Microstructure and properties of 6061 aluminum alloy by MIG wire and arc additive manufacturing
-
摘要: 探索MIG电弧增材制造6061铝合金构件的工艺成形性,并对成形件不同区域的微观组织及力学性能开展研究.结果表明,当送丝速度/焊接速度的比值P在0.5 ~ 1之间,且送丝速度在5 ~ 7 m/min之间时,可获得良好焊道形貌;堆积焊道层与层之间交界处为结合层,其余区域为沉积层,结合层和沉积层呈现出沿堆积高度方向灰白色带依次交替的形貌,并都呈现出各种尺寸大小的气孔多发的状态;显微硬度和拉伸测试发现:沿着堆积方向硬度变化不大,结合层硬度低于沉积层,且硬度波动性更大;不同区域水平方向强度差异不大,堆积方向强度比水平方向略低,平均断后伸长率分别为18%和22.6%,两个方向拉伸断口皆以韧窝为主,属于韧性断裂.Abstract: The deposition formability of MIG wire and arc additive manufacturing of 6061 aluminum alloy components is investigated, and the microstructure and mechanical properties of different areas of the deposited parts are studied. The results show that: when the ratio of wire feeding speed/welding speed(F/T) is between 0.5 and 1, meanwhile the wire feeding speed is between 5 and 7 m/min, a good weld bead morphology can be obtained; the interfaces between layers are the bonding layers, and the rest regions are the deposition layer. The bonding layer and the deposition layer show a morphology of alternating gray and white bands along the stack height direction, bonding layers are easier to produce the pore defect; micro hardness and tensile tests show that the hardness changes little along the deposition direction, the hardness of the bonding layer is lower than that of the deposition layer, besides the hardness fluctuation is greater; there is little difference in the strength and plasticity of the horizontal direction in different regions. ; The strength is slightly higher in the deposition direction than the horizontal direction, and the elongation after fracture is 5.6% and 3.4% respectively. The tensile fractures in both directions are mainly dimples, which indicates ductile fractures.
-
0. 序言
电弧增材制造技术是根据零件的数字三维模型,通过电弧为热源将金属焊丝熔化,并逐层堆积出零件的新型先进数字化制造技术.电弧增材制造的热输入和熔池体积大于激光增材,其成形精度相对更低,但成形效率高,制造成本低,适用于铝合金、钛合金、高强钢等材料的中大型尺寸复杂金属零构件的直接制造[1-2].6061铝合金属于Al-Mg-Si系,具有中等强度、抗腐蚀性强、焊接性能好等特点;在固溶加人工时效处理的条件下,具有较高的硬度、较好的塑性以及优良的冷加工性,可用作结构材料[3],因此6061铝合金被广泛应用在航天航空、船舶、农业、汽车等领域中作为中大型、强度和耐蚀性能要求高的工业型材[4].
目前铝合金的电弧增材制造的研究主要有两个方面:成形件的形貌控制以及其力学性能控制.在形貌控制上主要研究电流方式、焊枪角度等工艺条件对成形件形貌及尺寸的影响规律[5-7].在力学性能控制上研究通过辅助措施或热处理来优化成形件微观组织和力学性能[8-9].而关于6061铝合金电弧增材制造的研究至今未见文献报道,仅见一些关于6061铝合金焊接接头性能的研究[10-13],其焊接接头的拉伸性能一般小于基材,并且在焊道与基材交界处硬度高于焊道区域.
文中开展对MIG电弧增材制造6061铝合金的工艺、微观组织和力学性能的研究,设计试验探索不同工艺参数下的焊道形貌和堆积成形可行性,采用优化的工艺参数堆积成形薄壁件,并研究薄壁件不同区域的微观组织与力学性能,为电弧增材制造6061铝合金中大型零构件的工业应用提供工艺研究基础.
1. 试验方法
试验所用原材料包括:6061铝合金焊丝(直径是1.2 mm)和6061铝合金焊接基板(450 mm × 150 mm × 8 mm),焊丝化学成分如表1所示.电弧增材制造系统主要由ABB工业机器人(IRB1600)、沙福全数字控制MIG焊机(DIGIPULS III 420)等组成,焊接模式选用2T + 一元化焊接成形.堆积结束后,分别在上部、中部和下部3个区域用线切割机取立方体金相试样(15 mm × 10 mm × 10 mm)和拉伸试样(依据国家标准GB2651—89,试样总长50 mm,标距部分长38 mm,宽度3 mm,厚度2 mm).金相试样经过砂纸研磨和高氯酸电解抛光后,用凯乐试剂腐蚀处理并在光学显微镜下观察微观组织.采用维氏硬度计测量试样截面沿堆积方向的硬度变化.在万能材料试验机上进行拉伸试验.拉伸测试结束后使用扫描电镜分别观察3个区域拉伸试样的断口形貌.所有试样的取样位置如图1所示,其中上部、中部、下部试样沿着水平方向,与焊接方向平行;竖直试样沿着堆积方向,与焊接方向垂直.
表 1 焊丝化学成分(质量分数,%)Table 1. Chemical composition of welding wireSi Fe Cu Mn Mg Cr Zn Ti Al 0.4 ~ 0.8 0.7 0.15 ~ 0.4 0.15 0.8 ~ 1.20 0.04 ~ 0.35 0.25 0.15 余量 2. 试验结果与讨论
2.1 成形可行性
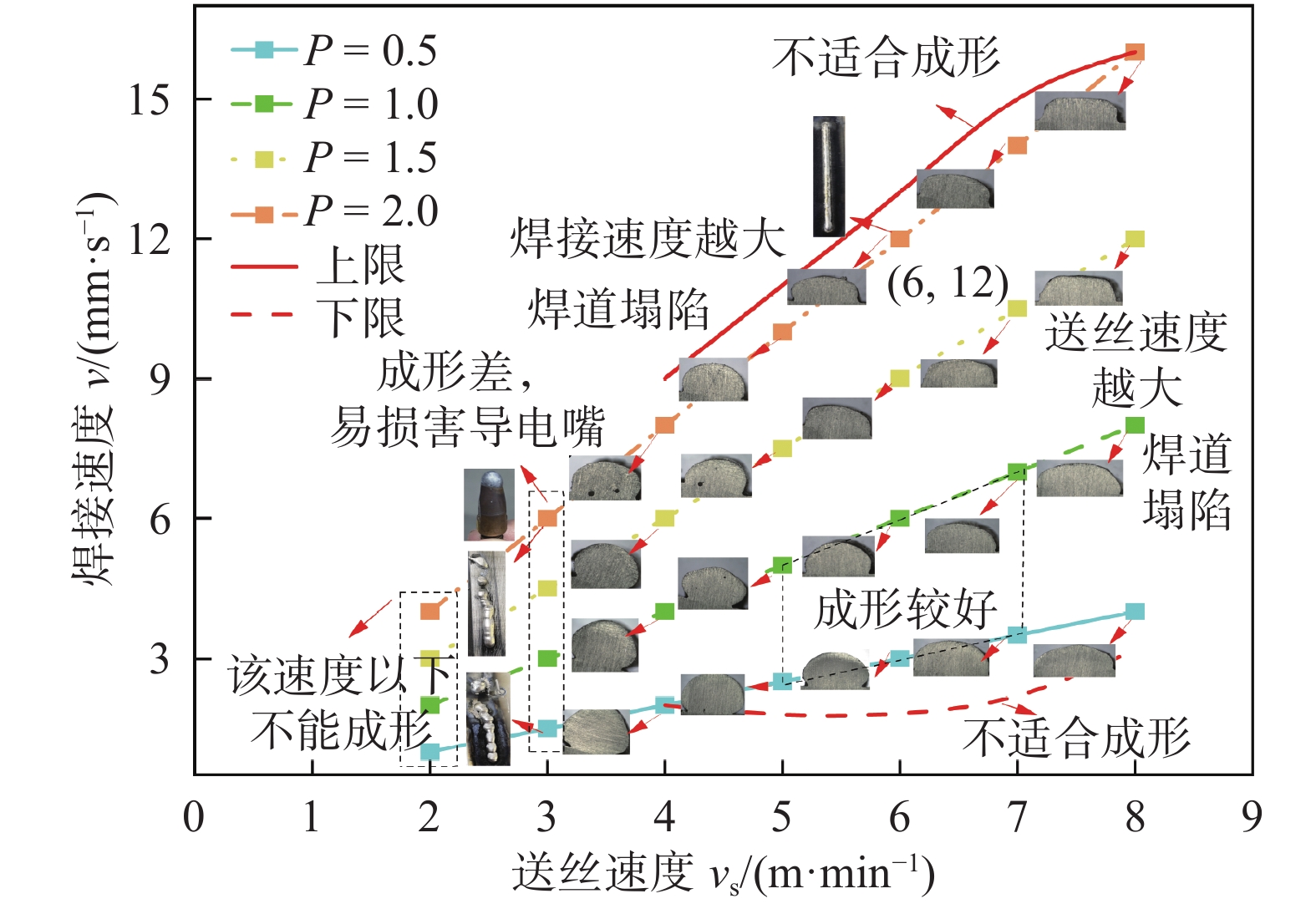
电弧增材制造的焊道形貌受到多个工艺参数影响,其中受送丝速度和焊接速度的影响最大.为了探究电弧增材6061铝合金堆积可行的工艺参数窗口,设计一系列的探究试验(表2).其中焊接电压固定为20 V,焊丝伸出长度为15 mm,保护气体(纯氩气)流量为15 L/min,每层堆积结束后调整焊丝长度,确保焊丝底端到工件的距离为3 mm.利用机器人控制焊枪垂直于基板进行堆积,电弧增材制造工艺试验结果如图3所示.
表 2 探究试验工艺参数Table 2. Used process parameters in experiments编号 送丝速度
vs/(m·min−1)焊接速度
v/(mm·s−1)1 ~ 4 2 1,2,3,4 5 ~ 8 3 1.5,3,4.5,6 9 ~ 12 4 2,4,6,8 13 ~ 16 5 2.5,5,7.5,10 17 ~ 20 6 3,6,9,12 21 ~ 24 7 3.5,7,10.5,14 25 ~ 28 8 4,8,12,16 图2所示结果表明,当MIG送丝速度小于3 m/min时,改变焊接速度,都不能完整成形,并且极易烧坏导电嘴;当送丝速度为3 ~ 4 m/min时,由于电流太小导致焊接过程不稳定,焊道会呈不规则的间歇环状,增大焊接速度则不规则的程度减弱.
当送丝速度介于5 ~ 7 m/min,且送丝速度和焊接速度的比值在0.5 ~ 1倍之间时可以获得宽度适中、成形良好的焊道. 当比值在0.5以下时,送丝速度相对焊接速度偏小,导致热输入量小,且单位时间内金属填充量不足,故焊道形状细窄,不利于多层堆积成形. 若比值增大至1以上,送丝速度相对焊接速度过高,导致单位时间内金属填充量偏多,这将造成焊道变粗和容易发生熔池塌陷,亦不利于堆积成形.综上所述,电弧增材6061铝合金MIG焊接参数在送丝速度和焊接速度的比值在0.5 ~ 1之间,且送丝速度选择5 ~ 7 m/min之间时可获得良好焊道形貌.
2.2 微观组织
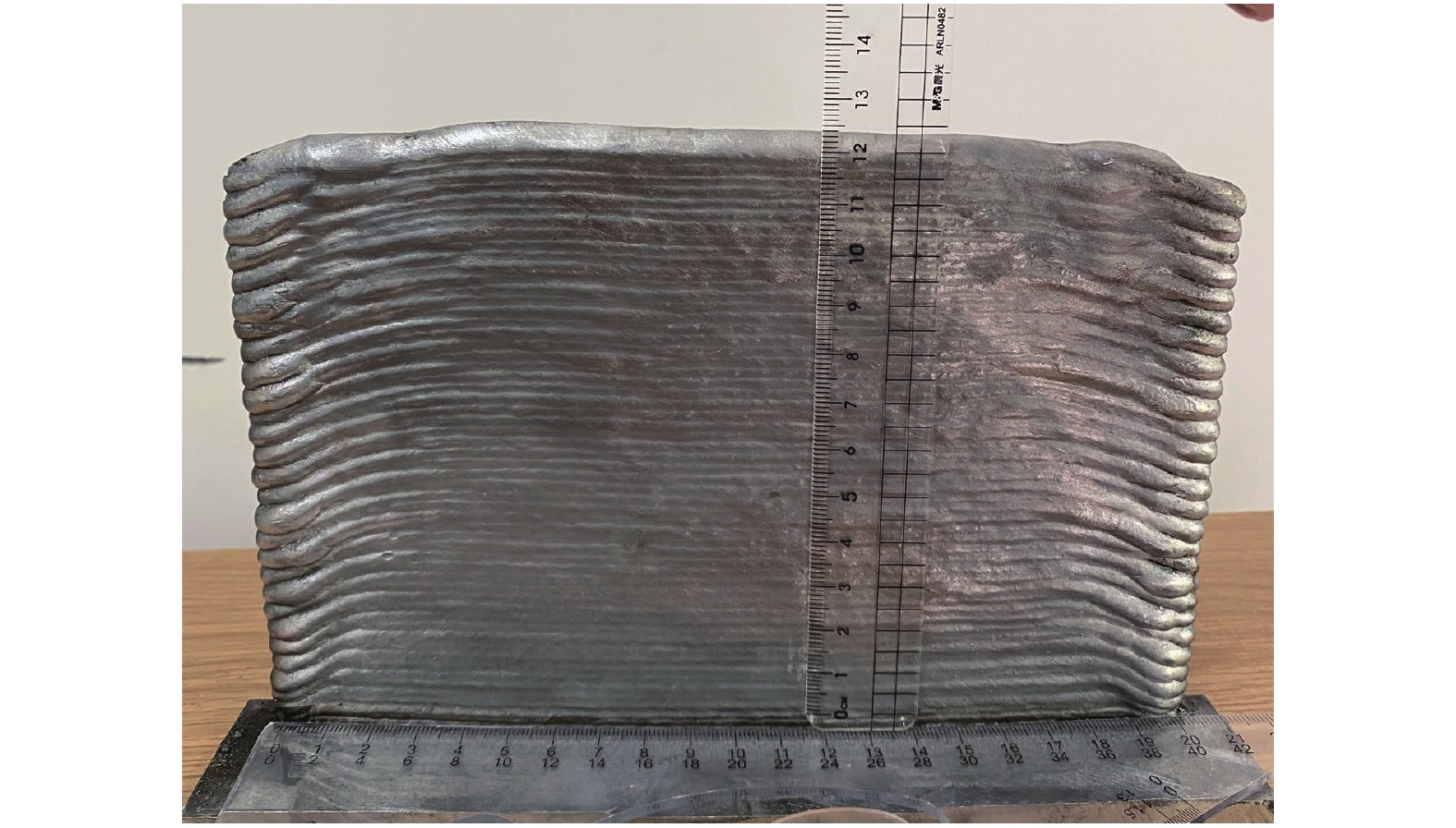
堆积微观组织和力学性能成形试样时,选择堆积形貌最佳的焊接参数.其中送丝速度为6 m/min,焊接速度为6 mm/s,采用逐层往复堆积的方式,层数为60层.图3为堆积成形薄壁件宏观形貌,图中可以看出薄壁件起弧端和熄弧端略微坍塌,薄壁件侧壁有明显的层间条纹特征.薄壁件两端坍塌是因为焊接启停时焊接参数的非线性变化,焊道首尾部支撑不良而在电弧冲击下引起的熔池失稳.
堆积前先对基板进行预热,有利于焊丝的充分熔化减少误差;起弧之前保护气提前打开,使堆积起弧端焊前被纯氩气充分保护;电弧熄灭阶段,停止送丝并且保护气体延迟关闭,能够避免多余的焊丝堆积,有利于形成均匀的堆积层;每层堆积结束后用钢刷清理焊道表面的黑黄色氧化物,当成形件整体温度降至75 ℃左右时再进行下一道堆积.
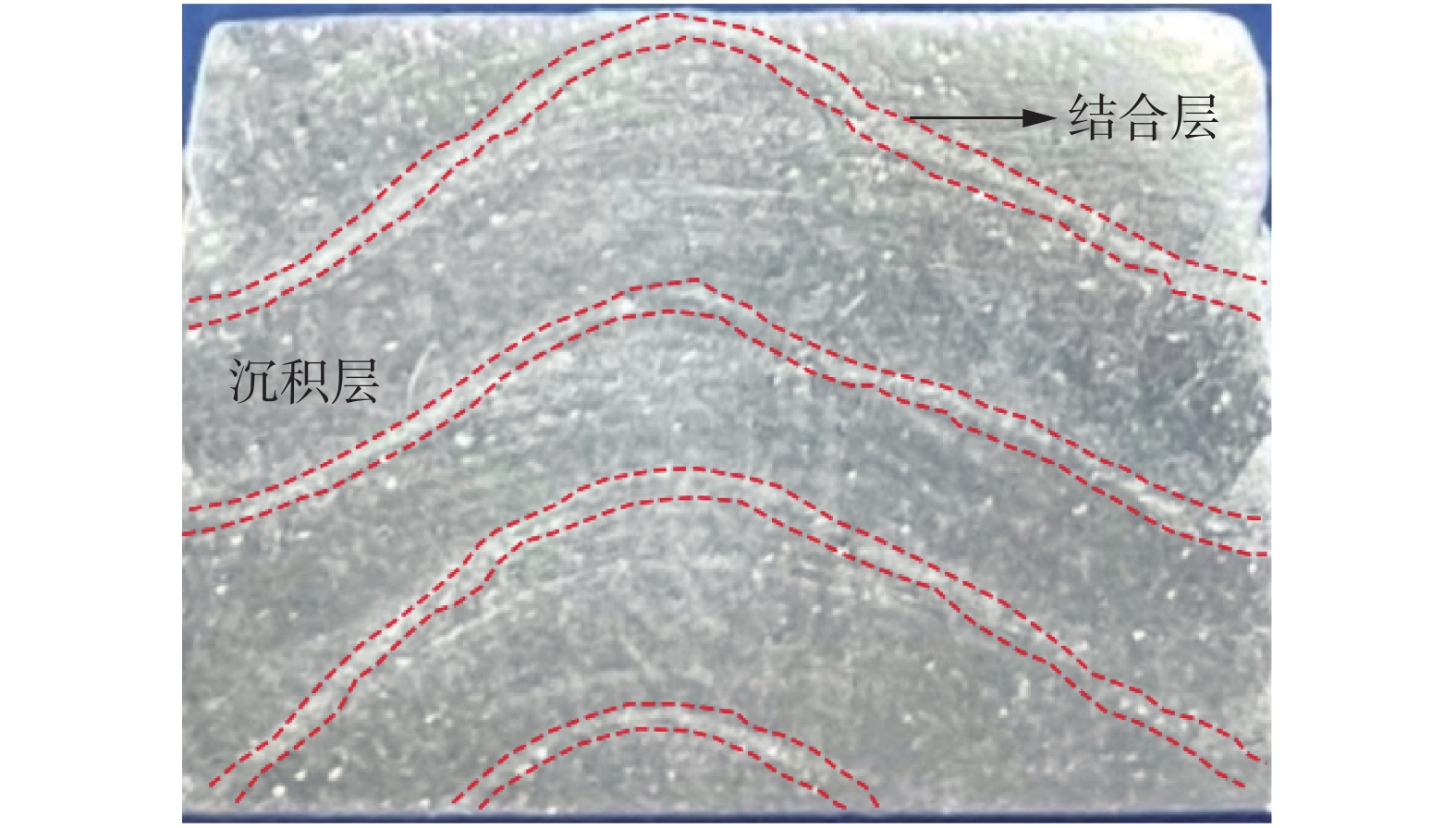
图4为腐蚀过后的金相试样表面,焊道层与层之间的交界处为结合层,结合层大致位于下一层堆积对已堆积焊道的重熔区域,对应的主要是堆积熔池的底部区域.截面上,除结合层外的其余区域为沉积层,沉积层主要对应的是堆积熔池的中上部区域.如图4所示,在亮光照射下,结合层和沉积层呈现出沿堆积高度方向灰白色带依次交替的形貌.
图5表示不同区域金相试样的微观组织.从图中可以发现,无论是沉积层还是结合层都呈现出各种尺寸大小的气孔多发的状态,但二者的气孔分布具有不同的特点,这与堆积成形时熔池不同区域具有不同的冷却速率有关.结合层对应的是熔池底部,靠近已有的冷却焊道和基板,热传导面积大,冷却速率快,凝固界面上析出的气体不易逃逸出来,从而在结合层形成了数量多、以小孔为主的密集气孔分布.而沉积层对应的是熔池中上部,冷却速率相对较慢,熔池对流更充分,更有利于气体逸出到熔池外,因此沉积层气孔数量比结合层少.部分从结合层逃逸出来的小气泡以及沉积层中析出的气体,不断上浮、聚合、长大,若最终未能从熔池表面逃逸出来,则被俘获在沉积层中,形成体积更大、数量相对更少的气泡分布[14].
在试样下部区域还出现了“液滴”状物质,这是由于在堆积成形过程中,当焊道的温度处在共晶温度与液相线温度之间时,材料会发生共晶反应,造成一种局部“液化”现象[15].相比于其它金属,铝合金有着更快的冷却速率,且电弧增材制造过程中有着复杂的热环境,因此有更能满足“液化”现象所需的条件:堆积成形过程中,若已堆积焊道对下一层堆积焊道的散热速率较慢,当温度达到液化线温度时,固态扩散会使组织中的β相溶解到α-Al基体中.在6061铝合金的电弧增材制造过程中,已堆积焊道对新一层焊道的冷却速率很快,导致这一过程会很快完成,从而使β相不能完全溶解到α-Al基体中,当温度达到共晶反应温度时,未溶解的β相会和α-Al基体发生共晶反应,形成共晶液相,焊道冷却后就会在原β相位置处形成“液化”现象[16].这种现象一般发生在堆积成形件的下部区域.
2.3 力学性能分析
2.3.1 硬度
硬度试样的显微硬度测试结果如图6所示,由图可知,随着堆积高度的增加,成形件整体显微硬度存在一定的波动但变化不大,上、中、下部区域沉积层的平均显微硬度值分别为78.3,77.4和75.4 HV,而结合层硬度值波动更明显,最低硬度值为67 HV,这是由于结合层存在气孔缺陷,导致硬度值下降.对比全部测试点发现,硬度最高出现在最顶端和最底端的沉积层,这是因为堆积开始和结束时接触基板和空气,散热条件良好,焊道冷却速度快,显微组织稳定,晶粒细化导致其硬度略有提高[17].
2.3.2 拉伸性能
如图1所示,分别在成形件上中下3区域各取5个拉伸试样测试,测试结果计算平均值如表3所示.表4则列出了其它焊接工艺得到6061铝合金焊接接头强度作为对比[10-13].可以看出,MIG电弧增材堆积的薄壁件屈服强度会略低,但抗拉强度高于其它工艺方式.这是因为,与其它焊接工艺相比,MIG电弧增材制造过程的稳定性更差,气孔缺陷产生的机率更高,降低了疲劳性能;而电弧增材多层堆积的热循环过程类似于对材料的一个反复热处理,提高了强韧性.由表3可知,在水平方向上不同区域的强度没有明显差异,其平均抗拉强度约为244.3 MPa,屈服强度约为123.5 MPa.与水平方向的均值相比,竖直方向上的抗拉强度和屈服强度均略低,而断后伸长率更高.这说明MIG电弧增材制造的6061铝合金存在各向异性.
表 3 不同位置拉伸性能对比Table 3. Comparison of tensile properties in different position位置 抗拉强度Rm/MPa 屈服强度ReL/MPa 断后伸长率A(%) 竖直 225.6 107.6 22.6 上部 240 122.7 19.2 中部 251 131.3 18.1 下部 239 116.7 16.8 表 4 不同工艺焊接接头性能对比Table 4. Properties comparison of welding joints by different processes工艺条件 抗拉强度Rm/MPa 屈服强度ReL/MPa 断后伸长率
A(%)文献[10]-TIG 175 120 9.2 文献[11]-CMT 185.4 155 10.1 文献[12]-EBW 191 156 5.2 文献[13]-FRW 195 121.96 10 图7为堆积成形薄壁件不同区域的拉伸断口形貌图.图7a,7b为竖直拉伸的断裂位置,竖直试样的断口一般在结合层,此处气孔密集数量众多.图中可以看出竖直断口处不仅有大量的中小型气孔,放大后还能看到大量的直径3 μm以下的微细气孔.相对地,在图7c,7d所示的水平试样位于沉积层的断口截面上,表现出数量相对更少、但体积却更大的气孔分布.此外竖直和水平试样的断口表面都均匀分布着细密的韧窝,这是典型的韧性断裂特征.电弧增材制造过程中,由于氢在固液态铝中的溶解度差别大,而且铝材料的导热率高,熔池冷却快,熔池中的氢不能及时逸出,以气体的形式存在于熔池中形成气孔,故气孔缺陷是铝合金电弧增材制造常见的现象,拉伸试样的气孔聚集位置会引起应力集中,更容易造成断裂[18].
通过变形加工 + 热处理的方式可以使多数气孔闭合,大幅提高增材制造铝合金构件的疲劳性能[19].MIG电弧增材制造6061铝合金的后处理工艺将在后续研究中进行.
3. 结论
(1) 6061铝合金的MIG电弧增材制造中,当送丝速度和焊接速度的比值介于0.5 ~ 1之间,且送丝速度在5 ~ 7 m/min之间时,可以获得良好的多层堆积形貌.
(2) 焊道层与层之间交界处为结合层,其余区域为沉积层,结合层和沉积层呈现出沿堆积高度方向灰白色带依次交替的形貌,并都呈现出各种尺寸大小的气孔多发的状态.下部区域成形过程中温度更快达到共晶温度,会使β相来不及溶解与α-Al基体发生共晶反应,形成“液化”现象.
(3) 沿着堆积方向硬度变化不大,结合层硬度低于沉积层,且硬度波动性更大.不同区域水平方向强度差异不大,竖直和水平方向断后伸长率分别为22.6%和18%,成形件的力学性能存在各向异性.
-
表 1 焊丝化学成分(质量分数,%)
Table 1 Chemical composition of welding wire
Si Fe Cu Mn Mg Cr Zn Ti Al 0.4 ~ 0.8 0.7 0.15 ~ 0.4 0.15 0.8 ~ 1.20 0.04 ~ 0.35 0.25 0.15 余量 表 2 探究试验工艺参数
Table 2 Used process parameters in experiments
编号 送丝速度
vs/(m·min−1)焊接速度
v/(mm·s−1)1 ~ 4 2 1,2,3,4 5 ~ 8 3 1.5,3,4.5,6 9 ~ 12 4 2,4,6,8 13 ~ 16 5 2.5,5,7.5,10 17 ~ 20 6 3,6,9,12 21 ~ 24 7 3.5,7,10.5,14 25 ~ 28 8 4,8,12,16 表 3 不同位置拉伸性能对比
Table 3 Comparison of tensile properties in different position
位置 抗拉强度Rm/MPa 屈服强度ReL/MPa 断后伸长率A(%) 竖直 225.6 107.6 22.6 上部 240 122.7 19.2 中部 251 131.3 18.1 下部 239 116.7 16.8 表 4 不同工艺焊接接头性能对比
Table 4 Properties comparison of welding joints by different processes
工艺条件 抗拉强度Rm/MPa 屈服强度ReL/MPa 断后伸长率
A(%)文献[10]-TIG 175 120 9.2 文献[11]-CMT 185.4 155 10.1 文献[12]-EBW 191 156 5.2 文献[13]-FRW 195 121.96 10 -
[1] 陈晓晖, 张述泉, 冉先喆, 等. 电弧功率对MIG电弧增材制造316L奥氏体不锈钢组织及力学性能的影响[J]. 焊接学报, 2020, 41(5): 42 − 49. doi: 10.12073/j.hjxb.20190818001 Chen Xiaohui, Zhang Shuquan, Ran Xianzhe, et al. Influence of arc power on microstructure and mechanical properties of 316L austenitic stainless steel manufactured by MIG arc additive manufacturing[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2020, 41(5): 42 − 49. doi: 10.12073/j.hjxb.20190818001
[2] Xiong J, Yin Z, Zhang W. Forming appearance control of arc striking and extinguishing area in multi-layer single-pass GMAW-based additive manufacturing[J]. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2016, 87(1): 579 − 586.
[3] Bradford R L, Cao L, Klosterman D, et al. A metal-metal powder formulation approach for laser additive manufacturing of difficult-to-print high-strength aluminum alloys[J]. Materials Letters, 2021, 300: 130113.
[4] Zhu P, Zhang Q, Xu H, et al. Experimental and numerical investigation on plasticity and fracture behaviors of aluminum alloy 6061-T6 extrusions[J]. Archives of Civil and Mechanical Engineering, 2021, 21(3): 1 − 18.
[5] 张兆栋, 曾庆文, 刘黎明, 等. 铝合金激光诱导MIG电弧增材制造成形尺寸规律[J]. 焊接学报, 2019, 40(8): 7 − 12. Zhang Zhaodong, Zeng Qingwen, Liu Liming, et al. Laser-induced MIG arc additive manufacturing of aluminum alloy forming size rules[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2019, 40(8): 7 − 12.
[6] Li Y, Yu S, Chen Y, et al. Wire and arc additive manufacturing of aluminum alloy lattice structure[J]. Journal of Manufacturing Processes, 2020, 50: 510 − 519. doi: 10.1016/j.jmapro.2019.12.049
[7] Ortega A G, Corona Galvan L, Salem M, et al. Characterisation of 4043 aluminium alloy deposits obtained by wire and arc additive manufacturing using a cold metal transfer process[J]. Science and Technology of Welding and Joining, 2019, 24(6): 538 − 547. doi: 10.1080/13621718.2018.1564986
[8] Chen Zhang, Ming Gao, Xiaoyan Zeng. Workpiece vibration augmented wire arc additive manufacturing of high strength aluminum alloy[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2019, 271: 85 − 92.
[9] Zhou Y, Lin X, Kang N, et al. Mechanical properties and precipitation behavior of the heat-treated wire + arc additively manufactured 2219 aluminum alloy[J]. Materials Characterization, 2021, 171: 110735. doi: 10.1016/j.matchar.2020.110735
[10] 吴兴欢, 张麦秋, 胡煌辉, 等. 6061铝合金不同焊接方式下接头性能及焊接成本的对比分析[J]. 科技创新导报, 2018, 15(20): 97 − 99. Wu Xinghuan, Zhang Maiqiu, Hu Huanghui, et al. Comparative analysis of joint performance and welding cost under different welding methods of 6061 aluminum alloy[J]. Science and Technology Innovation Herald, 2018, 15(20): 97 − 99.
[11] 刘强, 张亚雄, 张南南. 送丝速度对6061铝合金CMT焊接接头性能的影响[J]. 热加工工艺, 2016, 45(17): 222 − 224. Liu Qiang, Zhang Yaxiong, Zhang Nannan. The effect of wire feeding speed on the properties of 6061 aluminum alloy CMT welded joints[J]. Hot Working Technology, 2016, 45(17): 222 − 224.
[12] 常艳君, 董俊慧, 张毅. 6061铝合金焊接接头的组织与性能分析[J]. 焊接, 2006(1): 21 − 26. Chang Yanjun, Dong Junhui, Zhang Yi. Microstructure and performance analysis of 6061 aluminum alloy welded joints[J]. Welding, 2006(1): 21 − 26.
[13] 邱宇, 孟强, 董继红, 等. 6061-T6铝合金搅拌摩擦焊工艺及性能研究[J]. 塑性工程学报, 2021, 28(2): 86 − 91. Qiu Yu, Meng Qiang, Dong Jihong, et al. Research on the process and properties of friction stir welding of 6061-T6 aluminum alloy[J]. Journal of Plasticity Engineering, 2021, 28(2): 86 − 91.
[14] Derekar K, Lawrence J, Melton G, et al. Influence of interpass temperature on wire arc additive manufacturing (WAAM) of aluminium alloy components[C]//MATEC Web of Conferences, EDP Sciences, 2019: 05001.
[15] 孙佳孝, 杨可, 王秋雨, 等. 5356铝合金TIG电弧增材制造组织与力学性能[J]. 金属学报, 2021, 57(5): 665 − 674. Sun Jiaxiao, Yang Ke, Wang Qiuyu, et al. Microstructure and mechanical properties of 5356 aluminum alloy TIG arc additive manufacturing[J]. Acta Metall Sinica, 2021, 57(5): 665 − 674.
[16] 龙琼, 路坊海, 张玉兰, 等. Mg/Al异种金属焊接技术的研究现状及最新进展[J]. 轻金属, 2018(2): 47 − 53. Long Qiong, Lu Fanghai, Zhang Yulan, et al. Research status and latest progress of Mg/Al dissimilar metal welding technology[J]. Light Metal, 2018(2): 47 − 53.
[17] 戴青松, 欧世声, 邓运来, 等. 5083铝合金的热变形组织演变及晶粒度模型[J]. 材料导报, 2017, 31(14): 143 − 146,152. doi: 10.11896/j.issn.1005-023X.2017.014.030 Dai Qingsong, Ou Shisheng, Deng Yunlai, et al. Thermal deformation microstructure evolution and grain size model of 5083 aluminum alloy[J]. Materials Review, 2017, 31(14): 143 − 146,152. doi: 10.11896/j.issn.1005-023X.2017.014.030
[18] Toda H, Oogo H, Uesugi K, et al. Roles of pre-existing hydrogen micropores on ductile fracture[J]. Materials Transactions, 2009, 50(9): 2285 − 2290. doi: 10.2320/matertrans.M2009123
[19] Xue C, Zhang Y, Mao P, et al. Improving mechanical properties of wire arc additively manufactured AA2196 Al-Li alloy by controlling solidification defects[J]. Additive Manufacturing, 2021, 43: 102019.
-
期刊类型引用(15)
1. Mingtao Zhang,Tao Jiang,Yu Su,Zhonggang Sun,Yaxin Xu,Wenya Li. Study on the interfacial bonding behavior of dissimilar aluminum alloys via additive friction stir deposition. Progress in Natural Science:Materials International. 2025(02): 433-439 .  必应学术
必应学术
2. 王朝琴,石玗,王小荣. 基于双NURBS曲线的叶轮叶片工业机器人GMAW增材制造. 机床与液压. 2024(03): 17-21 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 肖珺,葛欣雨,盖胜男,陈树君,盛卫星,陈少君. 基于摆动激光扫描的GMAW焊缝成形调控. 焊接学报. 2024(04): 7-12+129 .  本站查看
本站查看
4. 陈吉兴,李晓泉,陈峰,汪天齐,吴星宇. MIG电弧增材Inconel 625合金组织特征. 焊接技术. 2024(06): 1-5+145 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 程龙,杨新岐,唐文珅,罗庭,王瑞林. 6061铝合金搅拌摩擦沉积增材修复工艺及修复区性能. 焊接学报. 2024(08): 12-23 .  本站查看
本站查看
6. 王家胜,舒林森. 切割速度对6061铝合金薄板激光切割温度场的影响. 制造技术与机床. 2023(06): 39-43 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 赵宇辉,贺晨,赵吉宾,邹健,王志国,何振丰. 增材/等材复合制备Sc/Zr改性Al-Mg合金工艺研究. 光学学报. 2023(07): 163-170 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 石寅晖,李洁,刘坤,邹家生,余文明,Gizo Bokuchava. 铝合金电弧熔丝增材制造的冶金缺陷研究现状与展望. 材料热处理学报. 2023(06): 1-10 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 蔡佳思,王新元,李秀梅,魏艳红,龙金卫,孔斌. 6061铝合金激光焊接头的软化机理. 焊接. 2023(07): 9-18 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 林清成,郭纯,李文清,李云,黄光灿,陈艳艳,张新宇. 铝合金电弧增材制造研究现状. 金属加工(热加工). 2023(09): 20-26 .  百度学术
百度学术
11. 李坤,张创创,龚虎虎,沙豪杰. 超声喷丸对6061铝合金耐腐蚀性能的影响. 黑龙江工业学院学报(综合版). 2023(08): 133-140 .  百度学术
百度学术
12. 何逸凡,王呈阳,贾舒茗,王大锋,马修斯,马冰,陈东高,张文治,杨文静,张龙. Mg含量对7A52铝合金MIG焊熔滴过渡及组织性能的影响. 兵器材料科学与工程. 2023(05): 76-81 .  百度学术
百度学术
13. 张铂洋,李旭,张玉娇,李英豪,宗然. 铝合金电弧增材制造研究现状. 表面技术. 2023(11): 111-127 .  百度学术
百度学术
14. 常子恒,李玉松,徐金鑫,罗少敏,李娟. ER5356铝合金MIG电弧增材构件的组织研究. 焊接技术. 2022(11): 6-10 .  百度学术
百度学术
15. 陈会子,孟祥晨,陈佳霖,谢聿铭,赵耀邦,黄永宪. 铝合金连续进给搅拌摩擦增材制造技术. 焊接学报. 2022(11): 63-67+166 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(17)



 下载:
下载: