FIP based simulation of short crack behavior at weld toe
-
摘要: 短裂纹的成核与早期扩展是疲劳裂纹演变过程的重要组成部分,对疲劳裂纹的演变行为和寿命预测具有重要意义. 针对焊趾局部的微观结构短裂纹,以微观敏感的疲劳指标参量为主要驱动力,基于泰森多边形方法构建了焊趾区域的晶粒模型,模拟了微观结构短裂纹的早期演变过程. 通过与试验结果对比,证实了微观敏感的疲劳指标参量及其计算模型的合理性和有效性. 仿真结果表明,疲劳寿命同时受晶粒所在位置、晶粒尺寸和晶粒取向等因素的影响,晶粒取向的随机性对裂纹宏观尺寸的分散性具有重要作用.Abstract: The nucleation and early growth stage of short crack are important parts of the evolution process and has significant influences on its evolution behavior and life prediction. For microstructural short cracks at the weld toes, taking the microstructure-sensitive fatigue index parameter as the main driving force, the grain model of the weld toe area was built based on the Voronoi method and the early evolution process of the microstructure short crack was simulated. By comparing with the fatigue test results, the rationality and validity of the microstructure -sensitive fatigue index parameter and its calculation models were confirmed. The simulation results showed that the fatigue life was affected by grain locations, grain sizes and grain orientations at the same time. The randomness of grain orientations played an important role in the dispersion of the macroscopic crack depth.
-
Keywords:
- FIP model /
- weld toe /
- short crack /
- crack simulation /
- early behavior
-
0. 序言
焊接结构具有承载能力高、省材料、质量轻、设计简单、生产效率高等优点,在汽车、轮船、桥梁、机械装备、运输管道等领域有广泛应用. 在循环载荷作用下,疲劳断裂是焊接结构的主要失效形式,大量统计资料表明,焊接结构的失效中80%以上是由疲劳引起[1]. 因此抗疲劳性能是焊接结构得以安全、可靠使用的重要保证.
焊接结构的疲劳断裂往往是由于焊接接头细节部位的疲劳累计损伤所导致,考虑到焊缝缺陷的固有存在,通常基于断裂力学方法预测焊接结构的剩余寿命[2]. 该方法首先假定存在一个初始裂纹,然后计算初始裂纹扩展至临界裂纹所需的循环次数,最后将该循环次数作为焊接结构的允许使用寿命. 研究表明,初始裂纹尺寸对剩余寿命有很大影响. 随着各种先进焊接工艺和焊后处理技术的发展,一些学者开始质疑焊接结构中初始缺陷(即初始裂纹)的存在性[3]. 进一步,即使存在初始裂纹,由于初始裂纹的尺寸非常小,直接采用传统的Paris扩展速率模型也无法有效预测小尺度裂纹(即短裂纹)的行为特性. 因此焊趾短裂纹早期行为的表征和建模具有重要研究意义.
短裂纹可以细分为微观结构短裂纹(microstructure short crack, MSC)、力学短裂纹(physically short crack, PSC)、物理短裂纹和化学短裂纹等多种概念[4-5]. 需要说明,这些概念主要试图采用不同的机理解释短裂纹的各种复杂行为,相互之间并不具备时间上的连续性,其中MSC面向材料晶粒尺度,能够较好地解释裂纹在微观尺度下的若干现象和行为,受到较多研究者的青睐,但这些研究中并没有考虑晶粒结构的影响. Tanaka研究了晶粒内部的裂纹成核和扩展机制,提出了一种裂纹成核的驱动力及其计算模型. 不同学者对Tanaka模型进行了修正、完善和验证[6],并在涡轮盘的裂纹萌生寿命预测方面获得了较好的效果[7]. McDowell等人[8-9]基于Tanaka模型的思想,提出了一种新的疲劳指标参量(fatigue indicator parameter, FIP),研究并构建了微观结构敏感的裂纹成核与扩展模型(后文简称为FIP模型),该模型在镍基材料裂纹早期行为的表征和描述方面被证实有较大优势,但针对焊接结构尚缺乏深入的研究.
基于上述现状,文中针对焊接结构中最易萌生裂纹的焊趾部位,采用泰森多边形方法建立焊趾局部区域的代表性体积单元(representative volume element,RVE)几何模型,基于微观结构敏感的FIP指标参量及其计算模型模拟了MSC的成核和早期扩展过程,研究了焊趾局部疲劳裂纹早期行为的影响因素.
1. 相关理论
1.1 疲劳裂纹的不同阶段
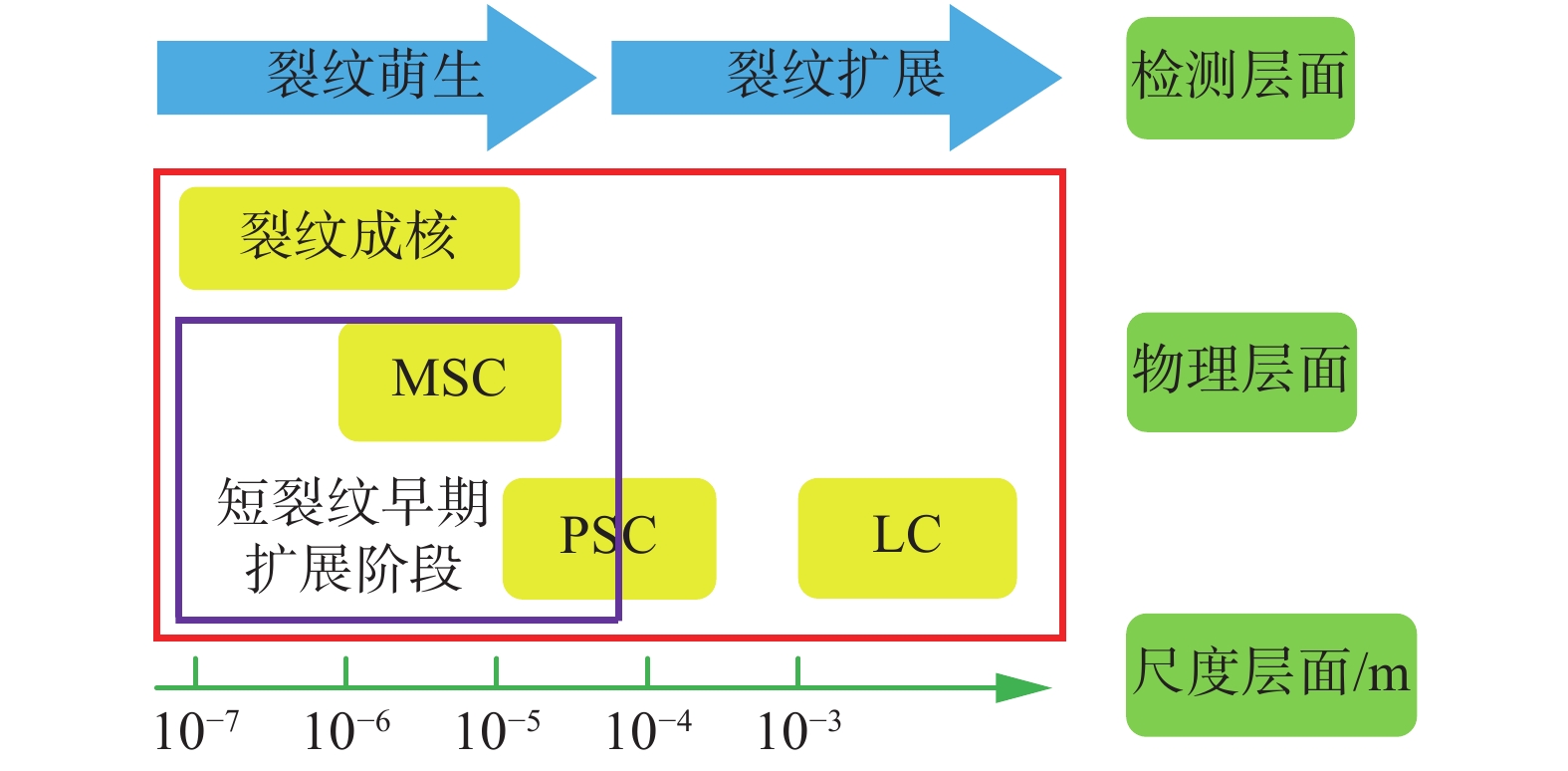
一般情况下,焊趾区域的疲劳损伤过程较为复杂,根据损伤机制的不同,可分为裂纹萌生和裂纹扩展等2个阶段. 然而裂纹萌生是一个与检测手段密切相关的概念,很难对应于实际的裂纹阶段. 目前的一种观点是将完整的疲劳过程分为4个阶段:成核(nucleation, Nuc)阶段、MSC阶段、PSC阶段和长裂纹(long crack, LC)阶段,如图1所示.
图1中,成核阶段的裂纹尺度一般在10−7~10−5 m量级,MSC阶段的裂纹尺度多在10−6~10−5 m量级,PSC阶段的裂纹尺度多在10−5~10−4 m量级,LC阶段的裂纹尺度则多大于10−3 m量级. 一些学者发现,MSC阶段和PSC阶段的裂纹扩展损伤机制相似,只是在裂纹扩展的晶粒数量上有所不同,建议在仿真研究中将其合并处理,文中采纳这种简化,并在文后简单记为MSC扩展阶段. 同时,裂纹成核阶段与MSC扩展阶段的界限非常模糊,文中将其进一步合并,并定义为裂纹早期阶段. 据此,整体疲劳寿命可定义如下
$$\begin{split} {N_{{\rm{Total}}}} &= {N_{{\rm{Nuc}}}} + {N_{{\rm{MSC}}}} + {N_{{\rm{PSC}}}} + {N_{{\rm{LC}}}} \\& = {N_{{\rm{Nuc}}}} + {N_{{\rm{MSC/PSC}}}} + {N_{{\rm{LC}}}} \\& = {N_{{\rm{Early}}}} + {N_{{\rm{LC}}}} \end{split} $$ (1) 式中:NTotal为总体疲劳寿命;NNuc为裂纹成核寿命;NMSC为微观结构短裂纹寿命;NPSC为力学短裂纹寿命;NLC为长裂纹寿命;NEarly为裂纹早期寿命. 对于焊接质量等级较高的焊接结构,已有研究表明裂纹早期阶段的疲劳寿命可以达到总疲劳寿命的70% ~ 90%,可见这一阶段对焊接结构的整体疲劳寿命起主导地位. 如果忽略裂纹早期阶段的疲劳寿命,必然显著低估整体疲劳寿命. 文中重点研究裂纹成核和早期扩展过程,其中的早期扩展阶段拟涵盖MSC和部分PSC阶段.
1.2 FIP模型
FIP参量的思想源自于Fatemi和Socie对多轴疲劳问题的研究[10-11],他们认为疲劳裂纹主要由滑移面上的不可逆损伤累积引发,考虑了滑移面上塑性剪切应变和峰值应力的综合作用,即
$${{FI}}{{{P}}^{(\alpha )}} = \frac{{\Delta {\gamma _{\rm{p}}}^{(\alpha )}}}{2}\left[ {1 + k\frac{{{\sigma _{\rm{n}}}^{(\alpha )}}}{{{\sigma _{{y}}}}}} \right]$$ (2) 式中:FIP为无量纲疲劳指标参量,该量数值越大,表示疲劳性能越差,反之该量数值越小,表示疲劳性能越好; α是具有不同晶粒取向的滑移系,
${{\Delta {\gamma _{\rm{p}}}^{(\alpha )}}}$ 是循环塑性剪切应变范围;${{\sigma _{\rm{n}}}^{(\alpha )}}$ 是峰值应力;σy是参考强度;k为材料常数.材料的晶粒尺度过于微小,在实际的裂纹早期行为仿真研究中,逐单元计算往往需要耗费巨大的计算资源,为此可以采用滑移带平均的FIP作为实际的疲劳驱动力. 平均FIP可以描述为
$${{FIP}}_{{{{\rm{ave}}}}}^{\left( \alpha \right)} = {{FIP}}_0^{\left( \alpha \right)}\left[ {1 - {R_{{\rm{GB}}}}{{\left( {\frac{d}{{{D_{{\rm{st}}}}}}} \right)}^{{m}}}} \right]$$ (3) 式中:
${{FIP}}_0^{\left( \alpha \right)} $ 是晶粒开裂前的平均FIP;RGB是穿晶阻力;d是裂纹长度;Dst是当前晶粒中的滑移带长度;m是与裂纹长度有关的材料参数.将裂纹成核定义为第一个晶粒完全开裂的过程,可以采用下式进行描述
$${N_{{\rm{Nuc}}}} = \frac{{{\alpha _{\rm{g}}}}}{{{d_{{\rm{gr}}}}}}{\left( {{{FIP}}_{{{{{\rm{ave}}}}}}^{\left( \alpha \right)}} \right)^{ - 2}}$$ (4) 式中:
$\alpha_{\rm{g}}$ 是不可逆性系数;dgr是微观结构的表征长度.MSC扩展模型可描述如下
$${N_{{\rm{MSC}}}} = \frac{{{D_{{\rm{st}}}}}}{\phi }{\left[ {A\frac{{{d_{{\rm{gr}}}}}}{{d_{{\rm{gr}}}^{{\rm{ref}}}}}{{FIP}}_{{{{\rm{ave}}}}}^{\left( \alpha \right)} - \Delta CTO{D_{{\rm{th}}}}} \right]^{ - 1}}$$ (5) 式中:ϕ是衡量裂尖塑性区不可逆特性的参数;ΔCTODth是控制位错是否发生的门槛值;A是比例常数,与
${{FIP}}_{{{{\rm{ave}}}}}^{\left( \alpha \right)} $ 和ΔCTOD相关;${d_{{\rm{gr}}}^{{\rm{ref}}}}$ 是参考距离,可以取平均晶粒大小.2. 裂纹早期阶段的行为仿真
2.1 二维RVE建模
文中仿真研究针对文献[12]的十字焊接接头试件及其单向拉伸疲劳试验结果进行,试件的局部示意图如图2所示. 文献的试验结果表明,疲劳裂纹萌生于焊趾表面,呈多裂纹形态,各裂纹萌生点均位于试件焊趾中部区域,因此垂直焊缝纵向抽取该区域的微小平面作为裂纹早期阶段疲劳过程仿真的对象,采用泰森多边形方法在其内部实现晶粒微观结构,建立二维RVE模型.
文献[12]的实施过程中曾经对十字焊接接头试件的焊缝材料进行金相检验,获得了焊趾区域材料的金相组织. 该试件的母材为Q345材料,金相图呈现不规则的多边形形状,并具有随机性,大部分晶粒为铁素体,少量为渗碳体. 焊缝材料的金相图呈现为多种不同的形态,但总体来说,也以铁素体和渗碳体为主,只是晶粒尺寸有明显差异. 考虑到裂纹更易于较软的铁素体内部成核,文中将二维RVE内部的晶粒结构全部考虑为铁素体组织.
采用数字图像技术,基于焊趾区域材料的金相图测得晶粒平均尺寸为21.87 µm,因此设定二维RVE模型内的平均晶粒尺寸为20 µm. 如前所述,MSC的尺度一般在100 µm量级,为涵盖该尺度并部分进入PSC尺度,二维RVE的边长取150 µm. 考虑到铁素体的微观结构为BCC结构,具有12个滑移系,疲劳失效主要沿滑移带发生,在二维RVE的晶粒内部设置随机方向的滑移带. 每个晶粒内部的滑移带相互平行,滑移带宽度设为2 µm. 图3所示为具有内部滑移带的二维RVE模型,其中包含56个晶粒,693个滑移带.
2.2 有限元计算模型
将二维RVE模型导入有限元软件中,并设置必要的仿真参数. 在微观结构层面,晶粒的材料属性具有各向异性特性,文中采用正态分布的弹性模量描述该特性,具体说,设置弹性模量的平均值为2.01 × 105 MPa,方差为6.66 × 103. 考虑到二维RVE模型截取于焊缝中部,可以看作为平面应变状态,再考虑到滑移带几何形状的显著不规则性,采用三角形平面应变单元(CPE3).
由图2可知,二维RVE的上方、左方和下方均截自于焊缝材料内部,承受焊缝内部截面的相互作用,右侧为自由表面,无载荷作用. 因此设定二维RVE的边界条件如图4所示. 采用节点位移方式施加上述边界条件,节点位移值通过有限元子模型方法获得.
2.3 计算过程
整个仿真过程按以下步骤实施.
(1)应力和应变计算阶段. 首先计算每个单元的应力张量历程和应变张量历程,然后根据晶粒取向计算各个滑移带中每个单元的
${{\sigma _{\rm{n}}}^{(\alpha )}}$ 和${{\Delta {\gamma _{\rm{p}}}^{(\alpha )}}}$ .(2) FIPave计算阶段. 遍历所有滑移带,按照式(2)和式(3)计算每个滑移带的
${{FIP}}_{{{{\rm{ave}}}}}^{\left( \alpha \right)} $ .(3)裂纹成核计算阶段. 按照式(4)计算每个滑移带的成核寿命,成核寿命最小的滑移带首先开裂.
(4) MSC扩展计算阶段. 某个晶粒内部出现裂纹成核,必然影响相邻晶粒的应力和应变状态,导致
${{FIP}}_{{{{\rm{ave}}}}}^{\left( \alpha \right)} $ 发生变化,这一行为的描述非常困难. 为了考虑前一个晶粒内已成核裂纹对后续晶粒疲劳行为的影响,文中将已有裂纹的晶粒内的失效滑移带的弹性模量设为1,将其等效处理为裂纹,然后重复上述步骤(1)~(3)计算过程,可依次获得相邻晶粒的${{FIP}}_{{{{\rm{ave}}}}}^{\left( \alpha \right)} $ ,进一步可以实现MSC的扩展过程.3. 寿命结果及其验证
3.1 寿命结果
按照上述步骤完成裂纹成核和扩展过程的仿真,将第一个晶粒完全开裂的循环次数定义为裂纹成核寿命,将裂纹的投影长度首次超过100 µm时所有开裂晶粒经历的循环次数定义为裂纹早期寿命,相关的仿真结果整理如表1所示.
表 1 MSC成核和扩展寿命Table 1. MSC nucleation and propagation lifetime阶段 晶粒号 滑移带号 裂纹成核寿命NNuc(万次) 短裂纹扩展寿命NMSC(万次) 裂纹早期寿命NEarly(万次) 成核阶段 24 4 6.247 5 — 23.435 4 早期扩展阶段 2 6 — 7.257 3 48 13 — 5.885 4 16 6 — 4.045 2 由表1可以看出,第24个晶粒首先开裂,开裂的滑移带为第4条,成核寿命为6.247 5万次;接下来,第2个晶粒、第48个晶粒、第16个晶粒依次开裂,开裂的滑移带依次为各自晶粒内部的第6条、第13条和第6条,各个晶粒内的裂纹扩展寿命依次为7.257 3万次、5.885 4万次和4.045 2万次. 不同晶粒内的裂纹扩展寿命具有相同的数量级,表明在晶粒尺度,MSC的成核寿命和扩展寿命基本在同一量级. 结合观察图3中的晶粒尺寸和相邻晶粒之间的滑移带方位差,还可看出MSC阶段的疲劳寿命主要受晶粒尺寸和取向的影响. 根据前述定义,仿真实例的MSC成核阶段的寿命为6.247 5万次,早期阶段的寿命为23.435 4万次. 此外,4个开裂晶粒的裂纹投影长度为110 µm.
3.2 与试验结果的比较
文献[12]的疲劳试验采用了2级载荷谱块,其中基线载荷谱块的应力变程为200 MPa,应力比为R = 0,标记载荷谱块的应力变程为100 MPa,应力比为R = 0.5. 首次基线载荷谱块的加载次数为30万次,后续基线载荷谱块的加载次数为10万次,标记载荷谱块的加载次数为5万次. 试件最终在第10个基线载荷谱块失效,总体寿命为154.8万次. 如果忽略标记载荷谱块加载次数的影响,总体寿命为117.9万次.
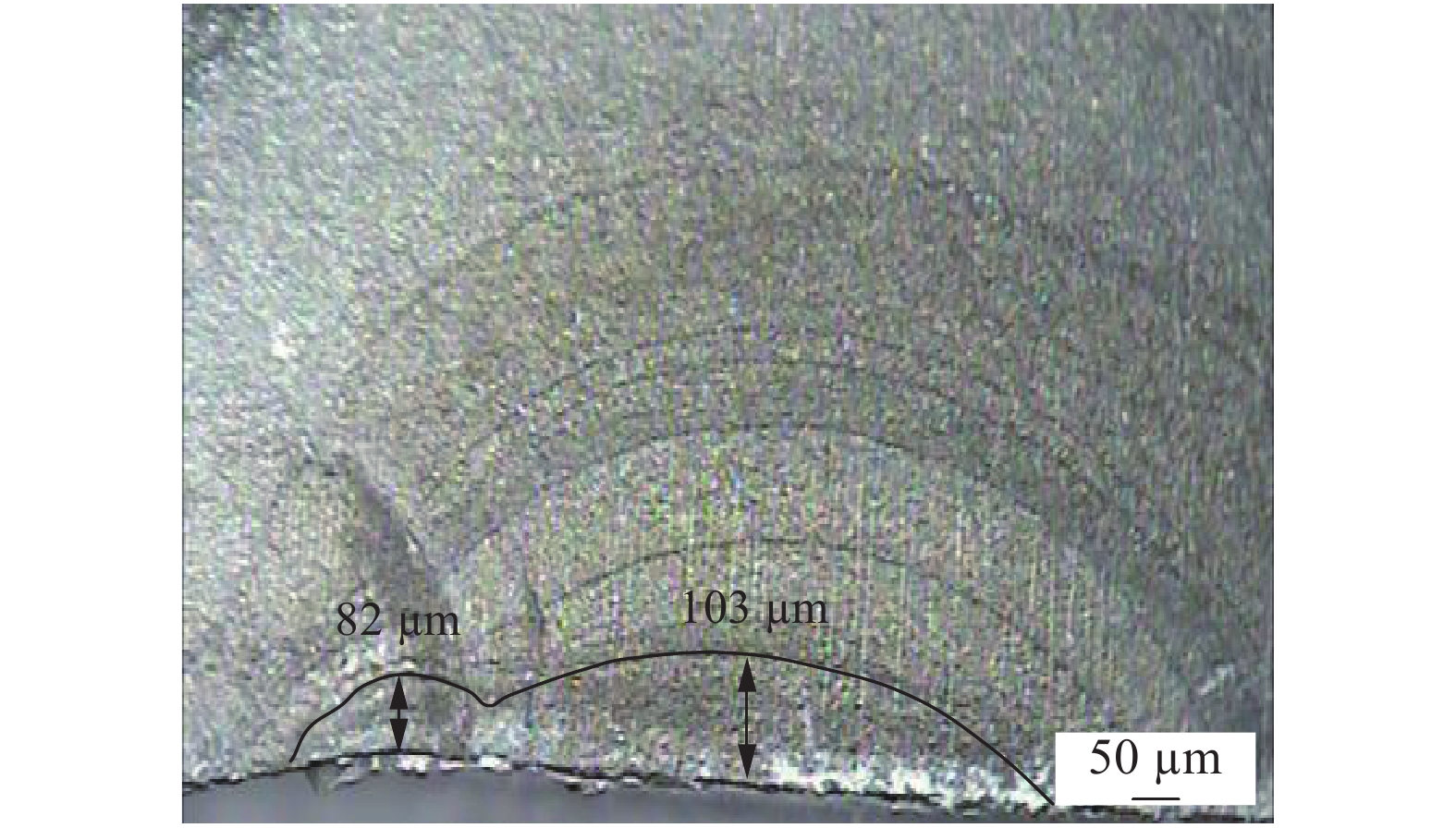
图5所示为疲劳断口中某个裂纹的演变形态,可以看到最终形成的裂纹前沿具有典型的半椭圆形状. 仔细观察裂纹早期阶段,可见2个明显的子裂纹(对应于图中实线). 采用反推技术,可知这2个子裂纹均对应第一次标记载荷谱,其试验寿命为30万次,与上述仿真结果中的早期寿命23.435 4万次接近. 此外,对图5中的2个子裂纹进行几何测量,测得裂纹深度值分别为82 和103 µm,与上述仿真结果中的投影裂纹长度102 µm相近. 可以看出,基于微观结构敏感的FIP指标参量及其计算模型具有合理性和有效性.
4. 进一步讨论
图6所示为裂纹成核计算的
${{FIP}}_{{{{\rm{ave}}}}}^{\left( \alpha \right)} $ 分布示意图,其中红色对应${{FIP}}_{{{{\rm{ave}}}}}^{\left( \alpha \right)} $ 数值最大的区域. 从该图可以看出,最大${{FIP}}_{{{{\rm{ave}}}}}^{\left( \alpha \right)} $ 对应的晶粒(第24个晶粒)位于二维RVE模型的右侧,对应于焊趾区域的自由表面. 根据式(4),具有最大${{FIP}}_{{{{\rm{ave}}}}}^{\left( \alpha \right)} $ 的滑移带的疲劳寿命最短,即首先发生裂纹成核现象,这与疲劳裂纹易萌生于自由表面的试验规律是一致的. 观察二维RVE模型右侧的若干个晶粒,其${{FIP}}_{{{{\rm{ave}}}}}^{\left( \alpha \right)} $ 具有明显差异,一些晶粒的${{FIP}}_{{{{\rm{ave}}}}}^{\left( \alpha \right)} $ 甚至远小于RVE模型内部的某些晶粒,这表明除了晶粒所在位置因素之外,晶粒尺寸和晶粒取向对晶粒内部的裂纹成核也具有重要影响.将晶粒24中形成裂纹的滑移带的弹性模量设置为1,按照相同的边界条件重新实施上述计算过程,可以发现裂纹成核之后的
${{FIP}}_{{{{\rm{ave}}}}}^{\left( \alpha \right)} $ 将重新分布,相邻的晶粒内部某个滑移带会具有最大值,因此可以将其视为下一条裂纹. 依次实施上述过程,可以得到裂纹穿透不同晶粒的演变过程,如图7所示. 可以看到,裂纹沿第24个晶粒、第2个晶粒、第48个晶粒、第16个晶粒依次前行,形成了一条曲折的路径,曲折形态主要受不同晶粒内部滑移带方向的影响. 将每个晶粒内部的扩展路径向水平方向投影,投影长度可看作为焊趾MSC在不同阶段的扩展深度. 对图7中的裂纹实际长度和投影长度分别测量,如表2所示. 可以看到,作为一种宏观层面的定量指标,裂纹扩展深度不仅受裂纹实际扩展路径长度的影响,也受晶粒内部滑移带倾角的影响. 对于具体的工程材料,沿裂纹演变路径的各个晶粒的实际取向具有高度随机性,导致最终的实际裂纹扩展深度值高度分散.表 2 MSC成核和扩展的裂纹长度Table 2. MSC nucleation and propagation crack length晶粒号 实际长度di/µm 投影长度ai/µm 倾角θ/(°) 比率 p(%) 24 20.6 15.7 139.8 76.21 2 36.9 34.1 22.4 92.41 48 48.1 35.8 138.1 74.42 16 23.2 16.8 136.3 72.41 总长 128.8 102.4 5. 结论
(1)采用滑移带的平均FIP作为焊趾MSC的驱动力,实现了焊趾裂纹的早期演变过程,获得了与试验结果相近的疲劳寿命与裂纹深度,验证了FIP指标参量及其计算模型的合理性和有效性.
(2)通过分析二维RVE模型中平均FIP的分布特征,证实了疲劳裂纹易萌生于试件自由表面的试验规律,同时表明疲劳寿命受晶粒所在位置、晶粒尺寸和晶粒取向等多种因素的影响.
(3)模拟了MSC在二维RVE模型中的演变过程,呈现出晶粒层面裂纹扩展路径的曲折特性,对比宏观层面的裂纹扩展深度参量,发现晶粒取向的随机性对裂纹宏观尺寸分散性具有重要影响.
-
表 1 MSC成核和扩展寿命
Table 1 MSC nucleation and propagation lifetime
阶段 晶粒号 滑移带号 裂纹成核寿命NNuc(万次) 短裂纹扩展寿命NMSC(万次) 裂纹早期寿命NEarly(万次) 成核阶段 24 4 6.247 5 — 23.435 4 早期扩展阶段 2 6 — 7.257 3 48 13 — 5.885 4 16 6 — 4.045 2 表 2 MSC成核和扩展的裂纹长度
Table 2 MSC nucleation and propagation crack length
晶粒号 实际长度di/µm 投影长度ai/µm 倾角θ/(°) 比率 p(%) 24 20.6 15.7 139.8 76.21 2 36.9 34.1 22.4 92.41 48 48.1 35.8 138.1 74.42 16 23.2 16.8 136.3 72.41 总长 128.8 102.4 -
[1] 张彦华. 焊接力学与结构完整性原理[M]. 北京: 北京航空航天大学出版社, 2007. Zhang Yanhua. Principles of welding mechanics and structural integrity[M]. Beijing: Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics Press, 2007.
[2] Zerbst U, Madia M, Vormwald M, et al. Fatigue strength and fracture mechanics-A general perspective[J]. Engineering Fracture Mechanics, 2017, 198: 2 − 23.
[3] 魏国前, 岳旭东, 党章, 等. 结合S-N曲线和断裂力学的焊接结构疲劳寿命分析[J]. 焊接学报, 2017, 38(2): 23 − 27. Wei Guoqian, Yue Xudong, Dang Zhang, et al. S-N and IEFM combined fatigue life analysis for welded structures[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2017, 38(2): 23 − 27.
[4] Zerbst U, Ainsworth R A, Beier H T, et al. Review on fracture and crack propagation in weldments-a fracture mechanics perspective[J]. Engineering Fracture Mechanics, 2014, 132(2): 200 − 276.
[5] Miller K J. The behavior of short fatigue cracks and their initiation Part I-A review of two recent books[J]. Fatigue Fract Eng Mater Struct, 1987, 10: 75 − 91. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-2695.1987.tb01150.x
[6] Xijia Wu. On Tanaka-Mura’s fatigue crack nucleation model and validation[J]. Fatigue Fracture Engineering Material Structure, 2018, 41: 894 − 899. doi: 10.1111/ffe.12736
[7] 牟园伟, 陆山. 基于材料微观特性的涡轮盘疲劳裂纹萌生寿命数值仿真[J]. 航空学报, 2013, 34(2): 282 − 290. Mu Yuanwei, Lu Shan. Numerical simulation of fatigue-crack-initiation life for turbine disk based on material microcosmic characteristics[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2013, 34(2): 282 − 290.(in Chinese)
[8] Mcdowell D L, Dunne F P E. Microstructure-sensitive computational modeling of fatigue crack formation[J]. International Journal of Fatigue, 2010, 32: 1521 − 1542. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfatigue.2010.01.003
[9] Castelluccio G M, Mcdowell D L. Mesoscale modeling of microstructurally small fatigue cracks in metallic polycrystals[J]. Materials Science & Engineering A, 2014, 598: 34 − 55. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2014.01.015
[10] Fatemi A, Socie D F. Critical plane approach to multiaxial fatigue damage including out-of-phase loading[J]. Fatigue Fract Eng Mater Struct, 1988, 11: 149 − 65. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-2695.1988.tb01169.x
[11] Stephens R I, Fatemi A, Stephens R R, et al. Metal fatigue in engineering[M]. 2nd ed. New York: John Wiley & Sons, 2001.
[12] 魏国前, 陈斯雯, 余茜, 等. 焊趾多裂纹的试验与仿真分析[J]. 焊接学报, 2019, 40(11): 75 − 81. doi: 10.12073/j.hjxb.2019400291 Wei Guoqian, Cheng Siwen, Yu Xi, et al. Test and simulation analysis of multiple cracks in the weld toe[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2019, 40(11): 75 − 81. doi: 10.12073/j.hjxb.2019400291
-
期刊类型引用(5)
1. 赵秋,唐琨,吴维青,李英豪,邓俊逸,陈鹏. 疲劳裂纹萌生与短裂纹扩展仿真方法. 机械科学与技术. 2025(02): 361-372 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 赵秋,唐琨,李英豪,吴维青. 基于Roe-Siegmund循环内聚力模型焊趾疲劳裂纹萌生仿真. 焊接学报. 2024(03): 61-67+132 .  本站查看
本站查看
3. 李阿虎,魏国前,何文波. 考虑焊趾形貌的T形焊接接头三点弯疲劳试验. 实验室研究与探索. 2023(03): 16-19+31 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 魏国前,郭子贤,闫梦煜,赵刚. 基于Pavlou方法的焊接结构疲劳寿命预测. 焊接学报. 2023(09): 16-23+129-130 .  本站查看
本站查看
5. 钟广生,魏国前,闫梦煜,冯梓彬. 焊趾半径对疲劳短裂纹演化行为的影响. 焊接学报. 2023(11): 88-95+133-134 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(0)



 下载:
下载: