High temperature creep behavior of friction stir welding joints for CLAM steel
-
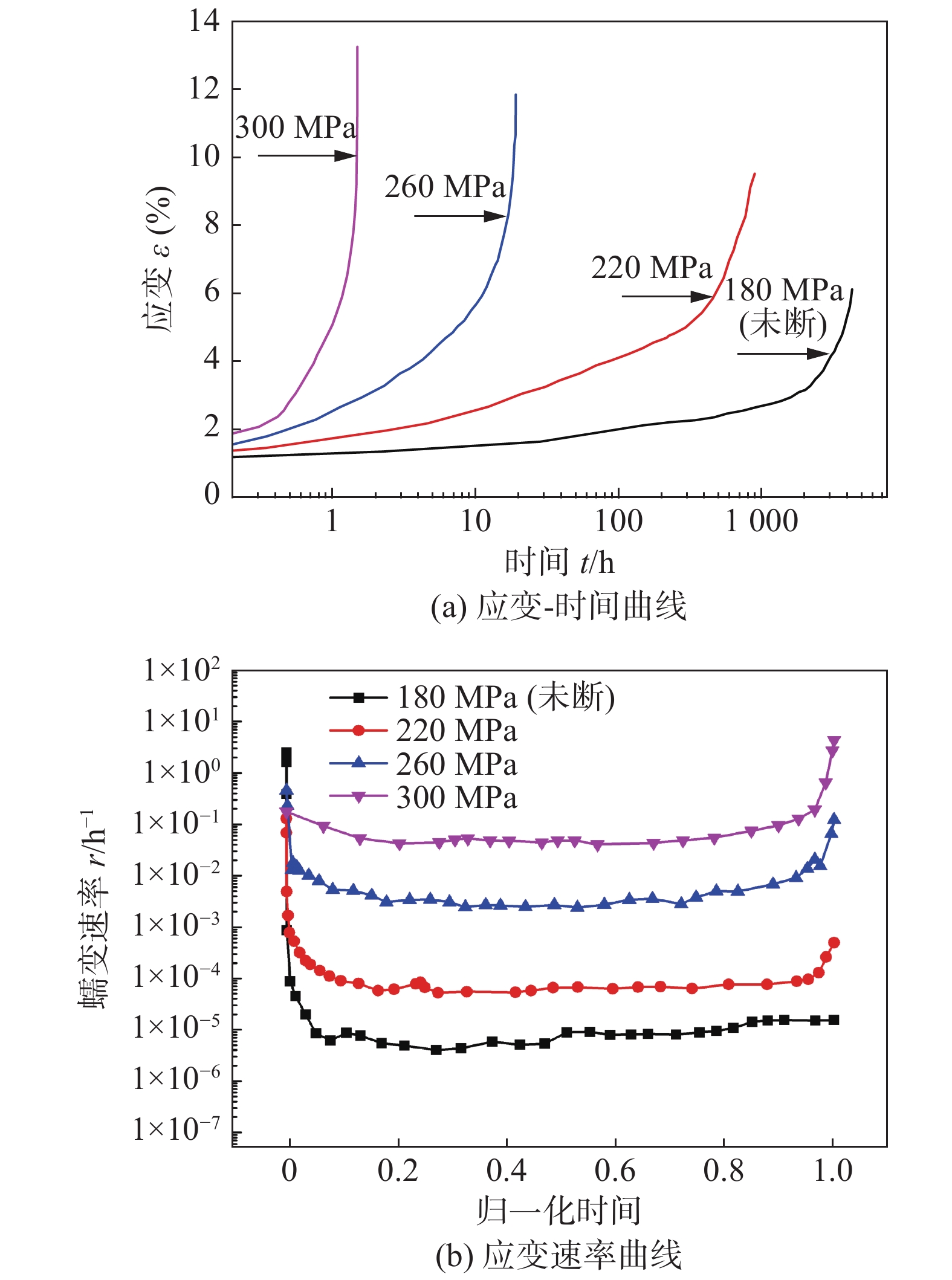
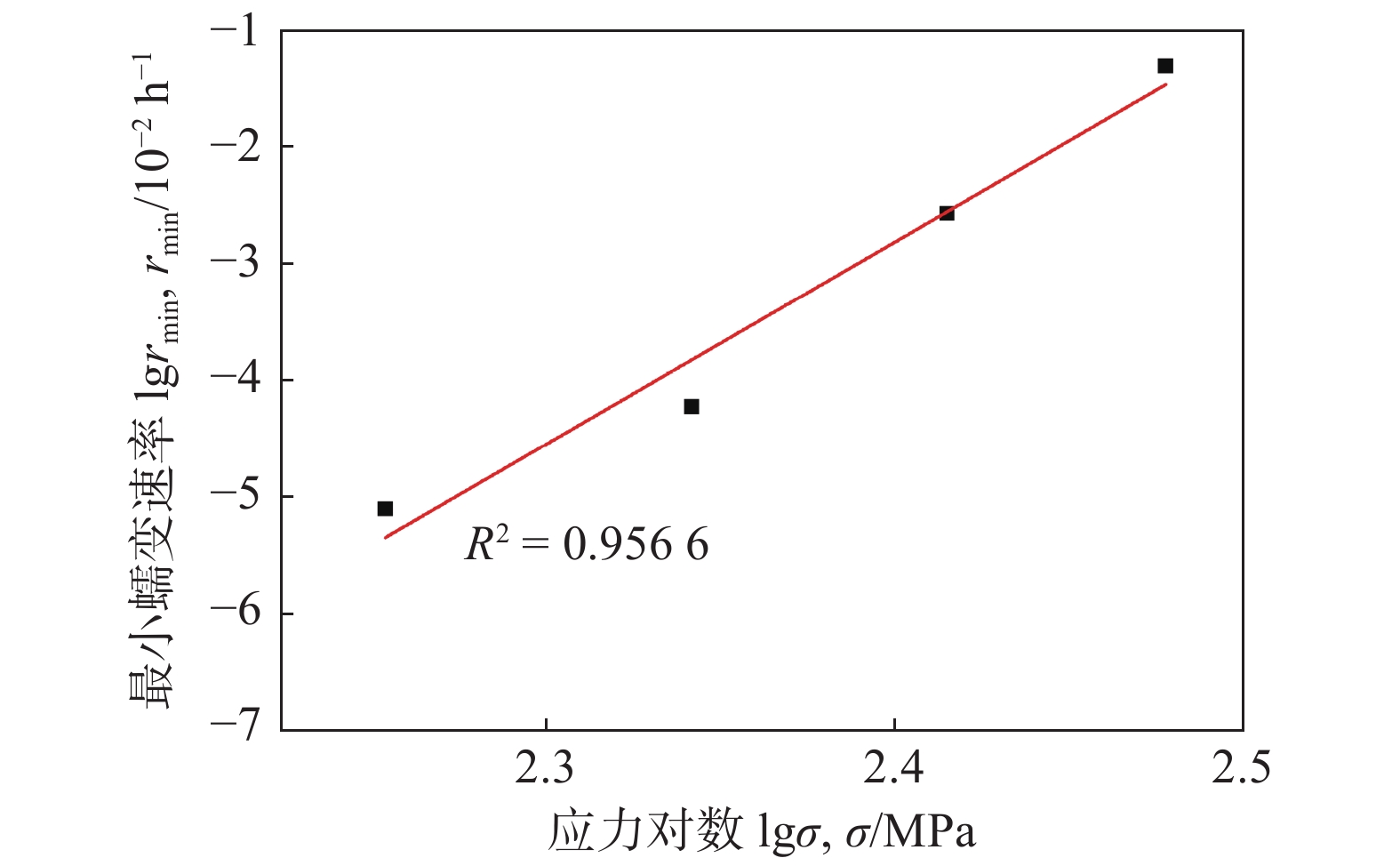
摘要: 针对核聚变堆用CLAM钢,对焊后热处理的搅拌摩擦焊接头在823 K条件和180~300 MPa应力水平下的单轴拉伸蠕变性能、断口形貌、显微组织进行了研究. 结果表明,当蠕变应力由300,260及220 MPa降低到180 MPa时,CLAM钢搅拌摩擦焊接头的蠕变寿命分别由1.5,19.2及883 h增加到6769 h以上. 临界热影响区是接头蠕变断裂的最薄弱区域,主要呈现位错控制的蠕变变形机制和穿晶韧性断裂模式. 在蠕变过程中临界热影响区组织发生回复并形成亚晶,导致位错强化作用降低;M23C6碳化物发生不同程度的粗化或周围生成Laves相,导致析出和固溶强化作用减弱;这些因素是CLAM钢FSW接头蠕变性能恶化的主要原因. 采用Monkman-Grant方程预测FSW接头在1×105 h蠕变寿命下的蠕变断裂强度估计为156 MPa,达到母材强度的88%.Abstract: The uniaxial creep tensile strength, fracture features and microstructures of friction stir welded joint with postweld heat treatment for CLAM steel have been investigated in the range of the creep applied stress from 180 MPa to 300 MPa at 823 K condition. It is found that the creep life of the FSW joints of CLAM steel increase from 1.5 h, 19.2 h and 883 h to above 6769 h respectively, when the creep stresses decrease from 300 MPa, 260 MPa and 220 MPa to 180 MPa. The inter critical heat affected zone is the weakest zone of creep rupture resistance for the FSW joint of CLAM steel, the joints mainly exhibit dislocation-controlled creep deformation mechanism and the transgranular ductile fracture mode. The microstructures of inter critical heat affected zone produce recovery and subgrain boundaries are formed in here during creep process, which result in the decrease of dislocation strengthening action; the coarser M23C6 carbides is produced or the coarser Laves phase around the M23C6 carbides is formed, which result in the reduction of precipitation and solution strengthening action, these issues are the main reasons for the deterioration of the creep performance of FSW joints. The creep fracture strength of FSW joint is estimated to be 156 MPa in the condition of 1 × 105 h creep life according to the Monkman-Grant equation, which reaches 88 % of the strength of base metal.
-
Keywords:
- low activation steel /
- friction stir welding /
- creep performance /
- microstructure /
- life prediction
-
0. 序言
智能制造是世界制造业发展的客观趋势,也是未来各制造企业转型升级的必然选择. 激光焊接由于具有高效、绿色、节能、易于柔性加工等突出技术优势,因此有望成为智能制造领域中的主流技术之一. 但是激光焊接过程中却存在大量的烟尘、飞溅、等离子体等诸多干扰因素,所以在其工程应用中往往存在熔透质量控制不稳定的情况[1]. 因此可靠熔透在线检测是激光焊接智能制造领域的重要问题[2]. 但是,有效的透状特征信号仅产生在匙孔底部一个只有0.05 ~ 0.4 mm的微小区域内,属于介观尺度范畴,并且完全被大量喷射物质和周围高辐射信号所掩盖. 因此,常规检测方法主要围绕焊接过程中的各种声、光、热、磁等间接信号展开研究[3-8]. 但是,间接测量受外界影响因素较大,测试可靠性难以保证. 为了弥补上述不足,国内外学者竞相开展深入研究,不断有新的检测技术问世. 发展趋势主要呈现为:(1)在检测方法上,通过多传感融合测试的方法来弥补单一检测手段的不足[9-11];(2)在数据分析上,通过模糊算法或计算机深度学习来提高算法模型的可信性[12-19];(3)在新检测手段上,研发新一代传感检测技术等几个方面[20-23]. 虽然这些方法能够解决一些实际问题,但是由于依然受宏观采样手段局限,无法将介观尺度熔透信号有效分离,导致检测数据中有效信号占比过低,数据分析极为困难. 所以开拓更微观领域的检测技术研究、获取更高的信号辨识精度有望成为未来检测行业发展的一个全新方向.
论文将在国内率先开展介观尺度下的激光焊接特征研究,挖掘匙孔内更深层次的物理特性,并结合激光焊接热反应本质,通过大数据统计分析实现熔透信息的抽象化特征提取,寻找一条激光熔透可靠检测新途径. 该项研究对于提高激光焊接熔透质量在线精确控制能力、促进智能化激光制造技术发展具有非常重要的实际意义.
1. 试验方法
为了能够较深入的解激光熔透焊接时在介观尺度下匙孔内究竟发生了什么,存在那些物理特性,试验将从介观影像信息及介观信号特征入手,对3 mm厚TC4钛合金激光熔透焊接试验及5 mm厚试板非熔透焊接试验开展深入研究. 具体工艺参数为光纤激光功率3.5 kW,焊接速度1.0 m/min,离焦量 + 2 mm,氩气流速15 ml/min.
1.1 介观尺度影像信息获取方法
介观尺度影像信息的分辨率一般要比普通高清影像至少高一到两个数量级,所以在获取匙孔内介观尺度影像信息时,常规拍摄手段已无法满足技术需求,因此光学检测手段是一个尤为关键的环节. 试验选取了具有超远距离显微成像及高光学穿透效果的自研发显微镜头组[24]作为拍摄镜头,该镜头由一组变倍镜头、变焦镜头、物镜镜头组成,具有0.8 m ~ 1.5 m超长的工作距离、10 mm较大的拍摄景深和不足1°极小的视场角. 由于其突破了传统显微镜毫米级别的物距极限,达到了可以满足焊接头同轴监控的1.5 m物距需求,并可获得3X倍以上光学放大的成像效果,因此可以实现匙孔底部影像的高分辨率获取,满足文中试验的光学放大需求. 同时,试验还选取FastCam Ultima 512高速摄像机进行数字化记录,满足电子放大和高速采集需求. 通过光学放大 + 电子放大后达到约1万倍的复合放大效果,实现匙孔底部介观尺度影像信息的高清捕捉.
1.2 介观熔透信号的提取方法
由于激光焊接熔透信号的产生区域属于介观尺度范畴,常规的光学信号提取方法难以将其有效分离,因此需要采用文献[24]中所述的提取方法,将光谱透视、红外显微成像、介观尺度信号寻位及萃取等技术手段相结合. 先以匙孔内壁热激发态辐射源作为直接检测信号,利用不同发光体的谱段特性分离并抑制等离子体等干扰信号,使匙孔内的热激发信号得到有效增强,实现光谱透视显像效果. 同时通过自制的超远距离显微镜头组,利用红外显微成像原理,在激光焊接头同轴光路后端提取到匙孔内壁热激发信号的红外显微实像. 然后通过微距相机观测光学镜头组成像位置,并根据介观尺度影像试验结果确定实像中的熔透特征位置. 最后通过调节三维调节机构将感应区域同样为介观尺度的传感器芯片高精度定位置至熔透特征区域,由于选取的传感器光感直径仅为200 μm,在成像透镜光学放大倍数为3X倍时,实际检测精度要小于0.07 mm,所以可实现介观尺度信号的高清辨识. 试验装置内部组成如图1所示.
2. 试验结果与分析
2.1 介观熔透区域的影像特征
试验获得的介观熔透区域的影像信息如图2所示. 但是,研究发现这些影像信息只有在特殊拍摄手段,并且在一定谱段下(1100 nm ~ 1300 nm)才能被清晰的捕捉到. 同时,通过光谱比对可知,这种影像辐射光源也不同于焊接激光束、等离子体以及其它激光焊接释放光信号的增强谱段,所以分析认为是匙孔内的一种新的光源. 这种光源的产生大概率为激光束轰击匙孔内壁时由于能量跃迁而激发出的一种热激发态现象. 并且由于该信号产生于匙孔内壁表面,受匙孔形态变化的直接影响,因此可以较好的反映出匙孔的内部状态变化. 同时,这种由于热激发而产生的信号在红外一些特殊谱段下几乎不受什么影响,而同样在该谱段下的等离子体等喷射物质却会受到极强的抑制. 因此,可以有效穿透喷射物遮挡,使匙孔内部的特征信息透视显现出来.
此外,从图2中还可以看到影像中心存在一个直径约150 μm的低灰度区域. 通过动态观察发现这一区域呈周期闪动形式存在. 但是在相同条件下的非熔透焊接中,这一区域却并不存在. 从技术上分析只要有匙孔存在,匙孔内壁表面的热激发信号就能够被捕获到,但事实却不是这样. 所以这一现象最可能的产生原因是,在激光熔透焊接时由于存在激光束贯穿母材时刻,使得匙孔底部产生缺口,由于缺口处的热激发信号消失形成了这种低辐值的介观熔透区域. 而该区域周期闪动的原因是由于激光焊接时匙孔底部并不是处于一个稳定状态,而是随着激光束的穿透效果和匙孔底部的不断收缩,呈现出底部缺口闭合与打开交替出现的特征行为. 由于该介观区域与激光熔透状态关联性较强,因此,该信号可以作为一种熔透识别的直接检测信号.
2.2 介观熔透信号的物理特征分析
2.2.1 隐蔽性
从上述试验中可知,除非在特定的拍摄条件下,介观熔透区域影像或介观熔透信号是非常难以捕捉的. 从其产生机理上分析,首先,熔透特征区域在的空间位置上位于匙孔的最底部,同时激光焊接时释放光信号的辐射功率都是千瓦级以上,而匙孔内壁的热激发信号只有毫瓦级,所以极易被匙孔内部及上方强烈的光辐射完全掩盖;其次,在特征信号的产生区域上,常规激光焊熔透特征区域(通常指适度熔透焊接,其产生区域约0.05 ~ 0.4 mm)一般不足匙孔开口面积的1/20,即熔透信号在匙孔内混合检测信号中的有效占比非常低. 并且,在信号强度对比上,相比于匙孔内壁的热激发信号,熔透信号为强度更低的低幅值信号,在周围高辐值信号干扰下识别难度更大[5]. 所以,常规检测方法难以将这种匙孔内部的介观尺度低幅值熔透信号有效分离出来. 因此,介观熔透信号具有较强的隐蔽性.
2.2.2 指向性
为了研究在介观信号的区域性差异,试验借助光学显微检测手段极高的分辨能力,针对激光匙孔显微实像中介观区域辐值变化开展了不同检测位置的对比性测试. 试验采用了3500 W-4500 W- 3000 W 阶跃式的激光输出,并以1 mm/min的焊接速度,对3 mm厚的钛合金板进行了变功率激光熔透试验. 实际的焊缝熔透情况只有在4500 W时为“适度熔透”焊缝,在3500 W和3000 W时均为未熔透. 图3为不同检测位置上的介观尺度信号对比结果,图3(a)的信号提取位置正好位于熔透特征区域上,而图3(b)的检测位置则稍有偏差,如图4所示. 在图4中,白色光斑区为匙孔显微实像的投射区域,黄色圆圈代表熔透特征信号的产生位置,红色方框为传感器感应芯片位置. 显然,此时熔透特征信号出现区域与传感检测区域并未重合,图3(b)的实际检测位置偏离熔透特征区域中心位置约200 μm,但同样处于匙孔内部.
从对比试验中可以发现即使同样是在匙孔内部,但检测位置只偏离了熔透特征区域200 μm,对于熔透状态识别的测试敏感度就产生了较大的差别. 说明,介观熔透信号具有较高的指向性,在高精度检测时信号的提取位置对检测结果的有效性至关重要.
2.2.3 波动性
在研究介观熔透信号的行为特征中发现,虽然该信号中蕴藏了大量的激光熔透信息,但是往往被其表面的巨幅波动所掩盖. 如图5,为试验提取到的实际介观熔透信号,从中可以发现焊接过程中介观熔透信号存在一种极为复杂的波动性行为,而且从匙孔的影像信息上同样可以得到这一结论.
为了得到这种波动特征下的更深层次信息,试验首先选择对信号进行细化分解,研究每个波动周期的行为特征. 但是从图6的试验结果上发现介观信号的每个时间周期并不规则,在值域上的波动幅度也相差较大,说明介观熔透信号的出现并没有明显的规律性,同时信号强弱变化也更趋于随机波动. 分析其原因在于激光焊接本身就是一个极为剧烈的热物反应过程,很多因素会直接影响到匙孔底部介观熔透信号. 比如,匙孔的湮灭与形成、匙孔通道内壁的强烈波动、匙孔底部缺口的闭合与打开,甚至是匙孔内突然喷出的高辐值喷射物质,都会对匙孔底部的介观熔透信号产生极大的影响[25-30]. 所以在整个焊接过程中介观熔透信号都会伴随着焊接状态瞬息间发生着剧烈变化[31].
2.2.4 趋势性
由于在介观信号波动规律性研究中无法获得有效熔透信息,所以试验进一步尝试从介观信号的宏观趋势特征方面展开研究. 首先,将检测信号的所有轨迹去除后,然后重新去观察信号的分布特征. 此时,可以发现信号的巨幅波动已经消失,取而代之的是其在整个值域分布上呈现出一种规则的点阵分布. 在每一个值域范围内的点阵分布密度都极为规则,静态特征一目了然. 为了更准确的描述这一特征,试验利用计算机逐个计算单位区间的信号密度并形成密度函数,然后根据其空间的密度分布情况,将其转化为等效的概率密度模型[32]. 由此,就在不遗漏任何一个数据点的情况下,将这种极为复杂的焊接信号转化成了一个简单的特征模型[33],如图7(b)所示.
显然,介观熔透信号的宏观分布特征可以通过图7(b)中的特征模型较好的反映出来. 为了深入研究这种抽象化模型特征的主要影响因素,首先,在相同的焊接条件下进行了大量重复性试验,并在其中任取两组试验,结果如图8所示. 对比发现尽管每次试验的测试数据在信号轨迹上都完全不同,但是,如果数据点足够,它们的特征模型形却非常相似. 说明,介观熔透信号的这种趋势性特征重复性较好,且受信号自身的波动影响非常小.
然后,试验对不同焊接条件和不同熔透状态下的介观信号进行了大量对比试验. 具体为,分别以4000 W较小激光功率和6000 W较大激光功率,对3 mm厚和5 mm厚TC4钛合金试板进行了熔透试验. 并对所获得的熔透焊缝以及非熔透焊缝的介观信号特征模型进行了比对,试验结果如图9所示.
通过观察不难发现,不同状态下所得到的信号特征模型在几何形态、信号密度及概率区间范围等方面都均存在明显差异. 说明介观熔透信号的趋势性特征受焊接条件影响较为直接,不同焊接状态、锁孔形状、匙孔底部介观熔透区域的尺寸、停留时间及占空比等因素变化,都会导致特征模型形状的明显不同. 并且经过试验反复验证发现在不同焊接状态下特征模型的形貌特征均有较为“唯一”的存在形式,且模型的抽象特征极有可能是受到了焊接热反应本质的直接影响[34].
而激光焊接的熔透和非熔透状态为两种不同的焊接状态,为了验证介观信号趋势性特征能否对熔透状态也能有效识别,于是在相同功率输出的条件下进行了不等厚试板的焊接试验. 具体选取了300 mm × 150 mm × 4 mm钛合金试板,焊前先将钛板背面机加出2个矩形凹槽,凹槽最深位置距试板上表面厚度为1.5 mm,试板实物及熔透鉴定点位置如图10(a)所示. 焊接时在不等厚钛合金试板的正面施加2400 W功率激光进行表面堆焊,焊接速度2 m/min,保护气成分工业高纯Ar,信号采样频率5000 Hz. 整个焊接过程中所有热输入条件均未发生改变,在焊接4 mm厚度位置时激光束未穿透试板形成非熔透区域,在焊接1.5 mm厚度时激光束穿透了试板形成熔透区域. 这一过程的介观熔透信号原始图像如图10(b)所示,相应位置的特征模型见图10(c).
通过对比相同焊接热输入条件下熔透与非熔透特征模型的几何形态可知,介观信号的分布特征与焊接熔透行为间确实存在较好的一致性. 充分利用介观信号的这种“唯一性”和“可靠性”特点,有望实现在复杂介观熔透信号大数据中对非熔透、微熔透、适度熔透、过度熔透等不同熔透信息进行定性及定量有效识别[35-36]. 此外,在本文中尚未对介观信号特征模型的几何特征进行深入探讨,由于这些特征起源于匙孔,而匙孔行为又与焊缝熔深、气孔、夹杂等其它焊接质量均密切相关,因此深入开展介观信号模型的几何特征与焊接质量的映射规律研究,或采用人工智能自动识别方法建立识别模型,或可为激光焊接微观领域研究开辟一条新途径.
3. 结 论
(1)首次进入到介观尺度领域开展了匙孔内部熔透特征基础理论研究. 试验结果表明介观熔透信号具有隐蔽性强、指向性高、波动性大、趋势性显著的物理特性.
(2)将介观信号的分布情况抽象提取后,所得到的模型呈现出规则的点阵分布形式. 并且研究证明在相同焊接条件时,该模型的几何特征受信号的自身波动影响非常小而且多次测量重复性较好,说明其具有明显的趋势性特征. 而在不同的熔透状态下,该趋势性特征又存在较大差异. 因此,借助模型的趋势性特征可以对激光焊接熔透状态进行有效的在线监测.
(3)提出的介观信号检测手段和特征模型提取方法,对于智能化和数字化激光焊接制造具有特殊的指导意义,可为焊接微观领域研究开辟一条新途径.同时,采用人工智能识别方法分析介观信号特征模型的几何特征,或将获得更为有效的焊接质量检验结果,因此有望应用于智能焊接制造领域.
-
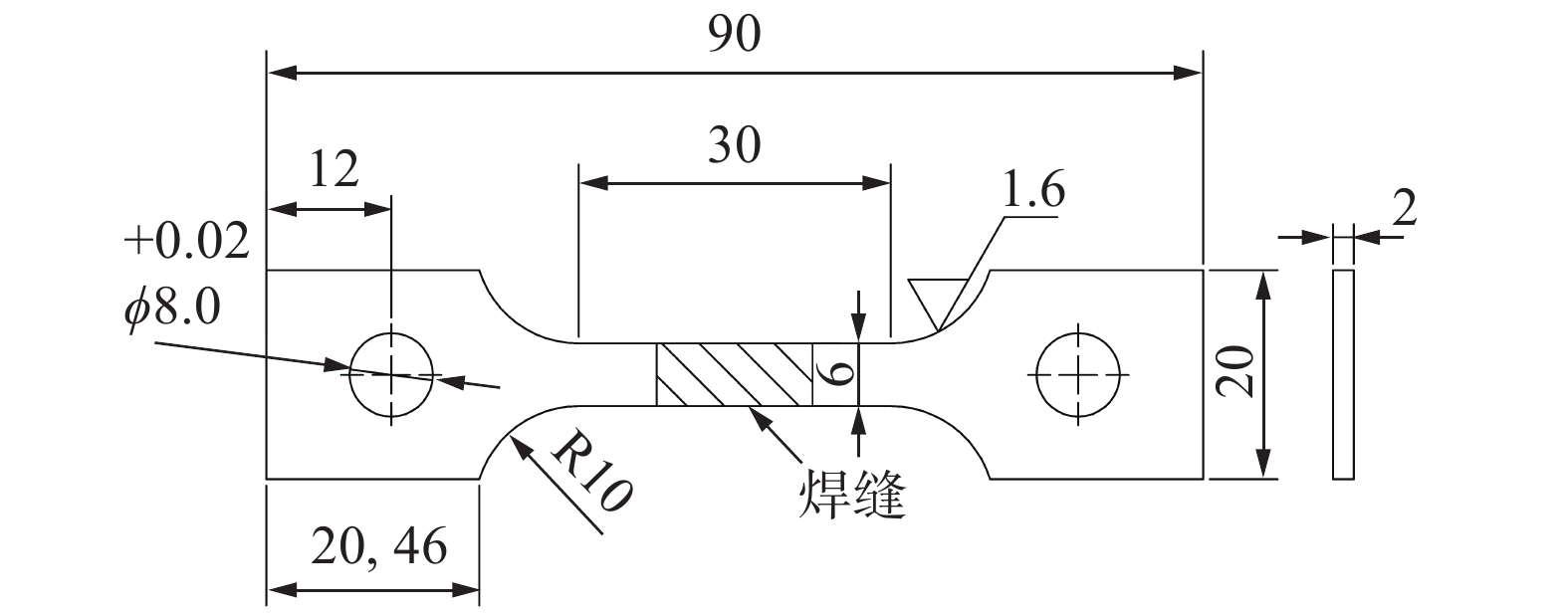
表 1 CLAM钢的化学成分(质量分数,%)
Table 1 Chemical composition of CLAM steel
C Cr Mn V W Ta Si N Fe 0.098 8.7 0.56 0.19 1.4 < 0.002 0.11 0.005 3 余量 表 2 焊接接头最小蠕变速率和断裂时间
Table 2 Minimum creep rate and fracture time of welded joints
应力水平σ/MPa 最小蠕变速率rmin/h−1 断裂时间t/h 180 8.09×10−6 6 769 (未断) 220 6.02×10−5 883 260 2.68×10−3 19.2 300 4.89×10−2 1.5 -
[1] 黄群英, 李春京, 刘少军, 等. 中国实验包层模块材料研发进展[J]. 核科学与工程, 2009, 29(3): 260 − 265. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0258-0918.2009.03.011 Huang Qunying, Li Chunjing, Liu Shaojun, et al. R & D status of materials for test blanket modules in China[J]. Nuclear Science and Engineering, 2009, 29(3): 260 − 265. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0258-0918.2009.03.011
[2] Tan L, Katoh Y, Tavassoli A A F, et al. Recent status and improvement of reduced-activation ferritic-martensitic steels for high-temperature service[J]. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 2016, 479: 515 − 523. doi: 10.1016/j.jnucmat.2016.07.054
[3] Sklenicka V, Kucharova K, Svoboda M, et al. Long-term creep behavior of 9%-12% Cr power plant steels[J]. Master Character, 2003, 51: 35 − 37. doi: 10.1016/j.matchar.2003.09.012
[4] 姜志忠, 黄继华, 胡杰, 等. 聚变堆用CLAM钢激光焊接接头显微组织及性能[J]. 焊接学报, 2012, 33(2): 5 − 8. Jiang Zhizhong, Huang Jihua, Hu Jie, et al. Microstructure and mechanical properties of laser welded joints of CLAM steel used for fusion reactor[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2012, 33(2): 5 − 8.
[5] Aubert P, Tavassoli F, Rieth M, et al. Review of candidate welding processes of RAFM steels for ITER test blanket modules and DEMO[J]. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 2011, 417(1−3): 43 − 50. doi: 10.1016/j.jnucmat.2010.12.248
[6] Das C R, Albert S K, Sam S, et al. Mechanical properties of 9Cr–1W reduced activation ferritic martensitic steel weldment prepared by electron beam welding process[J]. Fusion Engineering & Design, 2014, 89(11): 2672 − 2678.
[7] 许乐, 温建锋, 涂善东. P92钢焊接接头蠕变损伤与裂纹扩展数值模拟[J]. 焊接学报, 2019, 40(8): 80 − 88. Xu Le, Wen Jianfeng, Tu Shandong. Numerical simulations of creep damage and crack growth in P92 steel welded joints[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2019, 40(8): 80 − 88.
[8] Albert S K, Tabuchi M, Hongo H, et al. Effect of welding process and groove angle on type IV cracking behavior of weld joints of a ferritic steel[J]. Science & Technology of Welding & Joining, 2013, 10(2): 149 − 157.
[9] Wang J, Lu S, Dong W, et al. Microstructural evolution and mechanical properties of heat affected zones for 9Cr2WVTa steels with different carbon contents[J]. Materials & Design, 2014, 64(12): 550 − 558.
[10] Noh S, Ando M, Tanigawa H, et al. Friction stir welding of F82H steel for fusion applications[J]. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 2016, 478: 1 − 6. doi: 10.1016/j.jnucmat.2016.05.028
[11] Manugula V L, Rajulapati K V, Reddy G M, et al. A critical assessment of the microstructure and mechanical properties of friction stir welded reduced activation ferritic–martensitic steel[J]. Materials & Design, 2016, 92: 200 − 212.
[12] Zhang C, Cui L, Wang D, et al. The heterogeneous microstructure of heat affect zone and its effect on creep resistance for friction stir joints on 9Cr–1.5 W heat resistant steel[J]. Scripta Materialia, 2019, 158: 6 − 10. doi: 10.1016/j.scriptamat.2018.08.028
[13] 雷玉成, 张鑫, 陈玲, 等. 中国低活化马氏体钢TIG焊焊接接头的高温蠕变性能分析[J]. 焊接学报, 2016, 37(3): 5 − 8. Lei Yucheng, Zhang Xin, Chen Ling, et al. Analysis on creep properties of TIG welding joints of China low activation martensitic steel[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2016, 37(3): 5 − 8.
[14] Norton F H. The creep of steel at high temperatures[M]. McGraw-Hill Book Company, Incorporated, 1929.
[15] Betten J. Creep mechanics[M]. Springer Science & Business Media, 2008.
[16] Deng K K, Li J C, Xu F J, et al. Hot deformation behavior and processing maps of fine-grained SiCp/AZ91 composite[J]. Materials & Design, 2015, 67(2): 72 − 81.
[17] Lee J S, Armaki H G, Maruyama K, et al. Causes of breakdown of creep strength in 9Cr-1.8W-0.5Mo-VNb steel[J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2006, 428(1/2): 270-275.
[18] 叶有俊, 王一宁, 姜勇, 等. 基于碳化物相分析法的 P92 钢寿命无损评价[J]. 压力容器, 2020, 37(8): 1 − 5, 23. Ye Youjun, Wang Yining, Jiang Yong, et al. Nondestructive life assessment based on carbide phase analysis of P92 steel[J]. Pressure Vessel Technology, 2020, 37(8): 1 − 5, 23.
[19] Zhang X, Lei Y, Chen L, et al. Study on creep properties for TIG welded joints of CLAM steel[J]. Journal of Fusion Energy, 2016, 35(2): 299 − 304. doi: 10.1007/s10894-015-0024-3
-
期刊类型引用(2)
1. 申志康,李冬晓,孙中刚,马良超,刘小超,田艳红,郭伟,侯文涛,朴钟宇,杨新岐,李文亚. 搅拌摩擦沉积增材制造机理及展望:机遇与挑战. 机械工程学报. 2025(02): 56-85 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 蔺春发,戴宇轩,韩雨蔷,李响,常宝平,李远喜. 搅拌摩擦辅助电弧增材制造铝合金研究进展. 中国材料进展. 2024(10): 944-952 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)




 下载:
下载: