Pressureless sintering behavior of nano-silver paste for large area chip interconnection
-
摘要: 文中采用化学还原法制备出一种可以用于低温烧结的纳米银膏,通过对低温无压烧结纳米银焊点的组织结构、力学性能和失效模式进行了分析,系统地讨论了无压烧结焊点中烧结银组织的渐进性组织演变规律,获得了互连焊点尺寸对烧结银连接性能和可靠性的影响. 在烧结温度250 ℃,保温时间1 h的条件下,焊点面积小于等于3 mm × 3 mm时,无压烧结焊点强度可以达到70 MPa以上. 随着尺寸的增加,焊点抗剪强度逐渐降低,但焊点尺寸为10 mm × 10 mm时仍然保持20 MPa以上的抗剪强度. 断面形貌表征结果显示,焊点面积越大,烧结银层塑性变形程度越低. 所有尺寸焊点的断面形貌从中心到边缘处均存在渐进性的组织演变,边缘处均呈现剧烈的塑性变形.Abstract: A nano-silver paste which can be used in low temperature sintering was prepared by chemical reduction method. By analyzing the microstructure, mechanical properties and failure modes of pressureless low temperature sintered nano-silver joints, the gradual microstructure evolution of the pressureless sintered silver joints was systematically discussed, and the influence of joint size on the connection performance and reliability of sintered silver was obtained. By heating the joint to 250 ℃ with the sintering time of 1 hour, the shear strength of pressureless sintered joint reached 70 MPa or more when the joint area was less than or equal to 3 mm × 3 mm. As the joint area increased, the shear strength of the solder joint gradually decreased. However, when the solder joint size was 10 mm × 10 mm, the shear strength remained above 20 MPa. The fracture interface morphology showed that the larger the joint area, the lower the plastic deformation of the sintered silver. It was interesting that there was a gradual microstructure evolution from the center to the edge of the joints of all sizes, and violent plastic deformation occurred at the edges.
-
0. 序言
以SiC,GaN为代表的第三代半导体材料具有禁带宽度大、热导率高、饱和电子漂移速率高、临界击穿电场强度高以及抗辐射性能好等优异物理特性,可以实现高温、高频、强辐射的环境下稳定服役,在电动汽车、风力发电和航空航天等领域具有广阔应用前景[1-2]. 电子封装中常用的无铅焊料和导电胶等互连材料,由于其焊接温度高、使用温度有限、导热性差、高温可靠性差等局限[3-4],难以满足第三代半导体材料在应用中对封装材料苛刻要求.
纳米银膏是目前电子领域最具潜力的连接材料. 纳米银具有比表面积大和表面能高的特点,可以在远低于熔点的温度下形成多孔烧结网络,得到高导电导热、力学性能优异、高温稳定性好的烧结体,满足第三代半导体器件低温连接高温服役的需求,得到了广泛的关注和研究[5-6]. 在加热烧结过程中,常施加约1~20 MPa的辅助压力,以促进纳米银颗粒的致密化和烧结银填料层与基体的界面连接[7-8]. 芯片面积越大,需要施加的辅助压力也会随之增加,但是过高的辅助压力可能对芯片表面造成损伤,影响器件性能和产品良率[9]. 因此,实现纳米银膏在低温无压条件下的封装互连将进一步推动第三代半导体在功率模块中的应用.
文中制备了平均粒径为189 nm的纳米银颗粒,用于烧结不同尺寸的纳米银低温无压烧结焊点,通过表征烧结银层的微观组织形貌和显微维氏硬度,对焊点的力学性能和断裂模式进行分析和讨论,获得了无压烧结焊点中烧结组织的渐进性组织演变规律,为无压烧结焊点研究提供了新的理论支撑.
1. 试验方法
1.1 试验试剂
试验原料均为分析纯,硝酸银(AgNO3)购自国药集团化学试剂有限公司;聚乙烯吡咯烷酮(PVP,Mw=58000),抗坏血酸(C6H8O6),氢氧化钠(NaOH)和乙二醇(C2H6O2)购自阿拉丁股份有限公司;乙醇(C2H5OH)购自安徽安特食品股份有限公司;去离子水为实验室自制.
1.2 纳米银膏的制备
采用化学还原法制备纳米银颗粒,具体过程为:称取0.5 g聚乙烯吡咯烷酮和2 g抗坏血酸溶于50 g去离子水中,用0.1 mol/L的NaOH溶液将pH调到9. 称取2 g硝酸银溶于50 g去离子水中. 将硝酸银溶液一次性加入PVP和抗坏血酸混合溶液中,反应1 h. 反应结束后,用离心机分离出纳米银沉淀,用去离子水和无水乙醇分别清洗2次. 将纳米银沉淀置于真空烘箱中干燥,获得纳米银粉末. 将纳米银粉末与乙二醇溶剂按9∶1的比例,用行星式重力搅拌机混合均匀获得纳米银膏.
1.3 无压烧结焊点的制备
烧结试验中,小尺寸焊点选用银基板作为上焊盘与下焊盘,尺寸分别为1.5 mm × 1.5 mm和5 mm × 5 mm,厚度均为0.5 mm. 大尺寸焊点选用铜镀镍银基板作为上焊盘与下焊盘,其中上焊盘尺寸分别为3 mm × 3 mm,5 mm × 5 mm,8 mm × 8 mm,10 mm × 10 mm,下焊盘尺寸均为15 mm × 15 mm,厚度均为1 mm. 将焊盘置于乙醇中超声清洗5 min,取出下焊盘后,将表面的乙醇去除并进行钢网印刷,印刷银膏的面积略大于上焊盘面积. 完成印刷后将上焊盘表贴于印刷后的银膏上,用镊子轻轻按压上焊盘确保上焊盘与印刷银膏之间充分润湿. 将完成贴片的焊点置于烘箱中,以10 ℃/min的速率升温至250 ℃,保温时间1 h.
1.4 纳米银膏和无压烧结焊点的表征和性能测试
采用X射线衍射仪(XRD,D/Max 2500,Rigaku)对制得的纳米银颗粒进行物相分析. 采用扫描电子显微镜(SEM,S4700,Hitachi)对纳米银颗粒的形貌进行表征. 采用热分析仪(STA449,Netzsch)对纳米银颗粒进行差示扫描量热法(DSC)分析.采用SEM对无压焊点截面和断面的微观组织形貌进行表征,并用其附带的X射线能谱仪(EDS)对断面进行成分分析. 采用数显显微维氏硬度计(HVD-100AP)对无压焊点焊缝的硬度分布进行测量,压力荷载为25 g,加载时间为10 s,每个测试点间隔0.5 mm. 采用推拉力测试机(MFM1200)对无压焊点进行抗剪强度的测试.
2. 试验结果及分析
2.1 纳米银颗粒的表征
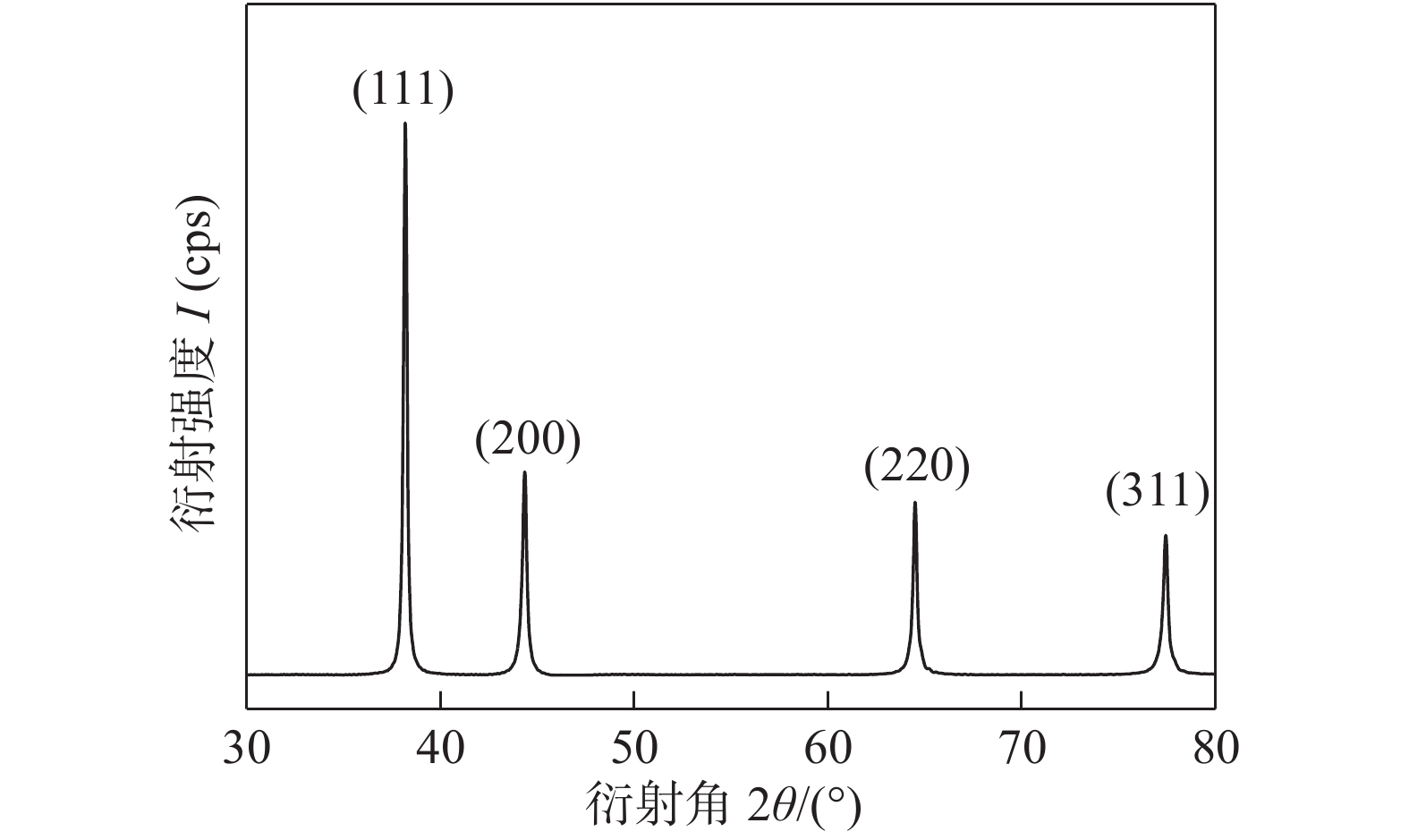
对制得的纳米银颗粒进行XRD物相分析,结果如图1所示. X射线衍射图谱中,在2θ等于38.18°,44.34°,64.5°和77.44°的位置出现了4个明显的衍射峰,分别对应银的PDF标准卡片(JCPDS 04-0783)上的(111),(200),(220)和(311)晶面,说明制备的纳米银颗粒为面心立方结构,结晶性良好,并且没有其它杂质生成.
纳米银颗粒的微观形貌和粒度分布如图2所示. 图2a中SEM表明反应产生的银颗粒形貌均匀,为近球形结构,颗粒之间界限清晰,没有团聚现象的发生,尺寸主要分布在100~300 nm之间,平均直径为189 nm. 在纳米银颗粒的形成和长大过程中,PVP会吸附在颗粒表面,产生空间位阻作用,使银颗粒均匀稳定地分散在溶液中,同时作为银颗粒表面的包覆层,防止银颗粒发生团聚. 图2d中TEM高倍形貌可以看出制备的纳米银颗粒表面的包覆层厚度仅为1~2 nm,较薄的包覆层有利于促进纳米银的烧结过程,减少烧结体中残留的有机物,提高烧结体的性能[10].
通过热分析仪对纳米银颗粒进行热行为分析,获得如图3所示的DSC曲线. 在158和174 ℃处观察到的两个放热峰是纳米银颗粒烧结的放热峰和有机包覆层分解的吸热峰叠加形成的. 对金属颗粒而言,放热峰一般对应非晶态金属颗粒的结晶、不稳定金属颗粒的再结晶或者是加热过程中原子在纳米颗粒表面的扩散[10]. 纳米银颗粒通过原子扩散和再结晶等过程,降低表面能和晶格畸变能,促进烧结颈的形成和长大,对应了DSC曲线中155~190 ℃之间的放热峰. 在167 ℃处出现的吸热峰是由于在纳米银烧结过程中,有机包覆层PVP经过解吸附,然后发生分解,生成CO2和NO2[11].
2.2 无压焊点截面微观组织形貌与显微维氏硬度
图4为1.5 mm × 1.5 mm无压焊点截面不同位置的微观组织形貌,在焊点边缘处,烧结组织和烧结颈明显粗化,形成了粗大且连续的烧结网络,纳米银烧结层与基板之间通过烧结颈形成了可靠的冶金连接. 而焊点中心处的纳米银烧结过程滞后,烧结组织和烧结颈细小,烧结质量较差,纳米银烧结层与基板界面处通过有限的烧结颈连接. 这是由于焊点边缘处的纳米银可以充分与外界进行热交换和空气交换,实现组织的充分扩散与烧结,中心处的纳米银在烧结过程中,溶剂和有机物的挥发和热分解受阻,烧结过程滞后,组织烧结不完全.
根据Castro的研究,纳米银的低温烧结可以分为3个阶段[12]. 第一个阶段是纳米颗粒的接触和烧结颈的形成. 第二个阶段是烧结颈的长大阶段,纳米银颗粒的表面原子向烧结颈扩散使烧结颈长大,颗粒间形成不规则的孔隙,多孔连续烧结网络初具雏形. 第三个阶段是孔隙的球形化和缩小阶段,此时大部分孔隙封闭,不规则的孔隙逐渐发展成球形并不断缩小,甚至消失. 在焊点中心处,纳米银之间通过原子迁移和扩散形成烧结颈,形成了多孔连续烧结网络,但是烧结颈的尺寸较小,平均尺寸为500 nm,烧结组织内的孔隙小而多,孔隙率为14.75%. 在焊点边缘处,烧结颈进一步长大,晶粒粗化,烧结颈的平均尺寸达到1 μm以上,细小的孔隙逐渐球形化并消失,留下较大的孔洞,此时孔隙率为10.45%,烧结组织更加致密.
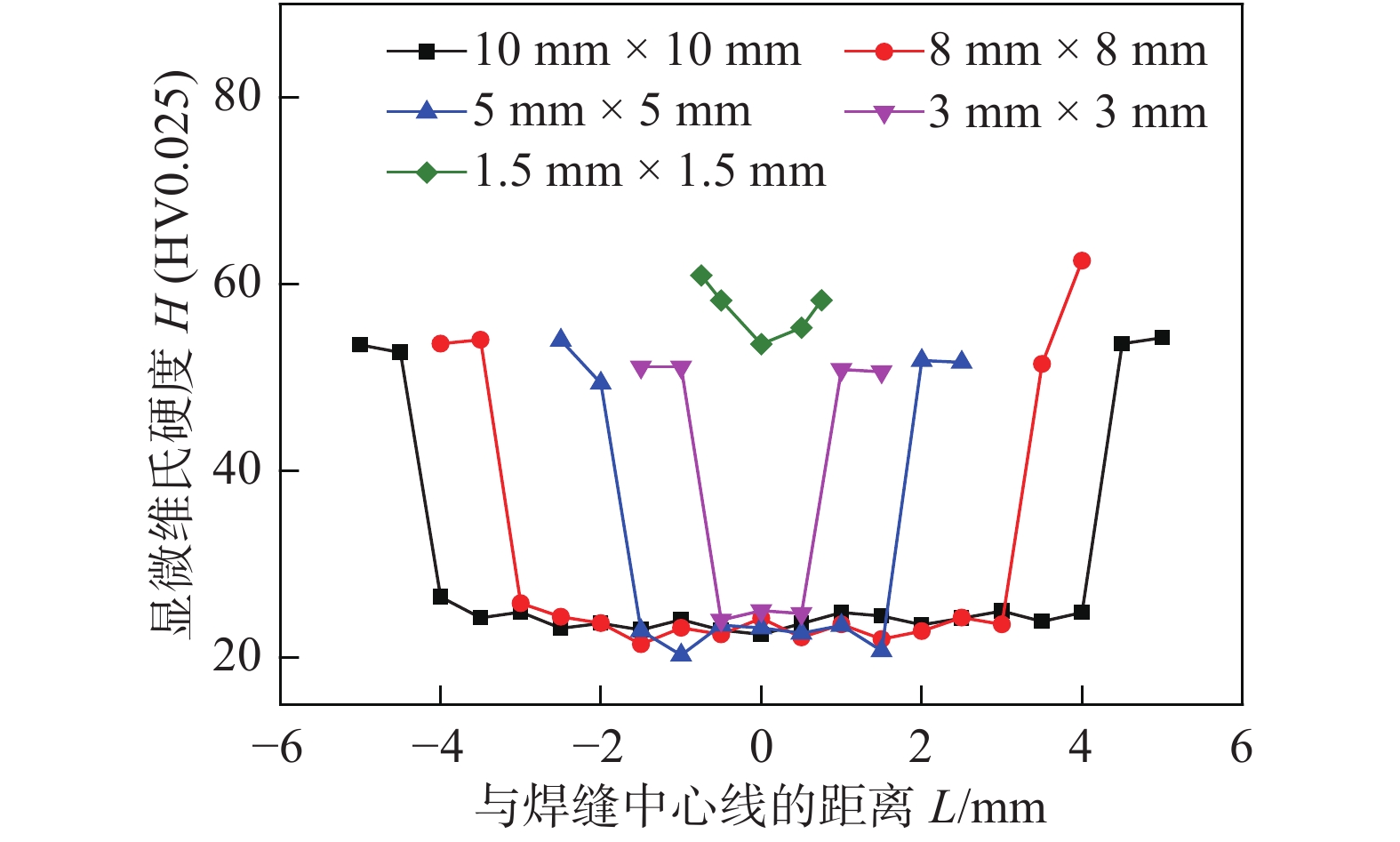
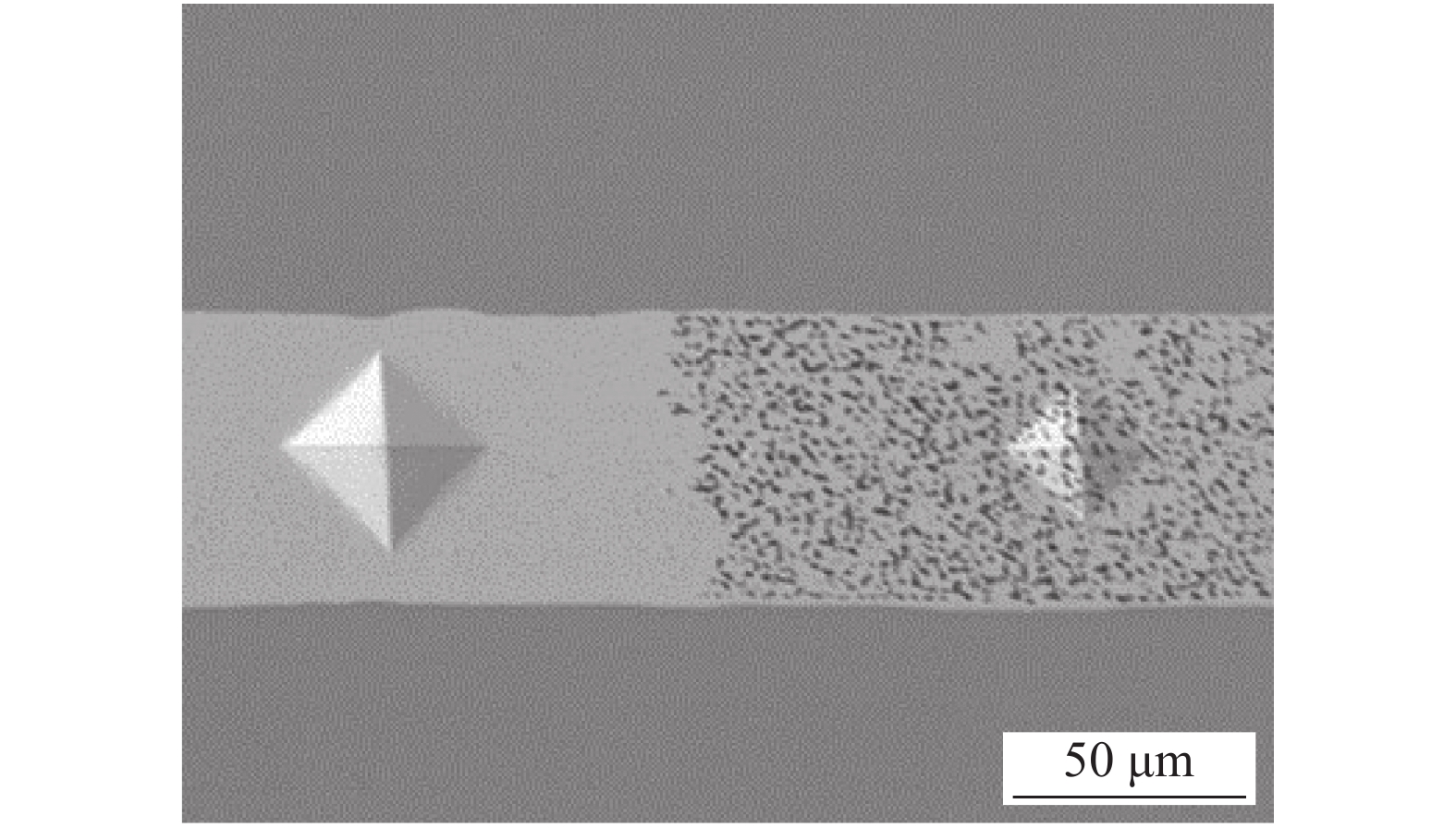
图5为不同面积的无压焊点截面的显微维氏硬度分布. 可以看出,不同面积的无压焊点截面的硬度沿中心呈对称分布. 面积为1.5 mm × 1.5 mm的无压焊点截面的硬度较高,为(50~60) HV0.025,中心处的硬度略低于边缘处. 面积大于3 mm × 3 mm的无压焊点截面中心处的硬度为(20~25) HV0.025,只有边缘处硬度的一半,存在明显的分界线,分界线两边的烧结组织和硬度出现显著的差别,如图6所示. 当焊点面积大于3 mm × 3 mm时,中心处的纳米银与外界热空气交换不充分,烧结过程滞后,烧结组织中的孔隙小而多,使得烧结组织硬度较低,磨抛过程中带来的银颗粒容易将孔隙填充,无法观察到微观组织形貌. 烧结组织和硬度出现显著变化的位置处于距离焊点边缘700 μm ± 200 μm处,当焊点面积增大时,出现组织烧结质量较差的面积比例随之增大.
2.3 保温时间对无压烧结焊点剪切强度的影响
图7是不同保温时间制备的无压烧结焊点的截面微观组织形貌. 可以看出,保温时间为0 min银颗粒就可以实现烧结颈的形成和长大,连成多孔连续烧结网络,烧结银层与基板界面间形成了冶金连接,但是烧结组织较为细小,孔隙多. 延长保温时间可以促进烧结过程中的体积扩散,减少晶体缺陷,提高烧结组织的致密度和均匀性,促进孔隙的球形化和缩小[13]. 结合图3银颗粒的DSC曲线,这是因为250 ℃的烧结温度远高于银颗粒烧结的放热峰和有机物分解的吸热峰温度范围,使得银颗粒具有较大的驱动力,烧结速率高.
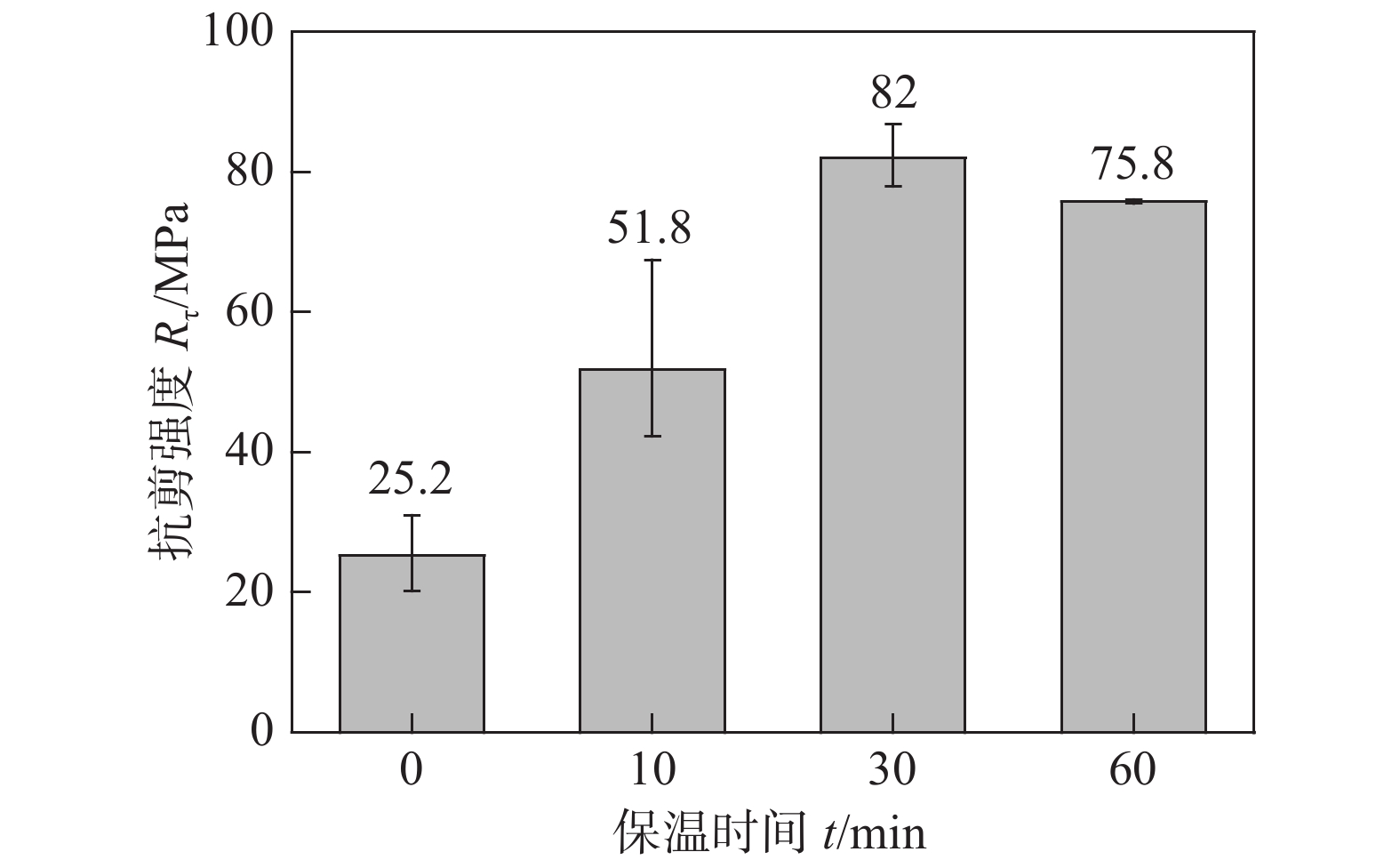
图8为不同保温时间下3 mm × 3 mm无压烧结焊点的抗剪强度. 当保温时间为0 min时,焊点的抗剪强度较低,仅为25.2 MPa. 延长保温时间,焊点的抗剪强度提升明显,保温10 min得到的抗剪强度为51.8 MPa,两倍高于保温时间为0 min的焊点强度. 保温时间达到30 min以上,抗剪强度均高于70 MPa,实现良好的接合. 结合图7a推测,当焊点升温到250 ℃后就停止烧结,银颗粒之间虽然已经通过表面扩散和晶界扩散形成烧结网络,但晶粒之间烧结颈较为细小,孔隙率高,导致抗剪强度较低. 当保温时间达到30 min以上,烧结组织之间体积扩散充分,晶体缺陷浓度降低并趋于稳定,抗剪强度提高.
图9为不同保温时间制备的无压烧结焊点在剪切试验后的断面形貌. 不同保温时间制备的焊点断面均呈现出塑性断裂的特征,烧结组织在剪切力方向上被拉长变形. 保温时间为0和10 min的焊点断裂位置主要发生在烧结银层内靠近上焊盘的界面处,断面变形的烧结组织较为细长,孔隙细小. 保温时间延长至30 min和1 h时,超过一半以上面积在烧结银层内部靠近下焊盘的界面处断裂,发生塑性变形的烧结组织变得粗大,并且烧结组织塑性变形的程度加剧. 增加保温时间可以让银颗粒之间进行充分的扩散和物质转移,获得烧结质量更好的组织.
2.4 焊点面积对无压烧结焊点抗剪强度的影响
图10为不同焊点面积对抗剪强度的影响. 当焊点面积小于3 mm × 3 mm时,无压烧结焊点强度可以达到70 MPa以上. 随着焊点面积的增大,抗剪强度呈现下降的趋势. 当焊点面积达到10 mm × 10 mm时,抗剪强度仍有20 MPa以上. 由于推拉力测试机的测试上限为200 kg,部分面积为8 mm × 8 mm和所有面积为10 mm × 10 mm的无压焊点在达到推拉力测试机的测试上限后,焊点未被破坏,因此可以认为面积为10 mm × 10 mm的无压焊点抗剪强度超过20 MPa.
不同面积的无压焊点进行剪切试验后的断面形貌如图11所示. 从图中可以看出,无压焊点失效位置主要发生在烧结银层内部. 面积为5 mm × 5 mm和8 mm × 8 mm的基板是铜镀镍银基板,断裂位置部分发生在了基板的镀银层与镀镍层之间,如图12所示,说明纳米银烧结层与基板界面形成了可靠的冶金连接,连接强度高于基板镀层之间的连接强度. 随着面积的增大,焊点内部溶剂和有机物的分解和挥发不充分,烧结银层内部出现了大小不一、分布不均匀的孔洞和裂纹,容易造成应力集中.
图13为不同面积的无压焊点的断面形貌,文中分别对边缘处以及中心处的断面微观组织进行形貌观察. 焊点的断裂形式主要为晶内断裂,表现出一定的塑性变形行为. 面积为1.5 mm × 1.5 mm和3 mm × 3 mm的无压焊点抗剪强度均高于70 MPa,焊点中心处的烧结银出现了轻微的塑性变形,随着观察位置向焊点边缘处推移,烧结银塑性变形程度加剧,整体呈现出渐进性的组织变形演变规律. 边缘处的烧结银在应力作用下烧结组织被拉长变形,呈现剧烈的塑性变形,说明边缘处的烧结银组织能承受的极限应力大于中心处的烧结银,同时也对应了边缘处的烧结颈大于中心处烧结颈的这一现象. 当焊点面积增加到5 mm × 5 mm和8 mm × 8 mm时,断面微观组织形貌从中心到边缘仍然呈现渐进性的烧结组织演变规律,但塑性变形程度相较于面积为3 mm × 3 mm的焊点进一步降低,与抗剪强度的降低相对应. 其中8 mm × 8 mm面积的焊点中心处出现了晶间断裂特征,说明中心处组织烧结的滞后性. 随着焊点面积的增大,中心处的溶剂和有机物的挥发和热分解的路径变长,中心出现不均匀烧结组织的占比增加,抗剪断面中塑性变形程度和塑性变形量随之降低.
![]() 图 13 不同面积的无压焊点断面不同位置的微观组织形貌Figure 13. Fracture interface microstructure morphology of the pressureless joints with different areas.(a) 1.5 mm × 1.5 mm center; (b) 1.5 mm × 1.5 mm edge; (c) 3 mm × 3 mm center; (d) 3 mm × 3 mm edge; (e) 5 mm × 5 mm center; (f) 5 mm × 5 mm edge; (g) 8 mm × 8 mm center; (h) 8 mm × 8 mm edge
图 13 不同面积的无压焊点断面不同位置的微观组织形貌Figure 13. Fracture interface microstructure morphology of the pressureless joints with different areas.(a) 1.5 mm × 1.5 mm center; (b) 1.5 mm × 1.5 mm edge; (c) 3 mm × 3 mm center; (d) 3 mm × 3 mm edge; (e) 5 mm × 5 mm center; (f) 5 mm × 5 mm edge; (g) 8 mm × 8 mm center; (h) 8 mm × 8 mm edge3. 结论
(1) 通过化学还原法制备出平均尺寸为189 nm的纳米银颗粒,银颗粒形貌均匀,分散性好,PVP包覆层有效阻止团聚现象的发生.
(2) 保温时间延长,焊点抗剪强度提高; 焊点面积增大,抗剪强度降低. 保温时间达到30 min以上,面积小于3 mm × 3 mm时,无压烧结焊点的抗剪强度高于70 MPa. 当面积达到10 mm × 10 mm时,仍有20 MPa以上的抗剪强度.
(3) 焊点面积越大,断面中烧结银层塑性变形程度越低. 所有尺寸焊点的断面从中心到边缘处均存在渐进性的组织演变,边缘处呈现剧烈的塑性变形.
-
图 13 不同面积的无压焊点断面不同位置的微观组织形貌
Figure 13. Fracture interface microstructure morphology of the pressureless joints with different areas.(a) 1.5 mm × 1.5 mm center; (b) 1.5 mm × 1.5 mm edge; (c) 3 mm × 3 mm center; (d) 3 mm × 3 mm edge; (e) 5 mm × 5 mm center; (f) 5 mm × 5 mm edge; (g) 8 mm × 8 mm center; (h) 8 mm × 8 mm edge
-
[1] Kaminski N, Hilt O. SiC and GaN devices – wide bandgap is not all the same[J]. IET Circuits, Devices & Systems, 2014, 8(3): 227 − 236.
[2] Iwamuro N, Laska T. IGBT history, state-of-the-art, and future prospects[J]. IEEE Transactions on Electron Devices, 2017, 64(3): 741 − 752. doi: 10.1109/TED.2017.2654599
[3] Wang F, Chen H, Huang Y, et al. Recent progress on the development of Sn-Bi based low-temperature Pb-free solders[J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2019, 30(4): 3222 − 3243.
[4] Zhang H, Chen C, Jiu J, et al. High-temperature reliability of low-temperature and pressureless micron Ag sintered joints for die attachment in high-power device[J]. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Electronics, 2018, 29(10): 8854 − 8862. doi: 10.1007/s10854-018-8903-9
[5] Liu W, An R, Wang C, et al. Recent progress in rapid sintering of nanosilver for electronics applications[J]. Micromachines, 2018, 9(7): 346. doi: 10.3390/mi9070346
[6] Fang H, Wang C, Wang T, et al. Pressureless low-temperature sintering of plasma activated Ag nanoparticles for high-power device packaging[J]. Materials Letters, 2019, 256: 126620. doi: 10.1016/j.matlet.2019.126620
[7] Paknejad S A, Mannan S H. Review of silver nanoparticle based die attach materials for high power/temperature applications[J]. Microelectronics Reliability, 2017, 70(3): 1 − 11.
[8] Feng J, Mei Y, Li X, et al. Characterizations of a proposed 3300-V press-pack IGBT module using nanosilver paste for high-voltage applications[J]. IEEE Journal of Emerging and Selected Topics in Power Electronics, 2018, 6(4): 2245 − 2253. doi: 10.1109/JESTPE.2018.2820046
[9] Hong W S, Kim M S, Oh C, et al. Pressureless silver sintering of silicon-carbide power modules for electric vehicles[J]. JOM, 2020, 72(2): 889 − 897. doi: 10.1007/s11837-019-03815-y
[10] Jiu J, Zhang H, Koga S, et al. Simultaneous synthesis of nano and micro-Ag particles and their application as a die-attachment material[J]. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Electronics, 2015, 26(9): 7183 − 7191. doi: 10.1007/s10854-015-3343-2
[11] 王特. 基于表面活化的银纳米焊膏无压低温烧结工艺及机理研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2019. Wang Te. Pressureless low-temperature sintering of silver nano-solder paste based on surface activation[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2019.
[12] Castro R, Benthem K V. Sintering[M]. Springer, 2013.
[13] Wang T, Chen X, Lu G, et al. Low-temperature sintering with nano-silver paste in die-attached interconnection[J]. Journal of Electronic Materials, 2007, 36(10): 1333 − 1340. doi: 10.1007/s11664-007-0230-5
-
期刊类型引用(10)
1. 陈澄,尹红波,王成,倪大海,谢璐,曾超林. 钼铜载体与铝合金外壳的无压纳米银胶低温烧结强度. 半导体技术. 2025(01): 95-100 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 黄玺,张亮,王曦,陈晨,卢晓. 电子封装用纳米级无铅钎料的研究进展. 材料导报. 2024(23): 136-148 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 黄天,甘贵生,刘聪,马鹏,江兆琪,许乾柱,陈仕琦,程大勇,吴懿平. 电子封装低温互连技术研究进展. 中国有色金属学报. 2023(04): 1144-1178 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 官紫妍,吴丰顺,周龙早,李可为,丁立国,李学敏. 功率模块纳米银烧结技术研究进展. 电子工艺技术. 2023(04): 1-6 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 傅必成,方毅,张乐,李道会,齐放,宋利军,祝温泊. Fluxless bonding with silver nanowires aerogel in die-attached interconnection. China Welding. 2023(02): 32-41 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 杜伟,强军锋,余竹焕,高炜,阎亚雯,王晓慧,刘旭亮. 电子封装用纳米复合焊膏的研究进展. 材料导报. 2023(19): 162-172 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 龙旭,种凯楠,苏昱太. 烧结银细观孔隙结构对宏观力学性能的影响. 焊接学报. 2023(12): 15-20+27+137-138 .  本站查看
本站查看
8. 齐苗苗,贺晓斌,刘双宝,杨婉春,祝温泊. Ag-Cu固溶体颗粒制备及低温烧结互连接头性能. 焊接学报. 2022(07): 97-101+119 .  本站查看
本站查看
9. 杨婉春,胡少伟,祝温泊,李明雨. 低温烧结纳米银膏研究进展. 焊接学报. 2022(11): 137-146+169-170 .  本站查看
本站查看
10. 王刘珏,瞿昀昊,吉勇. 颗粒形貌对银焊膏无压烧结行为的影响. 材料导报. 2022(S2): 347-351 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(10)



 下载:
下载: