Microstructure and mechanical properties of bimetallic intertexture structure fabricated by plasma arc additive manufacturing
-
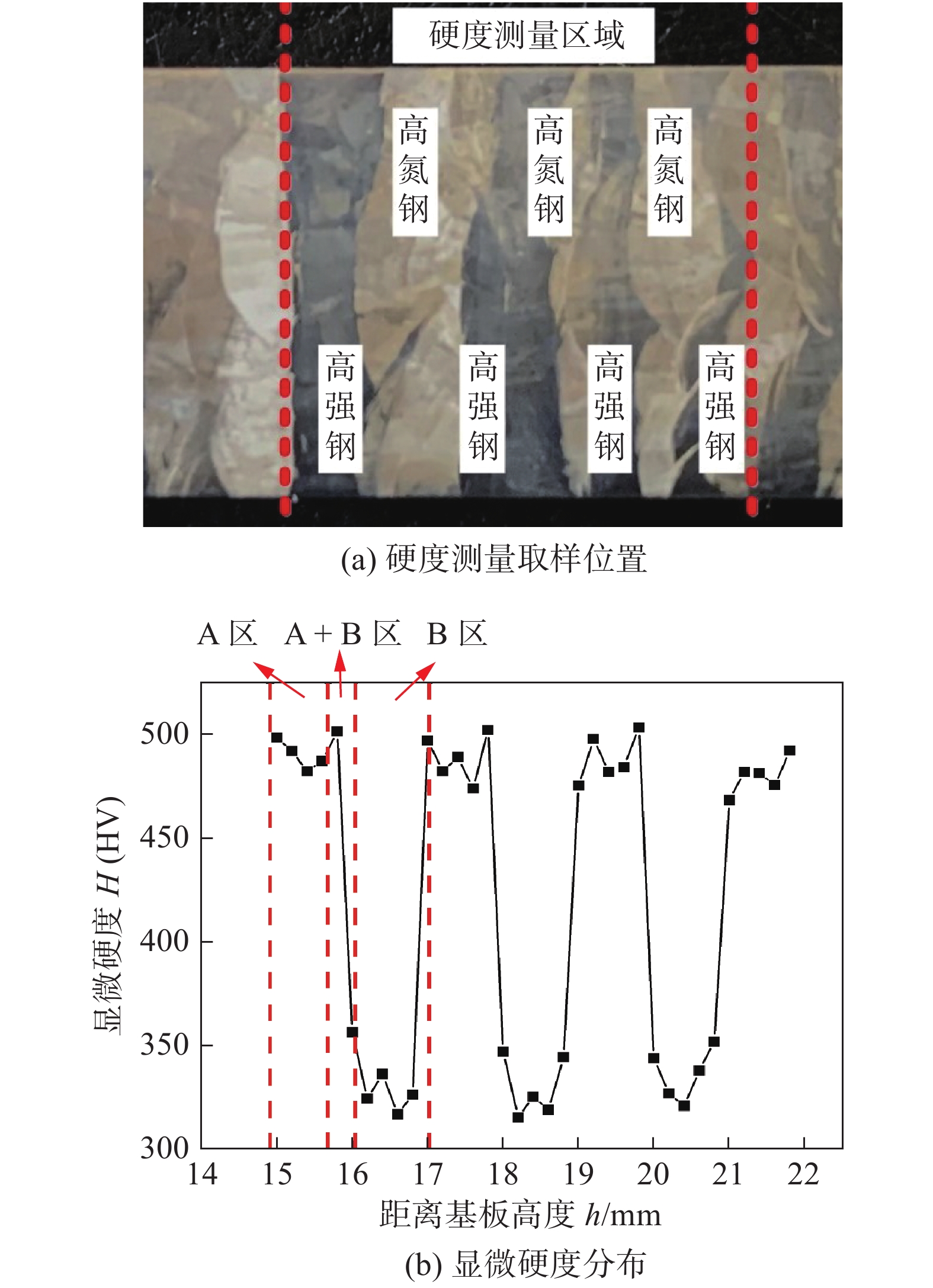
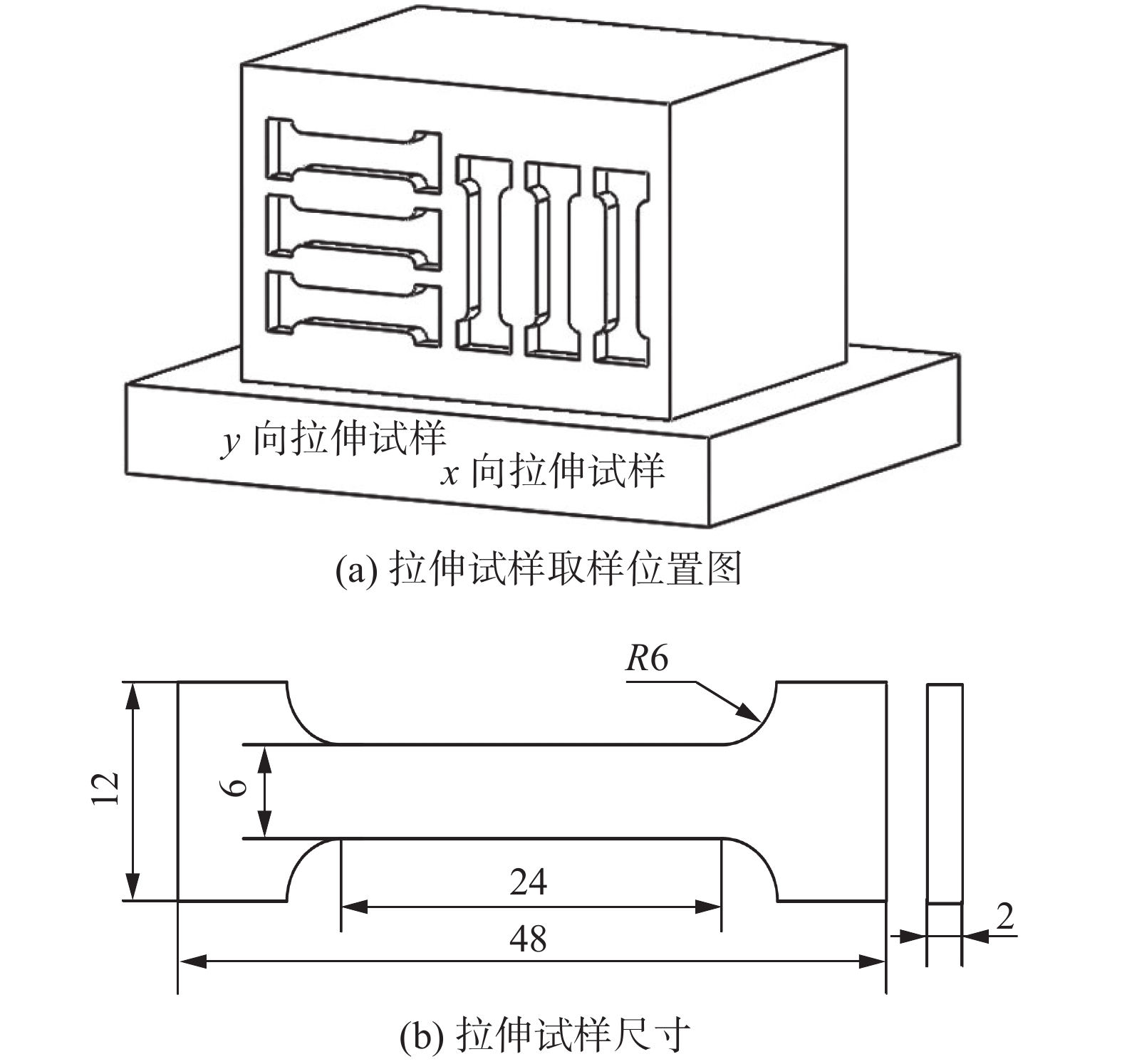
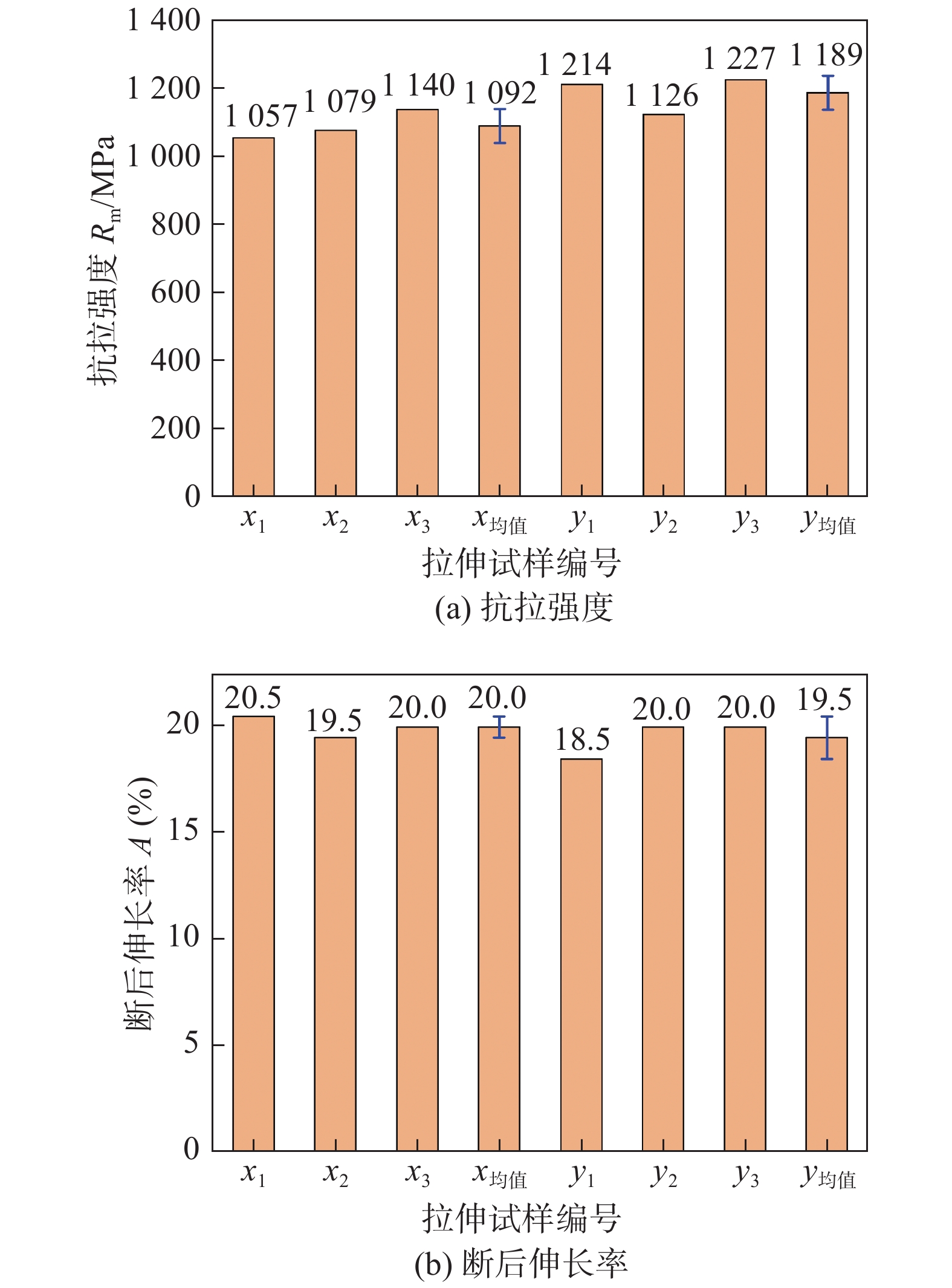
摘要: 以18Ni高强钢和高氮奥氏体不锈钢为丝材,采用等离子弧增材制造高强钢-高氮钢双金属交织结构,通过对高强钢-高氮钢双金属交织结构的微观组织观察、显微硬度及抗拉强度等力学性能试验研究了双金属交织结构的组织转变特征及其与力学性能关系. 结果表明,在高氮钢区域显微组织主要为奥氏体等轴晶及树枝晶,高强钢区域为板条状马氏体. 高强钢区域硬度变化范围为480 ~ 500 HV;高氮钢区域硬度变化范围为310 ~ 320 HV. 拉伸试验结果表明,交织结构在x向抗拉强度均值为1 092 MPa,略低于y向抗拉强度1 189 MPa;x向断后伸长率均值为20.0%,与y向断后伸长率19.5%相差不大;断口呈暗灰色、明显纤维状,分布有大量的等轴韧窝,韧窝尺寸大而深,断口边缘存在明显剪切唇区,属于韧性断裂.Abstract: Using 18Ni high strength steel and high nitrogen austenitic stainless steel as wires, bimetallic intertexture structure of high strength steel and high nitrogen steel was fabricated by plasma arc additive manufacturing. The microstructure and mechanical properties of bimetallic intertexture structure of high strength steel and high nitrogen steel were studied by microstructure observation, microhardness and tensile strength test. The results indicate that the microstructure in high nitrogen steel region are mainly equiaxed crystals and dendrite of austenite, the microstructure of high strength steel area is lath martensite. The hardness of the high strength steel area varies from 480 to 500 HV, the hardness of high nitrogen steel area varies from 310 to 320 HV. The tensile test results show that the average tensile strength of the intertexture structure in the x direction is 1 092 MPa, which is slightly less than the tensile strength in the y direction of 1 189 MPa. The average elongation after fracture in the x direction is 20.0%, which is not much different from the elongation after fracture in the y direction which is 19.5%. The fracture presents dark gray and obviously fibrous, with a large number of equiaxed dimples distributed, the dimples are large and deep, and there is an obvious shear lip area on the edge of the fracture, which is a ductile fracture.
-
-
表 1 丝材与基板化学元素组成(质量分数,%)
Table 1 Chemical component of wire and substrate
材料 Ni Mo Co Cr N Mn Ti C Fe 基板 8.0 — — 18 — 2.0 — 0.08 余量 丝材1 5.37 2.38 — 21 0.58 6.85 — 0.027 余量 丝材2 18 4.6 11.5 — — 0.1 1.3 0.03 余量 表 2 等离子弧增材工艺参数
Table 2 Parameters of plasma arc additive manufacturing
增材电流I/A 增材速度v/(cm·min−1) 送丝速度v1/(m·min−1) 离子气流量Q1/(L·min−1) 保护气体流量Q/(L·min−1) 离子气及保护气类型 120 20 0.8 1.2 19 纯Ar 表 3 各点化学元素组成(原子分数,%)
Table 3 Chemical element component of each point
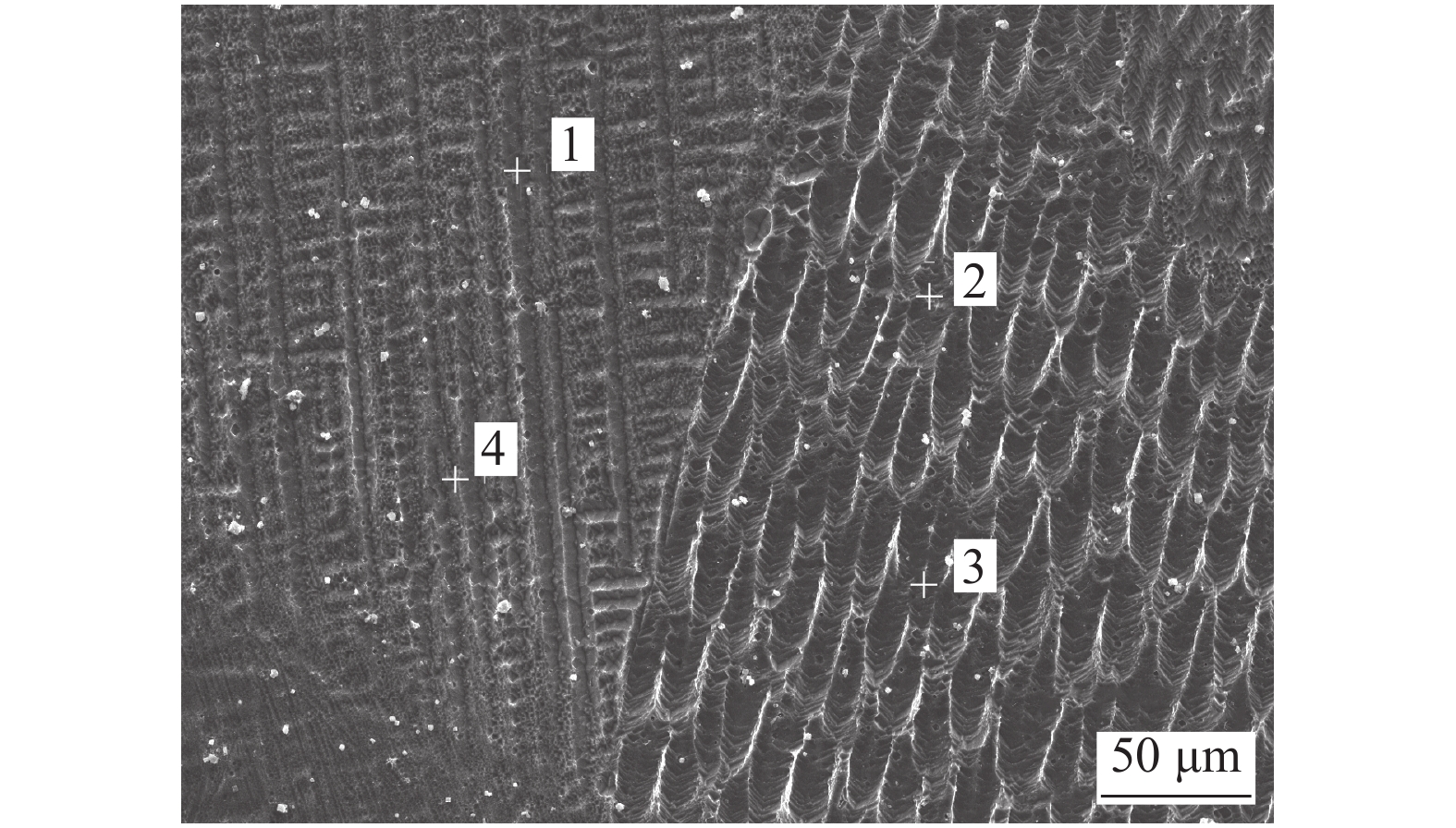
位置 Ni Mo Co Cr Mn Ti Fe 1 18.18 4.71 11.71 — — 1.15 63.09 2 6.37 2.38 — 20.97 6.81 — 62.09 3 4.24 4.51 — 22.76 5.74 — 60.12 4 19.56 5.24 12.01 — — 1.45 61.37 -
[1] 杨东青, 熊涵英, 黄勇, 等. 高氮奥氏体焊丝焊接超高强钢接头组织和性能[J]. 焊接学报, 2020, 41(12): 44 − 48. doi: 10.12073/j.hjxb.20200830001 Yang Dongqing, Xiong Hanying, Hunag Yong, et al. Microstructure and properties of ultra-high strength steel joints welded with high nitrogen austenite wire[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2020, 41(12): 44 − 48. doi: 10.12073/j.hjxb.20200830001
[2] Rajkumar V, Arivazhagan N. Role of pulsed current on metallurgical and mechanical properties of dissimilar metal gas tungsten arc welding of maraging steel to low alloy steel[J]. Materials and Design, 2014, 63: 69 − 82. doi: 10.1016/j.matdes.2014.05.055
[3] 明珠, 王克鸿, 王伟, 等. 焊丝含氮量及焊接电流对高氮钢焊缝组织和性能影响[J]. 焊接学报, 2019, 40(1): 104 − 108. doi: 10.12073/j.hjxb.2019400021 Ming Zhu, Wang Kehong, Wang Wei, et al. Effects of nitrogen content and welding current on microstructure and properties of the weld of high nitrogen austenite steel[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2019, 40(1): 104 − 108. doi: 10.12073/j.hjxb.2019400021
[4] Korobeinikov I, Perminov A, Heller H P, et al. Inert gas atomization of high-nitrogen TRIP-steels[J]. Advanced Engineering Materials, 2019, 21(5): 89 − 97.
[5] Zhang Xiaoyong, Zhou Qi, Wang Kehong, et al. Study on microstructure and tensile properties of high nitrogen Cr-Mn steel processed by CMT wire and arc additive manufacturing[J]. Materials and Design, 2019, 166: 1 − 15.
[6] 李冬杰, 陆善平, 李殿中, 等. 高氮钢焊缝的组织和冲击性能研究[J]. 金属学报, 2013, 49(2): 129 − 136. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1037.2012.00514 Li Dongjie, Lu Shanping, Li Dianzhong, et al. Research on microstructure and impact performance of high nitrogen steel weld[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2013, 49(2): 129 − 136. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1037.2012.00514
[7] Sun Qingjie, Sang Haibo, Liu Yibo, et al. Cross section scan trace planning based on arc additive manufacturing[J]. China Welding, 2019, 28(4): 16 − 21.
[8] Cunningham C R, Flynn J M, Shokrani A, et al. Strategies and processes for high quality wire arc additive manufacturing[J]. Additive Manufacturing, 2018, 22: 672 − 686. doi: 10.1016/j.addma.2018.06.020
[9] Hoefer K, Mayr P. 3DPMD-arc-based additive manufacturing with titanium powder as raw material[J]. China Welding, 2019, 28(1): 11 − 15.
[10] 刘东宇, 李东, 李凯斌, 等. E36 与 304 电子束焊接接头的组织及性能[J]. 航天制造技术, 2014(6): 29 − 33. Liu Dongyu, Li Dong, Li Kaibin, et al. Microstructure and properties of welded joint of E36 steel and 304 stainless steel by electron beam welding[J]. Aeronautical Manufacturing Technology, 2014(6): 29 − 33.
[11] Li J, Li H, Liang Y, et al. The microstructure and mechanical properties of multi-strand, composite welding-wire welded joints of high nitrogen austenitic stainless steel[J]. Materials, 2019, 12(18): 2944 − 2951. doi: 10.3390/ma12182944
[12] 曹嘉明. 电弧熔丝增材制造高强钢零件工艺基础研究[D]. 武汉: 华中科技大学, 2017. Cao Jiaming. Fundamental research on arc fuse additive manufacturing process of high strength steel parts[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong University of Science and Technology, 2017.
-
期刊类型引用(6)
1. 薛龙,毛雪松,黄继强,张瑞英,王瑃. 水下激光修复研究现状与发展趋势. 焊接学报. 2024(04): 120-128+136 .  本站查看
本站查看
2. 尤家玉,胡晨玙,张振海,王晓强,李永清,蔡志海,李竹影. 双相不锈钢水下湿法激光焊接接头组织及其失效行为. 稀有金属材料与工程. 2024(08): 2314-2320 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 巩鹏飞,李亚,柴斐,陈洪胜,高会良,王文先. TC4钛合金真空电子束焊温度场及成形性能. 焊接技术. 2023(08): 35-41+130 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 朱兆剑,韩柯,李洪亮,朱强. Inconel 690局部干法水下激光焊接接头组织及性能研究. 中国激光. 2023(16): 67-78 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 辛锋,文如泉. 卡尔曼级联滤波的激光焊接轨迹跟踪研究与应用. 激光杂志. 2023(11): 204-208 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 周超,李海新,杨振林,姜风春,王琪晨,张文杰. 水下湿法焊接接头质量控制技术研究现状. 焊接. 2021(06): 34-39+60+63 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(3)




 下载:
下载: