Tensile properties evolution of hydrogen-induced TA10 titanium alloy welded joints
-
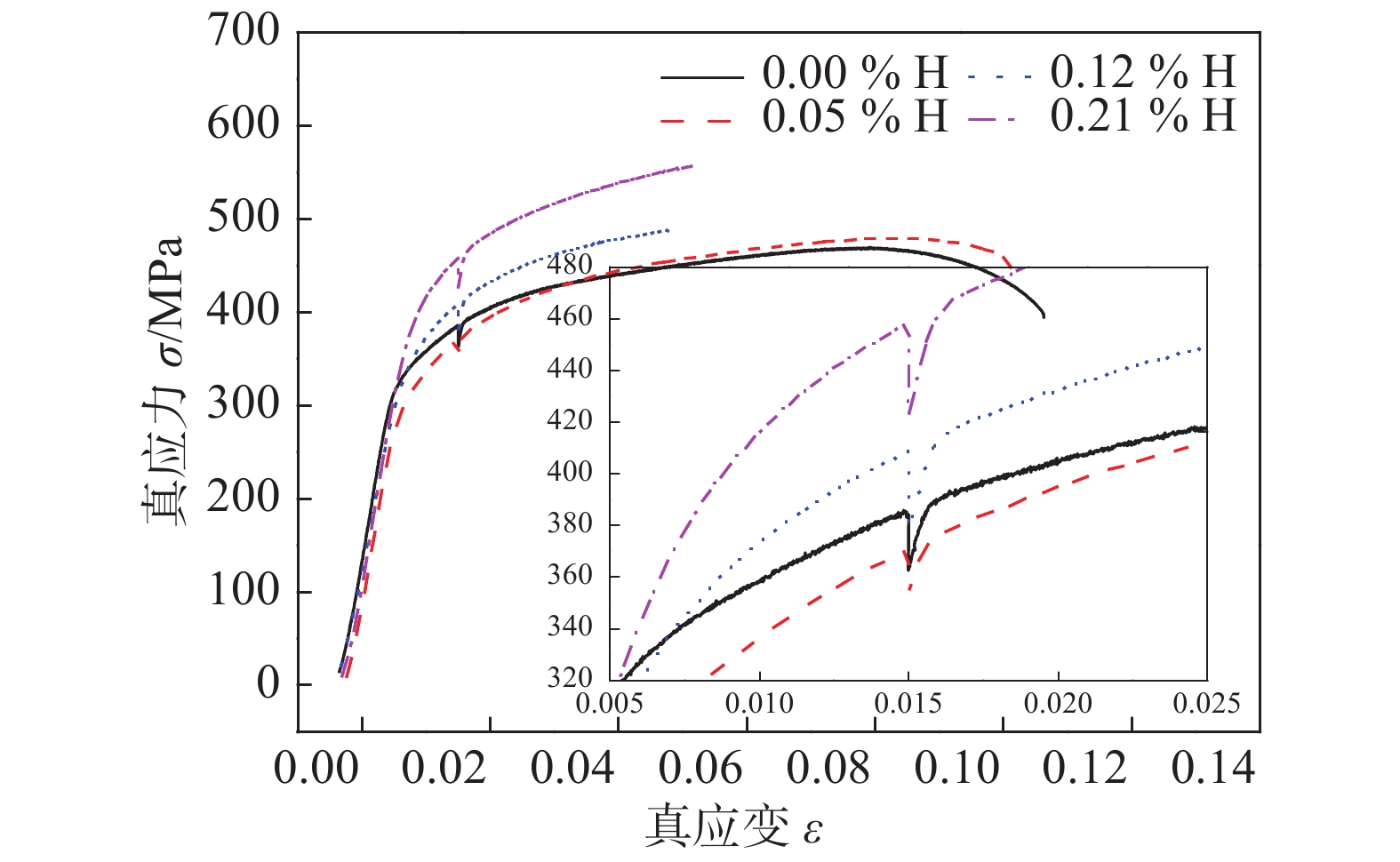
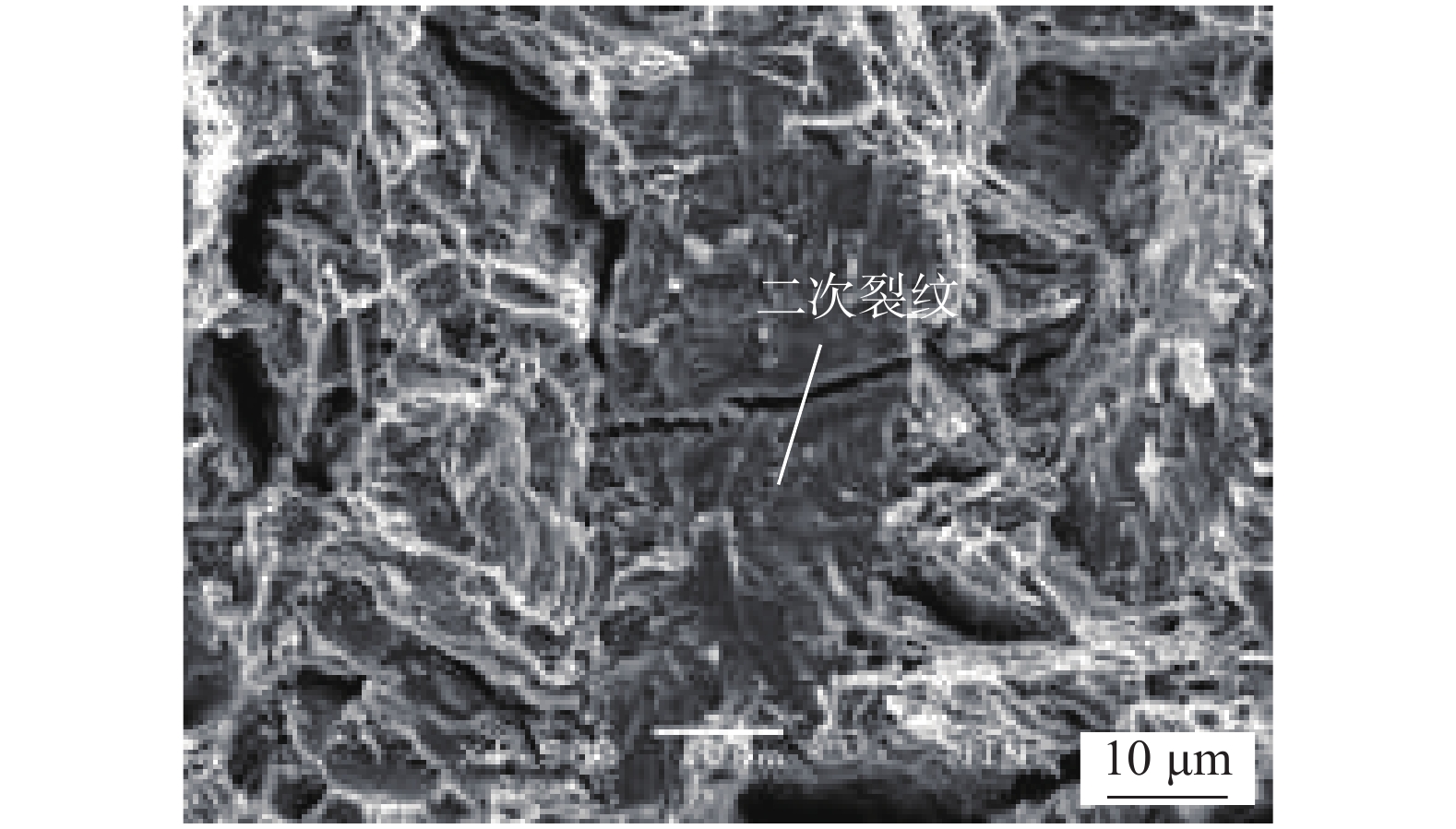
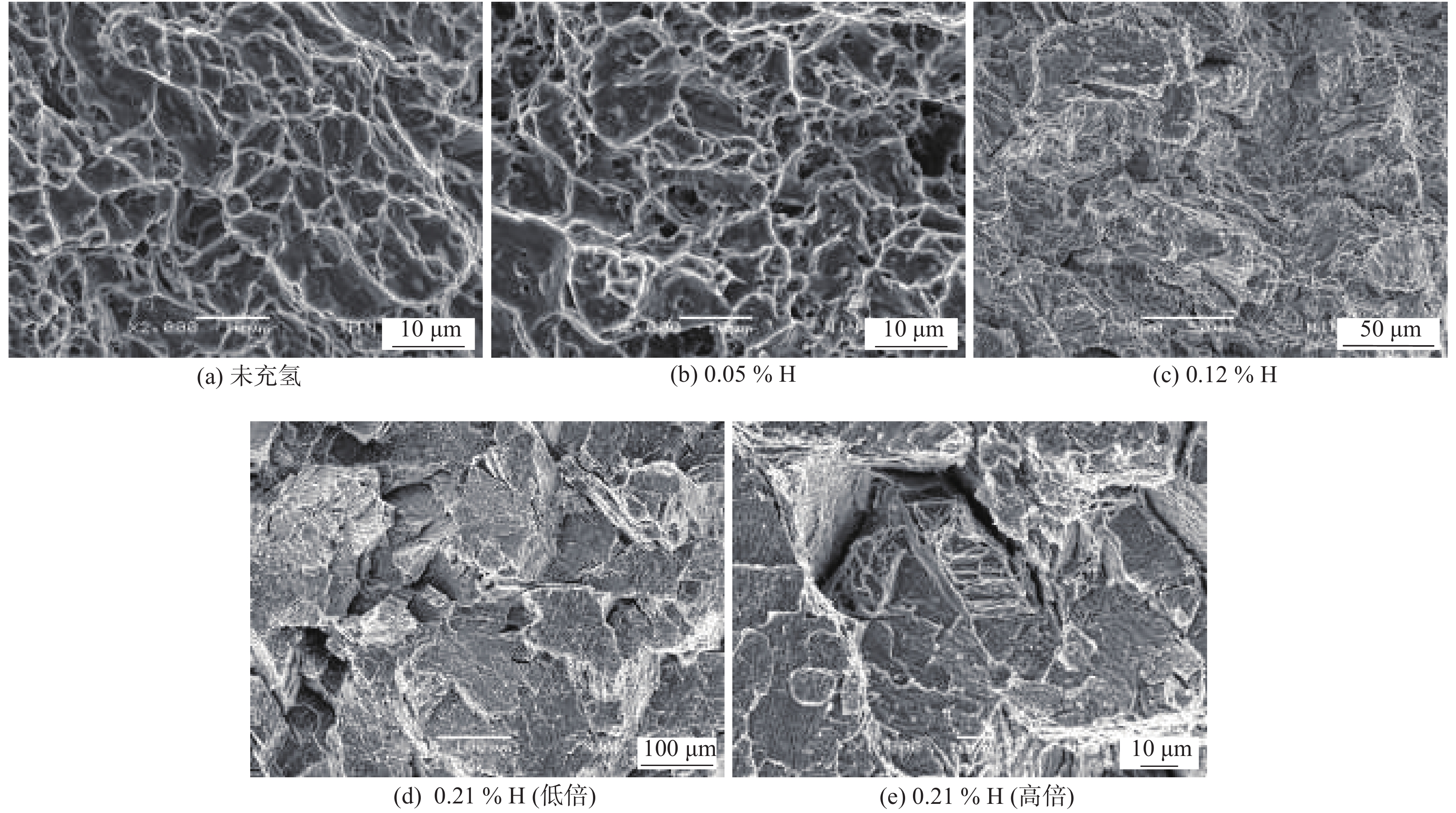
摘要: 钛合金焊接件低氢浓度下常发生氢脆失效,文中研究了充氢量对钛合金焊接接头拉伸性能的影响规律及其作用机制. 结果表明,随充氢量增加,室温强度明显提升,而塑性指标显著恶化. 充氢0.05% (质量分数)时,固溶氢对组织强化效果有限,抗拉强度略有增加;固溶氢降低了溶质原子对位错运动“钉扎”作用,屈服强度下降;固溶氢仅依靠扩散聚集,致局部微区氢浓度增加,其对塑性影响不大. 充氢0.12%后,氢化物“钉扎”作用加强,氢致位错交叉滑移更为困难,室温强度显著增加;脆性氢化物自身断裂、析出特征或加速与基体分离,致塑性显著下降. 未充氢或0.05% H时,焊接接头发生韧性断裂;充氢0.12%后,以脆性断裂为主;固溶氢、氢化物对断裂方式转变产生直接影响.Abstract: Hydrogen embrittlement of titanium alloy weldments often occur at low hydrogen concentrations. The effect of hydrogen content on tensile properties of titanium alloy welded joints and its mechanism were studied. The results show that with the increase of hydrogen content, the room temperature strength was significantly improved, the plasticity was significantly deteriorated. At 0.05 wt.% H, solid solution hydrogen had a limited effect on tissue strengthening and a slight increase in tensile strength; solid solution hydrogen reduced the "pinning" effect of solute atom on dislocation movement, yield strength decreased; solid solution hydrogen only depend on the diffusion and accumulation to cause the local micro-region hydrogen concentration to increase, which had a little effect on the plasticity. After 0.12 wt.% H, the "pinning" effect of the hydride was strengthened, the hydrogen-induced dislocation cross-slip was more difficult, and the strength at room temperature was significantly increased; the brittle hydride itself fractured, precipitated, or accelerated separation from the matrix, resulting in significant plasticity decline. When not charged with hydrogen or 0.05 wt.% H, the ductile fracture occurred in the welded joint; After 0.12 wt.% H, the brittle fracture was the main; solid solution hydrogen and the hydride had a direct effect on fracture mode transformation.
-
0. 序言
增材制造(additive manufacturing, AM)是一种实现复杂结构精密“控形”和高性能“控性”相结合的高端制造方式[1-4]. 对于轻质铝合金高性能增材制造成形构件,传统的熔化增材制造工艺在制造过程中存在构件热损伤严重,易产生气孔和裂纹缺陷等难题[5-6].
搅拌摩擦增材制造技术[7]衍生于搅拌摩擦焊[8-9],是一种固相增材制造技术,以低热输入和大塑性变形为主要特征,在高性能的轻质合金构件制造成形方面具有独特的优势. 搅拌摩擦增材制造过程中,材料并未达到熔点而一直保持热塑化态,热塑化的材料经过增材制造工具的“锻造”作用制造成形,避免了熔化增材制造工艺中的热损伤或气孔裂纹等缺陷,可获得性能良好的细晶组织,从而提高铝合金构件的性能. 根据制造工艺过程特点,将搅拌摩擦增材制造分为3种典型模式,即摩擦堆焊沉积式、板材叠加式及中空棒料摩擦沉积式. 最初,学者们研究的摩擦堆焊沉积式主要通过耗材与基板之间的摩擦形成冶金结合实现沉积成形[10],沉积层间存在界面弱连接且在外在成形控制方面和大型构件连续送料成形方面的研究仍缺少实质性的进展;He等人[11]采用板材叠加式对Al-Zn-Mg合金成形进行了研究,采用板材叠加的方式将多块板材向上堆叠,增材成形件仅焊核无缺陷的区域可有效使用,且在FSAM过程中各道次间需反复装夹;美国Meld公司开发了搅拌摩擦沉积增材技术[12],方形棒料受轴向推力作用,通过中空模具腔内与基板摩擦塑化成形,制造过程中方形棒料需多次换料装夹并重启,送料过程不连续. 综上,目前已开发的搅拌摩擦固相增材制造技术在送料方面具有不连续性[13-14],致使增材制造过程中的多次非稳定性过程,大型结构件制造时间较长,且堆积层间界面存在弱连接等技术瓶颈.
拟突破搅拌摩擦增材制造技术送料不连续和界面弱连接的难题,原创性地开发基于丝材的连续进给搅拌摩擦增材制造技术[15],研究增材制造工艺成形过程,揭示多层堆积层的结合界面成形特性,分析堆积层组织与性能,为铝合金搅拌摩擦增材制造高性能大型构件提供技术方案.
1. 试验方法
连续进给搅拌摩擦增材制造系统主要包括万洲焊接公司生产的WWW-LM3324-2D-3T龙门式数控搅拌摩擦焊机和自主研发的搅拌摩擦增材制造系统,该系统包括设有进料孔的储料腔、用于热塑化丝材并连续挤压与搅拌处理的搅拌头和实现连续送料的送丝机. 其中,送丝机的送丝轮采用V形槽和滚花结构设计以防止焊丝打滑,增大送丝力. 试验所用丝材为Al-Si合金丝材,直径为2.4 mm,基板采用6061-T4铝合金,尺寸为300 mm × 100 mm × 6 mm. Al-Si丝材及6061-T4铝合金基板的化学成分见表1.图1为连续进给搅拌摩擦增材制造示意图,在增材制造过程中,增材制造过程主要分为三个阶段,即:丝材输送段、材料热塑化段和增材成形段;丝材原料是从送丝通孔进入螺槽中,螺杆上的矩形螺纹会将丝材剪切成多个金属颗粒段,金属颗粒段以非塞流的形式沿螺槽向下运动;随塑化材料的连续积累,储料腔内的压力逐渐增高,颗粒状材料逐渐被压实并达到塑化状态;此时,非塞流输送转变成塞流输送,塑化态金属材料经过底部的搅拌针连续的搅拌处理,材料组织与成分更加均匀,最终经储料腔底部的轴肩端面与基板之间的间隙增材制造成形. 增材制造过程中采用的转速为1 100 r/min,行进速度为600 mm/min,送丝速度为3 000 mm/min,且搅拌针压入前一堆积层0.6 mm进行搅拌.
表 1 Al-Si合金和6061-T4板材化学成分 (质量分数,%)Table 1. Chemical compositions of Al-Si alloy and 6061-T4 sheet材料 Cu Mg Si Fe Mn Zn Ti Cr Al Al-Si 丝材 0.23 0.05 ~ 0.08 4.5 ~ 6.0 0.18 0.10 0.008 0.07 0.0001 余量 6061-T4板材 0.25 1.08 0.60 0.32 0.04 0.001 0.045 0.189 余量 增材制造完成后,采用线切割沿垂直行进方向选取单侧成形壁样件进行分析,切取5 mm厚的金相样品进行金相宏观形貌分析,腐蚀液为5%(体积分数)的氢氟酸水溶液,腐蚀时间为10 ~ 20 s;采用Keyence VHX-1000E超景深显微镜观察增材构件截面宏观形貌及各个区域的层间结合界面和堆积层不同区域的微观组织;在增材制造截面上采用HXD-1000TM数字式显微硬度仪进行硬度测试,加载载荷为0.98 N,保载时间为10 s,显微硬度测试点分布如图2所示,相邻测试点之间的距离为0.5 mm;沿堆积方向并排切取拉伸试样进行测试,拉试件尺寸如图3所示,采用SHIMADZUEHF-UV200K2型力学性能试验机进行拉伸性能测试,拉伸速率为0.5 mm/min,采用扫描电子显微镜(SEM, Merlin Compact)分析拉伸断口形貌.
2. 试验结果与讨论
2.1 过程分析
增材制造制备的多层闭环成形实际工艺过程及材料流动情况如图4所示. 在增材制造实际工艺过程中(图4a),热塑化材料的流动行为决定了增材制造构件的成形,如图4b所示,丝材经由增材制造搅拌头的剪切热塑化处理流入储料腔内,随着热塑化金属材料连续积累,储料腔内的压力升高,热塑化态的铝合金沿搅拌头上的螺槽向下流动,储料腔底部的静止端面对热塑化材料有一定的径向限位与锻造挤压作用,而搅拌头底部的搅拌针设计提高了塑化材料的动态流动性和均质性,搅拌针的搅拌处理作用避免了搅拌摩擦增材制造层间界面弱连接缺陷,提高了堆积层与层之间的结合致密性,最终组织及均匀态的铝合金材料经储料腔底部端面与前一堆积层之间的间隙增材制造成形. 选取铝合金搅拌摩擦增材制造特征成形构件单侧成形壁样件进行分析,如图5所示. 宏观形貌显示各堆积层成形良好且均匀一致,堆积层厚平均为1.2 mm,层宽为24 mm,证明了增材制造技术成形过程稳定.
增材制造成形件截面及特征区域层间界面形貌与微观组织形貌如图6所示. 堆积层与基板、堆积层与堆积层之间界面结合致密,无沟槽和弱连接等缺陷(图6a),表明在增材制造过程中搅拌针的搅拌处理作用可显著提高热塑化材料与基板之间的结合效果. 在增材制造过程中,储料腔底部的端面对热塑化状态材料的径向限位作用,使堆积层成形宽度保持在24 mm,与储料腔底部端面尺寸相一致,同时该端面也会对热塑化材料有一定的锻造挤压作用,使堆积层间及内部结合良好.
![]() 图 6 增材制造样件横截面及特征区域层间界面形貌与微观组织形貌Figure 6. The cross-section of the additive manufacturing specimen and its interfacial morphology and microstructures from the featured areas. (a) additive morphology; (b) interface A; (c) interface B; (d) interface C; (e) top section; (f) middle section; (g) bottom section
图 6 增材制造样件横截面及特征区域层间界面形貌与微观组织形貌Figure 6. The cross-section of the additive manufacturing specimen and its interfacial morphology and microstructures from the featured areas. (a) additive morphology; (b) interface A; (c) interface B; (d) interface C; (e) top section; (f) middle section; (g) bottom section堆积层间界面结合是确保增材制造成形的关键,因此进一步表征了堆积层与基板之间的界面,图6b ~ 图6d为未腐蚀的初始堆积层与基板的界面形貌. 在增材制造过程中,搅拌针侧面与热塑化材料之间发生相对剪切滑动,热塑化材料被连续不断地剪切挤压. 同时在搅拌针的侧向挤压与锻造挤压的共同作用下,初始堆积层与基板形成良好的界面. 进一步地,分析了增材制造成形件不同增材位置的微观组织形貌,图6e ~ 图6g依次为成形件沿堆积方向顶部、中部及底部的微观组织形貌. 在增材制造的连续制备成形过程中,热塑化态的铝合金材料在热力耦合作用下,发生严重的塑性变形,晶粒组织以动态再结晶的形式形成细小的等轴晶粒;堆积层的底部和中部区域受多次摩擦热输入的影响,晶粒尺寸略大于堆积层顶部.
2.2 显微硬度分布
沿堆积方向不同区域的显微硬度分布情况如图7所示,沿堆积方向,硬度值的波动较小,由于在增材制造过程中,铝合金材料一直维持热塑化态,摩擦热输入较小;通过显微硬度云图得出,增材制造成形件顶部堆积层的显微硬度平均值为44.8 HV ± 2.7 HV,中部堆积层的显微硬度平均值为42.8 HV ± 1.8 HV,底部堆积层的平均硬度值为41.6 HV ± 0.5 HV. 中部和底部堆积层在增材制造过程中经历了多次摩擦热输入的影响,堆积层中部和底部硬度的平均值要略低于顶部堆积层,整体堆积层的显微硬度分布较均匀. 由于搅拌头底部搅拌针对热塑化材料的搅拌处理作用,同一堆积层内部的晶粒尺寸分布具有一定的均匀性,证明热塑化材料得到了充分且均匀化的搅拌处理.
2.3 拉伸性能评价
图8为增材方向的拉伸性能测试结果,增材制造沿堆积方向的抗拉强度可达207.1 MPa ± 3.2 MPa,断后伸长率为19.6 % ± 5.3%. 搅拌针对热塑化材料的搅拌摩擦处理,提高了堆积层与层之间界面结合的致密性. 在3 000 mm/min的送丝速度下,冷金属过渡增材制造铝合金成形件沿堆积方向的抗拉强度为156 MPa,延伸率为13.9%[16],增材制造工艺成形件中铝合金沿堆积层方向的抗拉强度相比于冷金属过渡增材制造技术提高34%,断后伸长率提高41%. 连续进给搅拌摩擦增材制造铝合金优质性能成形较冷金属过渡增材制造工艺具有显著的优势.
图9为沿堆积方向选区A的拉伸断口形貌,从沿堆积方向的整体的SEM断口形貌来看(图9a),断口表面形貌具有大量的均匀分布的韧窝和局部的撕裂棱组成,选区断口形貌(图9b)中不存在气孔及裂纹等缺陷,塑性较好,表现为典型的韧性断裂模式.底部的堆积层在多次热循环的影响下,晶粒组织尺寸较大,因此会在底部堆积层优先开裂.
3. 结论
(1) 提出了连续进给搅拌摩擦增材制造方法,铝合金丝材经由送丝孔进入储料腔,搅拌头连续热塑化并向下挤压铝合金材料,搅拌针在堆积层间的搅拌作用有效地提高了堆积层间的界面结合,成功制备了成形良好的铝合金多层闭环结构件,各堆积层成形厚度平均为1.2 mm,证明了增材制造过程的连续性和稳定性.
(2) 连续进给搅拌摩擦增材制造过程中,热塑化材料被搅拌头连续剪切并向下挤压,搅拌针与热塑化材料之间发生相对剪切滑动,堆积层间界面结合良好,无沟槽和弱连接等缺陷,搅拌摩擦增材制造的堆积层各区域均为细小的等轴晶粒.
(3) 增材制造成形件整体的硬度值波动较小,增材方向的抗拉强度可达207.1 MPa ± 3.2 MPa,断后伸长率为19.6% ± 5.3%,拉伸断口表面中存在大量致密的韧窝,表现为典型的韧性断裂特征.
-
表 1 TA10合金及TA10焊丝主要化学成分 (质量分数,%)
Table 1 Chemical composition of TA10 alloy and TA10 welding wire
材料 Mo Ni Fe O C N H Ti TA10合金 0.32 0.75 0.08 0.014 0.01 0.03 0.004 余量 TA10焊丝 0.31 0.80 0.05 0.011 0.01 0.02 0.001 余量 -
[1] 张春波, 乌彦全, 朴东光, 等. TA19钛合金惯性摩擦焊接工艺[J]. 焊接学报, 2018, 39(12): 44 − 48. doi: 10.12073/j.hjxb.2018390295 Zhang Chunbo, Wu Yanquan, Piao Dongguang, et al. TA19 titanium alloy inertia friction welding process[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2018, 39(12): 44 − 48. doi: 10.12073/j.hjxb.2018390295
[2] Qi Dan, Zhu Ying, Guo Wei, et al. New Ti-Zr-Cu-Ni-La system brazing filler metals for the joining of titanium alloy[J]. China Welding, 2015, 24(2): 6 − 11.
[3] Li Xifeng, Chen Xin, Li Baoyong, et al. Grain refinement mechanism of Ti-55 titanium alloy by hydrogenation and dehydrogenation treatment[J]. Materials Characterization, 2019, 157: 109919. doi: 10.1016/j.matchar.2019.109919
[4] Panin P V, Manokhin S S, Dzunovich D A. Research on submicron-grained structure formation in titanium alloys upon reversible hydrogenation and plastic deformation[J]. Inorganic Materials Applied Research, 2018, 9(6): 1029 − 1034. doi: 10.1134/S2075113318060229
[5] 中国国家标准化管理委员会. GB/T 2651-2008 焊接接头拉伸试验方法[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2008. Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China. GB/T 2651-2008 Tensile test method on welded joints[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2008.
[6] Liu Quanming, Zhang Zhaohui, Yang Haiying, et al. Hydride precipitation in the hydrogenated 0.12wt.%H weld zone of Ti-0.3Mo-0.8Ni alloy argon-arc-welded joints[J]. The Journal of the Minerals, Metals & Materials Society, 2018, 70(9): 1902 − 1907.
[7] Liu Quanming, Zhang Zhaohui, Liu Shifeng, et al. The hydride precipitation mechanisms in the hydrogenated weld zone of Ti-0.3Mo-0.8Ni alloy argon-arc welded joints[J]. Advanced Engineering Materials, 2018, 20(5): 1700679. doi: 10.1002/adem.201700679
[8] 褚武扬. 氢损伤和滞后断裂[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 1988. Chu Wuyang. Hydrogen damage and delayed fracture[M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 1988.
[9] 苏娟华, 邵鹏, 任凤章. TA10钛合金高温流变行为及拉伸性能[J]. 材料热处理学报, 2018, 39(6): 14 − 20. Su Juanhua, Shao Peng, Ren Fengzhang. High temperature flow behavior and tensile properties of TA10 titanium alloy[J]. Transactions of Materials and Heat Treatment, 2018, 39(6): 14 − 20.
[10] 施金美. 钛合金环境氢脆的研究[D]. 上海: 上海大学, 2003. Shi Jinmei. Study on environmental hydrogen embrittlement of titanium alloy[D]. Shanghai: Shanghai University, 2003.
[11] Anand L, Mao Y, Talamini B. On modeling fracture of ferritic steels due to hydrogen embrittlement[J]. Journal of the Mechanics and Physics of Solids, 2019, 122: 280 − 314. doi: 10.1016/j.jmps.2018.09.012
[12] 袁宝国. 置氢Ti-6Al-4V合金室温变形行为及改性机理研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2010. Yuan Baoguo. Deformation behavior and mechanism of hydrogenated Ti-6Al-4V alloy at room temperature[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2010.
-
期刊类型引用(0)
其他类型引用(3)



 下载:
下载: