Welding processes and microstructures of weld bead of Zr-Sn-Nb-Fe-Cr and Zr-Nb-Fe zirconium alloy
-
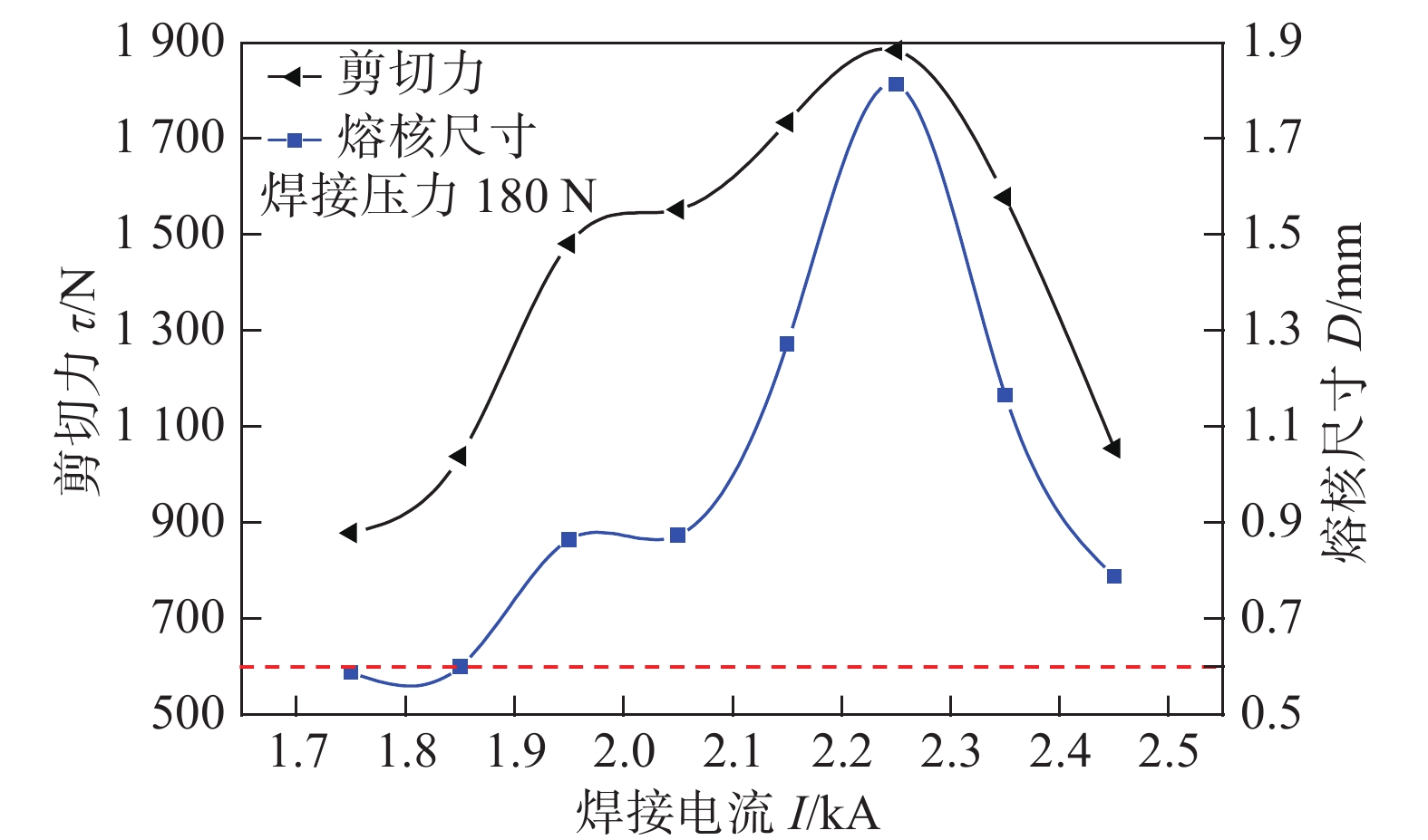
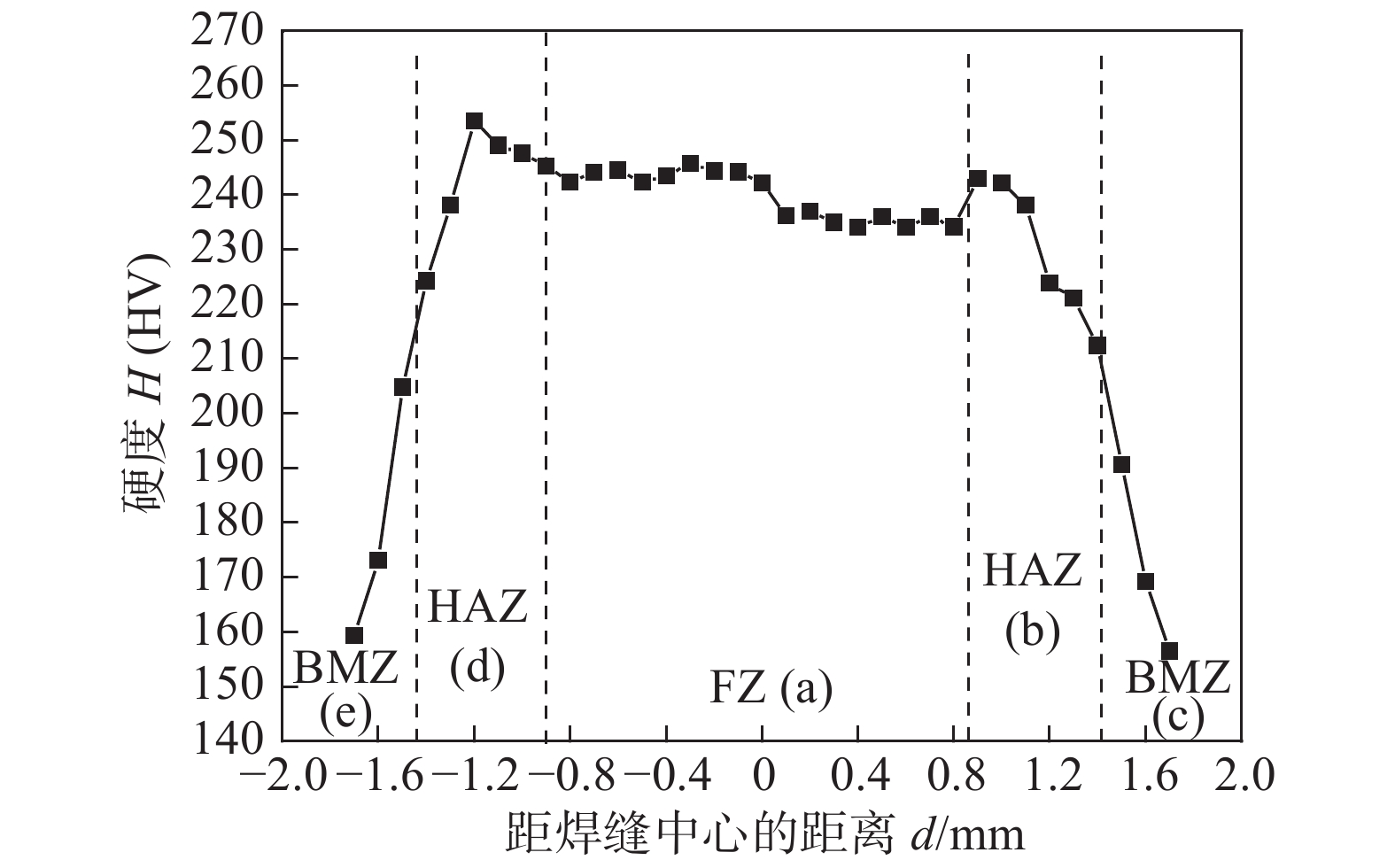
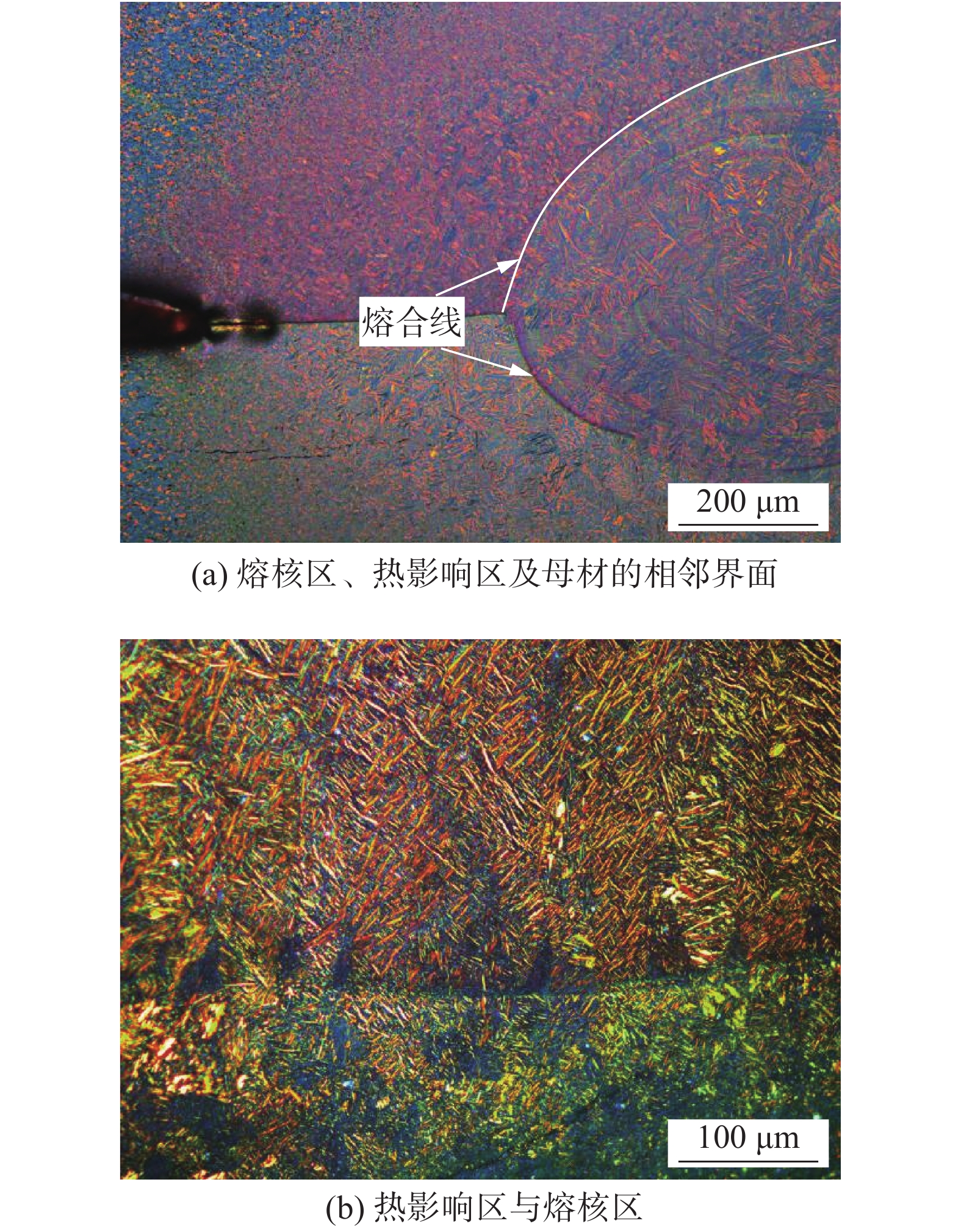
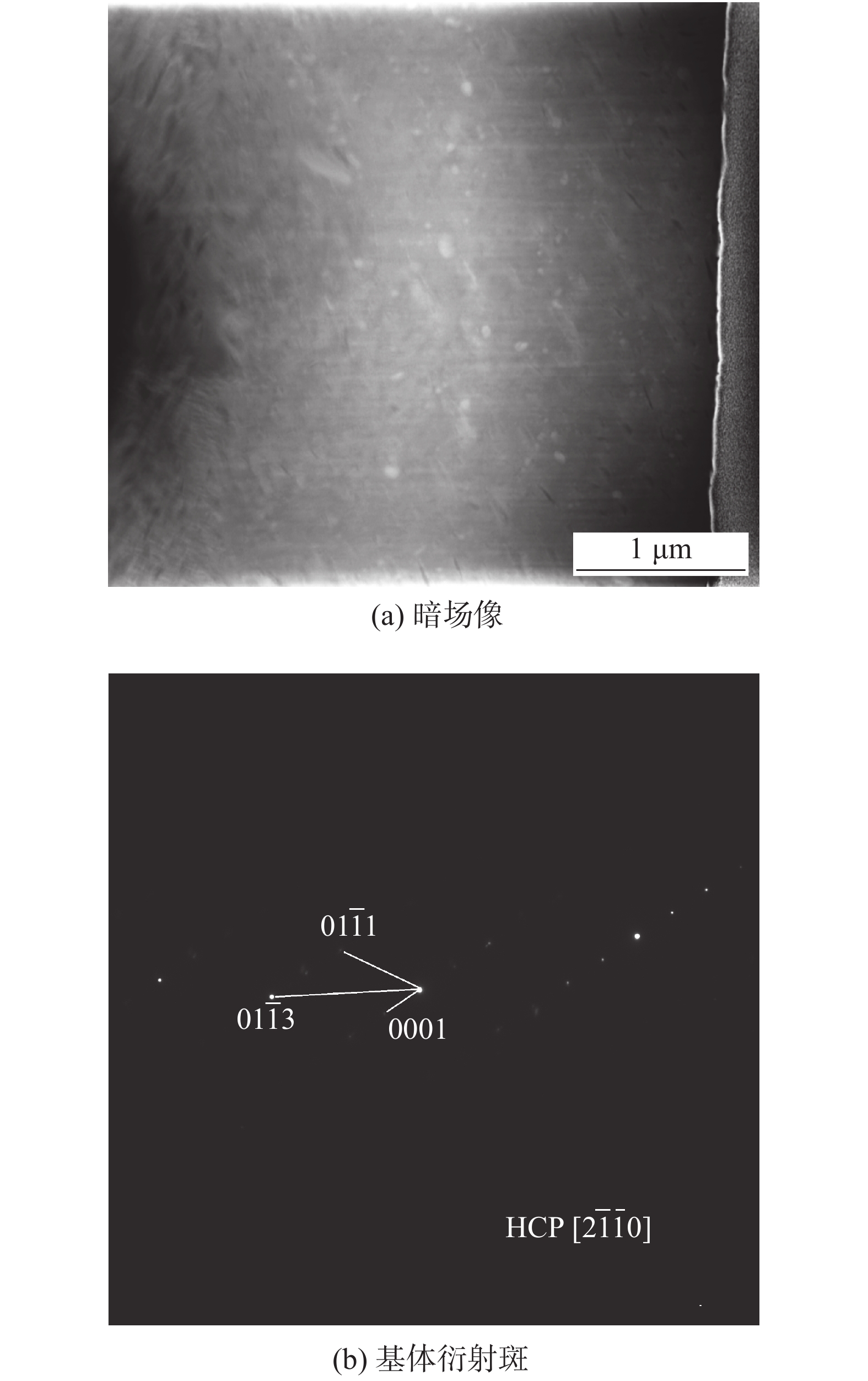
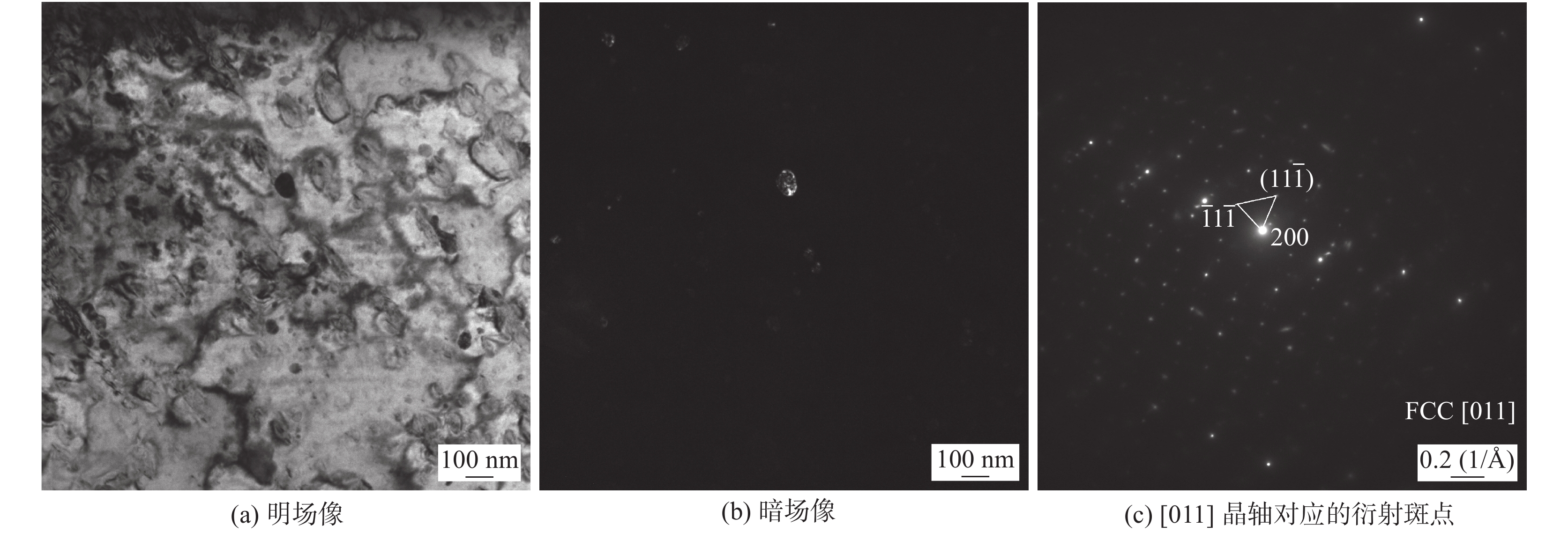
摘要: Zr-1.0Sn-0.50Nb-0.50Fe-0.14Cr与Zr-1.30Nb-0.30Fe锆合金是目前正在研制开发核燃料组件用两种新型Zr(-Sn)-Nb-Fe系锆合金. 针对新型燃料组件骨架压力电阻点焊,采用不同的焊接工艺参数对Zr-1.0Sn-0.50Nb-0.50Fe-0.14Cr导向管与Zr-1.30Nb-0.30Fe焊舌片进行研究,并对较优焊接参数下的焊接接头力学性能、显微硬度、金相显微组织及熔核区形貌和析出相进行了分析. 结果表明,增大焊接电流和减小焊接压力,焊点剪切力和熔核尺寸随之增加,断裂方式由界面断裂转变为纽扣断裂;焊接电流对熔核尺寸及剪切力影响最大,焊接压力的增加,焊点剪切力和熔核尺寸均减小,但焊接压力的适当增大提高了形核稳定性. 在电阻点焊不平衡的急速冷却条件与电磁搅拌作用下,熔核区形成非平衡淬火针状板条状组织结构,析出的细小Fe2(Nb0.35, Zr0.65)和Fe2 (Nb0.3, Zr0.7)第二相粒子呈圆形或长条棒状分布于基体α-Zr与β-Zr晶粒内、晶界处及板条组织中,从而提高了熔核区及热影响区的显微硬度,含Nb的细小弥散析出FCC第二相增强了焊缝抗水侧腐蚀性能.Abstract: Zr-1.0Sn-0.50Nb-0.50Fe-0.14Cr and Zr-Nb-Fe alloys were the two new developed zirconium alloys which used in fuel assembly. In this paper, different welding parameters of the Zr-1.0Sn-0.50Nb-0.50Fe-0.14Crguide thimble welded toZr-1.30Nb-0.30Fe tab by using pressure resistance spot welding method were studied. The mechanical properties and microstructures of the optimum welding parameters of the weld bead were studied. The result showed that the shear strength and nugget size increased as the welding current increased and the welding force decreased. The Failure mode of the weld bead changed from junction surface fracture to button fracture as the welding current increased. The welding current was the key factors on the mechanical properties and microstructure. As the increasing of the electrode force, the welding shearing strength and the diameter of the welding core size decreased. Under the imbalance express cooling, the fusion zone consists of a mixture of α-Zr and β-Zr phases among which lamellar structure. The fine Fe2(Nb0.35, Zr0.65) and Fe2(Nb0.3, Zr0.7) second phases particles were precipitated inter and intergranular in the grains, so the mechanical and anti-water corrosion properties were improved.
-
Keywords:
- zirconium alloys /
- resistance welding /
- microstructure
-
0. 序言
电阻点焊是一种重要的连接技术,由于它具有操作简单、自动化程度高、焊接效率高等优点,现已广泛应用于航空航天、汽车、船舶以及电子等行业领域[1]. TC2钛合金是一种近α钛合金,具有良好的塑性、焊接性、稳定性等优点,近些年来广泛应用于飞行器以及发动机薄壁结构件中. 对于电阻点焊质量的评定,传统上常常采用焊后破坏性试验来加以确定,这种检验手段效率较低,易造成浪费. 因此,国内外许多学者尝试多种方法实时监控焊接质量. Xia等人[2]发现电阻点焊过程中电极位移的变化情况与焊接接头质量之间有密切的关系,并通过回归分析有效地对焊接质量进行预测. Summer-ville等人[3]利用电阻点焊过程中的动态电阻信号与超声波扫描信号预测电阻点焊熔核直径的大小做了比较,结果表明,运用动态电阻曲线监测焊接质量的精度更高. Bag等人[4]也发现电阻点焊过程中动态电阻的变化与熔核生长过程存在对应关系. Guan等人[5]对焊接过程中的超声波信号进行处理并发现超声波的变化与熔核直径密切相关. 在此基础上,研究者利用超声波预测熔核直径. 陈树君等人[6]通过监测焊接过程中电极压力的变化以监控是否发生喷溅,研究表明,电极压力曲线的突变可准确地检测出发生喷溅的焊接接头. 曾凯等人[7]研究了双相钢DP780的电阻点焊焊接过程,研究表明,焊接热输入是决定熔核直径的重要因素,焊接过程中焊接功率曲线的变化直接决定了焊接热输入的变化情况,因此焊接功率曲线与焊接质量有着密切的联系,而目前国内外对此方面的研究却鲜有文献参考.
采用数据采集系统获取了0.4 mm厚度的TC2钛合金在电阻点焊过程中功率曲线的动态变化过程,分析焊接功率曲线变化与熔核直径的之间关系,在此基础上利用克里金算法得到了焊接功率曲线特征值与熔核直径之间的预测模型. 该模型可作为一种有效预测熔核直径,并有望在实际电阻点焊生产中加以推广应用.
1. 试验方法
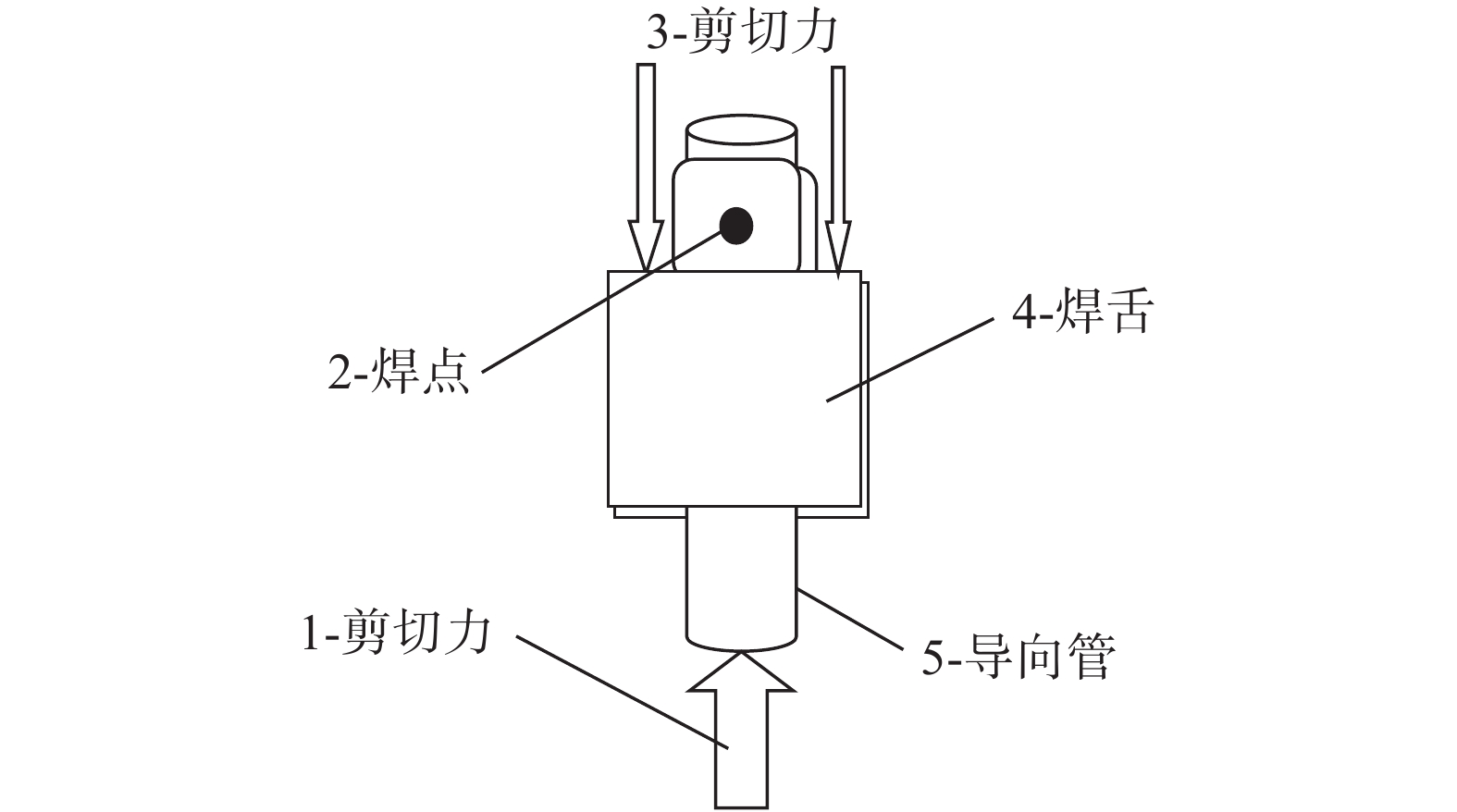
试验采用美国Amada Weld Tech公司研制的HF27精密电阻点焊机,该焊机采用高频交流电流进行焊接,其频率为25 kHz. 焊机的最大额定值为20 kVA,可提供的电极压力范围为22 ~ 450 N. 利用罗氏线圈测量焊接过程中焊接电流的变化情况,采用加持于上、下电极的双绞线获取电压的变化情况(图1). 焊接电流和电压信号经过数据采集系统以及模数转换、滤波等一系列处理后获取.
选取的焊接材料为TC2钛合金[8],作为一种α + β型钛合金,TC2钛合金集合了α型钛合金和β型钛合金的优点. 钛合金在高温状态下极易与空气发生化学反应,但在点焊过程中,熔融金属产生于上、下焊板接触面处,且一直在上、下电极压力作用下,保证了其与外界空气隔绝[9],所以钛合金的电阻点焊不需要特殊的保护措施. 焊前,对钛合金分别进行化学清洗与机械清洗,以防工件的表面质量影响焊接质量.
通过改变焊接工艺参数以获取不同的焊接接头.焊接工艺参数的范围为:焊接时间为4 ~ 12 ms,焊接电流为1.0 ~ 2.4 kA,电极压力76.2 ~ 203.2 N. 采用平头铜合金电极,电极端面的直径为3 mm,冷却方式为空冷. 在焊接过程中将焊接电流设置为恒定值,如图2所示.
采用Instron®5900R万能拉伸试验机在常温下对焊接接头进行剪切试验,加载速度为1 mm/min.采用游标卡尺测量拉伸后的试样以获得熔核直径.为了减小误差,从3个方向测量同一焊点,取其平均值. 焊点的抗剪力和失效能量从剪切试验中的载荷位移曲线中获取,焊点的失效能量为载荷位移曲线中载荷峰值点对应的曲线包围的面积.
2. 试验结果与分析
2.1 熔核直径对焊接功率曲线的影响
图3和图4分别为电极压力152.4 N、焊接时间12 ms、焊接电流1.6 kA时焊接功率和动态电阻曲线.图中3个标记的位置分别代表1 ms时功率值、功率的峰值以及拐点值. 从图3可以看出,在焊接初始阶段,焊接功率值迅速由零增大至峰值后缓慢减小到拐点,随之迅速减小. 由于焊接试验采用高频交流焊接电流,且焊接模式为恒电流模式,根据公式P = I 2R,焊接功率曲线在一定程度上反映了焊接过程中上、下电极之间动态电阻的变化情况. 峰值点对应于动态电阻曲线中的极值点,已有的研究表明,达到峰值点的时间与峰值反映了熔核的生长情况. 此后液态熔融金属的形成引起电阻值下降以及电流曲线的变化导致了焊接功率的下降. 焊接功率曲线包围的面积表明了整个焊接过程中输入到焊接区域的热量值. 需要指出的是,图3与图4中两信号并不完全一致,故而功率曲线中的大约前1 ms与后1 ms的变化趋势与电阻信号有所不同. 此外,焊接热输入可以仅仅通过焊接功率信号的积分获取,而如果需要利用动态电阻获取焊接热输入,需要动态电阻与电极间电压或者焊接电流相乘后且积分后才能获取. 因此,与动态电阻信号相比,焊接功率曲线与焊接热输入的关系更为密切.
表1为选取10个焊接试样在不同焊接工艺参数下的熔核直径、接头抗剪力以及失效能量值. 从表中可以看出,熔核直径、抗剪力和失效能量之间为正相关. 经过计算可知,熔核直径与抗剪力之间的相关系数是0.964,熔核直径与失效能量之间的相关系数为0.871. 因此可以将熔核直径作为评判焊接质量优劣的指标. 根据美国焊接学会的规范[10],认为熔核直径D大于4
$ \sqrt {t} $ 的焊点为合格焊点(t为焊板的厚度),然而对于微电阻点焊而言,该判定公式误差较大[11]. 根据试验结果,将该公式进行修正,认为对于0.4 mm厚度的钛合金,当熔核直径大于1.76 mm时,该焊点合格. 根据此判定规范,将所有的焊点分为3类:不合格焊点、合格焊点以及发生喷溅的焊点.表 1 焊接试验结果Table 1. Experimental results for the resistance spot welding电极压力
F/N焊接电流
I/kA焊接时间
t/ms熔核直径
D/mm抗剪力
R/N失效能量
Q/J100 1.4 6 0.85 1021.93 0.5 100 1.8 8 1.95 2426.85 3.18 75 1.6 8 1.63 2014.65 1.96 75 2.2 12 2.12 2685.03 3.92 125 1.0 8 1.22 1321.58 0.89 125 1.6 12 1.91 2240.36 3.51 125 2.2 4 1.68 1896.3 2.16 175 1.0 12 1.37 1193.1 0.51 175 1.6 4 1.28 1569.83 0.43 175 2.2 8 1.96 2883.94 4.36 图5为3类焊点的焊接功率曲线. 从图5可以看出,不同焊接质量的焊接功率曲线有很大差别. 发生喷溅的焊点,动态功率曲线在焊接的后半进程中有一个突降,这是由于喷溅导致焊接区域部分熔融金属从上、下焊板飞出后电阻值突降造成的,因此可以将这一特征作为判定喷溅是否发生的依据. 而虚焊情况下,功率曲线的峰值与拐点之间功率的差值明显小得多. 3类焊点功率达到峰值的时刻以及峰值的大小也明显不同. 它们的区别主要体现为:1 ms时刻的功率值P1、峰值时刻tm、峰值Pm、拐点值Pn以及功率曲线包围的面积. 在此基础上,从功率曲线中选取表征焊接质量的特征值、峰值与1 ms时刻功率值的差ΔP、峰值与拐点值的差ΔP1、功率曲线的下降率Ps = ΔP1/Pm、功率曲线包围的面积S. 由于焊接电流在1 ms 时突变,为了指明这一变化,故选取 1 ms时刻的功率值. 选取的特征值之间有很强的相关性,一般需要采用主成分分析法进行处理. 然而已有的研究表明,主成分分析对最终结果影响不大. 故不再对特征值进行处理[11]. 表2列出了提取的特征量与熔核直径之间的相关系数,所有的相关系数值均大于0.5. 图6为所提取的4个特征量与熔核直径之间的散点图. 该散点图是通过170个试验样本获取,初步描述了4个特征量与熔核直径之间的线性回归关系,因此可判定特征量与熔核直径有一定的映射关系. 需要采用具有非线性映射能力的计算方法更进一步获取提取的特征量与熔核直径之间更为精确的对应关系.
表 2 特征量与熔核直径之间的相关系数Table 2. Correlation coefficients among extracted features and nugget diameter功率上升值
ΔP/kW功率下降值
ΔP1/kW功率下降率
Ps焊接热输入
E/J0.52 0.81 0.87 0.90 2.2 熔核直径预测模型的建立与分析
电阻点焊熔核直径与焊接功率曲线特征量之间存在着相关关系. 为找出熔核直径与特征量之间的映射关系,根据监测功率曲线的变化预测熔核直径,达到实现接头质量在线检测的目的.
作为一种有效的模型预测手段,克里金算法的理论依据是贝叶斯插值模型,该方法最初用于估计地质学中矿床的含量. 克里金算法具有较高的精度,已广泛应用于环境科学、采矿业、遥感技术等领域中. 近些年来,不少研究者尝试将该算法应用于焊接生产中,取得了良好的效果[12].
从焊接功率曲线中提取的4个特征量作为自变量,焊接接头的熔核直径作为因变量. 运用Matlab软件中的DACE工具箱建立克里金模型. 该工具箱提供了3类回归模型和7种相关函数,能预测误差以及目标值验证等. 克里金算法中相关函数的选择、多项式回归模型以及相应的初始向量设置直接影响了预测模型的精度[13]. 选择高斯相关函数corrgauss,多项式回归模型regpoly2,模型参数的初始值为1,其上、下限为10和200. 任意选取250个试样样本中170个来建立克里金熔核直径预测模型,剩余的80个样本用于检测该模型的误差.
图7为克里金算法的预测结果. 该结果是将克里金模型运用于80个焊接接头得到. 经过计算可知,焊接接头熔核直径最大的预测误差大约为0.17 mm,对应的相对误差为8.7%. 由此可见,焊接功率曲线中的4个特征量可以有效表征3类焊点的功率曲线,利用克里金算法以及焊接功率曲线可以有效地预测熔核直径.
由于克里金算法为一种“黑箱”算法,故而无法获取熔核直径与提取的特征值之间的函数关系表达式,该问题需要在后续工作中进一步研究.
3. 结论
(1) 在恒电流的焊接模式下,焊接功率曲线的变化与动态电阻变化相一致;与动态电阻相比,焊接功率曲线与焊接热输入的关系更为密切,而焊接热输入直接决定了焊接区熔核的形成与长大过程.
(2) 不同焊接质量条件下的焊接功率曲线差别较大,从焊接功率曲线中选取了4个特征量用以表征曲线的变化. 特征量与熔核直径之间的相关系数均大于0.5,而焊接热输入与熔核直径之间的相关系数值高达0.9.
(3) 运用焊接过程中的焊接功率曲线来预测熔核直径的克里金算法预测值与实际值之间的最大误差大约是0.17 mm,对应的相对误差为8.7%, 这表明焊接功率曲线可以表征焊接接头的焊接质量.
-
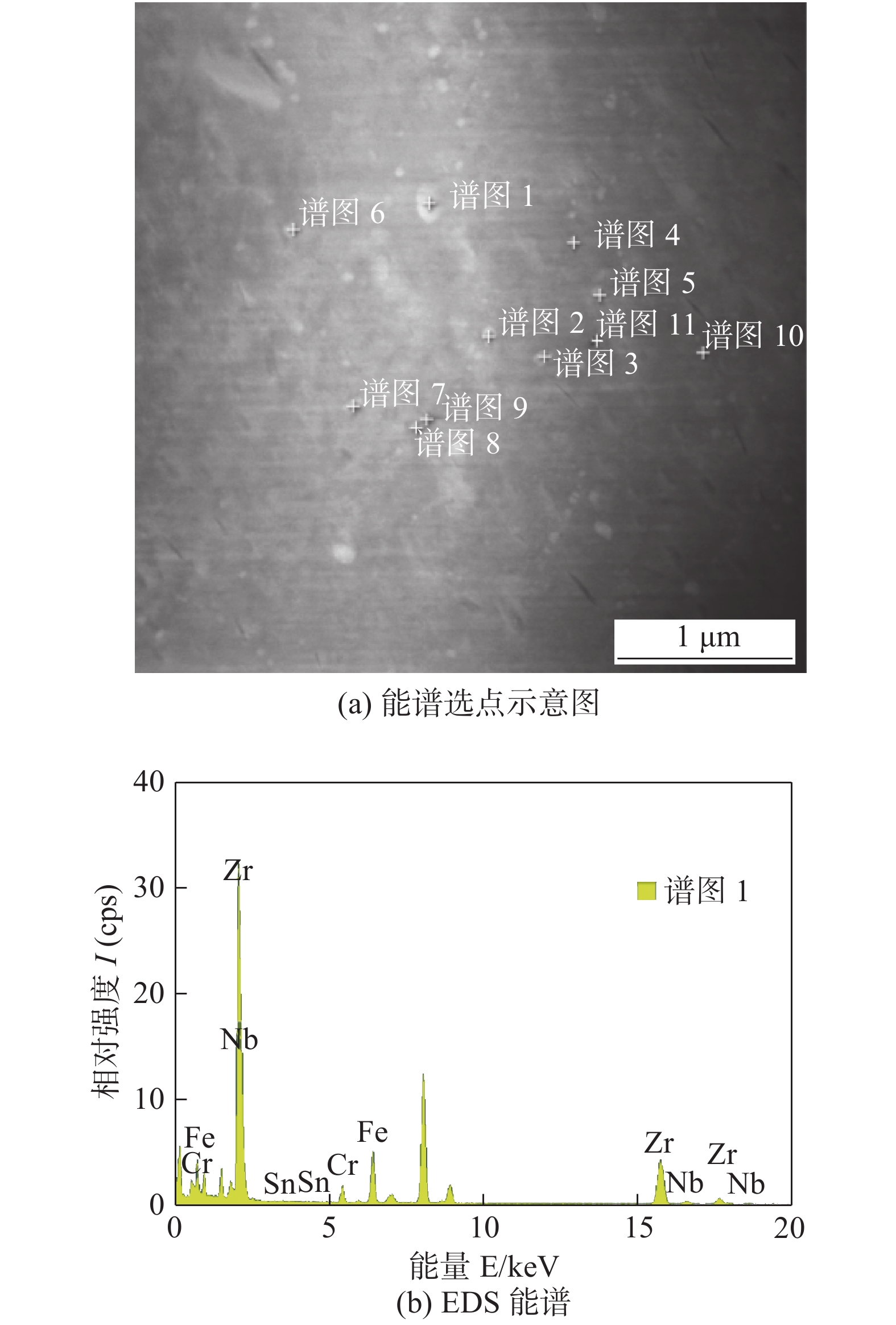
表 1 熔核区的EDS成分
Table 1 EDS of weld joint
谱图标签 化学成分(原子分数,%) 位置 Cr Fe Zr Nb Sn 1 0.24 0.76 96.07 2.55 0.38 熔核区 2 0.48 1.46 93.93 3.07 1.05 熔核区 3 0.11 0.22 97.57 1.75 0.36 熔核区 -
[1] 邱日盛, 栾佰峰, 柴林江,等. 锆合金第二相研究评述(Ⅱ): Zr-Sn-Nb-Fe系合金[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2012, 22(6): 1605 − 1615. Qiu Risheng, Luan Baifeng, Chai Linjiang, et al. Review of second phase particles on zirconium alloys (Ⅱ): Zr-Sn-Nb-Fe alloys[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2012, 22(6): 1605 − 1615.
[2] 吴磊, 汪兵, 崔军. 大型锆-钢复合板反应器的焊接技术及质量评价[J]. 压力容器, 2017, 34(4): 62 − 67. Wu Lei, Wang Bing, Cui Jun. Welding techniques and quality evaluation on zirconium-steel clad plates for large-scale reactors[J]. Pressure Vessel Technology, 2017, 34(4): 62 − 67.
[3] 杨锋, 尉北玲, 王旭峰. 核级锆合金研究现状及我国核级锆材发展方向[J]. 金属世界, 2016(3): 24 − 28. Yang Feng, Wei Beiling, Wang Xufeng. Research advance and future direction of nuclear graded zirconium alloy[J]. Metal World, 2016(3): 24 − 28.
[4] 刘鹏, 杜忠泽, 马林生, 等. 核级锆及锆合金腐蚀性能研究现状[J]. 热加工工艺, 2011, 40(22): 22 − 24. Liu Peng, Du Zhongze, Ma Linsheng, et al. Study status of corrosion properties of zirconium and zircaloy in reactor[J]. Hot Working Technology, 2011, 40(22): 22 − 24.
[5] 杨振飞, 史鹏, 敖冰云. 锆合金中的氢化物脱附行为研究进展[J]. 材料导报, 2020(5): 102 − 108. Yang Zhenfei, Shi Peng, Ao Bingyun. Research progress on the desorption behavior of hydrides in zirconium alloys[J]. Materials Review, 2020(5): 102 − 108.
[6] 曹殿鹏, 邹树梁, 肖魏魏,等. 锆合金表面耐事故涂层研究进展[J]. 核科学与工程, 2020, 40(2): 264 − 272. Cao Dianpeng, Zou Shuliang, Xiao Weiwei, et al. Research progress of accident tolerant coatings on zircalloy[J]. Nuclear Science and Engineering, 2020, 40(2): 264 − 272.
[7] 范清松, 王健, 石明华, 等. 新核燃料锆合金包壳管材中缺陷对超声检测的影响[J]. 无损检测, 2020, 42(1): 23 − 26,65. Fan Qingsong, Wang Jian, Shi Minghua, et al. Effects of the defect in new nuclear zirconium alloy cladding tube on its ultrasonic testing[J]. Nondestructive Testing, 2020, 42(1): 23 − 26,65.
[8] Atabakii M M, Hanzaei A T. Partial transient liquid phase diffusion bonding of Zircaloy-4 to stabilized austenitic stainless steel 321[J]. Mater Charact, 2010, 61: 982 − 991. doi: 10.1016/j.matchar.2010.06.010
[9] Kiran Kumar Nap, Szpunar J A, Zhang H. Microstructural studied and crystallographic orientation of different zones and δ-hydrides in resistance welded Zircaloy-4 sheets[J]. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 2011, 414: 341 − 351. doi: 10.1016/j.jnucmat.2011.03.027
[10] Shankar A R, Raju V R, Rao M N, et al. Corrosion of Zircaloy-4 and its welds in nitric acid medium[J]. Corrosion Science, 2007, 49: 3527 − 3538. doi: 10.1016/j.corsci.2007.03.029
[11] Ahmad M, Akhter J I, Iqbal M, et al. Microstructure and non-equilibrium phases in electron beam-welded joints of Al-Fe-Ce and Zircaloy-4[J]. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 2005, 341: 164 − 168. doi: 10.1016/j.jnucmat.2005.01.020
[12] Song K N, Kim S S. Determination of the optimum welding parameters for a laser welded spacer grid assembly for PWRs[J]. Journal of Laser Micro Nanoengineering, 2007, 2(1): 95 − 99. doi: 10.2961/jlmn.2007.01.0017
[13] Han Q, Kim D C, Lee H. Laser pulsed welding in thin sheets of ziracaloy-4[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2012, 212: 1116 − 1122. doi: 10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2011.12.022
[14] Santisteban J R, Vicente-alvarez M A, Vizcaino P, et al. TREMSIN AS. texture imaging of zirconium based components by total neutron cross-section experiments[J]. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 2012, 425: 218 − 227. doi: 10.1016/j.jnucmat.2011.06.043
[15] Ahmad M, Akhter J I, Akhtar M, et al. Microstructure and characterization of phases in TIG welded joints of zircaloy-4 and stainless steel 304L[J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2007, 42: 328 − 331. doi: 10.1007/s10853-006-1028-1
[16] Kruger R M, Adamson R B, Brenner S S. Effects of microchemistry and precipitate size of nodular corrosion resistance of zircaloy-2[J]. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 1992, 189: 193 − 200. doi: 10.1016/0022-3115(92)90532-P
[17] 朱梅生, 刘建章, 李中奎, 等. 8#新锆合金的组织与耐蚀性能的研究[J]. 稀有金属材料与工程, 1996, 25(4): 36 − 40. Zu Meisheng, Liu Jianzhang, Li Zhongkui, et al. Study on structure and corrosion resistance of 8~#new zirconium alloy[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 1996, 25(4): 36 − 40.
[18] Shishov V N, Peregud M M, Nikulina A V, et al. Structure-phase state, corrosion and irradiation properties of Zr-Nb-Fe-Sn systems alloys[C]//Zirconium in the Nuclear Industry, Fifteenth Symposium, ASTM STP 1505. West Conshohocken: ASTM International, 2009: 724−743.
[19] 徐启迪, 黄娇, 姚美意, 等. 添加S对Zr-Sn-Nb-Fe锆合金中第二相的影响[J]. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2015, 44(1): 122 − 125. Xu Qidi, Huang Jiao, Yao Meiyi, et al. Effect of S addition on the Second Phase Particles of Zr-Sn-Nb-Fe Zirconium Alloy[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2015, 44(1): 122 − 125.
[20] Kim H G, Park J Y, Ong Y H. Ex-reactor corrosion and oxide characteristics of Zr-Nb-Fe alloys with the Nb/Fe ratio[J]. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 2005, 345: 1 − 10. doi: 10.1016/j.jnucmat.2005.04.061
[21] 刘文庆, 钟柳明, 彭剑超, 等. 锆合金中第二相的研究[J]. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2011, 40(7): 1216 − 1219. Liu Wenqing, Zhong Liuming, Peng Jianchao, et al. Study of second phase particles in zirconium alloys[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2011, 40(7): 1216 − 1219.
[22] 陈乐, 杨忠波, 邱军, 等. 热处理工艺与合金成分对国产新型锆合金拉伸性能及显微组织的影响[J]. 核动力工程, 2017, 38(6): 129 − 133. Chen Le, Yang Zhongbo, Qiu Jun, et al. Effect of heat treatment on tensile properties and microstructure of new domestic zirconium alloys[J]. Nuclear Power Engineering, 2017, 38(6): 129 − 133.
[23] Wang Tao, Chuang Cai, Liqun Li, et al. Pulsed laser spot welding of intersection points for zircaloy-4 spacer grid assembly[J]. Materials and Desigh, 2013, 52: 487 − 494. doi: 10.1016/j.matdes.2013.05.037
[24] 刘波, 童慎修, 吴平. AFA3G燃料组件骨架导向管与格架的压力电阻焊工艺研究[J]. 核动力工程, 2002, 23(5): 70 − 74. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-0926.2002.05.018 Liu Bo, Tong Shenxiu, Wu Ping. Study on Pressure Resistance Spot Welding Process of Guide Thimble and Grid of AFA 3G Advanced Fuel Assembly Skeleton[J]. Nuclear Power Engineering, 2002, 23(5): 70 − 74. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-0926.2002.05.018
[25] 王刚. 影响格架与厚壁导向管(壁厚1.18mm)电阻点焊的因素及熔核形核原理的初步分析[C]//中国核学会核材料分会2007年度学术交流会, 2007. Wang Gang. Analysis on factors affecting spot welding of grid to thick guide thimble and principles of nugget formation [C]//Atomic Energy Science and Technology, 2007.
[26] 贺地求, 刘杭琪, 赖瑞林. MS1400/DP980钢的电阻点焊的工艺性能分析[J]. 焊接学报, 2018, 39(4): 104 − 108. doi: 10.12073/j.hjxb.2018390105 He Diqiu, Liu Hangqi, Lai Ruilin. Analysis on resistance spot welding process performance of MS1400 and DP980[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2018, 39(4): 104 − 108. doi: 10.12073/j.hjxb.2018390105
[27] Kim H G, Park S Y, Lee M H, et al. Corrosion and microstructural characteristics of Zr-Nb alloys with different Nb contents[J]. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 2008, 373: 429 − 432. doi: 10.1016/j.jnucmat.2007.05.035
[28] Jeong Y H, Kim H G, Kim D J, et al. Influence of Nb concentration in the alpha-matrix on the corrosion behavior of Zr-xNb binary alloys[J]. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 2003, 323: 72 − 80. doi: 10.1016/j.jnucmat.2003.08.031
[29] Jeong Y H, Kim H G, Kim T H. Effect of beta phase, precipitate and Nb-concentraion in matrix on corrosion and oxide characteristics of Zr-xNb alloys[J]. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 2003, 317: 1 − 12. doi: 10.1016/S0022-3115(02)01676-8
-
期刊类型引用(7)
1. 韩念梅,冯迪,陈家劲,吴彤,张保玲,唐建国. 焊前状态对7055铝合金焊接接头组织与性能的影响. 材料热处理学报. 2025(03): 226-238 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 许楠,张柏硕,齐天祥,刘朝阳,徐玉缀,宋亓宁,包晔峰. HSn70-1锡黄铜冷源辅助搅拌摩擦焊搅拌区的强化机制和应变硬化行为. 焊接学报. 2024(01): 17-22+130 .  本站查看
本站查看
3. 陈文雅,宋娓娓,汪洪峰. 聚丙烯塑料搅拌摩擦连接区性能分析. 塑料科技. 2024(12): 93-96 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 程哲闻,张可,吕晓辉,蒋元宁,石磊. 铝锂合金的搅拌摩擦焊及其改型工艺研究进展. 电焊机. 2023(03): 46-53+71 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 徐桂芳,张杰,宋瑞智,王嘉. 人工时效对喷射成形2195-T4搅拌摩擦焊接头组织与性能的影响. 材料热处理学报. 2023(05): 217-226 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 张贤昆,石磊,武传松,李胜利. 铝/钛异种金属超声振动强化搅拌摩擦焊接工艺试验研究. 航天制造技术. 2023(04): 7-11 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 苏海龙,骆宗安,谢广明,王浩. 真空搅拌摩擦焊机的研制. 焊接. 2022(10): 37-42 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(7)




 下载:
下载: