Welding thermal cycle of the laser-arc hybrid welding of the EQ70 steel and its effects on the microstructure evolution of the heat affected zone
-
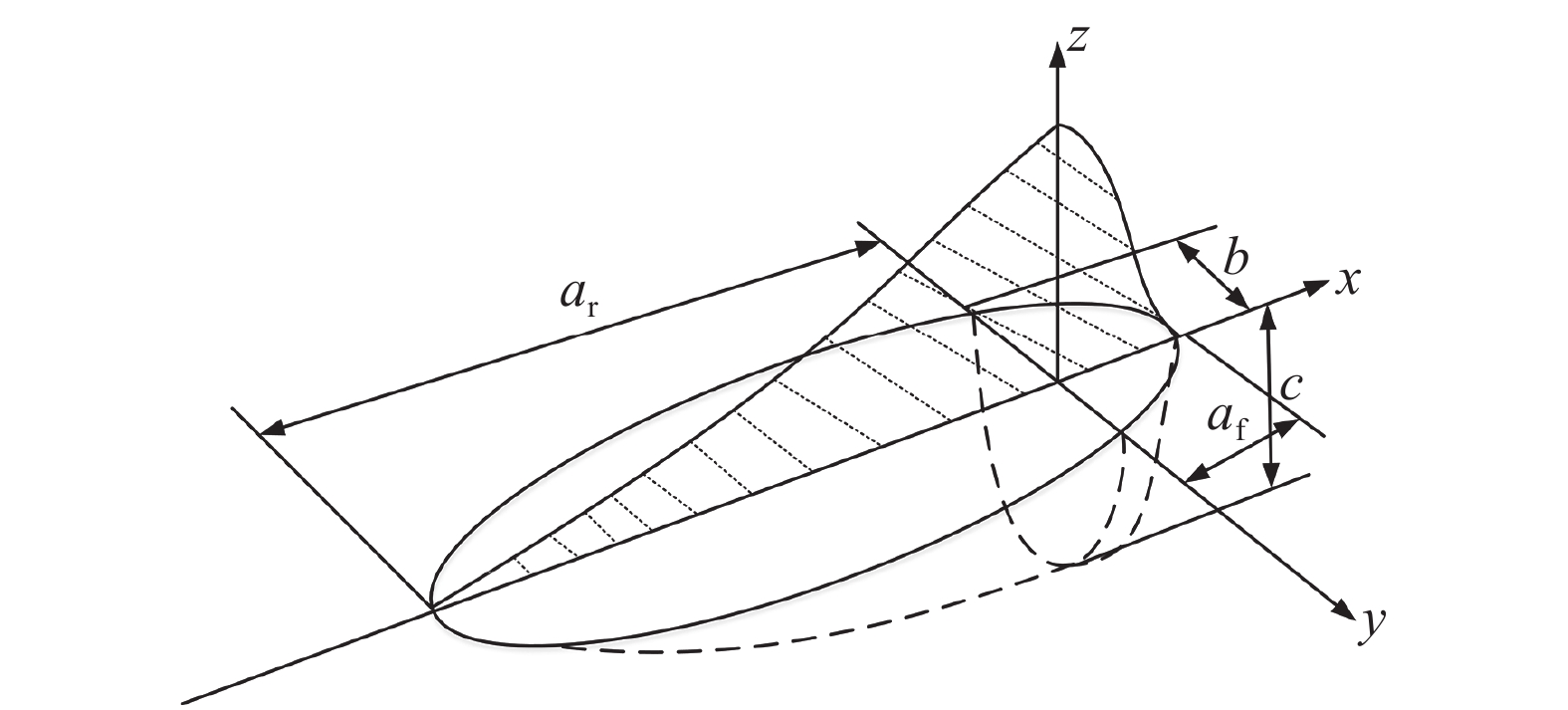
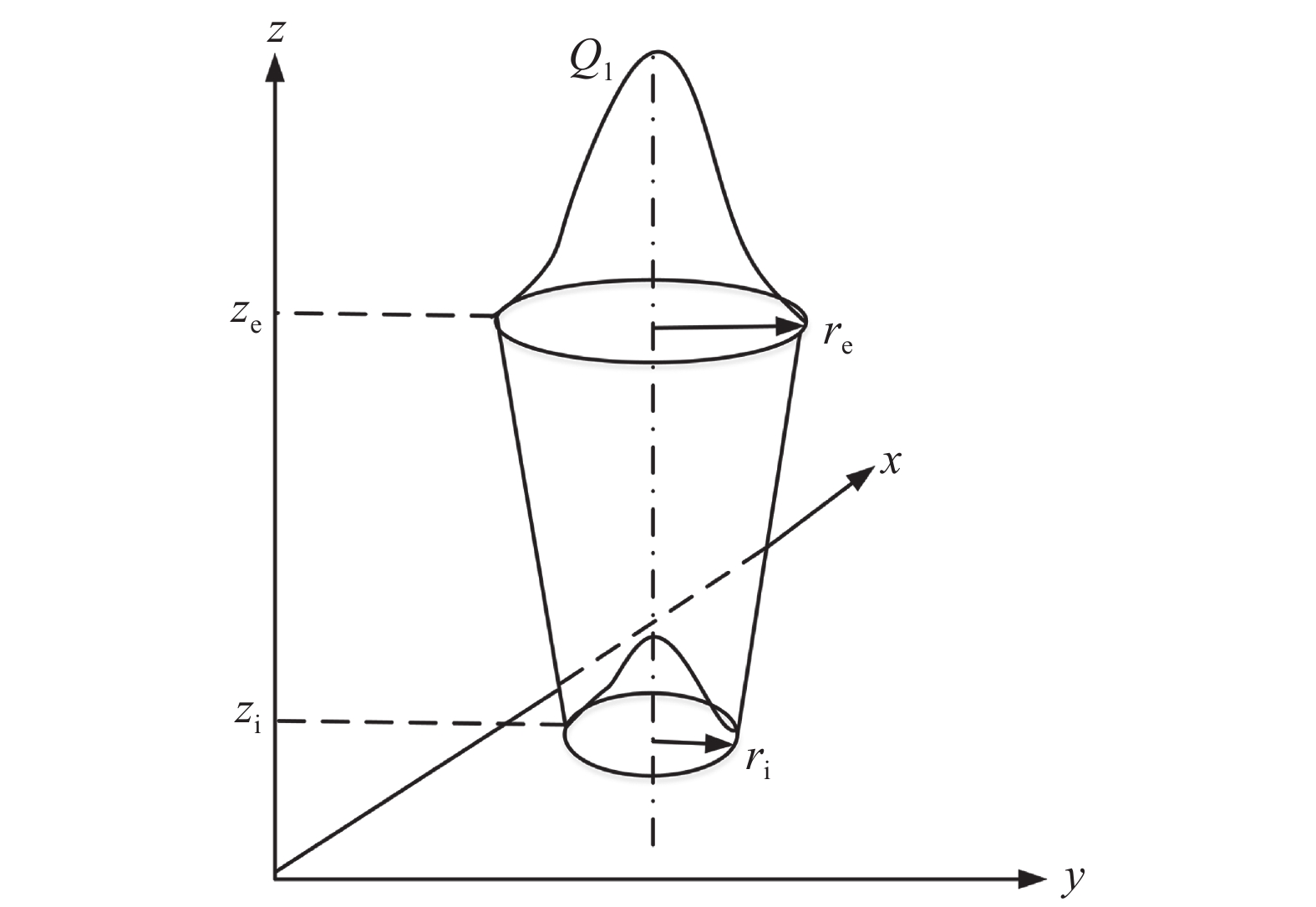
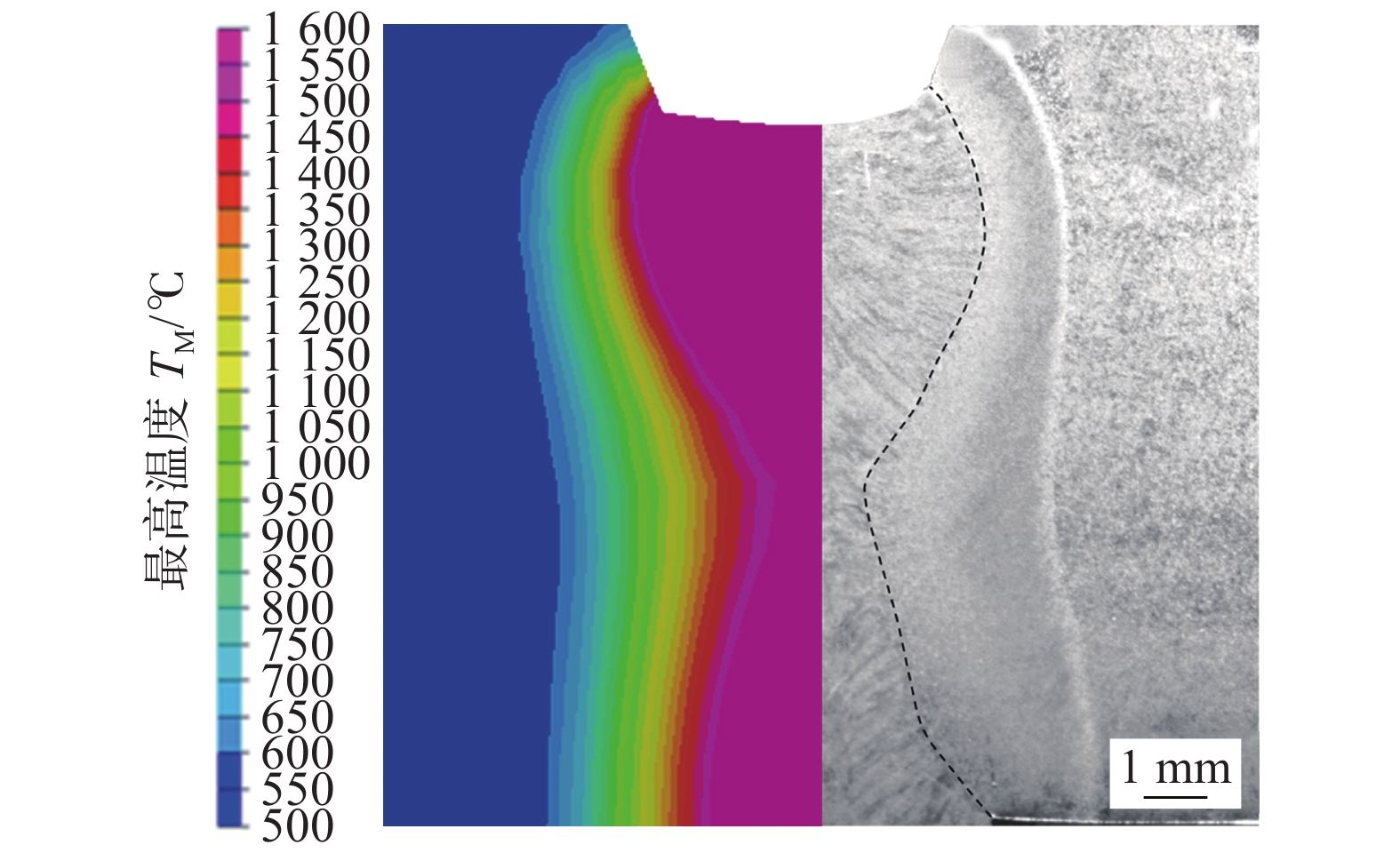
摘要: 采用Visul Environment 软件建立了EQ70钢激光电弧复合焊的三维模型,并利用SYSWELD软件对激光电弧复合焊焊接温度场进行了有限元数值模拟,结合热电偶测温法和热影响区的微观组织表征分析了激光电弧复合焊热循环特点及其对热影响区组织演变的影响. 结果表明,采用双椭球体+峰值递增锥体组合型热源可以准确模拟复合焊温度场,电弧区、过渡区、激光区相同热影响区微区具有相近的热循环,热影响区加热速度可达400 ℃/s,1 100 ℃以上停留时间为0.79~1.33 s,t8/5为4~6 s. 粗晶区、细晶区组织为板条马氏体,临界区组织为马氏体+晶界碳化物,亚临界区组织为回火马氏体. 激光电弧复合焊具有快速加热、高温停留时间短的特点,在一定程度限制了奥氏体晶粒的长大,粗晶区和细晶区平均晶粒尺寸分别为42.7,19.8 μm.Abstract: The Visul Environment software was used to establish the 3D model of the laser-arc hybrid welding joint of EQ70 steel. The temperature field of the laser-arc hybrid welding was numerically simulated by the SYSWELD software. The thermal cycle characteristics of the laser-arc hybrid welding and its effects on the microstructure evolution of the heat affected zone (HAZ) were analyzed, combined with the thermocouple thermometry and microstructure characterization. The results shown that the combined heat source with double ellipsoid and peak increasing cone could accurately simulate the temperature field of the laser-arc hybrid welding, and the arc zone, transition zone and laser zone had similar thermal cycles in the same HAZ micro-zones. The HAZ heating rate can reach to 400 ℃/s, the dwelling time above 1 100 ℃ was 0.79−1.33 s, and the t8/5 was 4−6 s. The coarse grained HAZ (CGHAZ) and the fine grained HAZ (FGHAZ) were mainly comprised of lath martensite. The microstructure of the inter-critically HAZ (ICHAZ) was martensite and grain boundary carbides. The sub-critically HAZ (SCHAZ) composed of tempered martensite. The rapid heating and short high temperature dwelling time of the laser-arc hybrid welding limited the austenite grain growth to some extent, and the average grain size of the CGHAZ and FGHAZ were 42.7 μm and 19.8 μm, respectively.
-
Keywords:
- EQ70 /
- laser-arc hybrid welding /
- thermal cycle /
- heat affected zone
-
-
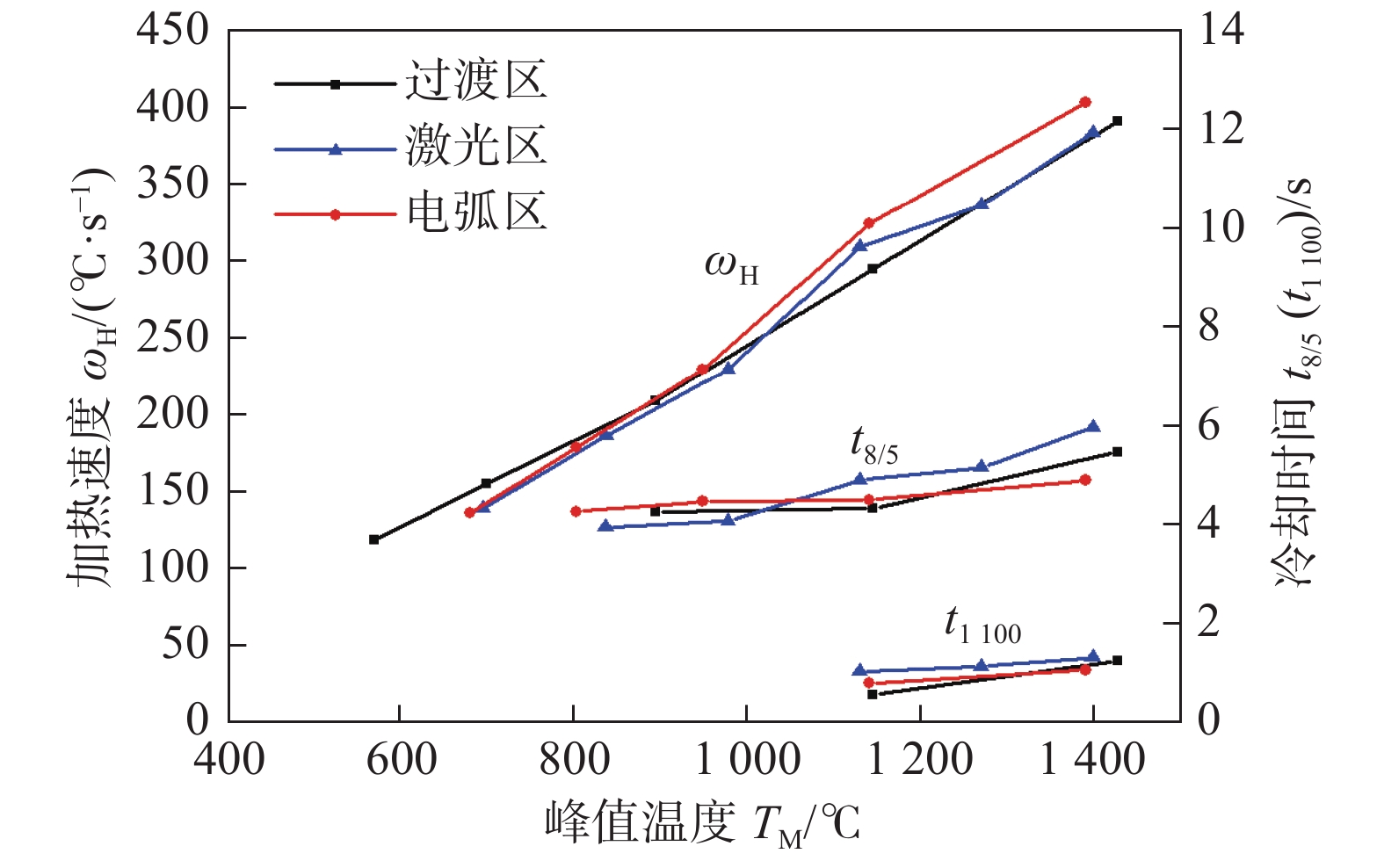
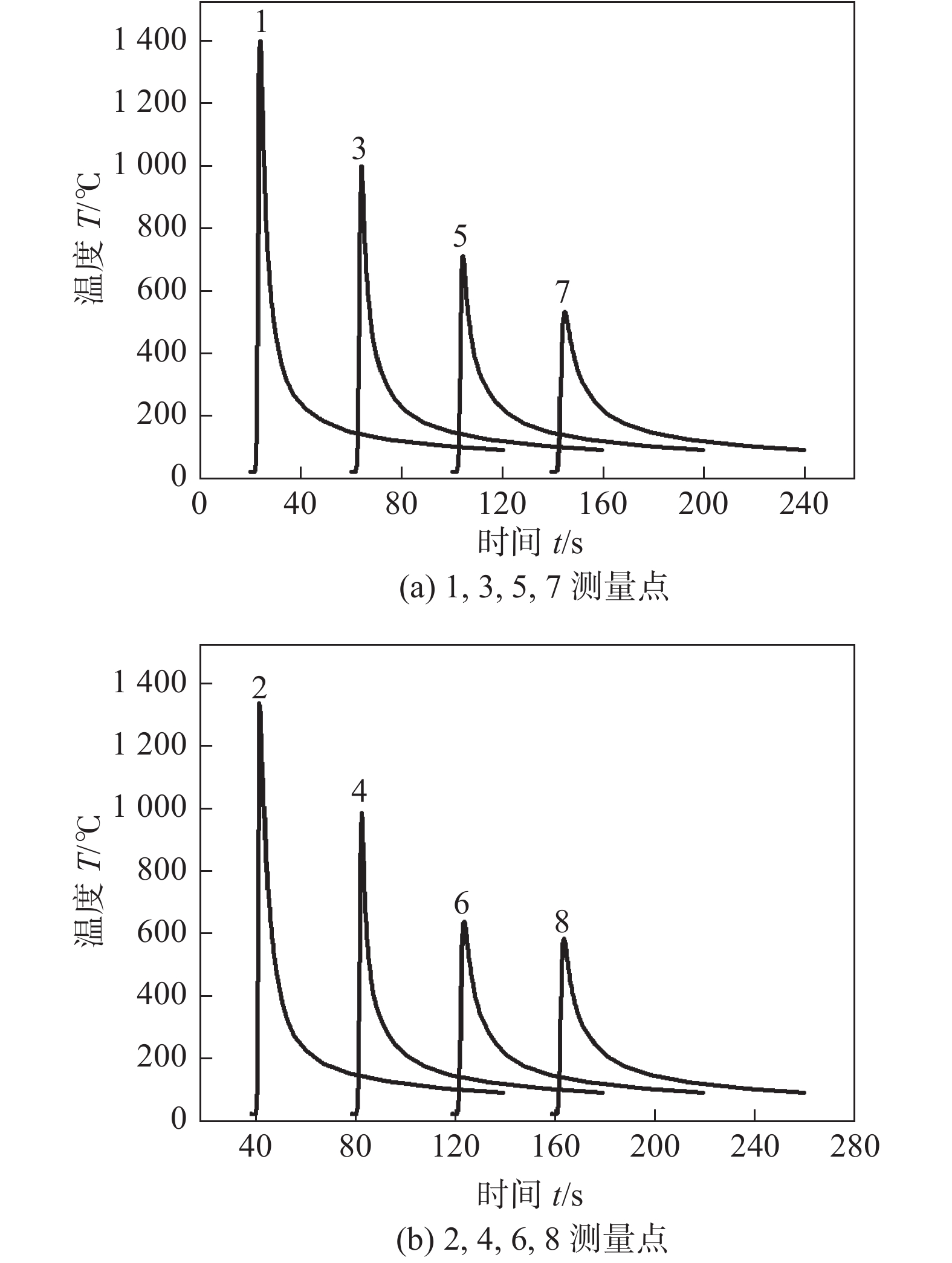
图 7 不同区域HAZ网格节点分布及其热循环曲线
Figure 7. Distribution and thermal cycle curves of HAZ mesh points in different zones. (a) arc zone mesh points distribution; (b) transition zone mesh points distribution; (c) laser zone mesh points distribution; (d) thermal cycle curves of arc zone mesh points; (e) thermal cycle curves of transition zone mesh points; (f) thermal cycle curves of laser zone mesh points
图 11 电弧区HAZ的微观组织
Figure 11. Microstructure of arc zone HAZ. (a) CGHAZ optical microstructure;(b) FGHAZ optical microstructure;(c) ICHAZ optical microstructure;(d) SCHAZ optical microstructure; (e) CGHAZ scanning electron microstructure; (f) FGHAZ scanning electron microstructure; (g) ICHAZ scanning electron microstructure; (h) SCHAZ scanning electron microstructure; (i) CGHAZ transmission electron microstructure
表 1 EQ70钢的化学成分(质量分数,%)
Table 1 Chemical compositions of EQ70 steel
C Si Mn P Cu Cr Mo V N B Al Ni Fe 0.12 0.25 1.09 0.004 0.28 0.58 0.53 0.04 0.003 9 0.000 9 0.074 2.46 余量 表 2 焊接工艺参数
Table 2 Welding process parameters
激光功率
P/kW焊接电流
I/A电弧电压
U/V焊接速度
v/(m·min−1)气体流量
Q/(L·min−1)光丝间距
DLW/mm激光离焦量
DL/mm激光与电弧夹角
α/(°)5.5 260 26.0~26.4 0.6 20 10 +6 55 表 3 不同区域HAZ网格节点的焊接热循环参数
Table 3 Welding thermal cycle parameters of different mesh nodes in different HAZs
区域 编号 峰值温度
TM/℃升至峰值温度
所需时间tp/s1 100 ℃以上停留
时间t1100/s冷却至1 100 ℃
时间tM/11/s800 ℃冷却至500 ℃
时间t8/5/s距焊缝中心距离
dWM/mm电弧区 A-1 1 427 3.59 1.24 0.70 5.47 2.76 A-2 1 145 3.81 0.56 0.35 4.33 3.28 A-3 892 4.16 — — 4.26 3.85 A-4 696 4.36 — — — 4.49 A-5 567 4.59 — — — 5.18 过渡区 T-1 1399 3.59 1.33 0.77 5.98 1.28 T-2 1270 3.71 1.12 0.65 5.17 1.77 T-3 1130 3.58 1.04 0.55 4.91 2.31 T-4 977 4.16 — — 4.08 2.92 T-5 834 4.36 — — 3.97 3.59 T-6 693 4.83 — — — 4.32 激光区 L-1 1390 3.39 1.06 0.77 4.91 1.72 L-2 1140 3.45 0.79 0.39 4.51 2.24 L-3 946 4.02 — — 4.47 2.84 L-4 800 4.36 — — 4.27 3.5 L-5 678 4.83 — — — 4.23 表 4 各测量点热循环参数
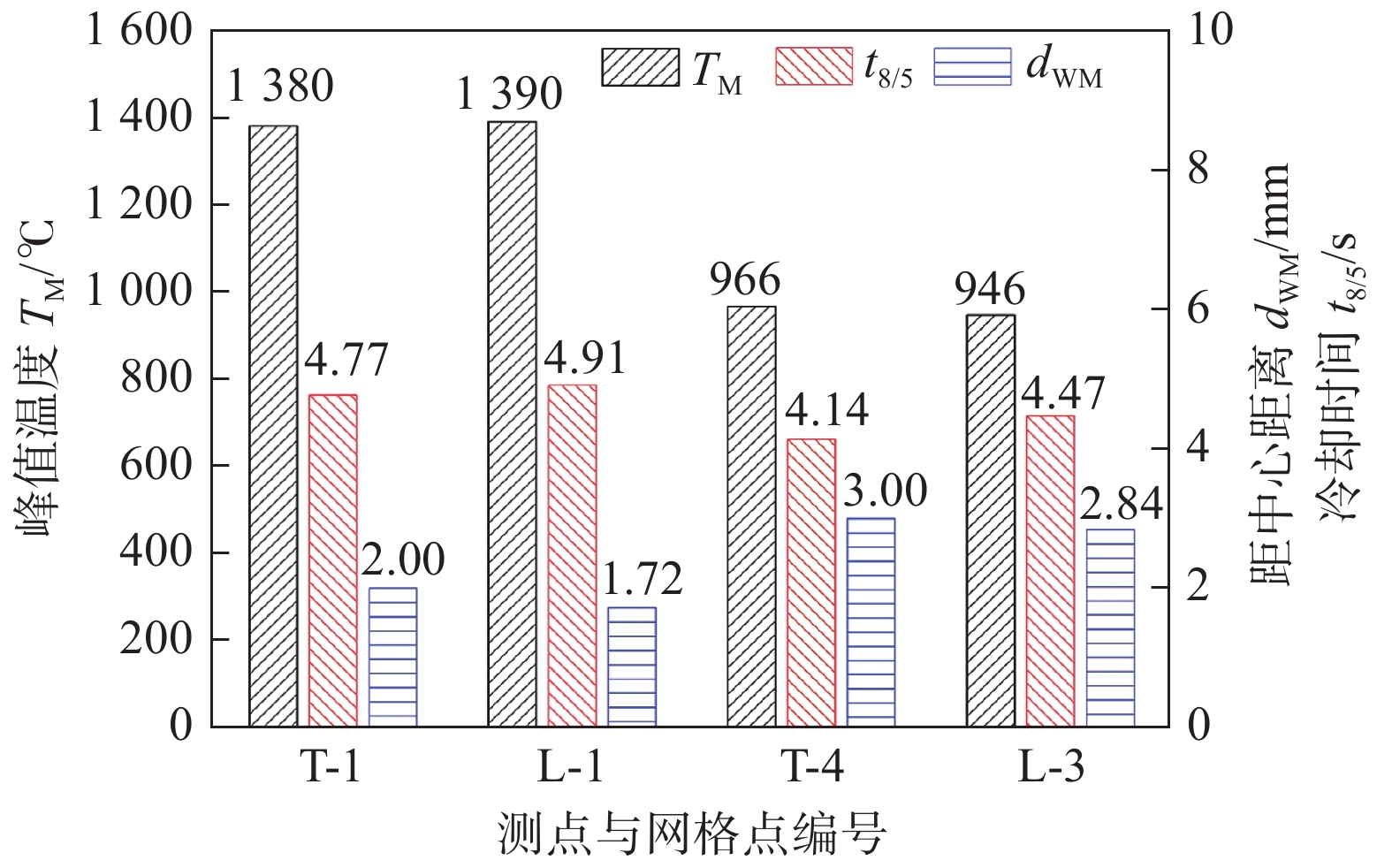
Table 4 Welding thermal cycle parameters of different measuring points
测点 峰值温度
TM/℃升至峰值温度
所需时间tp/s1 100 ℃以上停留
时间t1100/s冷却至1 100 ℃
时间tM/11/s800 ℃冷却至500 ℃
时间t8/5/s距焊缝中心距离
dWM/mmT-1 1380 3.41 1.13 0.71 4.77 2 T-2 1310 3.39 1.09 0.64 5.17 2 T-3 984 3.98 — — 4.33 3 T-4 966 3.98 — — 4.14 3 T-5 702 4.36 — — — 4 T-6 624 4.59 — — — 4 T-7 522 5.02 — — — 5 T-8 572 4.59 — — — 5 -
[1] Bappa Acherjee. Hybrid laser arc welding: State-of-art review[J]. Optics & Laser Technology, 2018, 99: 60 − 71.
[2] Zeng Huilin, Xu Yuanbin, Wang Changjiang, et al. Research on laser-arc hybrid welding technology for long-distance pipeline construction[J]. China Welding, 2018, 27(3): 53 − 58.
[3] 滕彬, 李小宇, 雷振, 等. 低合金高强钢激光-电弧复合热源焊接冷裂纹敏感性分析[J]. 焊接学报, 2010, 31(11): 61 − 64. Teng Bin, Li Xiaoyu, Lei Zhen, et al. Analysis on cold crack sensitivity of low alloy high strength steel weld by laser-arc hybrid welding[J]. Transactions of the China welding institution, 2010, 31(11): 61 − 64.
[4] 严春妍, 易思, 张浩, 等. S355钢激光-MIG复合焊接头显微组织和残余应力[J]. 焊接学报, 2020, 41(6): 12 − 18. doi: 10.12073/j.hjxb.20191014001 Yan Chunyan, Yi Si, Zhang Hao, et al. Investigation of microstructure and stress in laser-MIG hybrid welded S355 steel plates[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2020, 41(6): 12 − 18. doi: 10.12073/j.hjxb.20191014001
[5] 肖荣诗, 吴世凯. 激光-电弧复合焊接的研究进展[J]. 中国激光, 2008, 35(11): 1680 − 1685. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0258-7025.2008.11.004 Xiao Rongshi, Wu Shikai. Progress on laser-arc hybrid welding[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2008, 35(11): 1680 − 1685. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0258-7025.2008.11.004
[6] Wang X N, Zhang S H, Zhou J, et al. Effect of heat input on microstructure and properties of hybrid fiber laser-arc weld joints of the 800 MPa hot-rolled Nb-Ti-Mo microalloyed steels[J]. Optics & Lasers in Engineering, 2017, 91: 86 − 96.
[7] Hyatt C V, Magee K H, Porter J F, et al. Laser-assisted gas metal arc welding of 25-mm-thick HY-80 plate[J]. Welding Journal, 2001, 80(7): 163 − 172.
[8] Bao L L, Wang Y, Han T. Microstructure and mechanical characterization of high strength low alloy steel welded joint by hybrid laser arc welding[C]//2019 the 7th International Conference on Mechanical Engineering, Materials Science and Civil Engineering. IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering. Sanya, China, 2020: 247−256.
[9] Bao L L, Wang Y, Han T. Study on microstructure-toughness relationship in heat affected zone of EQ70 steel by laser-arc hybrid welding[J]. Materials Characterization. 2021, 171: 110788.
[10] 吴振, 王发展, 安高灵,等. 大型复杂结构件高效焊接热源[J]. 焊接学报, 2015, 36(10): 61 − 64. Wu Zhen, Wang Fazhan, An Gaoling, et al. Research on efficient welding heat source model for large and complex structures[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2015, 36(10): 61 − 64.
[11] Xu G, Wu C, Qin G. Three thermal analysis models for laser, GMAW-P and laser+GMAW-P hybrid welding[J]. China Welding, 2009, 18(1): 35 − 39.
-
期刊类型引用(5)
1. 冯栋,周卫涛,颉文峰. 焊接工艺对薄壁环形钛合金焊缝成形及承载能力的影响. 焊接. 2023(04): 55-59 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 乔永丰,雷玉成,姚奕强,王泽宇,朱强. 焊接方法对316L不锈钢焊缝抗辐照损伤性能的影响. 焊接学报. 2023(05): 77-83+94+133-134 .  本站查看
本站查看
3. 马寅,韩晓辉,李刚卿,杨志斌,宋东哲,靳月强. TC4钛合金激光-MIG复合焊接头组织性能. 电焊机. 2023(08): 93-97+114 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 曾俊谚,庄园,杨涛,钟玉婷,杨响明. 基于飞秒激光的钛合金表面微纳米结构制备及腐蚀行为. 焊接. 2023(08): 37-43 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 孙修圣. 钛管道K-TIG深熔焊工艺研究及应用. 压力容器. 2023(09): 23-30 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(5)



 下载:
下载: