Analysis of properties and failure mechanism of Ti600/Ni-25% Si joint
-
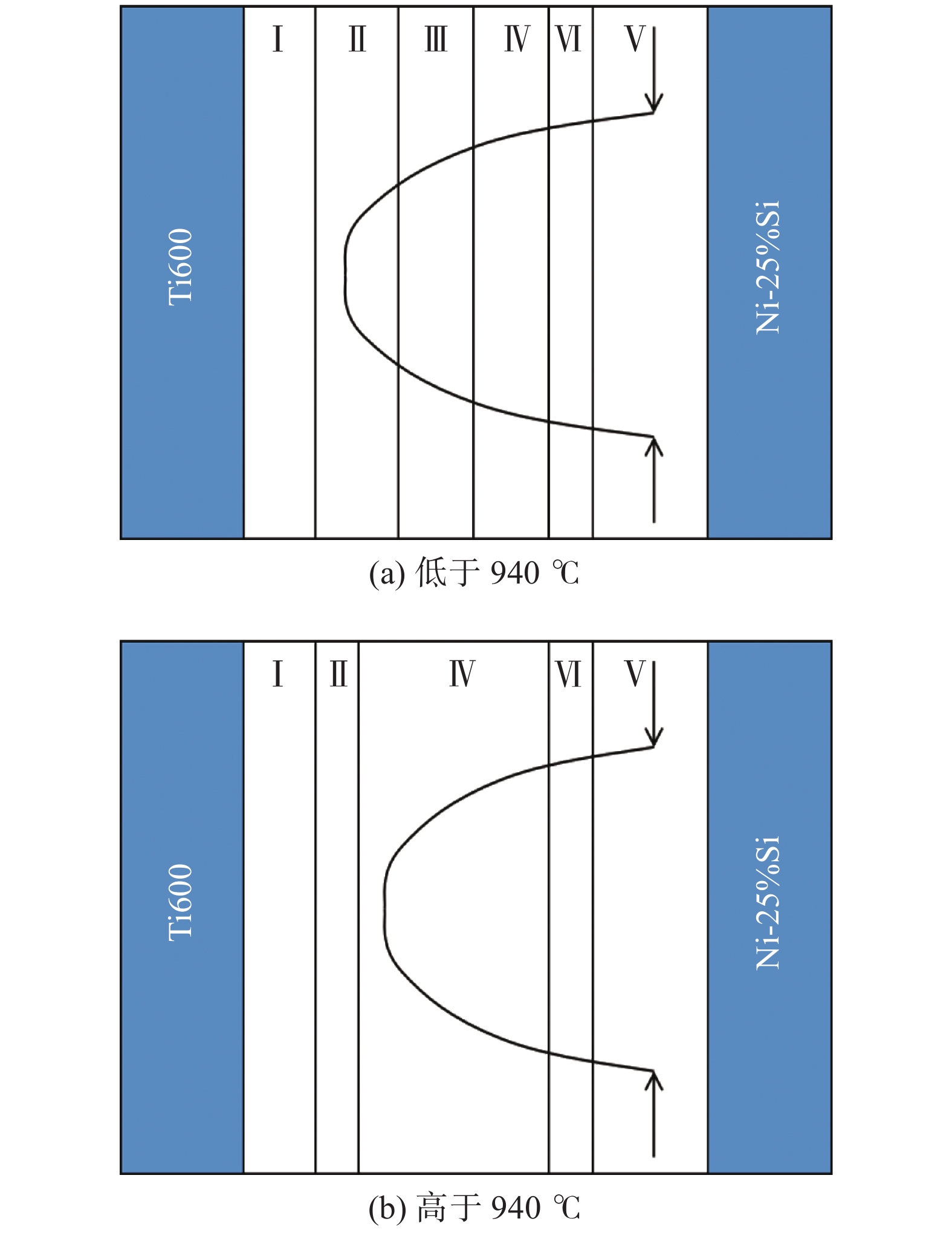
摘要: 采用Ti-Zr-Ni-Cu非晶钎料对高温钛合金Ti600和Ni-25%Si (原子分数,%)合金进行钎焊试验,重点研究了钎焊温度对镍硅与钛合金接头组织及性能的影响,结合接头组织特征及断口结构分析阐明了Ti600和Ni-25%Si合金钎焊接头的失效机理. 结果表明,钎缝内部包含多个区域,随着连接温度从900 ℃上升至980 ℃,包含(Ti,Zr)2Si和Ti2Ni相的区域逐渐消失,包含Ti5Si3和Ti2Ni相的区域逐渐变厚,最终占据全部钎缝. 力学性能分析表明,随着钎焊温度的升高,接头抗剪强度先增大后降低. 当钎焊温度为960 ℃时,接头的抗剪强度能够达到峰值177 MPa. 在脆性Ti2Ni相基体上弥散分布的Ti5Si3相颗粒破坏了Ti2Ni相的连续性,阻碍了裂纹在钎缝内部的扩展是钎焊接头抗剪强度提升的根本原因.
-
关键词:
- Ti600 /
- Ni-25%Si合金 /
- Ti-Zr-Ni-Cu非晶钎料 /
- 界面组织 /
- 力学性能
Abstract: Brazing of Ti600 to Ni-25%Si alloy was performed using Ti-Zr-Ni-Cu amorphous filler foil. The influence of brazing temperature on the microstructures and mechanical property of brazed joints have been studied and the strengthening mechanism of the Ti600/Ni-25%Si brazed joint was clarified. The results show that the brazing seam contains multiple reaction zones. With the increase of brazing temperature, the zone III comprised by (Ti,Zr)2Si and Ti2Ni disappears gradually while the zone IV with Ti5Si3 dispersing in Ti2Ni gradually occupies the brazing seam. As the brazing temperature increases, the shear strength of brazed joints first augmented, reached the peak value of 177 MPa at 960 ℃ and then decreased. The dispersing Ti5Si3 phase distributing in the brittle Ti2Ni phase, which hinders the crack propagation and strengthens the brittle Ti2Ni, improves the shear strength of the brazed joint obtained at elevated temperature. -
-
图 8 不同钎焊温度下的接头微观断口形貌
Figure 8. Fracture morphologies brazed by different temperature. (a) SEM images of the fracture surface brazed by 940 ℃/10 min; (b) the edge of fracture surface obtained by 960 ℃ /10 min; (c) the middle of fracture surface obtained by at 960 ℃/10 min; (d) the middle of fracture surface obtained by at 980 ℃/10 min
表 1 接头内部各点EDS分析结果及可能相(原子分数,%)
Table 1 Chemical composition and possible phase of each spot in the joint
点 Al Si Zr Sn Ti Ni Cu 可能相 A 11.00 1.58 1.84 1.57 76.38 6.55 1.07 α-Ti+β-Ti B 15.21 1.35 0.99 8.53 71.87 1.42 0.63 Ti3Al C 5.06 0.70 2.52 0.22 56.65 31.46 3.39 Ti2Ni D 6.71 1.08 7.58 0.72 55.84 18.11 9.96 (Ti,Zr)2(Cu,Ni) E 9.74 0.69 2.75 1.48 72.91 6.49 5.94 α-Ti+β-Ti F 2.26 29.41 27.79 1.89 30.10 5.73 2.82 (Ti,Zr)2Si G 14.45 1.34 1.44 1.48 73.37 4.19 3.73 α-Ti+β-Ti H 1.64 34.99 3.09 0.33 56.98 2.41 0.55 Ti5Si3 I 0.63 27.16 0.07 0.29 0.31 69.68 1.85 Ti31Si12 J 10.98 2.06 1.85 1.95 72.51 4.88 5.78 α-Ti+β-Ti 表 2 钎焊接头断口的EDS结果和可能相(原子分数,%)
Table 2 The ESD results and possible phase of the surface of d joints
点 Al Si Zr Sn Ti Ni Cu 可能相 A 0.22 26.90 0.11 0.41 0.39 70.20 1.77 Ni31Si2 B 4.19 1.07 3.44 0.66 57.28 29.31 4.06 Ti2Ni C 1.10 28.12 0.00 0.22 0.61 68.42 1.53 Ni31Si12 D 6.44 7.61 2.75 0.57 54.01 26.67 1.93 Ti2Ni E 4.07 30.90 6.13 0.47 52.51 4.79 1.13 Ti5Si3 F 4.26 0.68 1.44 0.36 58.65 32.64 1.96 Ti2Ni 表 3 接头两侧主要相的线膨胀系数与弹性模量
Table 3 CTE and Elastic modulus of the main phase near the brazing interface
主要相 线膨胀系数δ/(10−6 ℃−1) 弹性模量E/GPa TiN2 16 115 Ti600 8.5 109 Ni-25%Si 11.97 259 -
[1] Niu Y, Hou H, Li M, et al. High temperature deformation behavior of a near alpha Ti600 titanium alloy[J]. Materials Science And Engineering: A, 2008, 492(1−2): 24 − 28. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2008.02.036
[2] Cao L, Cochrane R F, Mullis A M. Lamella structure formation in drop-tube processed Ni–25.3 at.% Si alloy[J]. Journal of Alloys And Compounds, 2014, 615: S599 − S601. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2013.11.233
[3] Tokunaga T, Hashima K, Ohtani H, et al. Thermodynamic analysis of the Ni-Si-Ti system using thermochemical properties determined from ab initio calculations[J]. Materials Transactions, 2004, 45(5): 1507 − 1514. doi: 10.2320/matertrans.45.1507
[4] Yue X, He P, Feng J C, et al. Microstructure and interfacial reactions of vacuum brazing titanium alloy to stainless steel using an AgCuTi filler metal[J]. Materials Characterization, 2008, 59(12): 1721 − 1727. doi: 10.1016/j.matchar.2008.03.014
[5] Liu P. A study of phase constitution near the interface of Mg/Al vacuum diffusion bonding[J]. Materials Letters, 2005, 59: 2001 − 2005. doi: 10.1016/j.matlet.2005.02.038
[6] Cao J, Song X G, Li C, et al. Brazing ZrO2 ceramic to Ti–6Al–4V alloy using NiCrSiB amorphous filler foil: Interfacial microstructure and joint properties[J]. Materials Characterization, 2013, 81: 85 − 91. doi: 10.1016/j.matchar.2013.04.009
[7] Hong B, Yanyu S, Duo Liu, et al. Joining of SiO2 ceramic and TC4 alloy by nanoparticles modified brazing filler metal[J]. Chinese Journal of Aeronautics. 2020, 33(1):383−390.
[8] Yang Z, Zhang L, Tian X, et al. Interfacial microstructure and mechanical properties of TiAl and C/SiC joint brazed with TiH2–Ni–B brazing powder[J]. Materials Characterization, 2013, 79: 52 − 59. doi: 10.1016/j.matchar.2013.02.010
[9] Li S, Zhou Y, Duan H. Wettability and interfacial reaction in SiC/Ni plus Ti system[J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2002, 37(12): 2575 − 2579. doi: 10.1023/A:1015416312807
[10] Li X, Wang H, Wang T, et al. Microstructural evolution mechanisms of Ti600 and Ni-25% Si joint brazed with Ti-Zr-Ni-Cu amorphous filler foil[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2017, 240: 414 − 419. doi: 10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2016.10.021
[11] Lee J G, Choi Y H, Lee J K, et al. Low-temperature brazing of titanium by the application of a Zr–Ti–Ni–Cu–Bebulk metallic glass (BMG) alloy as a filler[J]. Intermetallics, 2010, 18(1): 70 − 73. doi: 10.1016/j.intermet.2009.06.012
[12] Xia C Z, Li Y J, Puchkov U A, et al. Crack analysis near vacuum brazing interface of Cu/Al dissimilar materials using Al–Si brazing alloy[J]. Materials Science Technology, 2009, 25(3): 383 − 387. doi: 10.1179/174328408X262409
[13] 孙德超, 柯黎明, 邢丽, 等. 陶瓷与金属梯度过渡层的自蔓延高温合成[J]. 焊接学报, 2000, 21(3): 44 − 49. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-360X.2000.03.012 Sun Dechao, Ke Liming, Xing Li, et al. Self-propagating high-temperature synthesis of gradient transitional layer between ceramics and metal[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2000, 21(3): 44 − 49. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-360X.2000.03.012
[14] Zuhailawati H, Saeed A M, Ismail A B, et al. Spot resistance welding of a titanium/nickel joint with filler metal[J]. Welding Journal, 2010, 89(5): 101s − 104s.
[15] He P, Feng J C, Zhou H. Microstructure and strength of brazed joints of Ti3Al-base alloy with TiZrNiCu filler metal[J]. Materials Science And Engineering: A, 2005, 392(1-2): 81 − 86. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2004.07.068
-
期刊类型引用(3)
1. 陶旭阳,何建萍,徐磊. 超薄板脉冲微束等离子弧焊熔池振荡频率特征. 轻工机械. 2020(03): 24-27+32 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 陶旭阳,何建萍,徐磊. 基于LabView脉冲微束等离子弧焊熔池振荡信息提取. 智能计算机与应用. 2020(03): 371-374 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 顾玉芬,席保龙,李春凯,石玗,代悦,丁彬. 基于熔池振荡的GTAW熔透实时传感与控制. 电焊机. 2020(12): 5-8+108 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(7)




 下载:
下载: