与组织控制研究[D]. 北京: 北京科技大学, 2017. Li Yongliang. Study on composition design and microstrucyure control about 700 MPa grade high strength beam steel for vehicles [D].Beijing: University of Science and Technology Beijing, 2017.
[20] 雍岐龙. 钢铁材料中的第二相[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 2006. Yong Qilong. Secondary phases in steels [M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 2006.
-
期刊类型引用(4)
1. 赵阳,刘旭明,张楠,王军生,潘辉. 准动态模型预估的Q960E大梁钢SR-CGHAZ疲劳裂纹扩展机理. 焊接学报. 2024(09): 84-93 .  本站查看
本站查看
2. 王越洋,李硕妍,王鑫,杨永强,郑春雷. 预热温度对Q960E钢焊接热影响区组织以及力学性能影响的研究. 大型铸锻件. 2024(06): 108-112 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 兰志宇,陈尹泽,李争. 液压支架用中厚Q960钢板机器人焊接工艺的确定. 机械工程材料. 2023(11): 12-17+24 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 陈振业,魏涛,吝章国,陈波,冯伟. 690 MPa级高强抗震耐候钢气体保护焊丝的研制. 机械制造文摘(焊接分册). 2022(04): 15-19 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)



 下载:
下载: