Study on erosion resistance of FeCoCrNiB0.2Mox coatings cladded by laser
-
摘要: 为改善钢材表面耐冲蚀性能,采用激光熔覆的方法在Q235基体上制备了高熵合金FeCoCrNiB0.2Mox(x = 0,0.5,1)涂层,使用光学显微镜观察了熔覆层的组织;利用X射线衍射仪分析了合金熔覆层的相组成以及晶格畸变;使用维氏硬度计和自制冲蚀设备,研究了Mo对熔覆层硬度和耐冲蚀性能的影响. 结果表明:FeCoCrNiB0.2Mox熔覆层由树枝晶组成,层间还可以观察到细晶区;由于激光熔覆较快的冷却速率抑制了金属间化合物的析出,高熵合金FeCoCrNiB0.2Mox激光熔覆层完全由单相BCC固溶体组成;FeCoCrNiB0.2Mox激光熔覆层硬度可达600 HV0.2以上;熔覆层耐冲蚀性能优良,冲蚀失重速率小于2.25 × 10−4 g/h;并且随着Mo元素含量的增加,涂层的晶格畸变增加,固溶强化效果更加显著,使得熔覆层硬度上升,因此FeCoCrNiB0.2Mox熔覆层的抗冲蚀性能上升;FeCoCrNiB0.2Mox系列涂层的冲蚀破坏主要以塑性微切削和锻压挤压为主.Abstract: To improve the erosion resistance of the steel, FeCoCrNiB0.2Mox High-entropy alloy coatings were prepared on Q235 steel by laser cladding. An optical microscope was used for structure observation. The phase composition and lattice distortion of the coatings were studied by XRD. The effect of Mo on hardness and erosion resistance were discussed. The results show that: The FeCoCrNiB0.2Mox coatings were composed of dendrites, and fine-grained regions can be observed between the layers. Because the higher cooling rate of laser cladding results an inhibition of the precipitation of intermetallic compounds, the FeCoCrNiB0.2Mox coatings are completely composed of single-phase BCC solid solution. An erosion rate below 2.25 × 10−4 g/h suggested that the FeCoCrNiB0.2Mox high-entropy coatings present a good performance on erosion resistance due to its high hardness which was higher than 600 HV0.2. And with the rise of Mo content, the lattice distortion of the coating becomes more severe, which leading to an increasing on hardness, and improvement of erosion resistance. Meanwhile, the slurry erosion mechanism of the FeCoCrNiB0.2Mox high-entropy coatings is micro-cutting and forging extrusion.
-
Keywords:
- metallic materials /
- high-entropy alloy /
- laser cladding /
- slurry erosion
-
0. 序言
当材料服役于高速流体中时,流体中携带的小颗粒将以一定速度冲击材料表面,对材料表面造成破坏的现象就是冲蚀[1]. 冲蚀将造成材料使用寿命、设备工作效率的大幅降低,增加设备的维护成本,造成资源的浪费[2]. 因此研发耐冲蚀材料,并通过表面处理提高材料的耐冲蚀性能受到了广泛关注[3]. 高熵合金因具有高硬度、优异的耐蚀性耐磨性和耐腐蚀性在能源、航空航天、管道工程等领域具有很高的发展潜力[4-6]. 张冲等人[7]研究了高熵合金FeCoCr0.5NiBSix在高温气体环境中的耐冲蚀性能,发现随着Si含量的增加,高熵合金FeCoCr0.5NiBSix的硬度也随之上升,因此该系列高熵合金的抗高角度冲蚀能力也随着Si含量的增加而升高. 董世知等人[8]的研究表明,WC与Al2O3可以减少机体材料对FeAlCoCrCuTi0.4高熵合金涂层的稀释,提升涂层的硬度,从而提高涂层耐冲蚀性能. 可见通过提高高熵合金的硬度可以在一定程度上提高材料的抗冲蚀能力. 段栋伟[9]则使用激光熔覆技术在675高强钢板上分别制备了Cr3C2-25%NiCr与Fe-Cr-B-Si-C涂层,显著改善了基体的耐冲蚀性能.
随着近年来对高熵合金研究的深入,发现高熵合金中B,Mo元素的加入可以显著提高高熵合金的硬度及耐磨性[10-14]. 但过量的Mo元素会促进金属间化合物的析出,恶化合金的性能[10, 15]. 同时,真空电弧熔炼作为制备高熵合金最为普遍的方法[16-17],该方法不但难以生产尺寸较大、形状复杂的零件,而且增加了贵金属的使用,提高了高熵合金的使用成本,这都限制了高熵合金在实际工程中的应用. 而激光熔覆过程具有高冷速的特点,可以抑制金属间化合物的产生,增加涂层材料的固溶度[18],并且涂层与基体能形成牢固的冶金结合,可以很好地发挥熔覆金属优异的性能[19-20]. 因此,文中利用激光熔覆方法在Q235表面制备了FeCoCrNiB0.2Mox熔覆层,研究了该涂层组织及抗冲蚀性能.
1. 试验方法
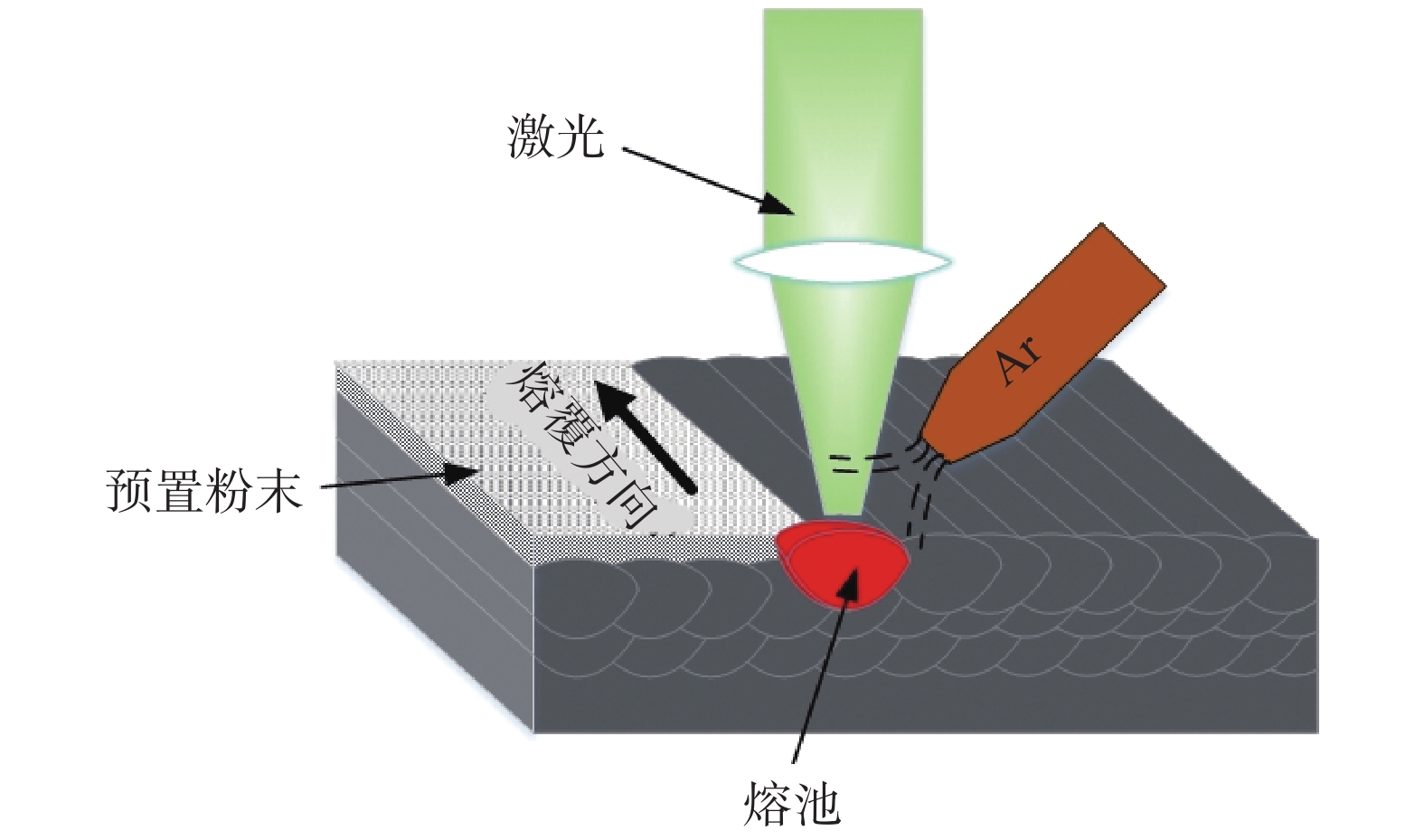
使用纯度高于99.6%的Fe,Co,Cr,Ni,Mo及硼铁粉作为涂层原料,并使用ND7型行星式球磨机对粉末进行24 h小时球磨,使粉末充分均匀混合,球磨罐和磨球均为氧化铝陶瓷,磨球直径为5 ~ 20 mm. 而后使用4.5% (质量分数)聚乙烯醇水溶液作为粘结剂将混合粉末预涂覆于喷砂后Q235基板上. 熔覆前对基板与预置粉末进行200 ℃ × 3 h预热处理,排除粉末中的水分与减少熔覆过程中产生的裂纹和气孔. 如图1所示,使用GD-ECYW300型光纤传输焊接机进行FeCoCrNiB0.2Mox熔覆层的制备,激光熔覆参数如表1所示,熔覆3层,每熔覆一层后均进行喷砂处理,而后根据前文所述步骤进行预置粉末. 熔覆层成分如表2所示. 使用X-ray Pert MPD PRO X射线衍射仪测量熔覆层组织构成,靶材为Cu,使用Kα1作为入射波,激光发生器功率为3 kW,以8°/min的扫描速率对涂层在20° ~ 100°范围内进行扫描. 使用HXD-1000TMC维氏硬度计对熔覆层截面硬度进行测量,测试载荷为1.96 N,保荷时间为15 s. 使用自制冲蚀试验机进行冲蚀试验,冲蚀设备如图2所示,使用120目石英砂作为冲蚀材料,水砂比为15%,冲蚀角为90°,输出转速为560 r/min,试样的线速度为3 m/s. 每冲蚀1 h后取出试样进行清洗、称重. 使用工具显微镜观察经2,4 h冲蚀后试样表面形貌,并分析冲蚀机理.
表 1 激光熔覆参数Table 1. Cladding parameters激光功率P/W 脉冲频率f/Hz 扫描速率v/(mm·min−1) 搭接率δ(%) 氩气流量q/(L·min−1) 300 24 140 50 10 表 2 FeCoCrNiB0.2Mox熔覆层所用化学成分Table 2. Chemical composition of FeCoCrNiB0.2Mox high-entropy alloys coating涂层 Fe Co Cr Ni B Mo 质量分数
w(%)摩尔比
n质量分数
w(%)摩尔比
n质量分数
w(%)摩尔比
n质量分数
w(%)摩尔比
n质量分数
w(%)摩尔比
n质量分数
w(%)摩尔比
nFeCoCrNiB0.2 24.5 1 25.9 1 22.8 1 25.8 1 0.9 0.2 — — FeCoCrNiB0.2Mo0.5 20.3 1 21.4 1 18.9 1 21.3 1 0.8 0.2 17.4 0.5 FeCoCrNiB0.2Mo 17.3 1 18.2 1 16.1 1 18.1 1 0.7 0.2 29.7 1 2. 试验结果及分析
2.1 组织与物相分析
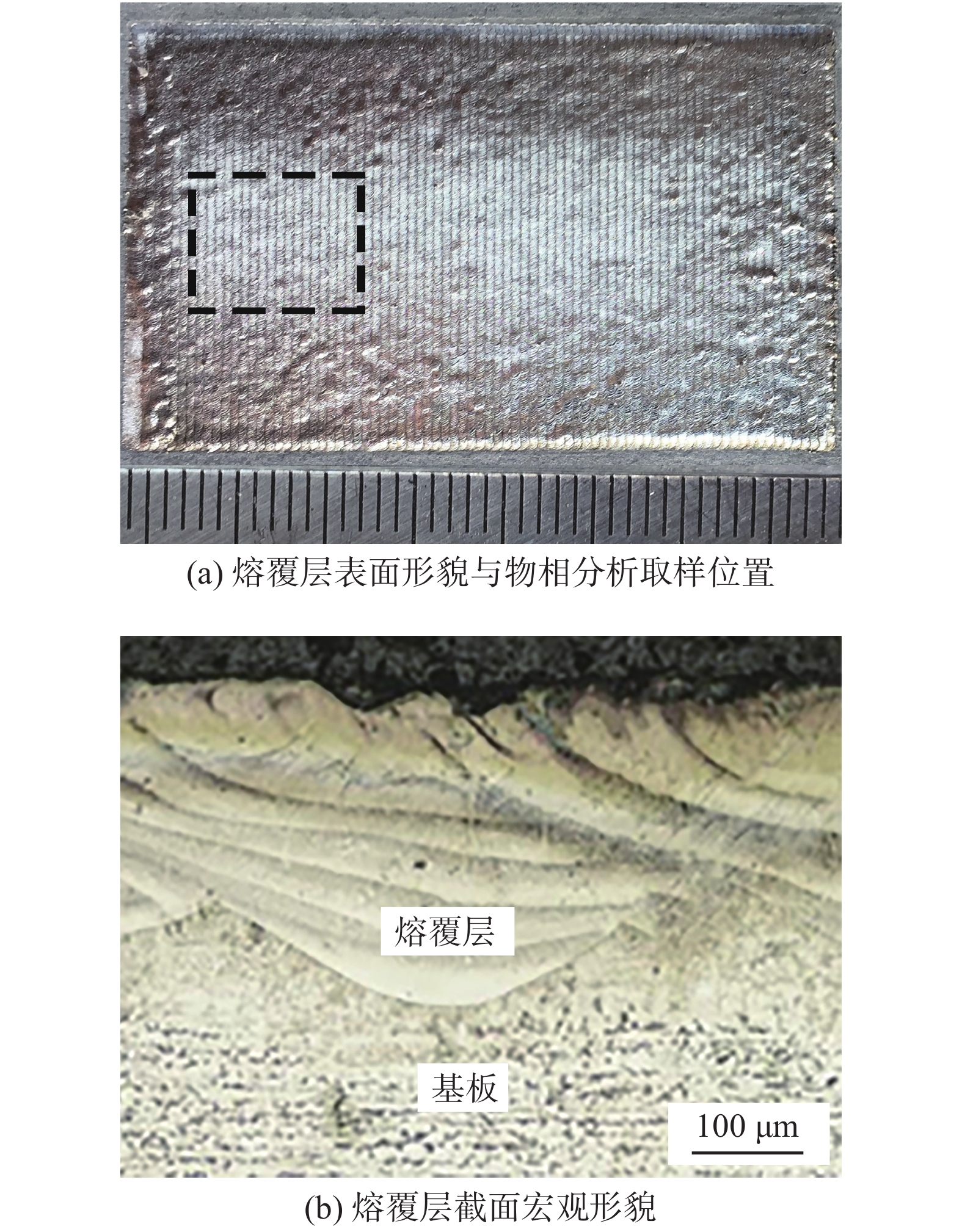
图3为高熵合金熔覆层形貌. 如图3a所示,熔覆层表面光洁度高,富有银白色金属光泽,无明显宏观裂纹与气孔. 图3b显示了熔覆层的截面宏观形貌,熔覆层与基板形成致密牢固的冶金结合,无裂纹、气孔等缺陷. 如图4所示,由于激光加热预置的合金粉与前道熔覆层使其熔化混合,形成熔池,并使前道熔覆层靠近熔合线位置的晶粒得到细化,同时熔池底部原熔覆层半熔化晶粒表面与熔池金属液具有相同的结构,减少了界面能,成为熔池中金属液非均匀形核有利位置. 晶核形成之后,晶粒垂直熔合线向熔池中心生长. 黄延禄等人[21]对激光熔覆过程的温度场进行了研究,发现激光熔覆过程中熔池表面金属液的凝固速度(R)最大,熔池底部的凝固速度最小,而温度梯度(G)的分布与凝固速度相反,呈底部最大,表面最小,自底部向表面递减. 但是高熵合金所含合金元素较多,近似于溶质浓度很大的合金,因此在
$G/\sqrt R$ 很大的熔覆层底部,熔覆层晶粒以树枝晶的形式生长.高熵合金FeCoCrNiB0.2Mox熔覆层XRD衍射图谱及标定结果如图5所示. 从图中可以看出,FeCoCrNiB0.2Mox高熵合金熔覆层在44°,65°和81°左右产生高陡而且尖锐的特征峰. 参比标准XRD衍射卡片可以判断该系合金由BCC单相固溶体组成. 由于在XRD图谱中没有发现与硼化物(M3B)对应的衍射峰出现,可以判断合金涂层中的B元素完全以间隙原子或置换原子的形式固溶在合金中,并没有以硼化物形式析出.
由于试样中晶格畸变存在,会导致XRD峰型宽化,并且试样中晶格畸变与Bragg衍射角与峰型宽度可以用式(1)表示,即
$$\varepsilon = \frac{{\Delta \beta }}{{229.2 {\rm{tan}}\theta }}$$ (1) 式中:ε为晶格畸变;Δβ为添加不同含量Mo元素后积分宽度变化;θ为Bragg衍射角. β的计算,先用Voigt型函数拟合XRD峰型,并计算峰型半高宽(2
${\omega _{\rm{V}}}$ )与积分宽度$\;{\beta _{\rm{V}}}$ ,而后根据经验式(2)计算所得[22],即$$\frac{\beta }{{{\beta _{\rm{V}}}}} = {{{b}}_0} + {{{b}}_{0.5}}\sqrt {\left( {\varphi - \frac{2}{{\text{π}} }} \right)} + {{{b}}_1}\varphi + {{{b}}_2}{\varphi ^2}$$ (2) 式中:b0 = 0.640 2;b0.5 = 1.418 7;b1 =−2.204 3;b2 = 1.870 6;φ =
${{2{\omega _{\rm{V}}}} / {{\beta _{\rm{V}}}}}$ .$$\Delta \beta = \sqrt {\left( {{\beta _0}^2 - {\beta _x}^2} \right)} $$ (3) 式中:β0为不含Mo元素试样的积分宽度;βx为Mo元素摩尔比分别为x (x = 0.5,1)时的熔覆层的积分宽度.
表3显示了3种熔覆层的平均晶格畸变量. 由表3可以看出,加入Mo元素后,衍射峰均向小角度侧发生偏移,并且晶格畸变程度增加. 这表明大半径Mo原子(原子半径为139 pm)以置换固溶体的形式进入到原有晶胞中,替代了原子半径较小的Fe,Co,Cr和Ni原子(原子半径分别为126,125,128和124 pm)的节点位置,使周围原子受到挤压,导致原子排列更加紧密,晶面间距变大,呈现膨胀畸变特征. 同时,由表3还可以看出低指数晶面(1 1 0)发生晶格畸变的程度小于高指数晶面(2 1 1). 随着Mo元素含量的增加,被置换的晶格节点增多,晶格畸变也更加严重.
表 3 高熵合金FeCoCrNiB0.2Mox熔覆层衍射峰特征参数与晶格畸变Table 3. Diffraction peak characteristic parameters and lattice distortion of FeCoCrNiB0.2Mox coating试样 衍射峰特征参数 (1 1 0) (2 1 1) FeCoCrNiB0.2 2θ 44.57 82.05 2ωV 0.524 75 0.841 14 βV 0.524 75 0.841 14 2ωV/βV 1 1 β0 0.857 072 1.059 625 FeCoCrNiB0.2Mo0.5 2θ 44.46 81.99 2ωV 0.528 1.049 48 βV 0.515 78 0.873 73 2ωV/βV 1.023 692 1.201 149 β0.5 0.916 243 1.676 132 ε 0.003 449 0.006 513 FeCoCrNiB0.2Mo 2θ 44.33 81.80 2ωV 0.615 05 1.197 99 βV 0.561 97 0.838 05 2ωV/βV 1.094 453 1.429 497 β1 1.147 529 2.470 984 ε 0.008 124 0.011 195 2.2 显微维氏硬度分析
3种熔覆层的显微硬度测试结果如图6所示,FeCoCrNiB0.2Mox的硬度均在600 HV0.2以上,明显高于基体硬度,并且合金涂层的硬度随着Mo元素含量的增加而上升. 这是因为FeCoCrNiB0.2的合金元素种类多,晶格畸变剧烈[23-24],严重阻碍了合金中位错的运动,固溶强化效果显著,使得该高熵合金涂层具有较高硬度. 同时由于多层激光熔覆过程中,后道熔覆层对前道熔覆层的再热作用,细化了后道熔覆层的组织,使得熔覆层中心的硬度略高于熔覆层表面硬度. 由表3与图6还可以推断,加入Mo元素之后,加剧了熔覆层的晶格畸变程度,从而提高了熔覆层硬度.
2.3 冲蚀失重分析
FeCoCrNiB0.2Mox熔覆层经4 h冲蚀后质量变化及拟合后曲线如图7所示. 由图7可得,经4 h冲蚀后高熵合金FeCoCrNiB0.2Mox熔覆层质量的变化均在毫克级别,质量变化仅占整个试样重量的万分之几,变化极小,这得益于FeCoCrNiB0.2Mox熔覆层极高的硬度. 图7直观地表明,当向高熵合金FeCoCrNiB0.2Mox中加入摩尔比分别为0,0.5,1的Mo元素时,对应试样的冲蚀失重速率(单位时间内的冲蚀失重)分别为2.25 × 10−4,7.5 × 10−5和2.41 × 10−5 g/h. 这表明了高熵合金FeCoCrNiB0.2熔覆层单位时间因冲蚀产生的失重最多,FeCoCrNiB0.2Mo0.5次之,FeCoCrNiB0.2Mo最少. 产生这种现象的原因是由于拥有较大原子半径的Mo元素加入后,挤压周围原子,增加了原有合金熔覆层组织的晶格畸变,对位错运动的阻碍增加,使其抵抗局部变形的能力上升,减小了随液态介质高速运动的硬质颗粒对材料的切削和锻压挤压作用,从而提升了熔覆层抗冲蚀性能.
2.4 冲蚀形貌特征
高熵合金FeCoCrNiB0.2Mox熔覆层经不同时间冲蚀试验后的形貌如图8所示. 由图8a中可以清楚地看出,FeCoCrNiB0.2熔覆层冲蚀破坏处呈现出明显的被切削后留下的划痕,划痕周围存在一定凸起,说明当随流体运动的带有尖锐棱角的硬质颗粒以一定速度冲击材料表面时,尖锐的棱角首先被压入熔覆层,由于砂砾做圆周运动,砂砾所受合外力并不足以提供向心力,受力过程如图9所示. 砂砾向远离转轴中心方向运动,划过材料表面,材料尚具有一定的塑性,被切削后的熔覆层材料部分未脱落,被挤到划痕两侧,留下切削过的划痕. 可以推断出FeCoCrNiB0.2熔覆层塑性较好.
![]() 图 8 冲蚀后高熵合金FeCoCrNiB0.2Mox表面形貌Figure 8. Microscopic morphology of high-entropy FeCoCrNiB0.2Mox after erosion test. (a) FeCoCrNiB0.2 after 2 h of erosion test; (b) FeCoCrNiB0.2 after 4 h of erosion test; (c) FeCoCrNiB0.2Mo0.5 after 2 h of erosion test; (d) FeCoCrNiB0.2Mo0.5 after 4 h of erosion test;(e) FeCoCrNiB0.2Mo after 2 h of erosion test; (f) FeCoCrNiB0.2Mo after 4 h of erosion test
图 8 冲蚀后高熵合金FeCoCrNiB0.2Mox表面形貌Figure 8. Microscopic morphology of high-entropy FeCoCrNiB0.2Mox after erosion test. (a) FeCoCrNiB0.2 after 2 h of erosion test; (b) FeCoCrNiB0.2 after 4 h of erosion test; (c) FeCoCrNiB0.2Mo0.5 after 2 h of erosion test; (d) FeCoCrNiB0.2Mo0.5 after 4 h of erosion test;(e) FeCoCrNiB0.2Mo after 2 h of erosion test; (f) FeCoCrNiB0.2Mo after 4 h of erosion test由图8c可以发现,部分蚀坑周围存在一圈均匀分布的凸起,这说明随流体运动的硬质颗粒接触到FeCoCrNiB0.2Mo0.5熔覆层表面后,首先被压入材料表面,挤压材料表面并留下一个凸出材料的挤压唇. 如图8d所示,经过4 h冲蚀后,FeCoCrNiB0.2Mo0.5熔覆涂层上的蚀坑不但在原有挤压唇的基础上不断扩展,同时也产生了被粒子切削过的犁沟. 随着Mo元素含量的增加,熔覆层材料硬度得到提高,熔覆层抵抗局部变形的能力上升,因而在图8e中,FeCoCrNiB0.2Mo熔覆层上,切削痕迹较浅,蚀坑较小,且未观察到挤压唇的存在. 而在图8f中,FeCoCrNiB0.2Mo熔覆层的蚀坑两侧也发现了材料表面被冲蚀颗粒切削过的犁沟状唇片,这意味着FeCoCrNiB0.2Mo熔覆层在发生冲蚀破坏的过程中也发生了一定程度的塑性变形,即当加入Mo元素摩尔比为1时,高熵合金FeCoCrNiB0.2Mo熔覆层仍具备较好的塑性,冲蚀破坏仍以粒子的微切削作用和锻压挤压为主.
3. 结论
(1)高熵合金FeCoCrNiB0.2Mox熔覆层均由BCC固溶体组成,且B元素能完全固溶到合金中,无第二相存在. 随着Mo元素含量的增加,X射线衍射峰向小角度侧偏移,积分宽度变大,说明Mo元素的加入增加了涂层的晶格畸变.
(2)高熵合金FeCoCrNiB0.2Mox熔覆层硬度可以达到600 HV0.2以上,远高于基体,并与Mo元素加入量呈正相关.
(3)高熵合金FeCoCrNiB0.2Mox熔覆层随着Mo元素含量的增加,冲蚀失重速率下降,冲蚀破坏机制以塑性微切削和塑性锻压挤压为主.
-
图 8 冲蚀后高熵合金FeCoCrNiB0.2Mox表面形貌
Figure 8. Microscopic morphology of high-entropy FeCoCrNiB0.2Mox after erosion test. (a) FeCoCrNiB0.2 after 2 h of erosion test; (b) FeCoCrNiB0.2 after 4 h of erosion test; (c) FeCoCrNiB0.2Mo0.5 after 2 h of erosion test; (d) FeCoCrNiB0.2Mo0.5 after 4 h of erosion test;(e) FeCoCrNiB0.2Mo after 2 h of erosion test; (f) FeCoCrNiB0.2Mo after 4 h of erosion test
表 1 激光熔覆参数
Table 1 Cladding parameters
激光功率P/W 脉冲频率f/Hz 扫描速率v/(mm·min−1) 搭接率δ(%) 氩气流量q/(L·min−1) 300 24 140 50 10 表 2 FeCoCrNiB0.2Mox熔覆层所用化学成分
Table 2 Chemical composition of FeCoCrNiB0.2Mox high-entropy alloys coating
涂层 Fe Co Cr Ni B Mo 质量分数
w(%)摩尔比
n质量分数
w(%)摩尔比
n质量分数
w(%)摩尔比
n质量分数
w(%)摩尔比
n质量分数
w(%)摩尔比
n质量分数
w(%)摩尔比
nFeCoCrNiB0.2 24.5 1 25.9 1 22.8 1 25.8 1 0.9 0.2 — — FeCoCrNiB0.2Mo0.5 20.3 1 21.4 1 18.9 1 21.3 1 0.8 0.2 17.4 0.5 FeCoCrNiB0.2Mo 17.3 1 18.2 1 16.1 1 18.1 1 0.7 0.2 29.7 1 表 3 高熵合金FeCoCrNiB0.2Mox熔覆层衍射峰特征参数与晶格畸变
Table 3 Diffraction peak characteristic parameters and lattice distortion of FeCoCrNiB0.2Mox coating
试样 衍射峰特征参数 (1 1 0) (2 1 1) FeCoCrNiB0.2 2θ 44.57 82.05 2ωV 0.524 75 0.841 14 βV 0.524 75 0.841 14 2ωV/βV 1 1 β0 0.857 072 1.059 625 FeCoCrNiB0.2Mo0.5 2θ 44.46 81.99 2ωV 0.528 1.049 48 βV 0.515 78 0.873 73 2ωV/βV 1.023 692 1.201 149 β0.5 0.916 243 1.676 132 ε 0.003 449 0.006 513 FeCoCrNiB0.2Mo 2θ 44.33 81.80 2ωV 0.615 05 1.197 99 βV 0.561 97 0.838 05 2ωV/βV 1.094 453 1.429 497 β1 1.147 529 2.470 984 ε 0.008 124 0.011 195 -
[1] Javaheri V, Porter D, Kuokkala V T. Slurry erosion of steel – review of tests, mechanisms and materials[J]. Wear, 2018, 408−409: 248 − 273. doi: 10.1016/j.wear.2018.05.010
[2] Yang K, Sun L, Liu Y Z, et al. Erosion–corrosion behavior of austenitic cast iron in an acidic slurry medium[J]. International Journal of Minerals, Metallurgy and Materials, 2015, 22(6): 598 − 603. doi: 10.1007/s12613-015-1112-0
[3] 董世知, 韦宝权, 隋心, 等. FeAlCrCuCoTi0.4高熵合金涂层冲蚀磨损性能[J]. 辽宁工程技术大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 37(2): 376 − 380. Dong Shizhi, Wei Baoquan, Sui Xin, et al. Erosion wear of FeAlCrCuCoTi0.4 high-entropy alloy coating[J]. Journal of Liaoning Technical University (Natural Science), 2018, 37(2): 376 − 380.
[4] Huang T D, Jiang L, Zhang C L, et al. Effect of carbon addition on the microstructure and mechanical properties of CoCrFeNi high entropy alloy[J]. Science China Technological Sciences, 2018, 61(1): 117 − 123. doi: 10.1007/s11431-017-9134-6
[5] Wang H, Ren K, Xie J, et al. Friction and wear behavior of single-phase high-entropy alloy FeCoNiCrMn under MoS2-oil lubrication[J]. Industrial Lubrication and Tribology, 2020, 72(5): 665 − 672.
[6] Lin D Y, Zhang N N, He B, et al. Tribological properties of FeCoCrNiAlB x high-entropy alloys coating prepared by laser cladding[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research International, 2017, 24(2): 184 − 189. doi: 10.1016/S1006-706X(17)30026-2
[7] 张冲, 吴旭晖, 戴品强. FeCoCr0.5NiBSix高熵合金涂层的高温冲蚀磨损性能[J]. 表面技术, 2019, 48(2): 166 − 172. Zhang Chong, Wu Xuhui, Dai Pinqiang. Erosion resistance of FeCoCr0.5NiBSix high entropy alloy coating on high temperature[J]. Surface Technology, 2019, 48(2): 166 − 172.
[8] 董世知, 孟旭, 马壮, 等. WC和Al2O3对氩弧熔覆FeAlCoCrCuTi0.4高熵合金涂层组织和耐冲蚀性能影响[J]. 焊接学报, 2019, 40(7): 127 − 132. doi: 10.12073/j.hjxb.2019400194 Dong Shizhi, Meng Xu, Ma Zhuang, et al. Influence of WC and Al2O3 on microstructure and erosion resistance of FeAlCoCrCuTi0.4 high entropy alloy coating cladded by arc[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2019, 40(7): 127 − 132. doi: 10.12073/j.hjxb.2019400194
[9] 段栋伟. 2种激光熔覆陶瓷金属耐磨涂层的微观结构及性能研究[J]. 材料保护, 2019, 52(8): 95 − 99. Duan Dongwei. Microstructure and properties of two kinds of ceramic-metal wear-resistant coating prepared by laser cladding[J]. Materials Protection, 2019, 52(8): 95 − 99.
[10] Shun T T, Chang L Y, Shiu M H. Microstructure and mechanical properties of multiprincipal component CoCrFeNiMox alloys[J]. Materials Characterization, 2012, 70: 63 − 67. doi: 10.1016/j.matchar.2012.05.005
[11] Nair R B, Selvam K, Arora H S, et al. Slurry erosion behavior of high entropy alloys[J]. Wear, 2017, 386−387: 230 − 238. doi: 10.1016/j.wear.2017.01.020
[12] Shu F, Yang B, Dong S, et al. Effects of Fe-to-Co ratio on microstructure and mechanical properties of laser cladded FeCoCrBNiSi high-entropy alloy coatings[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2018, 450: 538 − 544. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2018.03.128
[13] 张兴华, 孙宇航, 牛牧野, 等. 多主元高熵合金摩擦学性能的研究进展[J]. 材料保护, 2019, 52(11): 119 − 123. Zhang Xinghua, Sun Yuhang, Niu Muye, et al. Review of tribological properties of multi-principal high-entropy alloys[J]. Materials Protection, 2019, 52(11): 119 − 123.
[14] Wang S L, Cui L, He D Y, et al. Effect of molybdenum on the microstructure and wear resistance of hypoeutectic Fe-Cr-B-C hardfacing alloys[J]. China Welding, 2018, 27(4): 46 − 51.
[15] Anburaj J, Mohamed N S S, Narayanan R, et al. Ageing of forged superaustenitic stainless steel: precipitate phases and mechanical properties[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A: Structural Materials Properties Microstructure and Processing, 2012, 535: 99 − 107. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2011.12.048
[16] 李梦娇, 董应虎, 张瑞卿, 等. 高熵合金的制备方法及其应用进展[J]. 航空制造技术, 2019, 62(22): 58 − 63. Li Mengjiao, Dong Yinghu, Zhang Ruiqing, et al. Preparation method and application progress of high-entropy alloy[J]. Aviation Manufacturing Technology, 2019, 62(22): 58 − 63.
[17] 苏允海, 梁学伟, 邓越, 等. FeAlCuCrNiNbx系高熵合金堆焊层的组织及性能分析[J]. 焊接学报, 2020, 41(4): 38 − 43. Su Yunhai, Liang Xuewei, Deng Yue, et al. Microstructure and property analysis of FeAlCuCrNiNbx high-entropy alloy surfacing layer[J]. Transactions of The China Welding Institution, 2020, 41(4): 38 − 43.
[18] Wu W, Jiang L, Jiang H, et al. Phase evolution and properties of Al2CrFeNiMox high-entropy alloys coatings by laser cladding[J]. Journal of Thermal Spray Technology, 2015, 24(7): 1333 − 1340. doi: 10.1007/s11666-015-0303-6
[19] 黄灿, 杜翠薇, 代春朵, 等. 高熵合金涂层的研究进展[J]. 表面技术, 2019, 48(11): 15 − 22, 35. Huang Can, Du Cuiwei, Dai Chunduo, et al. Research progress of high-entropy alloy coatings[J]. Surface Technology, 2019, 48(11): 15 − 22, 35.
[20] 赵盛举, 祁文军, 黄艳华, 等. TC4激光熔覆NiCrCoAlY热循环特性及组织性能[J]. 焊接学报, 2020, 41(9): 89 − 96. doi: 10.12073/j.hjxb.20200521001 Zhao Shengju, Qi Wenjun, Huang Yanhua, et al. Research on thermal cycle characteristics and microstructure performance of TC4 laser cladding NiCrCoAlY[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2020, 41(9): 89 − 96. doi: 10.12073/j.hjxb.20200521001
[21] 黄延禄, 温宝贤, 黄铭. 激光熔覆加工温度场特征与凝固组织形成[J]. 应用激光, 2017, 37(5): 629 − 633. Huang Yanlu, Wen Baoxian, Huang Ming. Characteristics of temperature field in laser cladding and formation of structure during the solidification process[J]. Applied Laser, 2017, 37(5): 629 − 633.
[22] 骆军, 朱航天, 梁敬魁. 晶粒尺寸和应变的X射线粉末衍射法测定[J]. 物理, 2009, 38(4): 267 − 275. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0379-4148.2009.04.008 Luo Jun, Zhu Hangtian, Liang Jingkui. Determination of crystallite and strain by X-ray powder[J]. Physics, 2009, 38(4): 267 − 275. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0379-4148.2009.04.008
[23] Wang F, Inoue A, Kong F L, et al. Formation, thermal stability and mechanical properties of high entropy (Fe,Co,Ni,Cr,Mo)-B amorphous alloys[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2018, 732: 637 − 645. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2017.10.227
[24] Chen T K, Wong M S, Shun T T, et al. Nanostructured nitride films of multi-element high-entropy alloys by reactive DC sputtering[J]. Surface & Coatings Technology, 2005, 200(5−6): 1361 − 1365.
-
期刊类型引用(4)
1. 林添祥,冯美艳,练国富,陈昌荣,兰如清. 合金元素对激光熔覆高熵合金涂层硬度影响的研究进展. 精密成形工程. 2024(05): 201-224 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 张昆,李美求,魏轲,冯鹏云. 抗冲蚀磨损涂层制备技术及机理的研究进展. 焊接. 2022(04): 9-16 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 张志彬,张舒研,陈永雄,高洋洋,梁秀兵. 合金组元与含量对激光熔覆高熵合金涂层的影响研究综述. 中国表面工程. 2021(05): 76-91 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 鲁一荻,张骁勇,彭志刚. 合金元素对激光熔覆高熵合金涂层影响的研究进展. 焊接. 2021(10): 8-14+24+61 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(5)



 下载:
下载: