Microstructure and properties of ultra-high strength steel joints welded with high nitrogen austenite wire
-
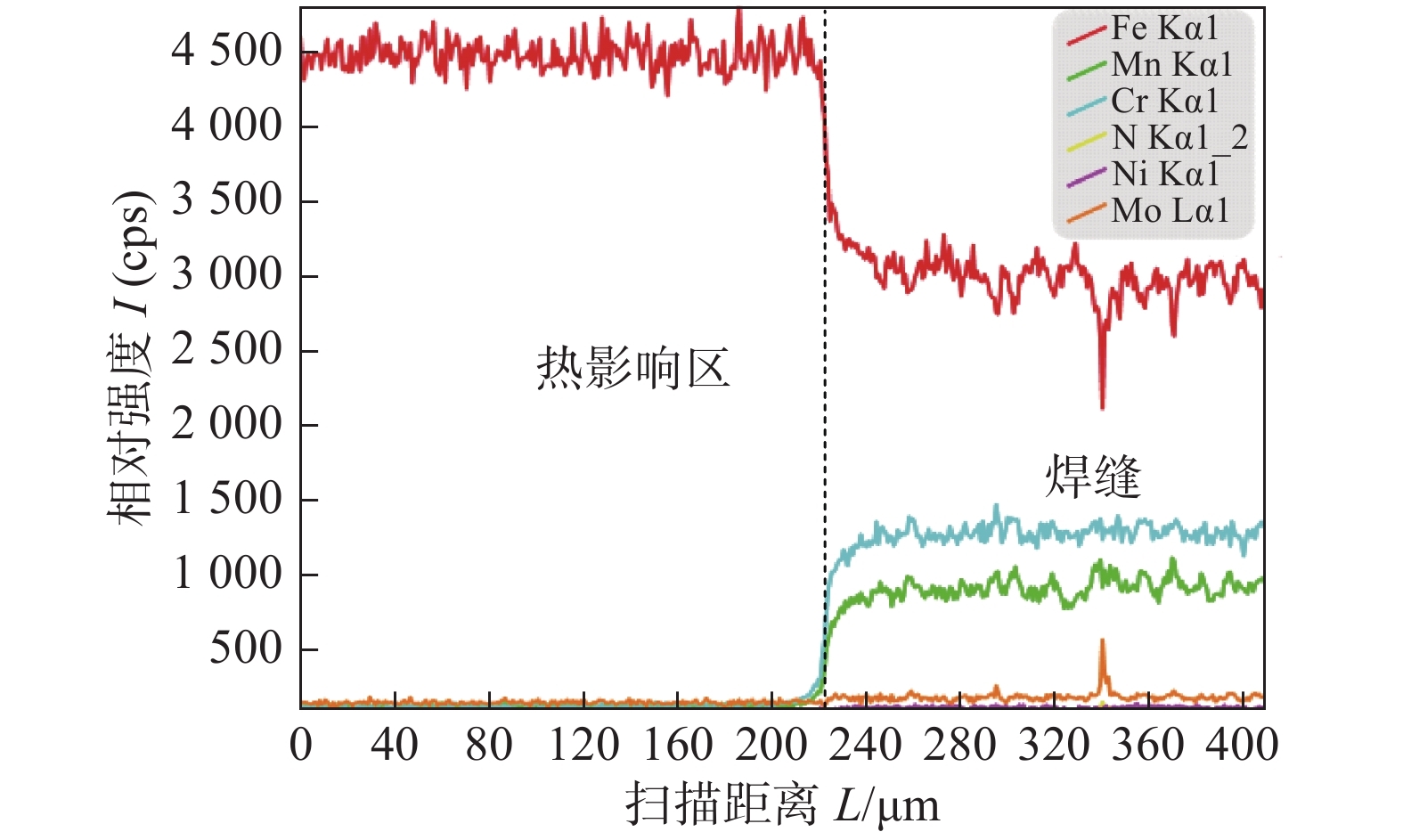
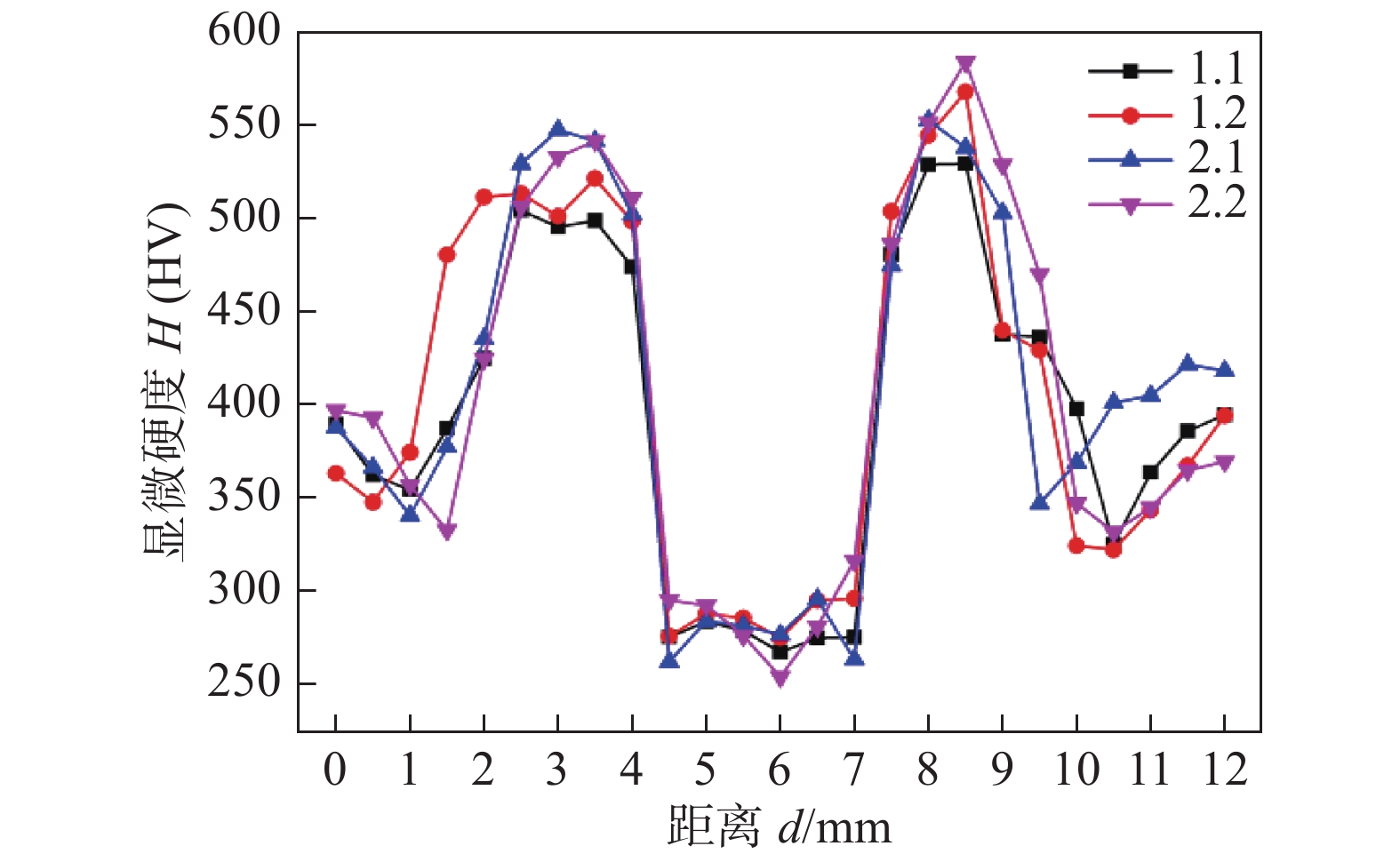
摘要: 为解决超高强钢焊接冷裂纹问题,采用强度低于母材的高氮奥氏体丝材进行GMAW工艺试验,研究在不同坡口角度下超高强钢焊接接头组织性能. 结果表明,采用该焊丝获得的接头焊缝成形良好,焊缝截面未见裂纹缺陷. 熔合线附近组织主要为针状和板条状马氏体,焊缝组织主要为奥氏体及被奥氏体基体所包围的铁素体树枝晶. 熔合线附近马氏体区硬度平均值为530 HV;焊缝区硬度平均值为275 HV. 相对于60°坡口接头,90°坡口接头熔合线附近马氏体组织硬度更高. 90°坡口接头的抗拉强度平均达到850 MPa,最高达887 MPa,而60°坡口接头抗拉强度平均仅为690 MPa.Abstract: In order to solve the problem of cold cracks in ultra-high-strength steel welding, the GMAW process experiment was carried out with high-nitrogen austenitic wire with lower strength than the base metal to study the microstructure and properties of ultra-high-strength steel welded joints at different grooved angles. The results show that welded joints are well formed without cracks according to cross-section of weld, the microstructure near the fusion line is mainly acicular and lath martensite, and the weld structure is mainly austenite and ferrite dendrites surrounded by austenite matrix; the average hardness of the martensite zone near the fusion line is 530 HV; the average hardness of the weld zone is 275 HV; compared to 60° grooved joints, the hardness of the martensite structure near the fusion line of 90° grooved joints are higher; The average tensile strength reaches 850 MPa, and the highest is 887 MPa, while the average tensile strength of 60° groove joints is only 690 MPa.
-
0. 序言
材料的润湿性是影响其焊接、熔覆和铸造过程的关键因素之一[1-2]. 材料表面的化学成分及形貌直接影响材料的润湿性. 已有研究表明,通过化学蚀刻[3]、机械加工[4-5]及高能束微加工[6]等手段使材料表面毛化、织构化和多孔化,显著改善了液体在材料表面的润湿性和铺展性.
多孔材料具有独特的三维开放结构,使液滴在多孔介质中表现出良好的润湿性和铺展性[7]. 根据Gambaryan-Roisman[8]的研究,多孔层可以分为5种典型结构:① 各向同性的开放式多孔结构;② 各向异性的多孔结构(孔隙为无相互连接的直道形式);③ 柱形阵列结构;④ 纤维垫结构;⑤ 由球形颗粒组成的各向同性结构.以上每种多孔结构都展现出特有的对材料润湿性能的改善.例如Tan等人[9]发现熔融塑料在钛合金表面的润湿性随着织构化微槽深度和宽度的增加而得以改善. Sun等人[10]提出了一种掩膜表面化学刻蚀的方法,使材料表面具有极端的润湿性,即超亲水性和超疏水性,并发现材料表面的疏水性和亲水性可以通过改变蚀刻时间来控制.
已有关于多孔化材料表面润湿性的研究主要集中在惰性(非反应)体系,却鲜有关于非惰性(可反应)材料润湿体系的润湿铺展行为的研究报道. 研究团队前期开展了织构化对铝合金/钢润湿铺展性的研究[11-12]:选用Al-5Si合金和钢作为典型的反应性润湿体系,研究了超快激光加工钢表面的微观纹理的润湿性和铺展行为. 结果表明,相比于微槽和微坑结构,Al-5Si合金在具有微/纳米条纹的钢表面具有更好的润湿性.此外Li等人[13]在不锈钢表面进行化学蚀刻纹理,研究了4043铝合金在不同纹理的301L不锈钢上的润湿行为. 结果表明,随着蚀刻时间的延长,扩散激活能下降,界面反应性增强,基底和金属间化合物(IMCs)的粗糙表面诱发了更强的毛细管力,从而导致液滴以更快的速度润湿铺展. Lai等人[14]采用化学刻蚀法制备了多孔Cu层,研究了液态Sn在多孔铜层的润湿性能. 结果表明,通过改变润湿温度和多孔微结构可以调节材料润湿性,并且润湿过程由界面冶金反应主导. 然而上述研究多是通过化学刻蚀以及各种高能束等技术对材料表面的改性,其对应① ~ ④类多孔结构. 针对⑤类多孔结构,仍缺乏对其反应润湿体系中润湿和铺展行为以及界面反应的相关研究.
文中针对多孔结构对材料表面润湿性的影响机制,选取Al-Si合金和钢作为典型反应润湿材料体系,研究液态Al-Si合金在钢表面多孔化高熵合金涂层的润湿铺展行为和界面反应机理.
1. 试验方法
试验选用纯度为99.99%的钴板、铬块、铁棒、锰片以及金属镍板为原材料,并按照等摩尔比例完成材料混合. 采用中频感应熔炼技术将金属先熔炼成合金棒,再通过电极感应熔化气雾化法,制备粒度范围15 ~ 53 μm的 FeCoNiCrMn高熵合金(HEA)球形粉末.利用扫描电子显微镜(SEM,Zeiss Sigma 300)、能谱分析仪(EDS)、X射线衍射仪(XRD,SmartLab 9 kW)和差式扫描量热仪(DSC, DSC404-F1 Pegasus)表征分析高熵合金粉末显微结构、化学成分、相组成和熔点等性能. 选用低碳钢为基板,其尺寸为40 mm × 30 mm × 1.8 mm. 试验前用砂纸打磨光滑,并放入无水乙醇中超声波清洗20 min, 以清除表面油污. 用自制的树脂铺粉器在基板表面预置300 μm厚的高熵合金粉末,烧结工艺原理及烧结工艺曲线如图1所示. 烧结试验真空度保持在5.0 × 10−3 Pa. 以25 ℃/min速率升温,500 ℃时保温20 min,以确保整个部件内无温差,再升至预定的烧结温度(1 000 ~ 1 200 ℃)进行保温(1 ~ 3 h),最后随炉冷却至室温. 将真空烧结后的多孔高熵合金涂层置于无水乙醇中超声清洗15 min,清除表面杂质.选用4%的硝酸酒精溶液腐蚀试样10 s,研究多孔高熵合金涂层显微组织结构. 通过光学显微镜(OM),SEM,EDS和纳米压痕测试进一步表征烧结样品.
采用座滴法测试Al-12Si合金在多孔高熵合金涂层钢表面的润湿铺展性.选取重约15 mg的Al-12Si合金放入通管中,多孔高熵合金涂层钢置于真空炉腔内.将烧结炉抽真空至5.0 × 10−3 Pa,以5 ℃/min的升温速率加热至800 ℃,并保温10 min以确保基材均匀加热. 将Al-12Si合金块从通管中滴落进行润湿铺展试验. 试验过程及示意图请参考文献[15].
原位润湿试验后,选用Keller’s(95 mL H2O + 2.5 mL HNO3 + 1.5 mL HCl + 1.0 mL HF)试剂腐蚀试样6 s,利用OM,SEM,EDS及透射电子显微镜(TEM,FEI Tecnai G2 F30)分析界面微观组织和相组成.
2. 试验结果与分析
2.1 高熵合金粉末
图2为电极感应熔化气雾化法所制备的合金粉末形貌及表征. 由图2a可见,合金粉末无明显粘连且为球形,粒度范围约为15 ~ 53 μm,Fe,Co,Cr,Ni和Mn元素成分基本相等( ~ 20% ,原子分数). 图2b为合金粉末XRD图样,3个衍射峰分别对应FCC(111)、(200)和(220)晶面. 为此认为合金粉末为FCC单相高熵合金. 通过差式扫描量热法得出FeCoNiCrMn高熵合金粉末熔点为1 325.8 ℃.
2.2 多孔高熵涂层
图3为保温时间3 h,烧结温度1 000,1 100和1 200 ℃条件下多孔高熵合金涂层SEM俯视图及横截面OM图. 当烧结温度为1 000 ℃时,粉末颗粒之间未能形成烧结颈(图3a). 随着温度升至1 100和1 200 ℃时,粉末颗粒之间形成了明显的烧结颈,粉末颗粒表面呈现明亮的金属光泽,且颗粒表面出现大量的亚微米级小孔(图3b和图3c). EDS结果显示,涂层内仅有Fe,Co,Ni和Cr元素,且各参数条件下各元素原子分数比接近1∶1∶1∶1;然而Mn元素含量为零 (表1). 分析认为,当真空腔内的真空度达到10−3 Pa,烧结温度达到1 056 ℃时,高熵合金粉末中的Mn元素达到其饱和蒸气压,导致了Mn元素的蒸发[16],致使烧结颗粒表面亚微米级小孔的出现.图4为烧结温度1 200 ℃,保温时间1,2和3 h条件下多孔高熵合金涂层SEM俯视图及横截面OM图.由图所知,颗粒之间形成了明显的烧结颈,粉末颗粒表面呈现明亮的金属光泽,颗粒表面出现因Mn元素挥发而形成的亚微米级小孔,EDS结果再次验证了烧结粉末中仅存在含量相近的Fe,Cr,Ni和Co元素,而缺乏Mn元素(表1).因此可以认为多孔涂层为FeCoNiCr高熵合金. 综合图3和图4可知,多孔高熵合金涂层为三维互连开放结构,孔隙位置及大小随机分布,厚度介于280 ~ 290 μm,如图5a 所示,其与⑤类多孔结构类似.进一步选取烧结温度1 200 ℃,保温时间3 h时获得的典型试验开展XRD相鉴定分析(图5b). 结果表明,多孔高熵合金涂层仍为单相FCC结构.
表 1 不同烧结工艺多孔涂层EDS点分析(原子分数,%)Table 1. EDS point analysis of porous coatings with different sintering processes温度T/℃ 时间t/h Fe Co Cr Ni Mn 1 000 3 20.68 20.71 20.55 19.65 18.41 1 100 3 27.75 26.67 23.39 22.19 — 1 200 3 28.78 25.67 21.61 23.94 — 1 200 2 28.08 26.37 22.10 23.45 — 1 200 1 27.73 26.72 23.41 22.14 — 通过显微照相法测得不同烧结工艺多孔高熵合金涂层的孔隙率及平均孔径(图6).图6a为保温时间3 h时孔隙率及孔径随温度的变化. 由图可知,随着烧结温度的升高,孔隙率和平均孔径逐渐降低,孔隙率由53.84%降低到44.63%,平均孔径由25.1 μm降低到15.1 μm. 图6b为烧结温度1 200 ℃时孔隙率及孔径随保温时间的变化. 由图可知,随着保温时间的增加,孔隙率随之降低,由48.93%降低到44.63%,但平均孔径变化不大,由16.2 μm降低到 15.1 μm.
图7为不同烧结工艺的高熵合金涂层/钢基材界面OM形貌.由图可知,钢基底和多孔高熵合金涂层之间形成了一层连续的反应层,说明在界面处发生了冶金结合,保证了基体和涂层之间良好的连接.表2总结了在不同保温时间和烧结温度下的界面反应层厚度. 随着保温时间和烧结温度的增加,反应层厚度随之增加. 值得注意的是,界面过渡层最厚仅为7.6 μm,这可能是由于高熵合金的迟缓扩散效应导致的[17].
表 2 不同烧结工艺界面过渡层厚度Table 2. Interfacial transition layer thickness for different sintering process温度T/℃ 时间t/h 过渡层厚度d/μm 1 000 3 1.9 1 100 3 5.4 1 200 3 7.6 1 200 2 7.4 1 200 1 6.3 为了研究多孔涂层以及界面层的显微组织,选取烧结温度1 200 ℃、保温时间3 h的样品开展深入分析.图8a为多孔高熵合金涂层界面SEM及EDS分析. 由图可见,多孔高熵合金涂层与钢基底之间新形成的过渡层厚度均匀且连续. 由EDS面扫描结果可知,界面处发生了明显的扩散,且无明显的成分偏析.其中Cr元素扩散距离显然大于Co和Ni元素,这是因为Cr元素在铁中的扩散系数最高( ~ 1.74 × 10−8 cm2/s)[18]. 图8b为界面纳米硬度曲线,由图可知界面处纳米硬度先增加后下降.钢基体和高熵合金纳米硬度分别为1.9 和4.3 GPa,均低于过渡层的纳米硬度( ~ 4.7 GPa).过渡层硬度的增加可归因为烧结过程中界面发生元素扩散而触发的固溶强化效应[19].
2.3 多孔高熵涂层润湿性
图9为Al-12Si合金在多孔高熵合金涂层(烧结温度1 200 ℃、保温时间3 h)表面润湿铺展后SEM俯视图及横截面图. 由图9a可知,重新凝固的Al-12Si合金形貌不规则,呈现润湿铺展局部的各向异性. 虽然多孔高熵合金涂层整体上表现为各向同性结构,但因其孔隙大小及分布随机,多孔涂层局部毛细力存在差异,导致上述现象的发生.由图9b可见,Al-12Si合金完全浸润到多孔高熵合金涂层结构中,达到完全润湿的效果(表观接触角为0°);同时横截面形貌也证实多孔高熵合金涂层为一种三维互连的开放结构.
图10a为Al-12Si合金熔体在多孔高熵合金涂层上表观接触角及润湿半径随时间的变化. 由图可知,液态合金的润湿及铺展过程可分为3个阶段:初始阶段I、快速铺展阶段II以及缓慢铺展阶段III.在初始阶段I,Al-12Si合金被加热到熔点并开始熔化,同时表面氧化物的形成促使液态合金逐渐内聚成球状 [11]. 在快速铺展阶段II,氧化膜开始发生破裂,液态金属与多孔高熵合金涂层表面直接接触,并快速渗透进多孔高熵合金涂层的微孔隙中;此后液态合金三相线开始移动,表观接触角急剧下降,呈指数下降趋势,且液滴底部润湿半径逐渐增加. 在缓慢铺展阶段III,表观接触角下降速率开始变缓,并逐渐达到稳定状态;同时,液滴底部润湿半径也随之缓慢下降.当动态润湿铺展即将结束时,多孔高熵合金涂层表面的液滴铺展半径开始迅速减小,直至完全浸润(表观接触角为0°).
Al-12Si合金液滴在多孔高熵合金涂层上的润湿及铺展过程与非反应性润湿体系相似,都包括了两个相互竞争的过程[20],即液滴在多孔涂层表面的铺展和液滴向多孔结构内部的浸润. 前者导致了液滴润湿半径的增长,后者则导致了液滴半径的收缩和多孔高熵合金涂层内湿润区的增长. 在阶段II,多孔高熵合金涂层表面的毛细铺展占主导地位,超过了液体渗入多孔层内而导致的液滴基底收缩,使得液滴底部半径逐渐增加,直到达到最大值.在阶段III,多孔高熵合金涂层内的毛细浸润却开始占主导地位,其超过了因毛细铺展而导致的液滴基底增加,表面铺展几乎停止,使得涂层表面液滴体积及表观接触角逐渐减小,液滴基底收缩,直至完全润湿.事实上,在整个润湿及铺展过程中,多孔高熵合金涂层内的湿润区一直在扩大,这与Starov根据流体力学方法得出的多孔介质的润湿理论模型相似[20].
图10b比较了Al-12Si合金在不同织构及涂层钢表面润湿及铺展的表观接触角大小,与其它工作[11, 13, 21]相比,可以看出多孔高熵合金涂层促进了Al-Si合金/钢反应润湿系统的润湿性和铺展性,其表观接触角为0°,达到了完全润湿的效果.钢表面烧结多孔化高熵合金涂层与其它工作中表面毛化[13]、织构化[11]以及镀层[21]相比,表现出以下典型特征:①独特的三维连通开放结构,增大了母材的比表面积,增强了材料表面的毛细力,可使液态合金快速浸润到孔隙结构当中,能够达到完全润湿的效果(表观接触角为0°);②相比于其它传统合金镀层,高熵合金涂层具有高熵效应及迟滞扩散效应,可促进界面反应及固溶体的形成,抑制界面金属间化合物及改善润湿性能,此结果在文中界面组织分析部分被证实.
2.4 界面微观组织及反应机理
图11为Al-12Si合金/多孔高熵合金涂层界面SEM照片. 根据界面组织形貌特征可将反应产物划分为4个区域:I,II,III和IV区. 由EDS分析可知,相比于II,III和IV区,与高熵合金相邻的I区相中Al(1.88 %,原子分数)和Si(2.04 %)元素含量特别低,Cr元素含量最高(50.91 %),Fe(33.76 %),Ni(4.46 %)及Co(6.45 %)3种元素成分介于中间(表3). 因此推测I区相为富铬的FCC固溶体,与相邻高熵合金具有相同的晶体结构(图5b). 与I区相邻且颜色较深的II区相中,Al元素的含量随之增加到了31.26 %.由于Al是一种BCC稳态元素[22],推测II区相为富含AlFe的BCC相. III和IV区已从高熵合金涂层骨架中分离,形成类似共晶组织的结构.由EDS分析可知,III区是富Al区,Fe,Co,Cr及Ni的原子比接近于1∶1∶1∶1(表3),因此推测其它合金元素溶解在铝中形成了富含Al的BCC固溶体. IV区相富Al和Ni,Al元素含量为26.72 %,Ni元素含量为38.24 %,而Cr元素含量较低,为2.82 %(表3),推测其为富AlNi的B2相.
表 3 图11中I-IV区的EDS点分析(原子分数,%)Table 3. EDS analysis at the points of the I-IV region in Fig. 11位置 Al Si Fe Cr Co Ni 可能相 I 1.88 2.04 33.76 50.91 6.45 4.96 富Cr-FCC II 31.26 4.61 29.57 6.45 13.83 14.28 富AlFe-BCC III 60.57 2.98 9.27 8.73 9.52 8.93 富Al-BCC IV 26.72 2.32 14.67 2.82 15.28 38.19 富AlNi- B2 为了鉴定Al-12Si/多孔高熵合金涂层界面反应相组成,进一步开展了TEM和SADPs分析. 图12为其界面微观结构(I-IV区)的高角度环形暗场相(high angle annular dark field, HAADF)、高分辨(HR-TEM)以及电子衍射斑点(selected area electron diffraction patterns, SADPs)分析. 结果表明,I区晶带轴为
$[1 \bar{2} 0 ]$ 方向、晶面间距为0.186 nm,鉴定为富Cr-FCC相,如图12a所示. II区晶带轴为$[1 \bar{1} \bar{1}]$ 方向、晶面间距为0.205 nm,鉴定为AlFe-BCC相(图12b).III区和IV区晶带轴方向分别为 [010]和[001],晶面间距为0.667及0.203 nm,分别鉴定为富Al(BCC)和富AlNi的B2相(图12c,12d). TEM和SAPDs分析进一步证实了EDS分析所推测的结果.界面反应产物的形成与材料体系中的溶解和扩散行为密切相关[23-24]. 在Al-12Si/多孔高熵合金涂层反应界面中,高熵合金在与铝熔体接触时即开始发生溶解,Fe,Co,Cr及Ni元素从高熵合金界面向熔体中扩散.由于各元素在铝熔体中的扩散系数不同,其中Cr元素的扩散系数最小[25],致使Cr元素容易在反应界面附近富集,形成I区富铬相. Tsai等人[22]的研究证实:Cr,Co及Fe为FCC稳态元素,Al和Ni为BCC稳态元素. 因此在高熵合金界面附近首先形成了一个富含铬的FCC相. 由EDS分析可知,II区中Al和Fe元素含量很高(31.26%和29.57%),Cr元素的含量很低(6.45%)(表3). 分析认为,界面发生了从FCC到BCC的相变. 从I区和II区相形态方面考虑,其形成机制被认为是扩散控制的冶金反应[26-27]. 在等温加热过程中,I区和II区相开始生长变厚,但由于高熵合金的迟滞扩散效应,导致界面元素扩散缓慢,使反应层增厚的范围非常有限,被限制在百纳米量级(图11).同时Fe,Co,Co和Ni元素不断向Al-12Si熔体中溶解扩散,导致熔体中各合金元素含量增加.当熔体开始冷却,温度及成分达到共晶点时,将诱发共晶反应,生成III和IV相,即富含Al的BCC和富含AlNi的B2相. Lu等人[28]在研究AlCoCrFeNi2.1共晶高熵合金时也报道了这种B2共晶结构.据报道,Al和Ni的负混合焓非常大,导致Al和Ni之间有很强的结合力;而Co,Cr和Fe的混合焓相似,它们之间的结合力很差,因此它促进了Al和Ni富集区的形成,这有利于B2共晶结构的形成.
3. 结论
(1)使用电极感应熔化气雾化法成功制备了粒度约15 ~ 53 μm的球形FeCoCrNiMn高熵合金粉末.借助真空烧结法,在低碳钢表面成功制备了多孔化高熵合金涂层. 多孔涂层呈现三维互连开放结构,孔隙位置及大小随机分布,其厚度介于280 ~ 290 μm,孔隙率介于44.63% ~ 53.84%,过渡层厚度介于1.9 ~ 7.6 μm.
(2)由于多孔高熵合金涂层独特的三维连通开放结构,使材料比表面积增大,毛细力增强,促进液态合金迅速向孔隙结构中的润湿铺展,进而实现了完全润湿(表观接触角为0°).
(3)合金熔体在多孔高熵合金涂层上的润湿铺展可分为初始阶段I、快速铺展阶段II及缓慢铺展阶段III. 在阶段II及阶段III的运动与非反应润湿相似,为毛细铺展和毛细浸润两者相互竞争的过程.前者使液滴表面润湿半径增大,后者使液滴表面半径收缩及涂层内润湿区的增长.
(4)在高熵合金迟滞扩散效应与高熵效应共同作用下,界面反应层中金属间化合物的形成受到显著阻碍,界面相结构由富Cr的FCC、富AlFe的BCC以及富AlNi的B2 + 富Al的BCC共晶状结构组成.
-
表 1 焊丝与母材化学元素组成(质量分数,%)
Table 1 Chemical component of wire and substrate
材料 C Ni Cr Mo Mn Si N 焊丝 0.071 2.32 21.59 1.21 16.95 — 0.79 母材 0.32 1.8 1.0 0.7 1.2 0.4 — 表 2 接头抗拉强度 (MPa)
Table 2 Tensile strength of joint
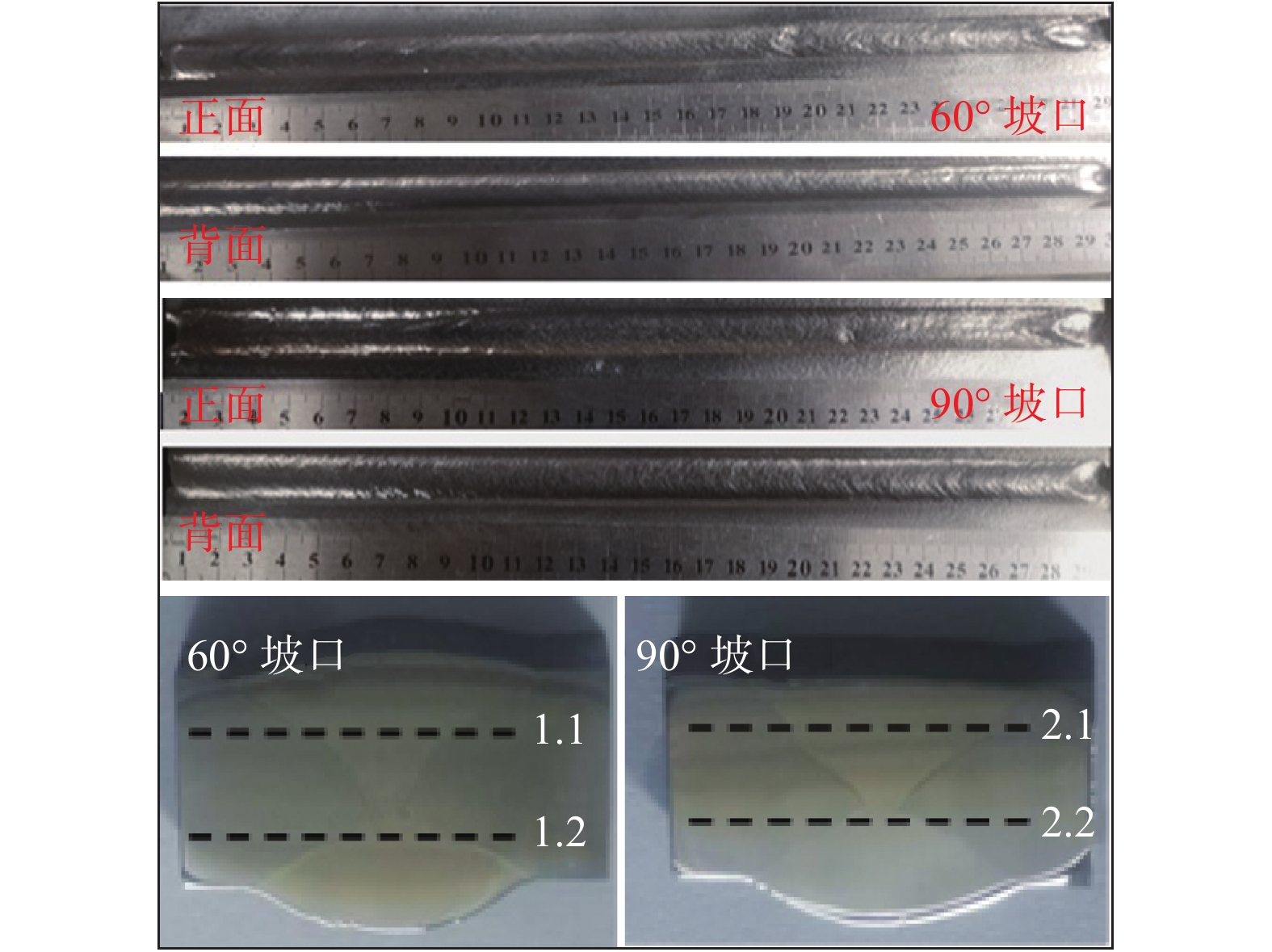
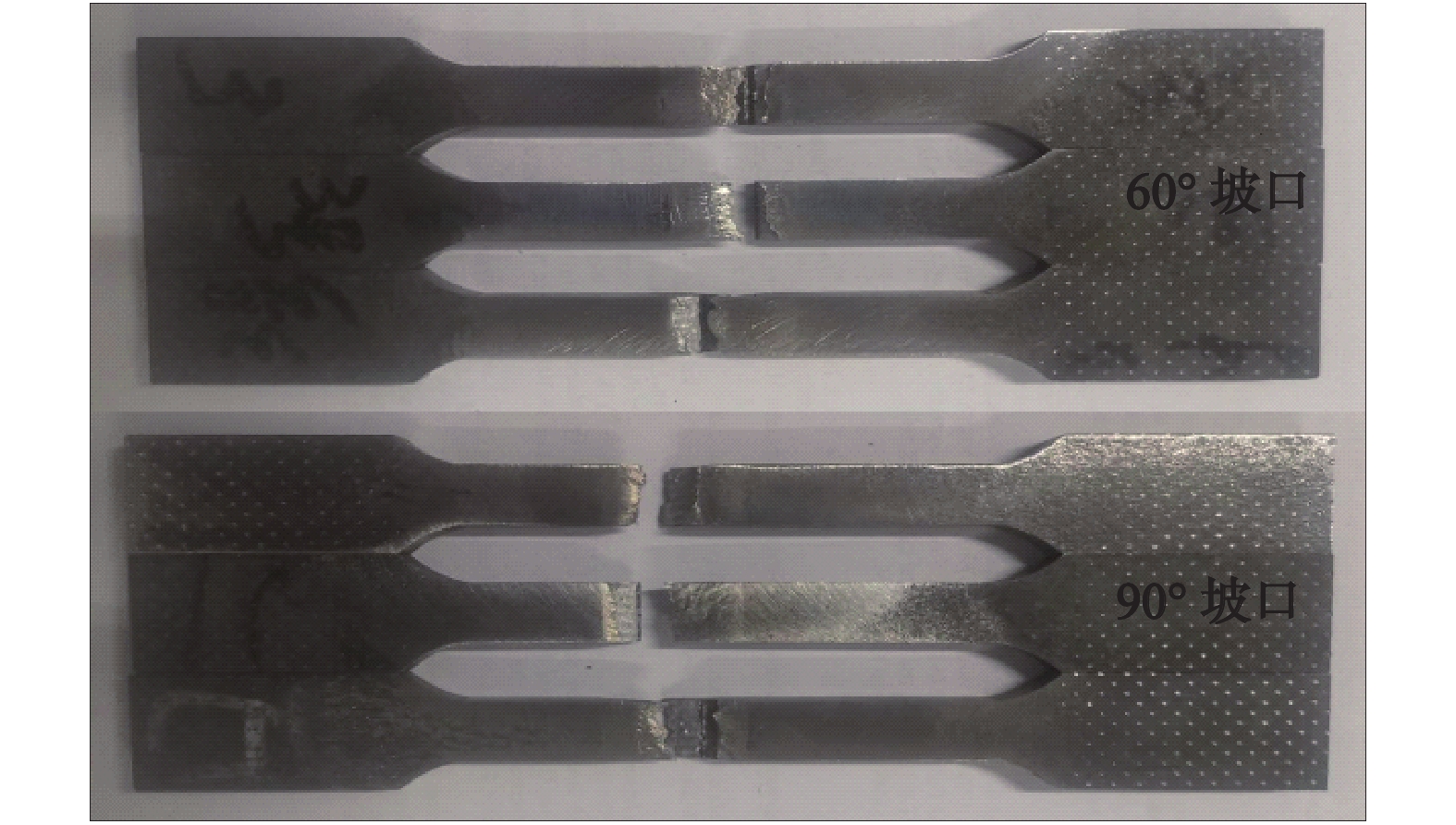
坡口角度 试样1 试样2 试样3 平均抗拉强度 60° 720 678 672 690 90° 887 834 829 850 -
[1] 成应晋, 刘海涛, 杜义, 等. 基于插销试验的10Ni8CrMoV钢焊接冷裂纹敏感性分析[J]. 材料开发与应用, 2016, 31(5): 13 − 18. Cheng Yingjin, Liu Haitao, Du Yi, et al. Analysis of 10Ni8CrMoV steel welding cold cracking susceptibility on the basis of implant test[J]. Material Development and Application, 2016, 31(5): 13 − 18.
[2] 管彦朋, 李亚江, 王娟. 1 000 MPa及以上级高强钢焊接性研究现状[J]. 机械制造文摘(焊接分册), 2015(3): 30 − 34. Guan Yanpeng, Li Yajiang, Wang Juan. Present situation of the study on the weldability of 1 000 MPa and above high strength low alloy steel[J]. Welding Digest of Machinery Manufacturing (Welding Volume), 2015(3): 30 − 34.
[3] 雷爱娣, 王立军, 蔡庆伍. 1 500 MPa级低合金超高强钢微观组织与力学性能[J]. 金属学报, 2010, 46(6): 687 − 694. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1037.2010.00687 Lei Aidi, Wang Lijun, Cai Qingwu. Microstructure and mechanical properties of 1 500 MPa grade ultar-high strength low alloy steel[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2010, 46(6): 687 − 694. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1037.2010.00687
[4] Berdnikova O, Pozniakov V, Alekseienko T, et al. Effect of the structure on the mechanical properties and cracking resistance of welded joints of low-alloyed high-strength steels[J]. Procedia Structural Integrity, 2019, 16: 89 − 96. doi: 10.1016/j.prostr.2019.07.026
[5] 滕彬, 李小宇, 雷振, 等. 低合金高强钢激光-电弧复合热源焊接冷裂纹敏感性分析[J]. 焊接学报, 2010, 31(11): 61 − 64. Teng Bin, Li Xiaoyu, Lei Zhen, et al. Analysis on cold crack sensitivity of low alloy high strength steel weld by laser-arc hybrid welding[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2010, 31(11): 61 − 64.
[6] 李大用, 杨东青, 王苹, 等. 高铬镍奥氏体焊丝焊接10Ni5CrMoV钢接头组织性能分析[J]. 焊接学报, 2017, 38(5): 87 − 91. doi: 10.12073/j.hjxb.20170519 Li Dayong, Yang Dongqing, Wang Pin, et al. Analysis of microstructure and performance of 10Ni5CrMoV steel joint welded by high chromium nickel austenitic wire[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2017, 38(5): 87 − 91. doi: 10.12073/j.hjxb.20170519
[7] 赵琳, 田志凌, 彭云, 等. 1Cr22Mn16N高氮钢激光焊接I. 焊接保护气体组成和热输入对焊缝氮含量及气孔性的影响[J]. 焊接学报, 2007, 28(8): 89 − 91. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-360x.2007.08.023 Zhao Lin, Tian Zhiling, Peng Yun, et al. Laser welding of 1Cr22Mn16N high nitrogen steel I. Influence of shielding gas composition and heat input on N-content and porosity of weld metal[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2007, 28(8): 89 − 91. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-360x.2007.08.023
-
期刊类型引用(0)
其他类型引用(2)




 下载:
下载: