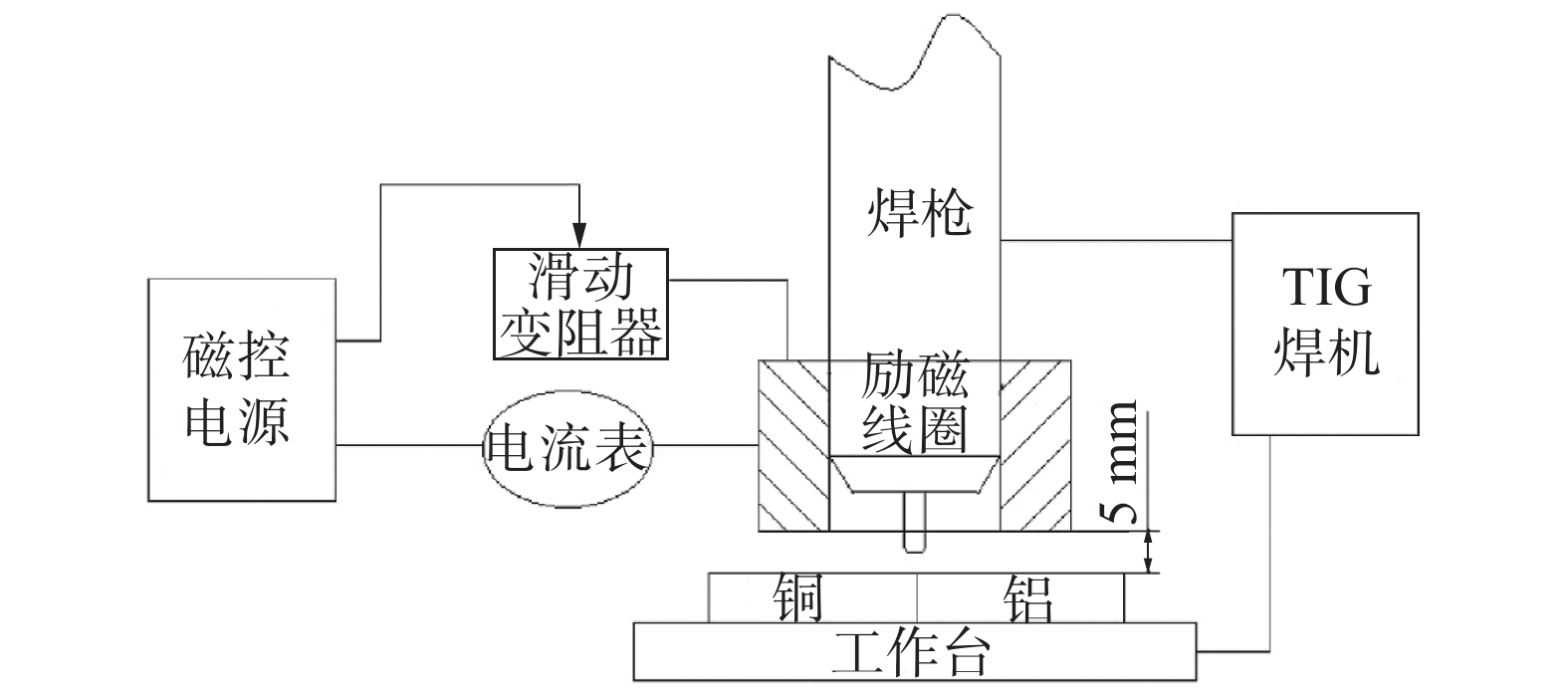
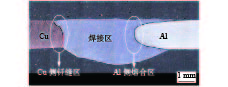
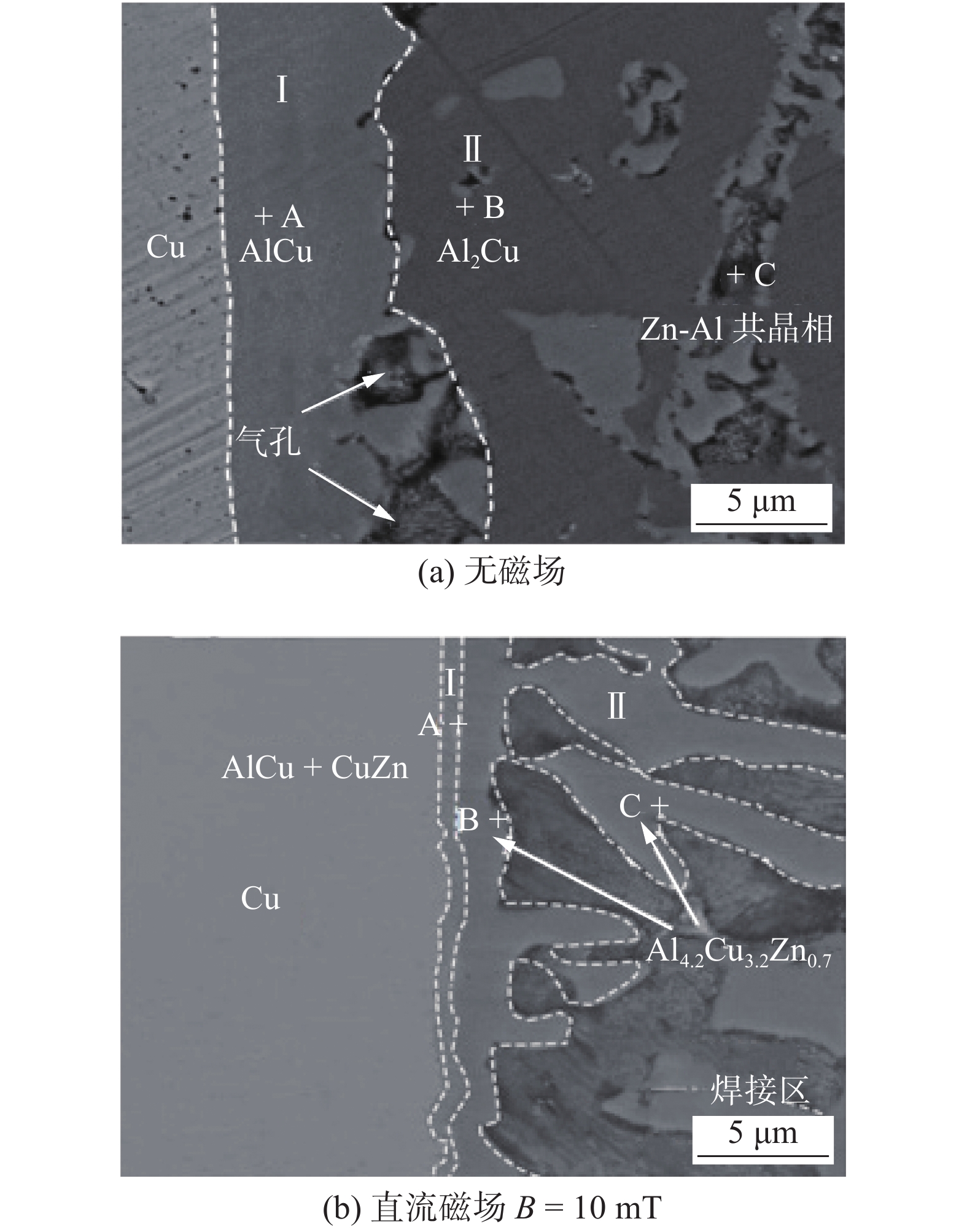
Effect of microstructure and mechanical properties on Al-Cu welding-brazing joint assisted by longitudinal DC magnetic field
-
摘要: 采用TIG焊进行铝铜异种材料熔钎焊对接试验,通过添加Zn-2%Al药芯焊丝调控焊缝成分,并施加纵向直流磁场调控界面组织,接头力学性能显著提高. 结果表明,相比于无磁场,在纵向直流磁场的作用下,Cu侧IMC层的形状、厚度和化合物种类均发生变化:平均厚度明显变薄,由32.8 μm降至14.6 μm;形状由平直变为弯曲,起到“机械咬合”作用;Cu侧IMC层Al4.2Cu3.2Zn0.7三元化合物的出现抑制了硬脆的AlCu与Al2Cu化合物的生长,接头性能升高. 添加直流磁场后,接头抗拉强度均比无磁场时高,且接头抗拉强度随着磁场强度的增加呈现先增大后减小的趋势. 当焊接电流I = 95 A,焊接电压U = 16 V,焊接速度v = 140 mm/min,磁场强度B = 10 mT时,接头抗拉强度最高,达到110.8 MPa,比无磁场升高了约24%.Abstract: TIG welding was used for butt welding of aluminum copper dissimilar materials. By adding Zn-2%Al flux cored wire to control the composition of the weld, and by adding longitudinal DC magnetic field to control the interface structure, the mechanical properties of the joint were improved. The results show that, compared with no magnetic field, the shape, thickness and compound types of IMC layer on the Cu side change under the action of longitudinal DC magnetic field: the average thickness of IMC layer decreases from 32.8 μm to 14.6 μm; the shape changes from straight to curved, which plays a role of “mechanical occlusion”; the appearance of ternary compound Al4.2Cu3.2Zn0.7 in IMC layer on Cu side inhibits the growth of hard and brittle AlCu and Al2Cu compounds, and improves the joint performance. After adding DC magnetic field, the joint tensile strength is higher than that without magnetic field, and the joint tensile strength increases first and then decreases with the increase of magnetic field strength. When welding current I = 95 A, welding voltage U = 16 V, welding speed v = 140 mm/min and magnetic field strength B = 10 mT, the tensile strength of the joint is the highest, reaching 110.8 MPa, which is about 24% higher than that without magnetic field.
-
0. 序言
铝合金密度低,导电性、导热性、耐腐蚀性、抗疲劳性优异,比强度和比模量较高,加工性能较好[1-3],已成为各工业领域应用较多的重要结构材料之一. 常用于金属构件成形的增材制造技术主要分为粉末床熔融(PBF)和定向能量沉积(DED)两类,由于铝合金易氧化,制成粉末的成本较高,使用PBF技术和送粉式DED技术的对铝合金制备的研究甚少,同时,铝合金对激光吸收率低和Al元素易挥发的特点,限制了激光熔丝增材制造和电子束熔丝增材制造在铝合金中的应用,因此现阶段使用电弧增材制造技术制备铝合金具有显著的优势[4].
电弧增材制造是以电弧为热源,利用离散—堆积的原理,将熔化的丝材逐层沉积,根据三维数字模型由线—面—体逐渐成形出金属零件的自下而上的先进增材制造技术,到目前为止,已用于该技术的铝合金主要有Al-Cu(2xxx)系列、Al-Mg(5xxx)系列、Al-Si(4xxx)系列、Al -Mg-Zn-Cu(7xxx)系列和其他一些成分的铝合金[5]. 与其它的增材制造技术相比,电弧增材制造技术成形尺寸大,设备简单,制造成本低,材料利用率和沉积效率高,对环境的污染小,平台灵活性强,可以实现无模具近净成形[6-7]. 然而该技术具有局部快速熔化、非平衡凝固和多层多道累积特点,得到的铝合金构件容易出现粗大柱状晶、气孔、夹杂、裂纹以及残余应力与变形等冶金缺陷,同时成形精度较低,需要后续进行机加工处理.
针对铝合金电弧增材制造技术,介绍了当前的研究情况以及工程化应用,综述了国内外对于减少冶金缺陷、改善组织和性能所采取的调控手段的研究现状,展望了未来需重点研究的方向,希望为接下来的研究工作提供一些参考.
1. 铝合金的电弧增材制造技术
1.1 铝合金电弧增材制造技术的研究概况
如图1所示,来自中国、俄罗斯、印度、澳大利亚、埃及、西班牙、英国、美国以及挪威等国家的多个科研单位已对铝合金电弧增材制造技术进行了广泛研究. 基于Web of Science引擎的数据,图2显示了各国家在铝合金WAAM研究领域发表高水平文章的数量占比,从图中可以看出,中国学者发表的高水平文章数量约占总数的一半,表明中国科研单位对铝合金电弧增材制造技术的研究更加充分和全面. 图3显示了2013年 ~ 2023年国内外有关铝合金WAAM主题已发表的高水平文章数量和被引频次,由图可知,尽管在2023年时铝合金WAAM主题的高水平文章发表数量略有减少,但总体呈逐年增加的趋势. 同时,这些文章的被引频次也在不断上升,特别是在2019年后上升速度显著加快,这表明采用电弧增材制造技术生产铝合金构件已取得了显著效果,并且引起了学术界的广泛关注.
1.2 铝合金电弧增材制造技术的工程化应用
1.2.1 航空航天工业
在航空航天工业中,铝合金作为一种重要的结构材料广泛应用于制造低温罐、机身和航天器外壳等飞行器结构,如图4所示. 知名的私营航天公司Relativity Space经过7年的研发,成功利用电弧增材制造技术打印了铝合金燃料贮箱结构,并于2023年3月发射了全球第一款完全由3D打印制造的火箭,这次发射证明了利用3D打印技术制造火箭结构的可行性,随后该公司计划在2024年发射Terran R火箭,该火箭由95%的3D打印部件构成,并完全可重复使用;2023年6月,Caracol公司与米兰理工大学(Polimi)机械工程系合作,利用铝合金的电弧增材制造技术为太空物流运输公司D-Orbit制造了火箭推进剂压力罐,这为航空航天领域的定制金属部件的按需生产提供了解决方案,铝合金压力罐最终将安装在运载卫星上,用于运输和释放立方体卫星进入轨道;2023年10月,NASA宣布成功测试了由电弧增材制造技术制备的铝合金火箭发动机喷嘴;同年12月,一种采用电弧增材制造技术打印的大型复杂铝合金卫星支架随捷龙三号运载火箭升空,进一步验证了电弧增材铝合金技术的可靠性.
1.2.2 汽车制造业
遵循从高端行业应用开始,逐步走向其他行业的规律,铝合金电弧增材制造技术逐渐在汽车制造行业得到了延伸和发展. 在2023年底,国内领先的电弧增材制造厂商英尼格玛,已实现大尺寸铝合金汽车零部件精细化打印,图5为英尼格玛铝合金电弧3D打印的汽车底盘. 由于WAAM技术更适合车身、驱动器和底盘中的部分,宝马集团于2015年开始探索WAAM,并于2021年安装机器人单元,图6为宝马采用电弧增材制造技术生产的铝合金零件实物图,基于多年的探索,集团计划从2025年开始在车辆中测试电弧增材制造的零件,而首选材料是铝合金.
2. 单一调控手段的研究现状
2.1 参数优化与工艺改进手段
2.1.1 工艺方法
在电弧增材制造常用的四种工艺方法中,PA-WAAM工艺热输入较低,加上铝合金具有导热性好的特点,会进一步加速熔池凝固,缩短气泡逸出的时间,促进氢气孔的形成,因此铝合金几乎不采用这种工艺方法. 南京工业大学的WANG等人[8]通过CMT-WAAM制备了AA 5356准原位构件,研究发现,WAAM AA 5356构件的极限拉伸强度(UTS)、屈服强度(YS)和断后伸长率均令人满意. Norwegian University of Science and Technology的HORGAR等人[9]采用AA 5183焊丝和AA 6082-T6支撑板进行了常规GMA-WAAM的初步试验,结果发现,得到的铝
合金构件的屈服强度和拉伸强度的平均值分别为145 MPa和293 MPa,高于许多已公布的数据. 哈尔滨工业大学的BAI等人[10]采用钨极惰性气体保护(TIG)增材制造技术制备了几种2219-Al零件,并进行了常规的力学性能分析,沉积构件平均硬度为77.5 HV0.2,平均极限强度为237 MPa.
为了提高沉积效率,北京理工大学等高校的国内学者研究了一些新的工艺方法,如图7所示[11-15]. 北京理工大学的FU等人[11]采用热丝GTA-WAAM技术制备了2024铝合金薄壁方形试样;太原理工大学的ZUO等人[12]采用基于TIG-MIG焊的增材制造系统,成功地制造了5356铝合金构件,验证了TIG-MIG电弧增材制造工艺的高效性;大连理工大学的MIAO等人[13]采用激光—电弧混合增材制造(LAHAM)方法制备了4043铝硅合金;北京航空航天大学齐铂金教授团队采用自主研发的新型超音频脉冲电弧(UFP)作为热源,制备了组织和力学性能优异的铝合金构件;CONG等人[14]研究了超音频脉冲电弧对WAAM 2024铝合金显微组织、孔隙率和力学性能的影响,结果表明,超声频率脉冲电弧可以细化晶粒,显著降低气孔率,提高显微硬度及其均匀性,并且改善性能的各向同性;KUANG等人[15]通过研究发现, UFP-MIG工艺基本消除了2219铝合金焊接接头中的焊接气孔,降低了Cu元素在共晶相中的偏析程度,进而提高了焊接接头的强度和塑性.
2.1.2 工艺参数
控制保护气体的成分和流速对电弧稳定性、成形质量和孔隙率有着极为重要的作用. 西安交通大学的LI等人[16]采用熔化极气体保护焊(GMAW)作为热源,研究了氮气(N2)和氩气(Ar)两种保护气体对5356铝合金薄壁试件焊缝成形、显微组织和力学性能的影响,如图8所示,研究表明,在相同的工艺参数下,采用N2作为保护气体进行单层单焊道焊接后,焊缝高度较高,宽度较窄,熔深较浅,试样的晶粒尺寸较小,然而,生成的AlN会降低UTS和塑性,所以Ar保护下的试样力学性能更优异;瑞典Luleå University of Technology的HAUSER等人[17]研究了保护气体流速对4043/AlSi5(质量分数,%)CMT-电弧增材制造过程中的气孔行为影响,如图9所示,试样中的孔隙率随着气体流速的增加而增加.
![]() 图 8 不同保护气体成分下铝合金构件的外观形貌和性能 [16]Figure 8. Morphology and mechanical properties of aluminum alloy components with various shielding gas composition
图 8 不同保护气体成分下铝合金构件的外观形貌和性能 [16]Figure 8. Morphology and mechanical properties of aluminum alloy components with various shielding gas composition![]() 图 9 不同保护气体流速下的孔隙率[17]Figure 9. Porosity of aluminium alloys with various gas flow rates
图 9 不同保护气体流速下的孔隙率[17]Figure 9. Porosity of aluminium alloys with various gas flow rates在层间温度的控制上,英国Coventry大学的DEREKAR等人[18]研究了层间温度变化对5356铝合金GMA-WAAM构件气孔率和力学性能的影响,如图10所示,发现用较高层间温度生产的WAAM试样显示出比用较低层间温度生产的试样少10.41%的孔隙率,拉伸性能相对更好;杨启杰等人[19]通过研究表明,当层间等待时间为20 ~ 30 s时,4043 铝合金电弧增材件的外观成形质量良好,拉伸性能最优.
![]() 图 10 不同层间温度下5356铝合金的孔隙率[18]Figure 10. Porosity of 5356 aluminum alloy under different interlayer temperatures
图 10 不同层间温度下5356铝合金的孔隙率[18]Figure 10. Porosity of 5356 aluminum alloy under different interlayer temperatures调节焊接速度和送丝速度等参数是对铝合金进行控“形”和控“性”最基本、最关键的手段. 李权等人[20]研究了EP/EN(正负半波占比)、扫描速度、送丝速度等工艺参数对成形2219铝合金微气孔缺陷的影响规律,结果发现,在热输入为230.5 J/mm和439. 5 J/mm时,平均气孔率均降低至0.2%以下;埃及Kafrelsheikh University的TAWFIK等人[21]采用GTA-WAAM技术制备了Al-Mg铝合金薄壁零件,研究了200 mm/min、320 mm/min和500 mm/min三种焊接速度(TS)对显微组织特征和拉伸性能的影响,结果表明,在500 mm/min的焊接速度下沉积的合金成形质量较好,气孔和裂纹较少,显示出更高的力学性能. 如图11所示,极限拉伸强度(UTS)为245.5 MPa,断后伸长率(EL)为35.28%.
![]() 图 11 不同焊接速度下Al-Mg铝合金的力学性能[21]Figure 11. The mechanical properties of Al-Mg aluminum alloy with different travel speed
图 11 不同焊接速度下Al-Mg铝合金的力学性能[21]Figure 11. The mechanical properties of Al-Mg aluminum alloy with different travel speed2.1.3 工艺过程
不恰当的工艺过程也会对铝合金电弧增材构件带来不利的影响,为获得组织和性能更理想的增材件,西安交通大学、北京理工大学的学者以及美国加州理工大学等高校的学者对工艺过程进行了优化.
西安交通大学的CHANG等人[22]研究了不同沉积顺序对
2319 /5B06异种铝合金增材薄壁件性能的影响,发现以2319 铝合金作为下半部、5B06铝合金作为上半部的沉积件比相反沉积顺序的对应构件表现出更好的力学性能,其极限抗拉强度、屈服强度和断后伸长率分别为258.5 MPa,139.3 MPa和5.6%,仅略逊于2319 铝合金母材的力学性能.纳米颗粒的添加可以细化晶粒,强化第二相,均匀组织,同时提高铝合金的强度和塑性,所以近几年受到了越来越多的关注. 美国California Institute of Technology的OROPEZA等人[23]成功使用TiC纳米颗粒增强的Al
7075 焊丝进行电弧增材制造得到了图12所示的Al7075 构件,并在其研究中表明,纳米颗粒能够控制高强度铝合金的凝固行为. 北京理工大学的FU等人[24]则将TiC纳米颗粒加入AA7075 的GTAW-WAAM中,制造了大尺寸超高强韧性TiC/AA7075 零件,研究发现,TiC/AA7075 试样具有优异且各向同性的力学性能,其强度为435 MPa± 10 MPa,断后伸长率为7.8 % ± 0.8%.![]() 图 12 原材料和制造样品[23]Figure 12. Raw materials and fabricated samples. (a) TiC nanoparticle-enhanced weld wire; (b) conventional butt weld; (c) single layer overlay; (d) 3D printed multi-layer
图 12 原材料和制造样品[23]Figure 12. Raw materials and fabricated samples. (a) TiC nanoparticle-enhanced weld wire; (b) conventional butt weld; (c) single layer overlay; (d) 3D printed multi-layer综上所述,通过优化参数和改进工艺等方法可以调节热输入的大小,当热输入大小合适时,使用电弧增材制造技术制得的铝合金构件的强度和塑性基本与铸造铝合金相当,甚至可以实现电弧增材铝合金的组织和性能稍优于铸造铝合金的目标. 但传统的工艺优化受限于材料本身的性质,无法显著改善成形质量和微观组织、减少内部缺陷以及大幅提高力学性能,难以满足航空航天等领域对铝合金结构件日益增长的应用需求.
2.2 热处理
在电弧增材制造中,热处理是有效地提高合金硬度和强度的常用方法. 来自Austrian Institute of Technology的KLEIN等人[25]研究了热处理前后AlZn5.5MgCu(ML7075)合金的WAAM加工性能、组织演变和力学性能,研究发现,热处理能够消除热裂纹,减少偏析,并且析出硬化相,可使试样的显微硬度值近乎翻倍;西北工业大学的ZHOU等人[26]分析了WAAM 2219铝合金在进行图13中所示的热处理后的组织演变和析出强化. 研究表明,当固溶温度从520 ℃升高到540 ℃时,可以获得大量纳米尺寸且均匀分布的θ′′相.
![]() 图 13 热处理示意图[26]Figure 13. The schematic diagram of the heat treatment.
图 13 热处理示意图[26]Figure 13. The schematic diagram of the heat treatment.虽然热处理改善组织和提高强度的能力突出,但其缺点也不容忽视. 如图14所示,上海交通大学的YANG等人[27]采用WAAM-CMT技术研究了热处理对AlSi7Mg0.6铝合金显微组织的影响,发现T6热处理试样在xOy面和xOz面的晶粒尺寸较沉积态试样分别增大了50.56%和53.62%;西安交通大学的FANG等人[28]通过CMT-WAAM制备了A357铝合金,研究了沉积态和热处理态零件的显微组织和力学性能,如图15所示,热处理后,顶部和底部区域孔隙的平均直径分别增加了4.2%和13.8%,这些大孔隙的存在显著降低了断后伸长率.
![]() 图 14 试样在不同状态下的电子背散射衍射图和晶粒尺寸分布统计图[27]Figure 14. Electron backscattered diffraction (EBSD) graphs and statistical diagrams of grain size distribution of samples in different states. (a-b) the as-deposited samples; (c-d) the T6 heat-treated samples
图 14 试样在不同状态下的电子背散射衍射图和晶粒尺寸分布统计图[27]Figure 14. Electron backscattered diffraction (EBSD) graphs and statistical diagrams of grain size distribution of samples in different states. (a-b) the as-deposited samples; (c-d) the T6 heat-treated samples![]() 图 15 沉积态试样和热处理试样的3D气孔图[28]Figure 15. 3D views of micropores of as-deposited and heat-treated samples
图 15 沉积态试样和热处理试样的3D气孔图[28]Figure 15. 3D views of micropores of as-deposited and heat-treated samples通过这一系列的研究可知,热处理后组织粗化,构件中原本的孔隙会聚集长大,并且产生次生孔隙,增加孔隙率,而且热处理有助于沉淀相的析出,这在提高强度的同时也会降低塑性,导致材料的强度与塑性失衡,容易发生断裂. 此外,并非所有的铝合金都适合通过热处理的方法提高力学性能的,只有Al-Cu合金(2系)、Al-Mg-Si合金(6系)和Al-Zn-Mg合金(7系)属于可热处理强化型铝合金,其余的则是不可热处理铝合金,只能采用其它辅助工艺进行强化.
2.3 电弧增材复合制造
大量的研究表明,不论是工艺优化还是热处理,都会因铝合金材料的类型或特点而受限,而熔池搅拌等辅助工艺则可以用于所有的铝合金材料,适用性和灵活性更强,强化效果更好. 在此基础上,结合“复合制造”的概念,将轧制等辅助工艺与电弧增材制造耦合协同工作的电弧增材复合制造逐渐成为了研究热点. 国外目前对电弧增材复合制造的研究甚少,而国内的西安交通大学、华中科技大学等高校在相关研究上已开展了较多的工作.
2.3.1 基于熔池搅拌的电弧增材复合制造
熔池搅拌是通过对熔池进行搅拌破碎枝晶,减少粗大柱状晶,促进细小等轴晶形成,进而有利于组织和性能优化的方法. 南京工业大学的DAI等人[29]采用图16中所示的WAAM与搅拌摩擦加工(FSP)相结合的复合增材制造(HAM)技术,成功制备了具有超细晶—等轴晶—柱状晶梯度组织的2319铝合金. 研究发现,与WAAM试样相比,WAAM/FSP试样的晶粒细化率达87.1%,显微硬度提高了17.5%,YS提高了48.1%,EL提高了15.4%.
![]() 图 16 WAAM + 层间FSP增材制造技术示意图[29]Figure 16. Schematic diagram of WAAM + interlayer FSP additive manufacturing
图 16 WAAM + 层间FSP增材制造技术示意图[29]Figure 16. Schematic diagram of WAAM + interlayer FSP additive manufacturing东北大学的HE等人[30]研究了FSP技术对4043铝硅合金WAAM成形组织演变和力学性能的影响,研究表明,与WAAM构件相比,引入层间FSP变形后EL的各向异性增强,原因在于FSP技术减少孔隙的能力有限,在搅拌之外的区域仍存在较多的气孔,如图17所示.另外,FSP的影响深度通常比沉积层的厚度浅[31],虽可以削弱由分层引起的各向异性,但由于在沉积下一层时,FSP的影响区域发生部分重熔加剧了组织的不均匀性,不均匀的组织也会造成断后伸长率的各向异性[32].
![]() 图 17 采用WAAM + 层间FSP方法制备的Al-Si合金的孔隙分布 [30]Figure 17. Pores distribution in the WAAM + interlayer FSP Al-Si alloy
图 17 采用WAAM + 层间FSP方法制备的Al-Si合金的孔隙分布 [30]Figure 17. Pores distribution in the WAAM + interlayer FSP Al-Si alloy2.3.2 基于表面强化的电弧增材复合制造
表面强化是通过激光或者超声对材料表面进行冲击进行强化的技术. 如图18所示,西安交通大学的JING等人[33]对典型的CMT-WAAM 2319铝合金进行了激光冲击表面处理(LSP),研究发现,激光冲击能有效地在WAAM 2319铝合金中形成深达1.3 mm的影响层,可在其影响层内的孔隙周围引起严重的应力集中而使孔隙塌陷,所以最终孔隙总数减少了65.3%,屈服强度和抗拉强度分别提高了151.2%和13.7%,疲劳寿命提高了一倍.
![]() 图 18 LSP系统示意图及LSPed样品近表面区域塌陷孔隙的SEM图[33]Figure 18. Schematic diagram of an LSP system and SEM image of collapsed pores in the near-surface zone of LSPed sample
图 18 LSP系统示意图及LSPed样品近表面区域塌陷孔隙的SEM图[33]Figure 18. Schematic diagram of an LSP system and SEM image of collapsed pores in the near-surface zone of LSPed sample位错密度的增加有利于强度的提高,但使合金更难变形,塑性降低,所以表面强化技术往往是以牺牲断后伸长率为代价而提高屈服强度和最终抗拉强度的. 南京航空航天大学的WANG等人[34]分析了超声冲击强化(UIT)对2219 WAAM构件的影响,如图19所示,与沉积态试样相比,UIT处理的试样UTS和YS提高,但是EL降低.
![]() 图 19 基于超声冲击强化的电弧增材复合制造[34]Figure 19. Hybrid arc additive manufacturing based on UIT technology
图 19 基于超声冲击强化的电弧增材复合制造[34]Figure 19. Hybrid arc additive manufacturing based on UIT technology值得注意的是,超声和激光的能量在试样中会逐渐被削弱. 北京航空航天大学的SUN等人[35]在研究中发现,激光冲击在表层和500 mm深的层中分别产生了高密度的位错和机械孪晶,使得硬化层厚度为1.2 mm的表面层的显微硬度显著提高,这充分说明了表面强化技术目前仅适用于试样表面区域的强化,不能对整个构件起到强化作用.
2.3.3 基于轧制的电弧增材复合制造
层间轧制是利用轧辊对沉积层进行碾压引起塑性变形提高工件尺寸精度,细化显微组织,缓解残余应力与变形,降低孔隙率,消除各向异性,使增材件具有与锻件相当的力学性能的工艺[36]. 东北大学的GU等人[37]基于CMT-WAAM技术,研究了15 kN,30 kN和45 kN三种载荷的层间轧制对WAAM 2319铝合金和5087铝合金孔隙率的影响,图20为试验设备图. 研究表明,在45 kN的轧制载荷下,直径大于5 μm的孔隙被消除;之后GU等人[38]同样施加15 kN,30 kN和45 kN的载荷,研究发现,与沉积态合金相比,轧制态合金中粗晶组织得到明显细化,并具有明显的轧制织构,45 kN轧制态合金的平均显微硬度、屈服强度和抗拉强度分别提高了40%,69%和18.2%,断后伸长率保持在20%以上. 英国Cranfield Univeristy的HöNNIGE等人[39]采用垂直层间轧制和侧轧控制WAAM 2319铝合金的残余应力与变形,结果发现,侧轧能逆转扭曲,缓解残余应力与变形的效果更好.
![]() 图 20 基于轧制的电弧增材复合制造设备图[37]Figure 20. Rolling and WAAM deposition setup
图 20 基于轧制的电弧增材复合制造设备图[37]Figure 20. Rolling and WAAM deposition setup由于冷轧需要配备高刚度的设备,生产成本高,效率低,华中科技大学的张海鸥教授团队[40]提出了采用图21所示的原位微轧制方法解决层间冷轧在电弧增材制造中存在的这些问题;HUANG等人[41]研究了微轧制与沉积态
4043 铝硅合金增材制造试样的组织和力学性能的差异,研究发现,与沉积态相比,微轧制态试样的抗拉强度和屈服强度分别达到了159 MPa和72 MPa,提高了18.6%和38.5%,断后伸长率从12.3%提高到16.2%. 但是该工艺仍具有使成形过程复杂化,影响成形效率的缺点,且受制于轧辊的尺寸及形状,装备灵活性低[42],不适用于几何形状复杂的构件.![]() 图 21 原位微轧制示意图[40]Figure 21. Schematic diagram of micro-rolling
图 21 原位微轧制示意图[40]Figure 21. Schematic diagram of micro-rolling2.3.4 基于其它辅助工艺的电弧增材复合制造
除熔池搅拌、表面强化和层间轧制这三种常用的方法外,还有一些辅助工艺也用于铝合金电弧增材复合制造中. 西安交通大学的FANG等人[43]研究了层间锤击对2319铝合金电弧增材构件力学性能、显微组织演变和强化机制的影响,图22展示了试验所用设备示意图及实物图. 在研究中发现,层间锤击细化了晶粒,因此试样的屈服强度和抗拉强度分别提高了60.6%和13%,但层间锤击试样的主要强化机制是利用塑性变形产生高密度的位错,这对断后伸长率不利. 另外,在生产过程中层间锤击受锤头形状的影响,不同区域的组织改性不均匀[44].
![]() 图 22 层间锤击设备示意图及实物图[43]Figure 22. Schematic diagram and physical view of interlayer hammering equipment
图 22 层间锤击设备示意图及实物图[43]Figure 22. Schematic diagram and physical view of interlayer hammering equipment武汉大学的ZHANG等人[45]将工件振动应用于CMT-WAAM中,如图23所示,利用试验探索了其对Al-Mg合金孔隙率和力学性能的影响. 结果表明,相比于未振动的试样,振动试样的平均晶粒尺寸减小了22.5%,孔隙率降低了5.14%,同时孔隙尺寸减小,最大抗拉强度提高了30 MPa. 然而在中间层微孔和不均匀组织的影响下,最大抗拉强度具有显著的各向异性.
![]() 图 23 工件振荡示意图[45]Figure 23. Schematic diagram of workpiece vibration
图 23 工件振荡示意图[45]Figure 23. Schematic diagram of workpiece vibration如图24所示,南京航空航天大学的ZHAO等人[46]将纵向交变磁场引入铝合金电弧增材制造系统,对有无外加磁场作用下的Al-5%Mg合金进行了全面对比研究. 结果发现,与未施加电磁力时相比,施加激励电流为2 A、激励频率为70 Hz的电磁力时,薄壁零件的表面精度得到了显著提高,表面波纹度降低了34%,第二相Al3Mg2的分布更加均匀,孔隙数量和尺寸大大减少;内蒙古工业大学的HU等人[47]研究了纵向直流磁场辅助下CMT-WAAM制备5356合金的表面形貌、显微组织和力学性能. 研究发现,纵向直流磁场的施加有效地抑制了驼峰的形成,并降低了沿晶界开裂的可能性,提高了显微硬度和拉伸性能. 和其他的辅助工艺相比,外加磁场在改善电弧形态和提高成形质量上优势突出,但降低孔隙率、细化晶粒、增加强化相和改善力学性能的效果不明显.
![]() 图 24 基于外部交变磁场的电弧增材复合制造[46]Figure 24. The schematic diagram of WAAM process with external alternating magnetic field
图 24 基于外部交变磁场的电弧增材复合制造[46]Figure 24. The schematic diagram of WAAM process with external alternating magnetic field3. 复合调控手段的研究现状
单一的调节工艺不能很好地平衡材料的强度与塑性、提高力学性能与消除各向异性等问题,限制了铝合金电弧增材复合制造技术的工业应用. 若发展基于多种工艺的电弧增材复合制造技术,可以突破单一调控手段固有的局限性,为瓶颈难题的解决提供新路径,在铝合金电弧增材制造的应用中具有巨大的发展潜力,目前国内已有学者做了相关的一些研究.
在复合调控手段中,通常将合金化、轧制等工艺方法与热处理相结合,充分利用热处理的优势优化组织与性能,同时通过其它工艺的作用消除热处理带来的组织粗化、孔隙率增加和塑性降低等问题. 兰州理工大学的HUANG等人[48]认为采用时效热处理与形成等轴晶粒的沉积策略相结合可以确保机械性能和各向异性的最佳平衡;西安交通大学的ZHOU等人[49]设计了Sc/Zr/Ti/Er微合金化2219铝合金,成功制备了薄壁构件并进行了热处理,如图25所示,结果发现,在T6和HT6热处理后,细小的等轴晶得以保持;英国Cranfield Univeristy的EIMER等人[50]发现通过将层间冷轧和沉积后热处理相结合,可以使材料的各向异性比未经层间轧制的热处理材料低,塑性比未经层间轧制的热处理材料高;西安交通大学的CHANG等人[51]提出了图26所示的一种新的复合后处理方法(HPTM),即在固溶和时效(AG)之间引入激光冲击强化(LSP),对比分析了T6处理和HPTM处理后AA2319铝合金增材试样的显微组织以及拉伸性能,结果发现,采用新型HPTM工艺制备的铝合金构件具有极高的强度,其屈服强度和抗拉强度比只进行T6热处理的分别提高38%和13%,整体上孔隙减少,验证了热处理复合激光冲击强化的有效性;美国UCLA的CHI等人[52]使用WAAM技术打印经纳米处理的AA6061丝材原料,分析了热处理前后试样的显微硬度分布、拉伸行为. 如图27所示,热处理后,6061试样的晶强度显著提高,韧性与商用锻造的AA6061相当.
![]() 图 25 基于微合金化 + 热处理的电弧增材复合制造[49]Figure 25. Hybrid arc additive manufacturing based on micro-alloying and heat treatment
图 25 基于微合金化 + 热处理的电弧增材复合制造[49]Figure 25. Hybrid arc additive manufacturing based on micro-alloying and heat treatment![]() 图 26 基于激光冲击强化+热处理的电弧增材复合制造[51]Figure 26. Hybrid arc additive manufacturing based on laser shock peening and heat treatment
图 26 基于激光冲击强化+热处理的电弧增材复合制造[51]Figure 26. Hybrid arc additive manufacturing based on laser shock peening and heat treatment![]() 图 27 试样的力学性能[52]Figure 27. Mechanical properties of samples
图 27 试样的力学性能[52]Figure 27. Mechanical properties of samples还有学者将其他的工艺方法相结合,也获得了不错的效果. 如图28所示,西安交通大学的JING等人[53]在电弧增材制造2219铝合金中采用螺旋轨迹振荡方式,并引入层间激光冲击强化(LSP),发现采用螺旋路径振荡模式显著减小了单个沉积层和重熔层的厚度,保留了连续沉积层之间的LSP作用的有益效果,延伸了硬化层的深度,减少了内部缺陷,最终得到试样的抗拉强度、屈服强度和断后伸长率分别提高了20.1%,19.1%和27.3%;南京航空航天大学的LYU等人[54]研究了超声振动和ZrO2颗粒在铝合金电弧增材制造工艺中的耦合应用方法,如图29所示,研究表明,在超声和颗粒的综合作用下,ZrO2颗粒可以均匀地分布在不同区域,增强了微观组织的均匀性,最终实现力学性能的显著改善,试验数据显示,超声振动和颗粒对强度和断后伸长率的综合影响分别达到13.8%和92.4%.
![]() 图 28 基于路径优化 + 激光冲击强化的电弧增材复合制造[53]Figure 28. Hybrid arc additive manufacturing based on path optimization and laser shock peening
图 28 基于路径优化 + 激光冲击强化的电弧增材复合制造[53]Figure 28. Hybrid arc additive manufacturing based on path optimization and laser shock peening![]() 图 29 基于添加颗粒 + 超声振动的电弧增材复合制造[54]Figure 29. Hybrid arc additive manufacturing based on particle addition and ultrasonic vibration
图 29 基于添加颗粒 + 超声振动的电弧增材复合制造[54]Figure 29. Hybrid arc additive manufacturing based on particle addition and ultrasonic vibration以上研究证实了基于多种工艺的电弧增材复合制造技术在铝合金中的可行性,值得后续进行下一步的研究. 然而现阶段的电弧增材复合制造虽涉及多种工艺和能量源,但只是简单的工艺叠加,只构成前后加工的顺序关系,还不属于严格的“协同制造”关系[55],并且在无可比拟的优势背后,存在着工艺过程复杂化的问题.
4. 结束语
针对电弧增材制造铝合金存在的问题,现阶段国内外学者主要通过工艺优化、热处理、电弧增材复合制造等手段进行调控,国外学者的研究主要集中在改变工艺方法和调整工艺参数上,国内学者的研究相对更全面些,尤其是在电弧增材复合制造技术的研究等方面. 从目前的研究内容来看,各种调控手段虽各具有其独特的优势,但都存在一定的局限性,且皆处于研究的初始阶段.
为实现铝合金电弧增材制造技术在各个领域的广泛应用,需从以下几个方面寻求突破.
(1)多工艺参数的实时动态调控. 工艺参数的选择对电弧增材制造铝合金的“控形”和“控性”起着关键的作用,现阶段电弧增材制造过程中工艺参数与成形尺寸、内部组织和力学性能之间的相关理论机制研究还不够深入. 构建精准的数学模型,在此基础上实时监测增材过程,对工艺参数进行动态调控,将是未来重要的研究发展方向.
(2)电弧增材复合制造的工艺协同. 随着增材技术的发展,基于多种工艺的电弧增材复合制造技术成为了未来电弧增材成形及性能控制的发展趋势. 但目前多种调控工艺的复合仅停留在相对分离的前后叠加的层面,离严格意义上的工艺协同控制尚有差距. 以同步或相互作用的方式加快实现电弧增材复合制造中不同工艺机制/能源/工具间的协同控制,以期达到显著改善工件性能的目标.
(3)电弧增材复合制造装备的智能化. 电弧增材复合制造需要多个装备进行配合完成工作,成形和性能的控制难度大. 目前的设备普遍存在自动化程度低的问题,构建复合控制成形和性能的加工装置,提高电弧增材平台的集成度和智能化水平具有重要的意义与价值.
-
-
[1] Zhou L, Li Z Y, Zhao H Y, et al. Microstructure and mechanical properties of TIG brazed joints of aluminium/brass dissimilar metals[J]. Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2015, 25(9): 2389 − 2395.
[2] Choudhury T, Ghorai A, Medhi T, et al. Study of microstructure and mechanical properties in friction stir welded aluminum copper lap joint[J]. Materials Today: Proceedings, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2020.03.238.
[3] Li G H, Zhou L, Shu F Y, et al. Statistical and metallurgical analysis of dissimilar friction stir spot welded aluminum/copper metals[J]. Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance, 2020, 29(3): 1830 − 1840. doi: 10.1007/s11665-020-04729-6
[4] Anbukkarasi R, Kailas S V. Influences of shape of the new interfaces and morphology of the intermetallics on mechanical properties of aluminum AA2024-pure copper joints by friction stir welding[J]. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2020, 106(11): 5071 − 5083.
[5] 刘彦峰, 周春生, 王献辉, 等. T2紫铜/2A12硬铝双金属复合材料的扩散连接[J]. 材料热处理学报, 2017, 38(2): 15 − 20. Liu Yanfeng, Zhou Chunsheng, Wang Xianhui, et al. Preparation of T2 copper/2A12 duralumin bimetallic composites by diffusion bonding[J]. Transactions of Materials and Heat Treatment, 2017, 38(2): 15 − 20.
[6] Mathivanan K, Plapper P. Laser welding of dissimilar copper and aluminum sheets by shaping the laser pulses[J]. Procedia Manufacturing, 2019, 36: 154 − 162. doi: 10.1016/j.promfg.2019.08.021
[7] Shankar S, Chattopadhyaya S. Friction stir welding of commercially pure copper and 1050 aluminum alloys[J]. Materials Today: Proceedings, 2020, 25: 664 − 667. doi: 10.1016/j.matpr.2019.07.719
[8] 周利, 李志勇, 赵洪运, 等. 铝/黄铜异种金属TIG填丝熔钎焊工艺[J]. 焊接学报, 2016, 37(12): 17 − 20. Zhou Li, Li Zhiyong, Zhao Hongyun, et al. TIG welding-brazing for Al/Cu dissimilar metals using filler material[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2016, 37(12): 17 − 20.
[9] Zhang Y, Li Y, Luo Z, et al. Feasibility study of dissimilar joining of aluminum alloy 5052 to pure copper via thermo-compensated resistance spot welding[J]. Materials & Design, 2016, 106: 235 − 246.
[10] 彭迟, 程东海, 陈益平, 等. 铝/铜异种材料等离子弧熔钎焊搭接接头工艺分析[J]. 焊接学报, 2016, 37(4): 65 − 68. Peng Chi, Cheng Donghai, Chen Yiping, et al. Analysis process of plasma arc melting brazing lap joint of dissimilar materials of aluminum and copper[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2016, 37(4): 65 − 68.
[11] Yang C, Jiang S Y, Bi H B. Numerical simulation study of metal transfer in MIG welding with magnetic control[J]. Applied Mechanics and Materials, 2014, 532: 545 − 548. doi: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMM.532.545
[12] Chen S J, Liu C H, Yu Y, et al. Influence of preset pulsed magnetic field on process stability of short circuiting transfer in gas metal arc welding[J]. Advanced Materials Research, 2011, 339: 440 − 443. doi: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.339.440
[13] Sun Q, Li J, Liu Y, et al. Arc characteristics and droplet transfer process in CMT welding with a magnetic field[J]. Journal of Manufacturing Processes, 2018, 32: 48 − 56. doi: 10.1016/j.jmapro.2018.01.017
[14] Chang Y L, Liu X L, Lu L, et al. Impacts of external longitudinal magnetic field on arc plasma and droplet during short-circuit GMAW[J]. International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2014, 70(9−12): 1543 − 1553. doi: 10.1007/s00170-013-5403-1
[15] 高亚楠. 纵向磁场作用下高速TIG焊接电弧行为及焊缝成形机理研究[D]. 沈阳: 沈阳工业大学, 2012. Gao Yanan. Research on high-speed TIG welding arc behavior and weld formation mechanism under longitudinal magnetic fields [D]. Shenyang: Shenyang University of Technology, 2012.
[16] 殷咸青, 罗键, 李海刚. 纵向磁场参数对LD10CS铝合金TIG焊焊缝组织的影响[J]. 西安交通大学学报, 1999, 7: 73 − 76. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-987X.1999.12.019 Yin Xianqing, Luo Jian, Li Haigang. Optimization of magnetic parameters for grain structure refinement of LD10CS aluminum alloy weldment[J]. Journal of Xi'an Jiaotong University, 1999, 7: 73 − 76. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-987X.1999.12.019
[17] 国旭明, 杨成刚. 磁搅拌对铝铜合金MIG焊缝形状、组织及性能影响[J]. 航空材料学报, 2007, 2: 18 − 21. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-5053.2007.02.004 Guo Xuming, Yang Chenggang. Effect of electromagneticstirring on the shape structure and mechanical properties of Al-Cu alloy MIG weld[J]. Journal of Aeronautical Materials, 2007, 2: 18 − 21. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-5053.2007.02.004
[18] Hicken G K, Jackson C E. Effects of applied magnetic fields on welding arcs[J]. Welding Journal, 1996, 45(8): 513 − 518.
[19] Abralov M A, Abdurakhmanov R U, Iuldashev A T. The effects of electro-magnetic action on the properties and structure of welded joints in the 01420 alloys[J]. Automatic Welding, 1977, 30(5): 52 − 55.
[20] Chen R, Wang C, Jiang P, et al. Effect of axial magnetic field in the laser beam welding of stainless steel to aluminum alloy[J]. Materials and Design, 2016, 109: 146 − 152. doi: 10.1016/j.matdes.2016.07.064




 下载:
下载: