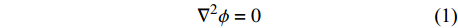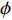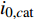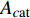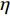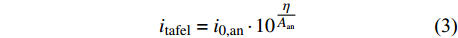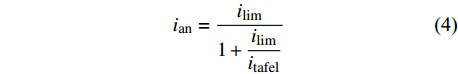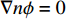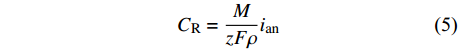Galvanic corrosion behavior and finite element simulation of overlaying welded nuclear steam turbine rotor
-
摘要: 采用宏观电化学试验和浸泡试验研究25Cr2Ni2MoV汽轮机转子堆焊焊接接头在80 ℃,3.5% Cl−环境下的电偶腐蚀行为. 电化学试验结果表明,焊缝为腐蚀薄弱区,腐蚀电位从高到低依次为热影响区、母材、焊缝. 浸泡试验结果表明,随着母材面积的增大,焊缝平均腐蚀厚度逐渐加深. 进一步利用宏观电化学测试所获的电化学参量建立焊接接头电偶腐蚀有限元模型对比浸泡试验结果. 结果表明,有限元仿真结果能有效模拟堆焊焊接接头的电偶腐蚀行为,为实际生产提供电偶腐蚀速率预测.Abstract: The galvanic corrosion behavior of 25Cr2Ni2MoV overlaying welded nuclear steam turbine rotor was investigated by macro-electrochemical tests and immersion tests in chloride solution at 80 ℃. The results of electrochemical experiments show that the weld metal is the weak corrosion zone, and the corrosion potential from low to high is the heat-affected zone, the base metal, and the weld metal. The results of the immersion tests show that as the area of the BM increases, the average corrosion thickness of the WM gradually increases Furthermore, the galvanic corrosion finite element model of welded joint was established by using the electrochemical parameters obtained from macro electrochemical test. The results show that the finite element simulation results can effectively simulate the galvanic corrosion behavior of overlaying welding joint and provide galvanic corrosion rate prediction for actual production.
-
Keywords:
- welded joint /
- galvanic corrosion /
- finite element simulation /
- immersion test
-
0. 序言
转子是核电汽轮机的核心部件,其工作环境严苛,长期在高温、高压、湿度大的运行工况下服役,可能存在磨损、腐蚀、断裂等失效问题[1-2]. 核电汽轮机转子尺寸巨大,制造难度大,生产周期长,若直接将受损的失效转子报废必然造成巨大的资源浪费. 堆焊修复技术借助一定的热源手段将合金材料熔覆于母体材料表面,能够恢复受损转子的几何形状,延长汽轮机的使用寿命,是解决这一关键问题的有效方法[3-4]. 但是,堆焊修复过程中的局部受热和冷却过程导致材料的显微组织发生变化,使焊接接头部位的力学性能及电化学性能发生改变[5],因此,汽轮机转子中堆焊修复产生的焊接接头能否在复杂的服役环境中保持优异的可靠性有待进一步验证.
焊接接头母材、焊缝和热影响区之间微观组织、成分、硬度等差异会导致熔合线附近存在电偶腐蚀效应[6-7]. Wang等人[8]对异种焊接金属进行电化学性能测试,发现具有较高腐蚀电位的A508作为阳极优先发生腐蚀,52M的腐蚀电位较低作为阴极被保护. Dhanapal等人[9]研究了pH、Cl−溶度和浸泡时间对焊接接头电偶腐蚀腐蚀速率的影响,发现低pH值、高Cl−浓度会加快腐蚀的速率,且腐蚀速率与浸泡时间呈正相关. 对于汽轮机焊接转子接头而言,NiCrMoV钢焊接接头的母材、热影响区以及焊缝之间存在电势差,使得材料在熔合线附近发生电偶腐蚀效应[10-12]. 随着温度的升高、阴阳面积比的增大,电偶腐蚀效应逐渐增强,但当阴阳面积比达到一定程度后,腐蚀效应又会减弱[13-14]. 上述研究均为基于试验结果获得的结论,但是在实验室环境下研究某一特定因素对电偶腐蚀的影响程度较为费时费力,而准确有效的数值仿真计算可以高效地解决这一问题. Deshpande[15]引入能斯特普朗特方程建立电偶腐蚀二维模型并对异种金属焊接接头进行浸泡试验,验证了模型的有效性. Snihirova等人[16]设计了Ti6Al4V/AA2024焊接接头的电偶腐蚀试验并采用有限元模拟其腐蚀深度,计算获得的腐蚀深度与试验结果一致. 因此,有限元模型的准确建立有利于减少腐蚀试验数量并应用于实际构件中的电偶腐蚀行为预测.
选用核电汽轮机转子钢堆焊焊接接头作为研究对象,模拟其严苛的工作环境,对不同阴阳面积比的焊接接头进行浸泡试验. 建立焊接接头电偶腐蚀有限元模型,模拟表面的电位及腐蚀深度. 进一步将计算结果与浸泡试验进行对比,验证有限元模型的准确性.
1. 试验材料
试验采用堆焊修复25Cr2Ni2MoV焊接接头,母材为25Cr2Ni2MoV,焊材为3NiCrMo-2.5UP,材料的化学成分如表1所示. 焊接采用埋弧焊堆焊焊接工艺,焊后热处理工艺为550 ℃,保温20 h.
表 1 25Cr2Ni2Mo转子钢母材和焊缝材料的化学成分(质量分数,%)Table 1. Chemical compositions of 25Cr2Ni2MoV welded joint base metal and weld材料 C Si Mn P S Cr Ni Mo V 母材 0.22 0.06 0.19 0.004 0.002 2.49 2.12 0.92 0.15 焊缝 0.12 0.15 1.25 0.005 1.20 1.20 2.51 0.74 0.1 1.1 微观组织及显微硬度测试
从堆焊焊接接头试样上切取包含母材、焊缝和热影响区的微观观察试样,试样尺寸为13 mm × 10 mm × 2 mm,使用200目 ~ 2 000目的砂纸依次进行打磨,打磨完成后对试样进行抛光,随后用4%硝酸酒精腐蚀其表面,通过光镜观察得到焊接接头各个区域的金相组织. 显微硬度的测量采用显微维氏硬度仪,测量参数为载荷1.96 N,保载15 s.
1.2 宏观电化学试验
将焊接接头母材、热影响区、远离熔合线的焊缝区以及靠近熔合线的焊缝区放置在80 ℃,3.5% (质量分数) NaCl溶液中进行电化学试验. 电化学工作站为辰华chi660e,试验采用三电极体系,铂电极为辅助电极,固态氯化银电极为参比电极,试样为工作电极. 将各个区域制作为10 mm × 10 mm × 2 mm试样,暴露于电解质溶液中的面积为1 cm2. 试验时,将试样浸泡于电解质溶液中10 min后开始进行开路电位的测试,随后进行极化曲线的测试,极化曲线的扫描范围为开路电位的 ± 0.4 VSCE,测试速率为0.001 VSCE/s.
1.3 浸泡试验
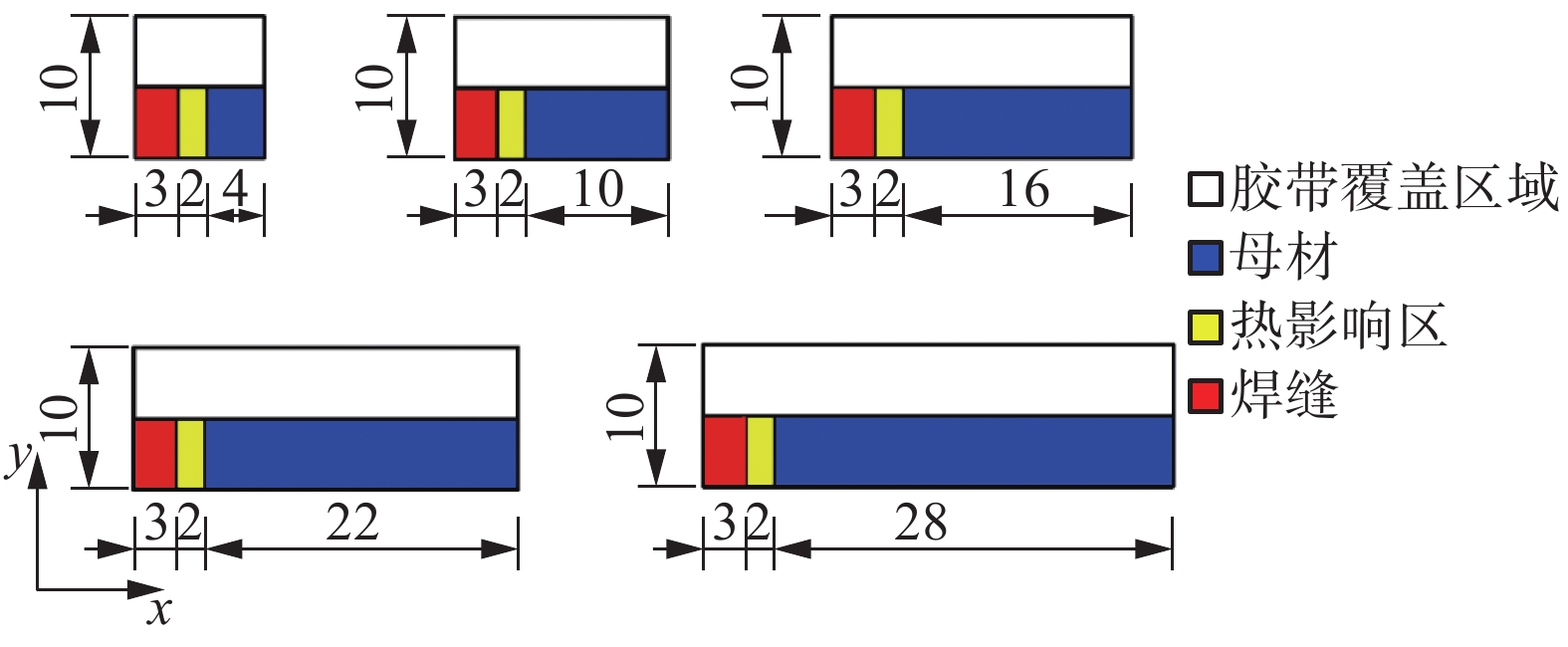
对不同阴阳极面积的25Cr2Ni2MoV焊接接头进行浸泡试验,试样的尺寸如表2所示. 为了分析不同阴阳极面积比对腐蚀程度的影响,各试样横截面的面积均为10 mm × 5 mm,试验前用环氧树脂将试样进行冷镶密封,仅暴露接头区域,为了对比不同区域的腐蚀深度用胶带贴住部分暴露表面,如图1所示. 试验环境为80 ℃,3.5%(质量分数)NaCl溶液,试样浸泡960 h后取出,去除表面腐蚀产物后用三维形貌仪(IMF)扫描其腐蚀深度.
表 2 浸泡试样尺寸及取样位置Table 2. Size and location of immersion test sample编号 取样位置 长度δ/mm 1 熔合线一侧WM长3 mm,
另一侧BM + HAZ长6 mm9 2 熔合线一侧WM长3 mm,
另一侧BM + HAZ长12 mm15 3 熔合线一侧WM长3 mm,
另一侧BM + HAZ长18 mm21 4 熔合线一侧WM长3 mm,
另一侧BM + HAZ长24 mm27 5 熔合线一侧WM长3 mm,
另一侧BM + HAZ长30 mm33 2. 试验结果与分析
2.1 焊接接头各区域的显微组织及显微硬度分布
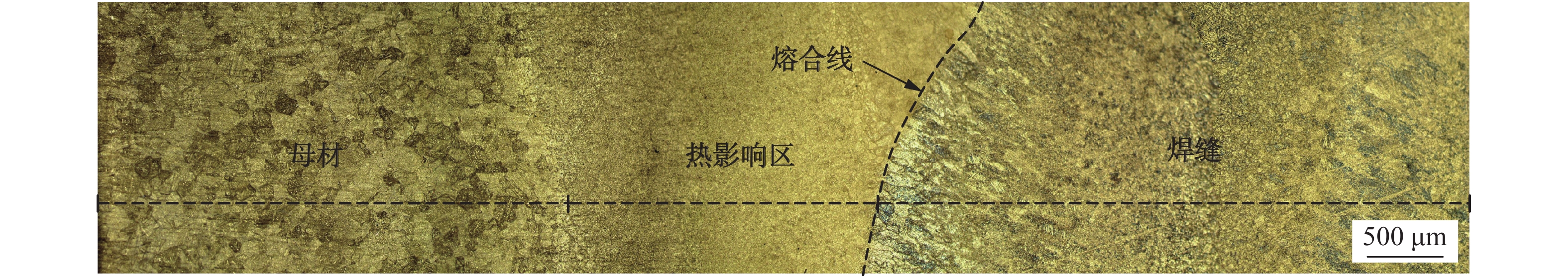
堆焊接头各区域的显微组织如图2所示,从图中可以看到母材主要由板条马氏体构成. 热影响区主要是由回火马氏体和回火贝氏体构成,由于堆焊过程引入大量热量使得回火马氏体的尺寸增大,由粒状增大到块状,从而导致热影响区晶粒尺寸从母材到熔合线依次增大,其宽度大约为2 mm. 焊缝由多道堆焊构成,其微观组织均为回火马氏体和回火贝氏体. 由于焊缝金属熔覆于母材表面时晶粒形核困难,形成柱状晶,随着温度的逐渐降低,形成等轴晶,故每层堆焊焊缝由柱状晶区和等轴晶区构成.
堆焊焊接接头各区域的显微硬度结果如图3所示,母材区的硬度较为均衡,平均硬度为279 HV,热影响区的硬度最高,其最高硬度达到396.17 HV,且硬度随着热影响区晶粒尺寸的增大而增大,而焊缝区域中,远离熔合线的焊缝的平均硬度小于靠近熔合线的平均硬度,到达第四层焊缝时硬度趋于稳定,且发现每层焊缝柱状晶区的硬度均高于等轴晶区.
2.2 宏观电化学测试
在80 ℃,3.5% (质量分数) NaCl溶液中测试母材、热影响区、远离熔合线焊缝和靠近熔合线焊缝的极化曲线的结果如图4所示. 焊接接头各区域的腐蚀电位和自腐蚀电流如表3所示. 从腐蚀电位和腐蚀电流看来,耐蚀性能从大到小依次为:热影响区,母材,靠近熔合线焊缝,远离熔合线焊缝. 运用Tafel外推法对母材和远离熔合线焊缝的腐蚀电位以及电流密度进行拟合,得到的腐蚀电位和腐蚀电流密度如表3所示. 电化学的结果表明,堆焊焊接接头中不同部位有明显的电位差,且远离熔合线的焊缝区域腐蚀电流密度最高,存在电偶腐蚀的风险,远离熔合线焊缝电位低,作为阳极优先发生电偶腐蚀.
表 3 焊接接头各区域腐蚀电位及自腐蚀电流Table 3. Electrochemical parameter of WM (far from FL), WM(close to FL), HAZ, BM区域 腐蚀电位E/VSCE 腐蚀电流密度i/(mA·cm−2) 母材 −0.741 0.011 87 热影响区 −0.711 0.012 19 靠近熔合线焊缝 −0.770 0.021 40 远离熔合线焊缝 −0.770 0.025 39 2.3 阴阳面积比对焊接接头电偶腐蚀深度的影响
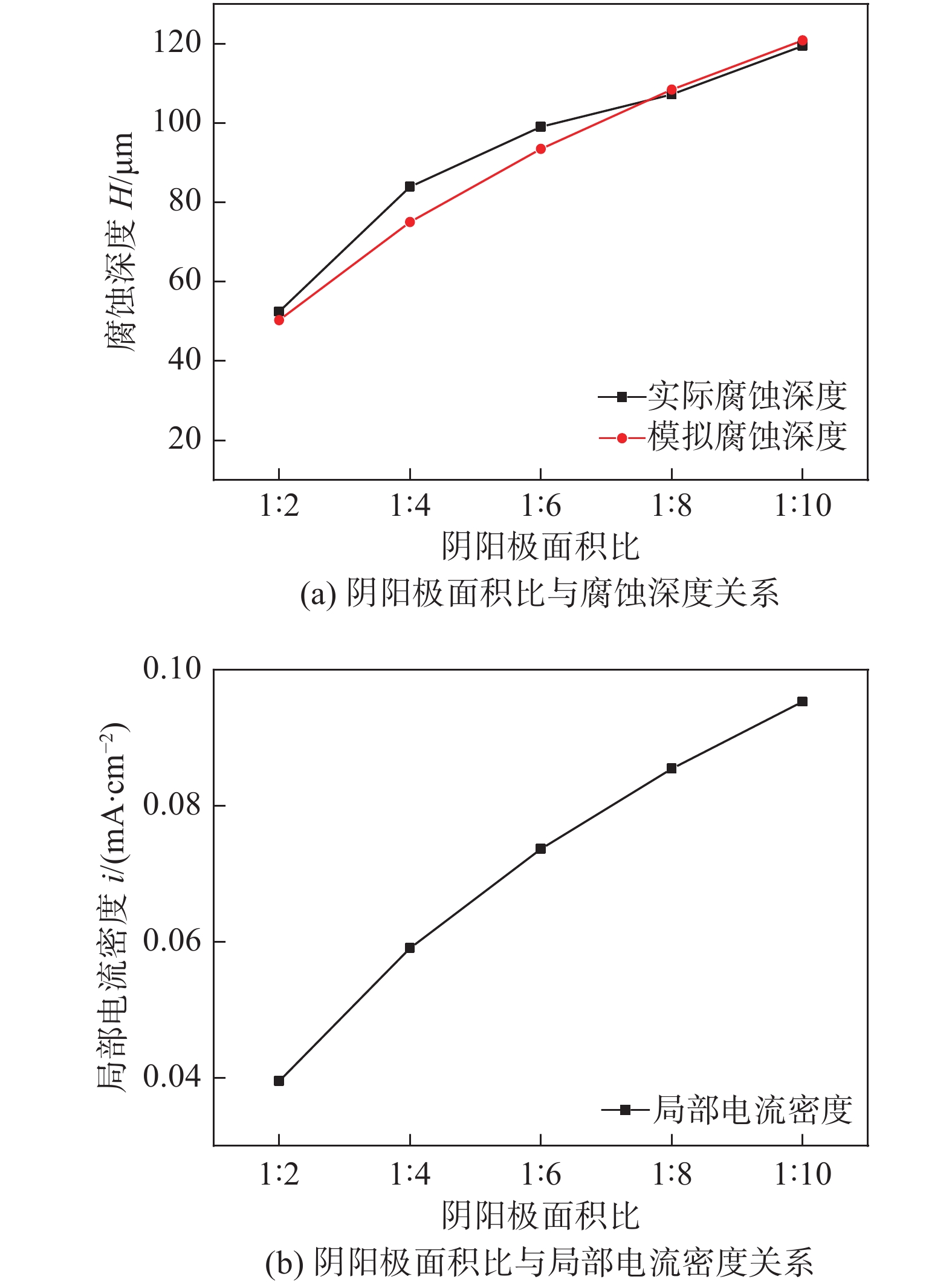
为了验证堆焊焊接接头附近的电偶腐蚀效应,试样浸泡960 h后用三位形貌仪观察焊接接头各个区域的厚度变化. 沿图1中x轴方向线扫描观察了5种尺寸的母材、焊缝和热影响区的厚度变化. 从图5a中可以看到不同阴阳极面积比下的焊缝都发生明显腐蚀,而焊缝和母材的厚度几乎没有发生变化,故熔合线附近发生了厚度突变. 焊缝的平均腐蚀深度与阴阳面积比的关系如图5b所示,可以明显看到,随着阴阳极面积比的增大,焊缝区域的腐蚀深度越深,且靠近热影响区焊缝的腐蚀深度小于远离热影响区的焊缝,这一结论与电化学试验结果一致.
图6为不同暴露面积接头中焊缝、热影响区、母材沿着图1中y轴方向线扫描的结果,与未发生腐蚀的区域相比,5种不同暴露面积的母材未发生明显腐蚀. 不同尺寸的焊缝区域的腐蚀厚度分别为52.47,83.9,99.05,107.18和119.41 μm,明显大于纯焊缝材料,而母材区域的腐蚀深度则小于纯母材的腐蚀深度. 可见其作为阴极被保护;而焊缝材料则作为阳极加速溶解. 而不同暴露面积下的热影响区也均未发生明显的腐蚀.
3. 有限元模型的建立及计算结果
3.1 几何模型
为了分析面积比对电偶腐蚀的影响规律及有限元模型的准确性,取与浸泡试验一致的面积比,如表2所示. 用于仿真的SWM∶SBM = 1∶2二维几何模型和网格划分情况如图7所示,图中所示网格一共12 408个域单元和432个边界元. 电极上方为电解质溶液,其厚度为10 mm.
3.2 控制方程
假定溶液中没有浓度梯度且呈电中性,且溶液没有流动,因此可以将控制方程简化为[15, 17-18]
$${\nabla ^2}\phi = 0$$ (1) 式中:
$\phi $ 为电解质电位(V).模拟的电偶腐蚀的阴极反应的电流密度可用阴极塔菲尔方程[19]进行计算
$${i_{cat}} = - {i_{0,c{\rm{at}}}} \cdot {10^{\tfrac{\eta }{{{A_{c{\rm{at}}}}}}}}$$ (2) 式中:
${i_{0,c{\rm{at}}}}$ 为阴极交换电流密度(A/m2);${A}_{c{\rm{at}}}$ 为阴极塔菲尔斜率;$\eta $ 为过电位.在阳极表面主要发生金属的溶解反应,故忽略其表面的还原反应,阳极反应的电流密度可以用阳极塔菲尔方程进行计算,即
$${i_{{\rm{tafel}}}} = {i_{0,{\rm{an}}}} \cdot {10^{\tfrac{\eta }{{{A_{{\rm{an}}}}}}}}$$ (3) $${i_{{\rm{an}}}} = \dfrac{{{i_{\lim }}}}{{1 + \dfrac{{{i_{\lim }}}}{{{i_{{\rm{tafel}}}}}}}}$$ (4) 式中:ilim为极限电流密度;Aan为阳极塔菲尔斜率;i0,an为阳极交换电流密度.
电解质上部和左右边界边界条件为
$\nabla n\phi = 0$ . 阳极金属表面主要发生溶解反应,其溶解速率[17]可以表示为$${C_{\rm{R}}} = \frac{M}{{zF\rho }}{i_{{\rm{an}}}}$$ (5) 式中:M为Fe的相对分子质量;F为法拉第常数;ρ为Fe的密度;z为阳极的电荷数.
3.3 计算结果
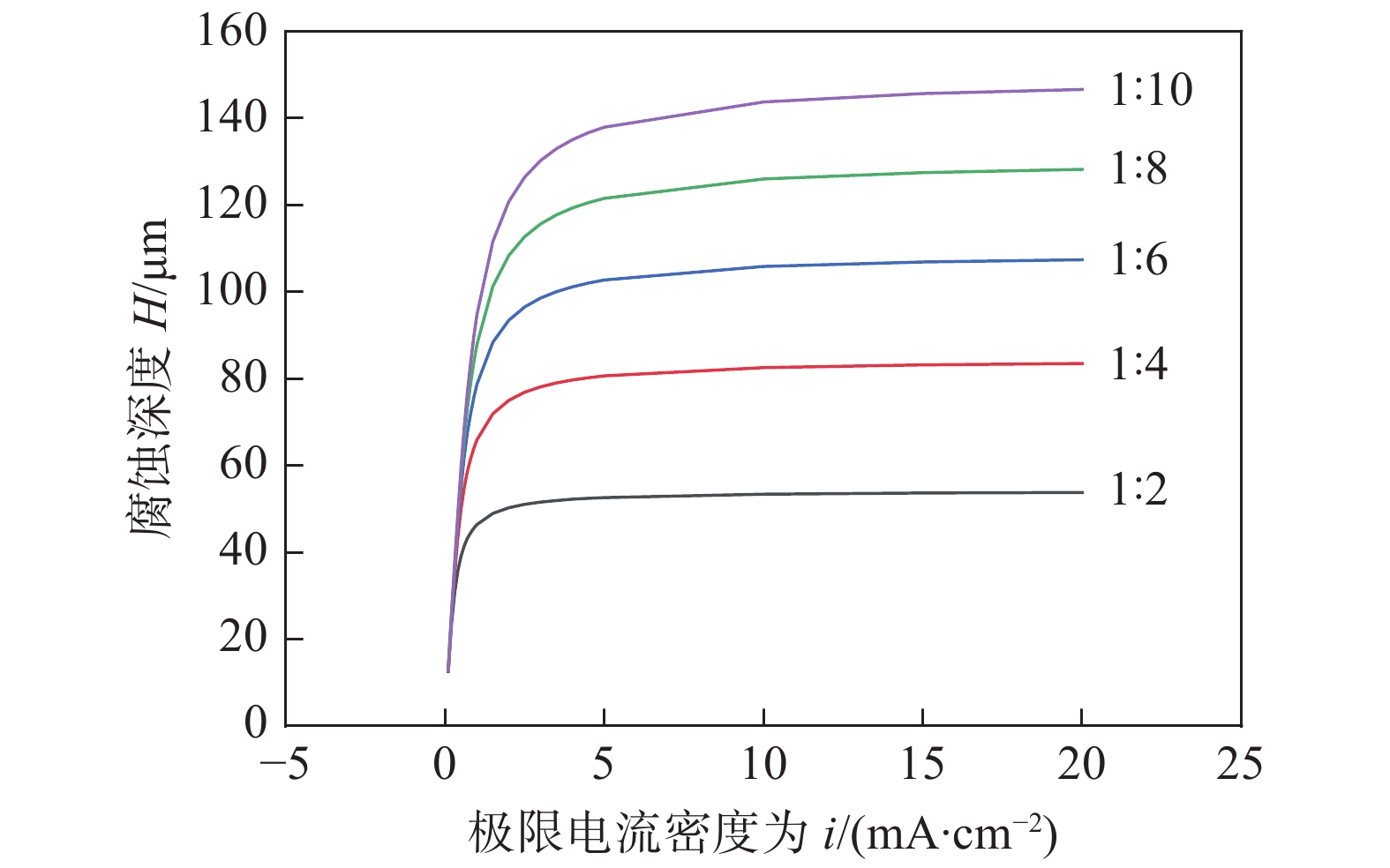
为验证电偶腐蚀有限元模型是否能准确描述堆焊焊接接头在腐蚀环境中的腐蚀趋势,建立了与浸泡试验相同条件的几何模型,模拟环境为质量浓度为3.5%NaCl溶液,模拟温度为80 ℃,所取的相关参数如表4和表5所示. 为确定模拟的极限电流密度大小,在保持其它模拟参数不变的情况下,取不同的极限电流密度值进行模拟,不同阴阳面积比模拟浸泡960 h的腐蚀深度结果如图8所示. 腐蚀深度随着极限电流密度的增大呈对数增长. 极限电流密度小于交换电流密度时,阳极表面的电化学反应受化学反应控制,故局部电流密度受阴阳面积比影响较小;当极限电流密度远大于交换电流密度时,极限电流密度对腐蚀深度的影响可以忽略不计,由公式(3)可知,此时阳极局部电流密度大小等于阳极交换电流密度. 综合考虑温度、溶氧量等腐蚀环境,最终确定极限电流密度为2 A/m2.
表 4 电偶腐蚀阴、阳极模拟参数Table 4. Cathode and anode simulation parameters of galvanic corrosion极性 交换电流密度
i0/(A·m−2)极化曲线斜率
A/VSCE平衡电位
Eeq/VSCE阴极 0.144 8 −0.149 −0.741 阳极 0.333 0 0.079 −0.770 表 5 其余模拟参数Table 5. Other simulation parameters密度
ρ/(kg·m−3)分子质量
M/(kg·mol−1)电解质电导率
S/(S·m−1)Pn极电荷数
z法拉第常数
F/(C·mol−1)气体常数
R/(J·mol−1·K−1)温度
T/K7874 0.056 3.78 2 96500 8.314 353.15 图9a为堆焊电偶模型焊缝与母材面积比为1∶2的焊接接头在80 ℃电解质电位以及电流方向,图9b为焊接接头的电极电位,可以看到焊接接头的阴极表面(母材表面)附近电解质电位小于阳极表面(远离熔合线的焊缝表面)附近电解质电位,且阳极表面的电极电位低于阴极表面的电极电位,从而导致阴极与阳极之间形成电位差,从而发生电偶腐蚀效应.
模拟不同阴阳面积比下堆焊接头阳极的平均腐蚀深度,计算结果如图10a所示,从图中可以看出,随着阴阳面积比的逐渐增大,平均腐蚀深度增大. 模拟的腐蚀深度结果与实际腐蚀图10b为模拟浸泡960 h后是阳极的局部电流密度,对比发现,随着阴阳面积比的增大,阳极表面的局部电流密度增大,增大了电偶腐蚀效应,使材料的腐蚀深度增大.
4. 结论
(1) 25Cr2Ni2MoV堆焊焊接接头中母材的金相组织主要是板条马氏体,热影响区则为回火贝氏体和不同尺寸的回火马氏体,每一道焊缝由马氏体和贝氏体构成,可以依据贝氏体的形貌将焊缝分为柱状区和等轴区. 堆焊焊接接头的化学成分及微观结构差异导致了材料的电化学性能差异.
(2) 25Cr2Ni2MoV堆焊焊接接头的腐蚀电位从高到低依次热影响区、母材、焊缝,具有较低腐蚀电位的焊缝作为阳极优先发生腐蚀,而母材则作为阴极被保护. 随着阴阳面积比的增大,阴极和阳极的腐蚀深度均加深,但阳极的增大程度远大于阴极.
(3)建立了堆焊焊接接头电偶腐蚀有限元模型并计算了阴阳面积比对腐蚀深度的影响. 计算发现腐蚀深度随着阴阳面积比的增大逐渐增大,与浸泡试验结果的趋势一致,说明所建立的电偶腐蚀模型可以用于模拟该材料在实际腐蚀环境下的电偶腐蚀效应.
-
表 1 25Cr2Ni2Mo转子钢母材和焊缝材料的化学成分(质量分数,%)
Table 1 Chemical compositions of 25Cr2Ni2MoV welded joint base metal and weld
材料 C Si Mn P S Cr Ni Mo V 母材 0.22 0.06 0.19 0.004 0.002 2.49 2.12 0.92 0.15 焊缝 0.12 0.15 1.25 0.005 1.20 1.20 2.51 0.74 0.1 表 2 浸泡试样尺寸及取样位置
Table 2 Size and location of immersion test sample
编号 取样位置 长度δ/mm 1 熔合线一侧WM长3 mm,
另一侧BM + HAZ长6 mm9 2 熔合线一侧WM长3 mm,
另一侧BM + HAZ长12 mm15 3 熔合线一侧WM长3 mm,
另一侧BM + HAZ长18 mm21 4 熔合线一侧WM长3 mm,
另一侧BM + HAZ长24 mm27 5 熔合线一侧WM长3 mm,
另一侧BM + HAZ长30 mm33 表 3 焊接接头各区域腐蚀电位及自腐蚀电流
Table 3 Electrochemical parameter of WM (far from FL), WM(close to FL), HAZ, BM
区域 腐蚀电位E/VSCE 腐蚀电流密度i/(mA·cm−2) 母材 −0.741 0.011 87 热影响区 −0.711 0.012 19 靠近熔合线焊缝 −0.770 0.021 40 远离熔合线焊缝 −0.770 0.025 39 表 4 电偶腐蚀阴、阳极模拟参数
Table 4 Cathode and anode simulation parameters of galvanic corrosion
极性 交换电流密度
i0/(A·m−2)极化曲线斜率
A/VSCE平衡电位
Eeq/VSCE阴极 0.144 8 −0.149 −0.741 阳极 0.333 0 0.079 −0.770 表 5 其余模拟参数
Table 5 Other simulation parameters
密度
ρ/(kg·m−3)分子质量
M/(kg·mol−1)电解质电导率
S/(S·m−1)Pn极电荷数
z法拉第常数
F/(C·mol−1)气体常数
R/(J·mol−1·K−1)温度
T/K7874 0.056 3.78 2 96500 8.314 353.15 -
[1] Mazur Z, Hernandez-Rossette A. Steam turbine rotor discs failure evaluation and repair process implementation[J]. Engineering Failure Analysis, 2015, 56: 545 − 554. doi: 10.1016/j.engfailanal.2014.10.010
[2] 温建锋, 轩福贞, 涂善东. 高温构件蠕变损伤与裂纹扩展预测研究新进展[J]. 压力容器, 2019, 36(2): 38 − 50. Wen Jianfeng, Xuan Fuzhen, Tu Shantung. Advances in predictions of creep damage and crack growth in components under high temperatures[J]. Pressure Vessel Technology, 2019, 36(2): 38 − 50.
[3] Mitchell K C. Weld repair of steam turbine rotors[D]. Swansea: Swansea University, 1999.
[4] Mazur-Czerwiec Z, Kubiak J, Hernández A. Welding repair of steam and gas turbine rotors made of Cr-Mo-V steel[J]. Welding International, 2000, 14: 203 − 210. doi: 10.1080/09507110009549165
[5] Li S, Dong H, Wang X, et al. Effect of repair welding on microstructure and mechanical properties of 7N01 aluminum alloy MIG welded joint[J]. Journal of Manufacturing Processes, 2020, 54: 80 − 88. doi: 10.1016/j.jmapro.2020.03.009
[6] Dak G, Pandey C. A critical review on dissimilar welds joint between martensitic and austenitic steel for power plant application[J]. Journal of Manufacturing Processes, 2020, 58(4): 377 − 406. doi: 10.1016/j.jmapro.2020.08.019
[7] Lin Y J, Lin C S. Galvanic corrosion behavior of friction stir welded AZ31B magnesium alloy and 6N01 aluminum alloy dissimilar joints[J]. Corrosion Science, 2021, 180: 1 − 5. doi: 10.1016/j.corsci.2020.109203
[8] Wang S, Ding J, Ming H, et al. Characterization of low alloy ferritic steel–Ni base alloy dissimilar metal weld interface by SPM techniques, SEM/EDS, TEM/EDS and SVET[J]. Materials Characterization, 2015, 100: 50 − 60. doi: 10.1016/j.matchar.2014.12.007
[9] Dhanapal A, Rajendra Boopathy S, Balasubramanian V. Corrosion behaviour of friction stir welded AZ61A magnesium alloy welds immersed in NaCl solutions[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2012, 22(4): 793 − 802. doi: 10.1016/S1003-6326(11)61247-8
[10] Zhu J, Xu L, Feng Z, et al. Galvanic corrosion of a welded joint in 3Cr low alloy pipeline steel[J]. Corrosion Science, 2016, 111: 391 − 403. doi: 10.1016/j.corsci.2016.05.032
[11] Weng S, Huang Y, Xuan F Z, et al. Correlation between microstructure, hardness and corrosion of welded joints of disc rotors[J]. Procedia Engineering, 2015, 130: 1761 − 1769. doi: 10.1016/j.proeng.2015.12.325
[12] 周鲁军, 董毅, 杨善武. E550钢埋弧焊接接头在模拟海洋大气环境中的腐蚀行为[J]. 材料热处理学报, 2020, 41(4): 173 − 180. Zhou Lujun, Dong yi, Yang Shanwu. Corrosion behavior of submerged arc welded joint of E550 steel in simulated marine atmospheric environment[J]. Transactions of Materials and Heat Treatment, 2020, 41(4): 173 − 180.
[13] 欧阳玉清, 黄毓晖, 翁硕, 等. 核电汽轮机焊接转子接头在氯离子环境中的电偶腐蚀行为[J]. 焊接学报, 2019, 40(6): 153 − 160. Ouyang Yuqing, Huang Yuhui, Weng Shuo, et al. Galvanic corrosion behavior of nuclear steam turbine welded joint in chloride environment[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2019, 40(6): 153 − 160.
[14] Oh S, Kim Y, Jung K, et al. Effects of temperature and operation parameters on the galvanic corrosion of Cu coupled to Au in organic solderability preservatives process[J]. Metals and Materials International, 2017, 23(2): 290 − 297. doi: 10.1007/s12540-017-6495-1
[15] Deshpande K B. Validated numerical modelling of galvanic corrosion for couples: Magnesium alloy (AE44)–mild steel and AE44–aluminium alloy (AA6063) in brine solution[J]. Corrosion Science, 2010, 52(10): 3514 − 3522. doi: 10.1016/j.corsci.2010.06.031
[16] Snihirova D, Höche D, Lamaka S, et al. Galvanic corrosion of Ti6Al4V -AA2024 joints in aircraft environment: Modelling and experimental validation[J]. Corrosion Science, 2019, 157: 70 − 78. doi: 10.1016/j.corsci.2019.04.036
[17] Yin L, Jin Y, Leygraf C, et al. A FEM model for investigation of micro-galvanic corrosion of Al alloys and effects of deposition of corrosion products[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2016, 192: 310 − 318. doi: 10.1016/j.electacta.2016.01.179
[18] Shi L, Song Y, Zhao P, et al. Variations of galvanic currents and corrosion forms of 2024/Q235/304 tri-metallic couple with multivariable cathode/anode area ratios: Experiments and modeling[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2020, 359: 1 − 10. doi: 10.1016/j.electacta.2020.136947
[19] 曹楚南. 腐蚀电化学原理[M]. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2008. Cao Chunan. Principles of electrochemistry of corrosion[M]. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2008.
-
期刊类型引用(4)
1. 刘文吉,朱鹏飞,于镇洋,杨嘉昇,肖宇. 基于电流多特征融合的窄间隙P-GMAW摆动电弧传感焊缝跟踪方法. 传感技术学报. 2024(04): 612-619 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 贾爱亭,洪波,李湘文,高佳篷,吴格飞,屈原缘. 基于轨迹在线识别的3D折线焊缝机器人摆动GMAW实时跟踪方法. 机械工程学报. 2022(14): 116-125 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 聂春萌,杨建伟. 虚拟现实系统中多自由度电磁跟踪方法仿真. 计算机仿真. 2019(04): 330-333 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 李高阳,洪宇翔,祝团结,刘锦. 一种摆动电弧CO_2焊焊缝表面状态自适应的新方法. 工程技术研究. 2019(16): 1-4 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(8)



 下载:
下载: