Pressureless sintering behavior of nano-silver paste for large area chip interconnection
-
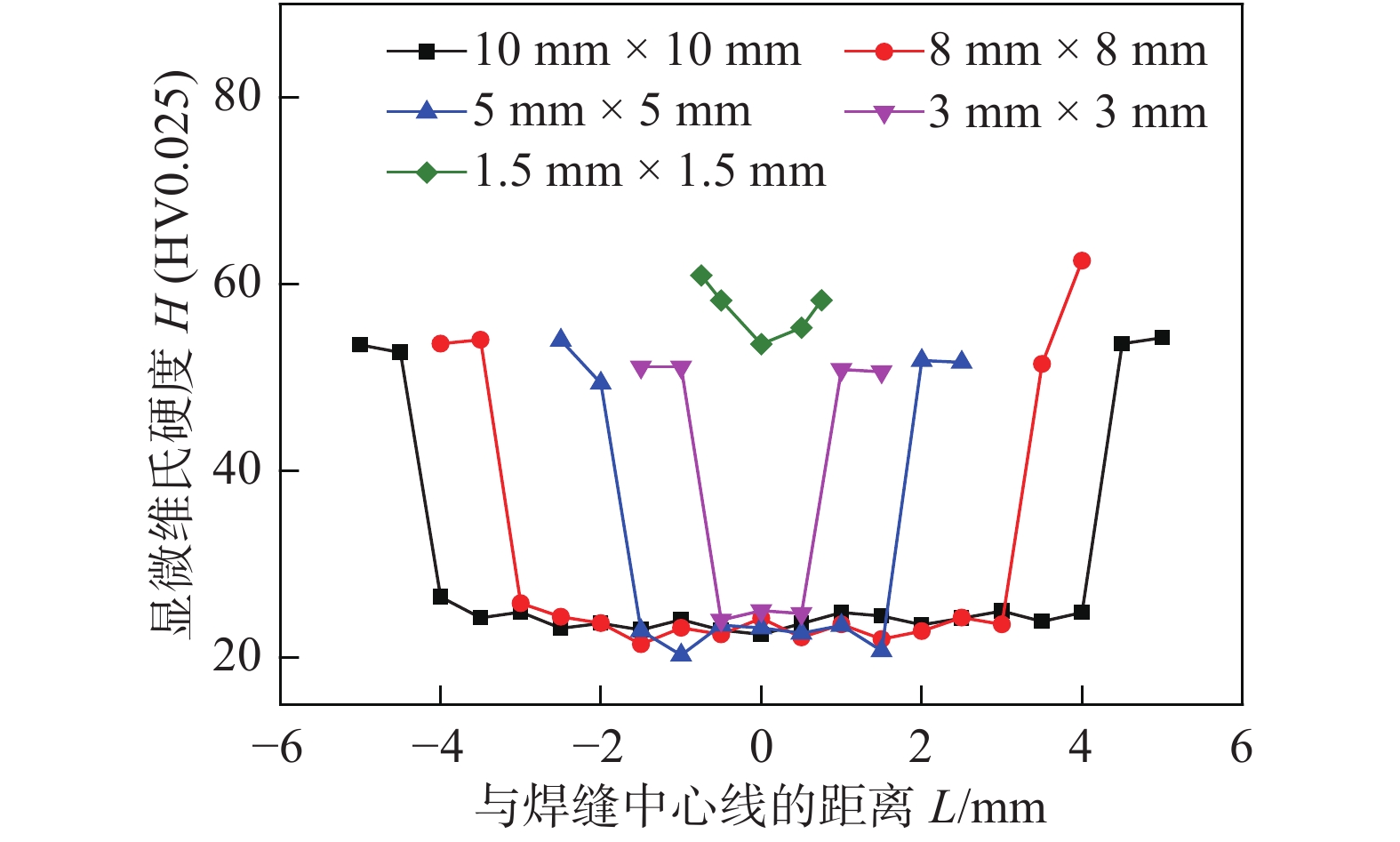
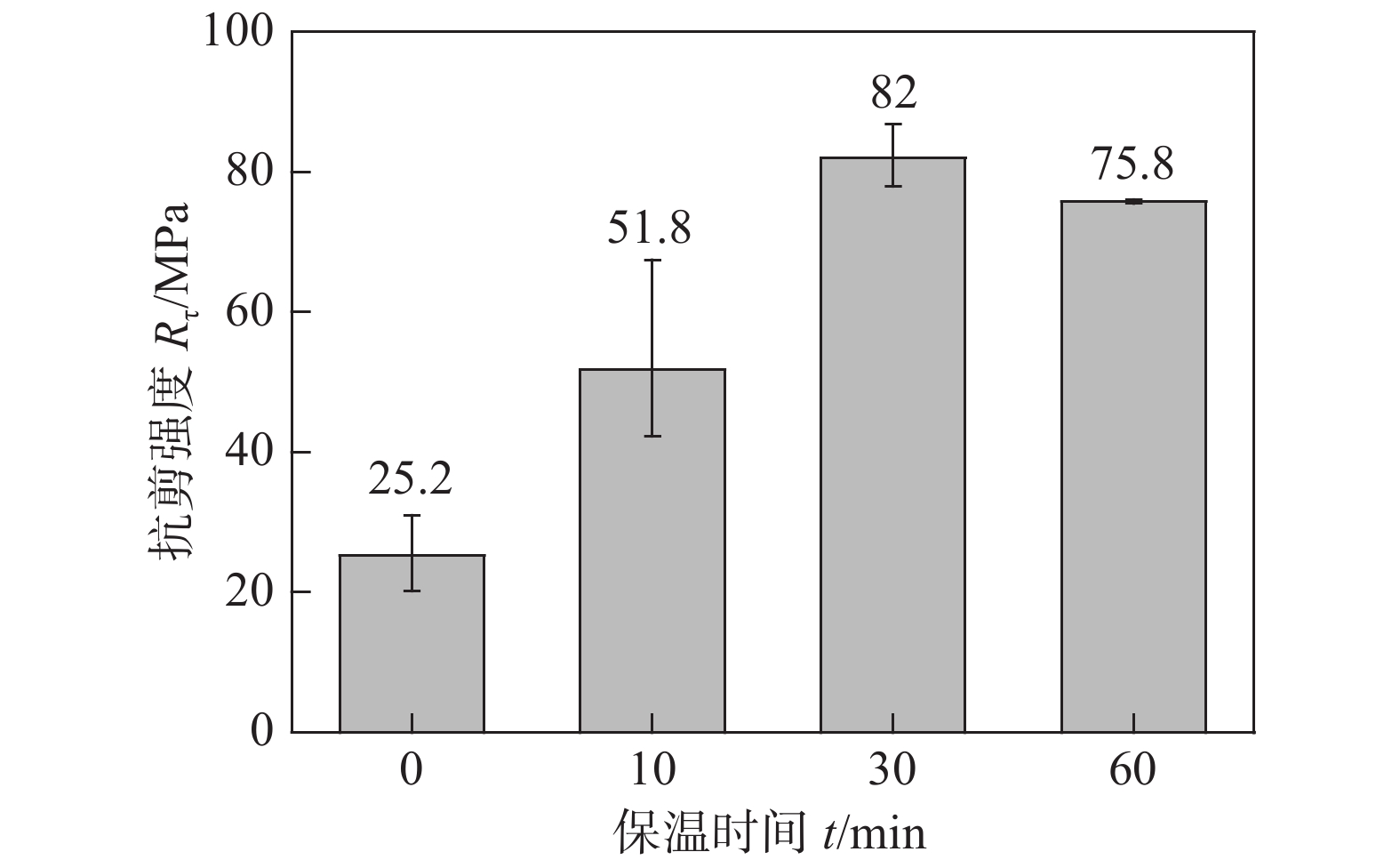
摘要: 文中采用化学还原法制备出一种可以用于低温烧结的纳米银膏,通过对低温无压烧结纳米银焊点的组织结构、力学性能和失效模式进行了分析,系统地讨论了无压烧结焊点中烧结银组织的渐进性组织演变规律,获得了互连焊点尺寸对烧结银连接性能和可靠性的影响. 在烧结温度250 ℃,保温时间1 h的条件下,焊点面积小于等于3 mm × 3 mm时,无压烧结焊点强度可以达到70 MPa以上. 随着尺寸的增加,焊点抗剪强度逐渐降低,但焊点尺寸为10 mm × 10 mm时仍然保持20 MPa以上的抗剪强度. 断面形貌表征结果显示,焊点面积越大,烧结银层塑性变形程度越低. 所有尺寸焊点的断面形貌从中心到边缘处均存在渐进性的组织演变,边缘处均呈现剧烈的塑性变形.Abstract: A nano-silver paste which can be used in low temperature sintering was prepared by chemical reduction method. By analyzing the microstructure, mechanical properties and failure modes of pressureless low temperature sintered nano-silver joints, the gradual microstructure evolution of the pressureless sintered silver joints was systematically discussed, and the influence of joint size on the connection performance and reliability of sintered silver was obtained. By heating the joint to 250 ℃ with the sintering time of 1 hour, the shear strength of pressureless sintered joint reached 70 MPa or more when the joint area was less than or equal to 3 mm × 3 mm. As the joint area increased, the shear strength of the solder joint gradually decreased. However, when the solder joint size was 10 mm × 10 mm, the shear strength remained above 20 MPa. The fracture interface morphology showed that the larger the joint area, the lower the plastic deformation of the sintered silver. It was interesting that there was a gradual microstructure evolution from the center to the edge of the joints of all sizes, and violent plastic deformation occurred at the edges.
-
-
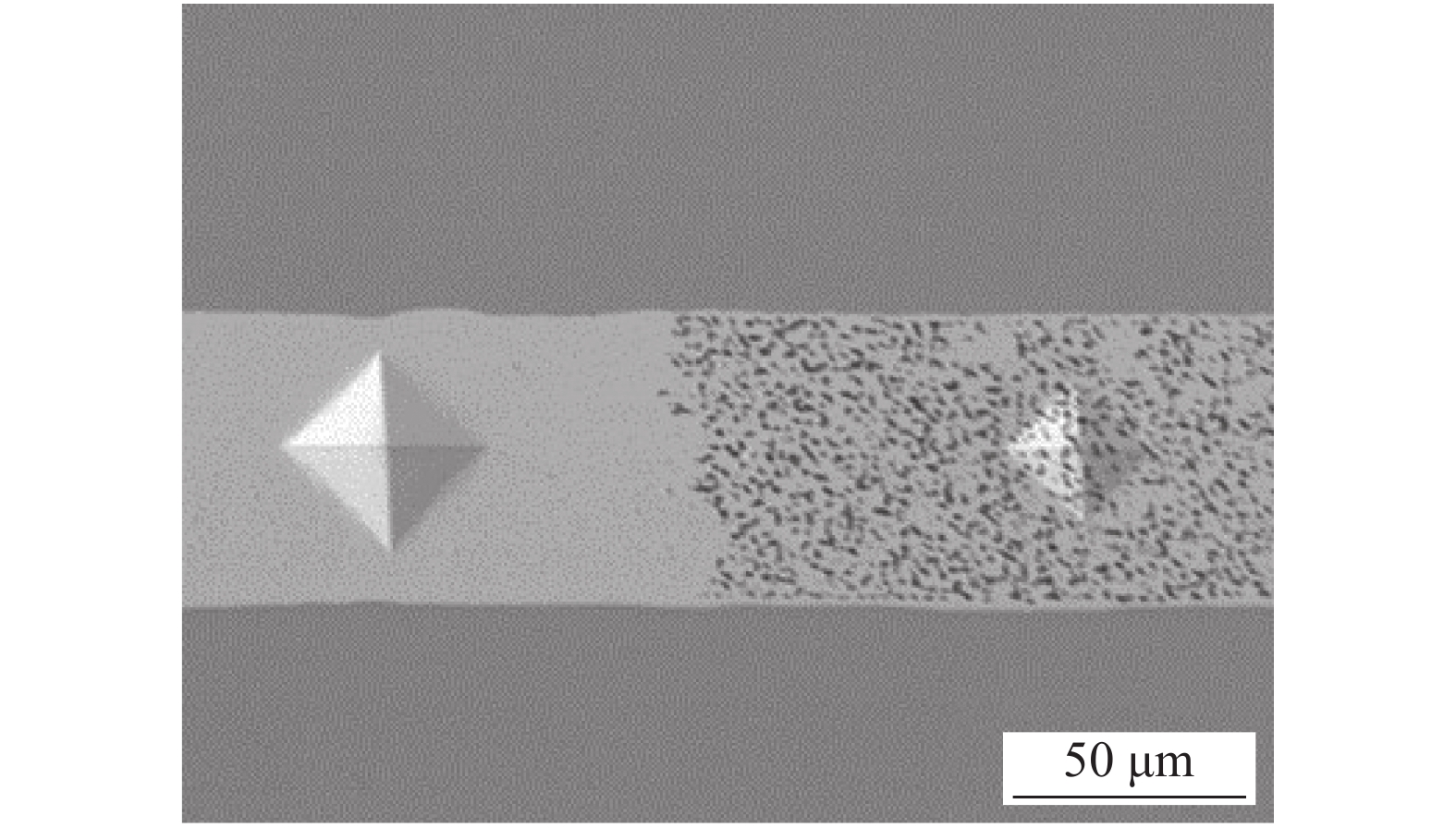
图 13 不同面积的无压焊点断面不同位置的微观组织形貌
Figure 13. Fracture interface microstructure morphology of the pressureless joints with different areas.(a) 1.5 mm × 1.5 mm center; (b) 1.5 mm × 1.5 mm edge; (c) 3 mm × 3 mm center; (d) 3 mm × 3 mm edge; (e) 5 mm × 5 mm center; (f) 5 mm × 5 mm edge; (g) 8 mm × 8 mm center; (h) 8 mm × 8 mm edge
-
[1] Kaminski N, Hilt O. SiC and GaN devices – wide bandgap is not all the same[J]. IET Circuits, Devices & Systems, 2014, 8(3): 227 − 236.
[2] Iwamuro N, Laska T. IGBT history, state-of-the-art, and future prospects[J]. IEEE Transactions on Electron Devices, 2017, 64(3): 741 − 752. doi: 10.1109/TED.2017.2654599
[3] Wang F, Chen H, Huang Y, et al. Recent progress on the development of Sn-Bi based low-temperature Pb-free solders[J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2019, 30(4): 3222 − 3243.
[4] Zhang H, Chen C, Jiu J, et al. High-temperature reliability of low-temperature and pressureless micron Ag sintered joints for die attachment in high-power device[J]. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Electronics, 2018, 29(10): 8854 − 8862. doi: 10.1007/s10854-018-8903-9
[5] Liu W, An R, Wang C, et al. Recent progress in rapid sintering of nanosilver for electronics applications[J]. Micromachines, 2018, 9(7): 346. doi: 10.3390/mi9070346
[6] Fang H, Wang C, Wang T, et al. Pressureless low-temperature sintering of plasma activated Ag nanoparticles for high-power device packaging[J]. Materials Letters, 2019, 256: 126620. doi: 10.1016/j.matlet.2019.126620
[7] Paknejad S A, Mannan S H. Review of silver nanoparticle based die attach materials for high power/temperature applications[J]. Microelectronics Reliability, 2017, 70(3): 1 − 11.
[8] Feng J, Mei Y, Li X, et al. Characterizations of a proposed 3300-V press-pack IGBT module using nanosilver paste for high-voltage applications[J]. IEEE Journal of Emerging and Selected Topics in Power Electronics, 2018, 6(4): 2245 − 2253. doi: 10.1109/JESTPE.2018.2820046
[9] Hong W S, Kim M S, Oh C, et al. Pressureless silver sintering of silicon-carbide power modules for electric vehicles[J]. JOM, 2020, 72(2): 889 − 897. doi: 10.1007/s11837-019-03815-y
[10] Jiu J, Zhang H, Koga S, et al. Simultaneous synthesis of nano and micro-Ag particles and their application as a die-attachment material[J]. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Electronics, 2015, 26(9): 7183 − 7191. doi: 10.1007/s10854-015-3343-2
[11] 王特. 基于表面活化的银纳米焊膏无压低温烧结工艺及机理研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2019. Wang Te. Pressureless low-temperature sintering of silver nano-solder paste based on surface activation[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2019.
[12] Castro R, Benthem K V. Sintering[M]. Springer, 2013.
[13] Wang T, Chen X, Lu G, et al. Low-temperature sintering with nano-silver paste in die-attached interconnection[J]. Journal of Electronic Materials, 2007, 36(10): 1333 − 1340. doi: 10.1007/s11664-007-0230-5
-
期刊类型引用(5)
1. 王通,孟惠民,葛鹏飞,李全德,巩秀芳,倪荣,姜英,龚显龙,戴君,隆彬. 2Cr-1Ni-1.2Mo-0.2V钢在NH_4H_2PO_4溶液中的电化学腐蚀行为研究. 中国腐蚀与防护学报. 2022(04): 551-562 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 苍雨,黄毓晖,翁硕,轩福贞. 环境变量对核电汽轮机转子钢焊接接头电偶腐蚀性能的影响. 中国腐蚀与防护学报. 2021(03): 318-326 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 黄毓晖,张建辉,胡语林,孙雯暄,徐宇斌,汪毅豪. 核电汽轮机转子堆焊焊接接头的电偶腐蚀行为及有限元仿真. 焊接学报. 2021(08): 33-39+99 .  本站查看
本站查看
4. 陈君,康凯,冯钜,熊长奇,曹丹,尹杰. 压水堆核电站结构材料的腐蚀行为研究进展. 西华大学学报(自然科学版). 2020(03): 104-112 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 黄毓晖,司晓法,翁硕,轩福贞. 疲劳损伤对核电汽轮机焊接转子接头应力腐蚀开裂敏感性的影响. 焊接学报. 2020(04): 12-19+37+97-98 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(3)



 下载:
下载: