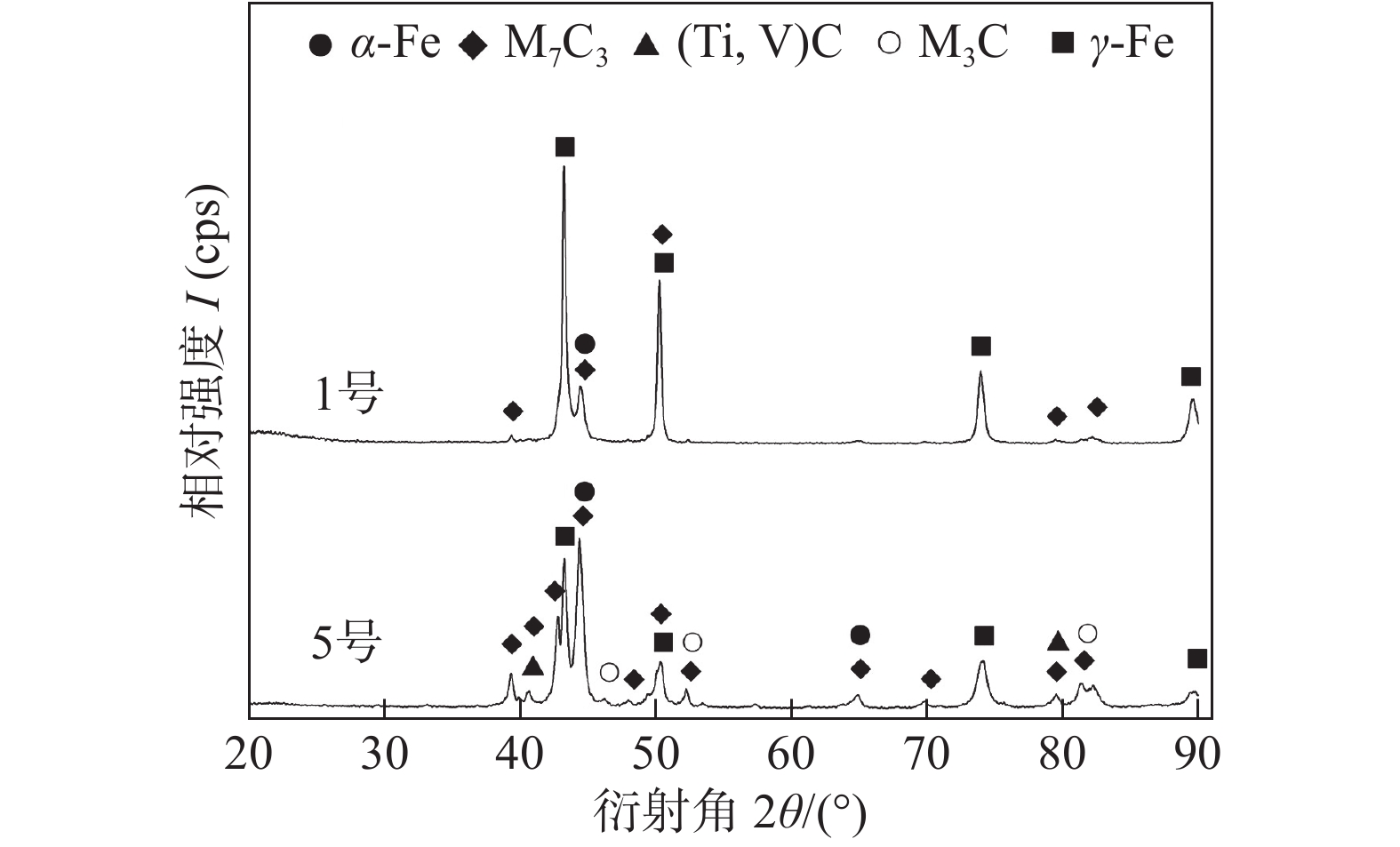
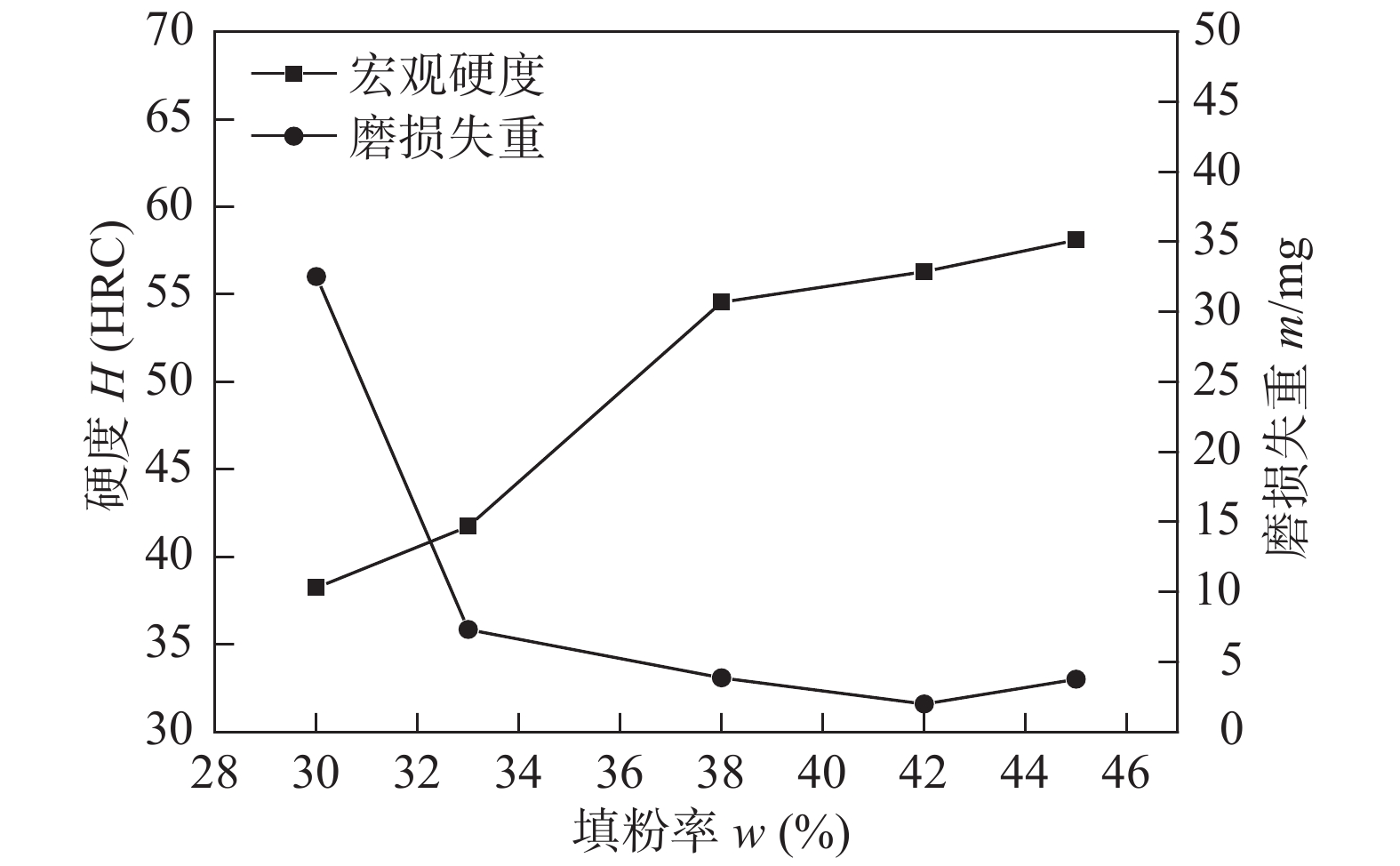
Effect of powder addition ratio on the microstructure and abrasive wear resistance of hardfacing alloys deposited by composite powder particles and solid wire
-
摘要: 粉末组分经干混、掺粘结剂湿混、旋转造粒、烧结和筛分等工序制备成10目 ~ 30目的复合粉粒,将之预置于焊道,以H08A实心焊丝为电弧载体,自保护明弧堆焊高铬合金. 借助光学显微镜、X射线衍射仪、扫描电镜等方法,研究了填粉率对复合粉粒和实心焊丝堆焊合金组织及耐磨性的影响. 结果表明,随着填粉率由30%提高至45%,该堆焊合金的显微组织由亚共晶转变为过共晶结构,主要基体由γ-Fe转变为α-Fe,M7C3相形态由沿晶断续网状或树枝状转变为颗粒状或块状. 磨损试验结果表明,该方法堆焊的高铬合金耐磨性优良,与药芯焊丝堆焊高铬合金相当,制备工艺更为简便且经济,合金磨损机制包括磨粒的微切削和显微剥落两种形式.Abstract: Composite powder particles with the size of 10-30 mesh were prepared by a series of processes including dry mixing, wet mixing with the addition of binding admixture, rotary pelleting, sintering and screen sizing on powder components. Those composite particles presetting on base metals were used as welding consumable together with solid wire which can be considered as arc carrier. High chromium alloys were deposited by the method of self-shielded open arc welding. The effects of powder addition ratio on the microstructure and abrasion resistance were investigated by optical microscopy (OM), X-ray diffraction (XRD) and scanning electron microscopy (SEM). The results indicate that, with powder addition ratio increases from 30% to 45%, the microstructure changes from the hypoeutectic to the hypereutectic. The dominant matrix converts changes from γ-Fe to α-Fe and the morphology of M7C3-type carbides transits from inter-granular reticular or dendritic shapes to granular or block-like ones. The results of wear test show that their abrasion resistance is excellent and corresponds to the one of flux-cored wire hardfacing alloys with such processing merits as simple and economic. The wear mechanism mode of hardfacing alloys includes micro-cutting and micro-spalling.
-
Keywords:
- composite powder particles /
- solid wire /
- open arc /
- hardfacing /
- high-chromium alloys
-
0. 序言
熔石英在微电子封装领域有着广泛的应用,但是由于其难加工、塑韧性差、对热冲击敏感等缺点,难以实现与其它材料的连接[1-2]. 钎焊具有连接强度高,工艺简单,接头形状尺寸适应性好等优点,是实现玻璃连接的常用方法. 目前,熔石英的润湿性是影响其钎焊接头质量的主要因素,人们主要通过提高熔石英的表面粗糙度来提升其润湿性能. Chen等人[3]使用离子轰击的方法来增加材料表面的粗糙度;Guo等人[4]通过激光加工的方式在材料表面刻蚀出周期性排布的微米级三角形沟槽,修饰后的样品钎焊接头连接良好. 然而,这些方法的加工尺寸太大,容易对母材基体造成损伤,降低接头质量.
飞秒激光由于其热影响区小、加工精度高、加工范围广等优点,作为一种典型的“冷加工”方式,在固体表面修饰方面有广泛的应用[5-6].Xu等人[7]发现飞秒激光诱导微纳结构后的熔石英具有良好的润湿性;Yong等人[8]使用飞秒激光制备了微米级沟槽阵列及槽内为纳米颗粒的多级结构,该微纳结构使得熔石英对水的润湿性大幅增加,达到超亲水性;上述研究表明制备多级微纳结构提高表面粗糙度是提升熔石英润湿性能和钎焊接头质量的有效手段.
国内外学者使用飞秒激光制备大面积多级微纳结构时的激光扫描速度较慢[9-10],导致加工效率低,限制了其实际生产应用. 文中采用高速飞秒激光对熔石英表面进行了多级微纳结构制备,阐明了高速飞秒激光诱导微纳结构的机理,分析了多级微纳结构提升熔石英润湿性的原因,验证了高速飞秒激光制备多级微纳结构改善熔石英钎焊能力的有效性.
1. 试验方法
采用的熔石英样品尺寸为30 mm × 30 mm × 5 mm,飞秒激光器为Coherent公司生产的Monaco飞秒激光器,集成了1 035 nm波长的固体振荡器和放大器,可实现在重复频率1 MHz下40 μJ的单脉冲能量输出,脉冲宽度300 fs ~ 10 ps内可调. 所有样品在试验前分别在丙酮、乙醇和蒸馏水中超声清洗3 min,之后将样品固定在工作台上,之后调节振镜z轴高度,将飞秒激光聚焦于样品待加工表面,通过电脑控制振镜系统进行x及y轴加工.
在熔石英表面加工过程中,选择脉冲宽度400 fs和重复频率1 MHz,扫描速度500 ~ 1 500 mm/s,峰值功率53% ~ 60%. 阵列加工选择平行沟槽,90°正交路径和45°交叉路径三种,沟槽间距为10 ~ 50 μm. 通过扫描电子显微镜和激光共聚焦显微镜观察样品表面微观形貌. 熔石英表面飞秒激光加工示意图如图1所示. 熔石英表面多级微纳结构制备完成后,通过接触角测量仪测量其表面润湿性. 测试过程中选择体积1 μL的去离子水为试验液滴. 采用CCD摄像机拍摄300 ms后去离子水在不同微纳结构上的润湿铺展形貌,分析微纳结构对润湿铺展行为的影响,优化微纳结构形貌. 最后,采用润湿角测量仪器,分析了优化后的微纳结构对促进Bi2O3-50%B2O3钎料在熔石英表面铺展的有效性. 钎料润湿铺展试验参数依据文献[11]选取,加热至650 ℃,加热速率为5 ℃/min,保温时间5 min.
2. 分析与讨论
2.1 飞秒激光热输入对微纳结构的影响
飞秒激光的热输入是决定能否诱导微纳周期性条纹结构的关键,而激光热输入的大小主要由激光扫描速度和峰值功率控制.图2为熔石英在重复频率1 MHz,55%峰值功率下不同扫描速度的微观形貌图. 当扫描速度为500 mm/s时,其边缘为片层状切削结构,底部存在一些纳米颗粒以及细丝. 随着扫描速度的增加,周期性条纹结构开始逐渐代替片层状切削结构. 扫描速度为1 000 mm/s时获得的沟槽内部已经完全变为周期性阵列结构,微纳条纹间距为400 ~ 500 nm.
由于1 000 mm/s时形成的微纳结构形貌较好,槽宽与槽深适宜,因此选择该速度来进一步研究能量大小对周期性微纳结构的影响.
图3为重复频率1 MHz,扫描速度1 000 mm/s时,不同输入能量所对应的熔石英表面加工形貌特征. 可以看出在53%的峰值功率下,沟槽内部微纳周期条纹成形较差,没有完全连接起来. 这是因为此时的能量不足以在整个加工面积上形成微纳周期条纹,只是由于激光能量分布的高斯特性,在中心能量较高区域达到了微纳条纹形成的条件,未能实现微纳周期性条纹的完全生长连接. 随着输入能量的增大,线槽内均形成良好的阵列微纳结构,微纳周期结构的条纹间距在400 ~ 500 nm之间.
2.2 微纳结构形成机制
微纳结构间距为400 ~ 500 nm之间属于亚波长结构[12]. 对于突破光学极限的亚波长条纹结构,当飞秒激光脉冲的前部入射到熔石英表面,在熔石英表面产生薄层等离子体,而激光脉冲的后部会通过参量过程驱动等离子体波,随着等离子体波的移动,在垂直于激光偏振的方向上出现了离子高度集中的区域,极强的库仑斥力会导致库仑爆炸的发生. 之后,剩余的等离子体自组装形成周期阵列结构. 对于近波长结构,经典理论[13]认为初始入射的激光可在材料表面产生结构缺陷或表面粗糙度,后续激光在形成表面缺陷的地方发生了激光光场的重新分布并导致能量的不均匀沉积,最终产生周期性结构.Huang等人[14]的研究表明,熔石英表面周期结构的类型随脉冲延迟和激光能量的变化而变化. 当激光能量较小时,易形成亚波长结构. 随着激光能量的增加,亚波长结构向近波长转变.
为了探究高速扫描条件下的能量阈值与点加工时的区别,文中以飞秒激光能量为研究对象,温度作为媒介,分别计算了微纳阵列点加工与高速扫描的能量阈值. 飞秒激光与熔石英作用时,可将激光脉冲看作一个个瞬时加入的点热源,当飞秒激光的重复频率较高时,在下一个激光脉冲来临时,上一个激光脉冲产生的热量仍有残留,造成热量的积累. 通过热传导过程来对其进行分析. 球坐标系下的一维热传导方程可表示为
$$\frac{\partial }{\partial }\left( {{r^2}\frac{{\partial T}}{{\partial r}}} \right) = \frac{{{r^2}}}{D}\frac{{\partial T}}{{\partial t}}$$ (1) 式中:T(r, t)为材料的温度;D为热扩散系数;r为激光传播方向坐标. 通过有限差分法进行求解,将飞秒激光照射后导致的温度分布表示成N个单脉冲导致的温度变化的叠加,即
$$T\left( {t,r,{\textit{z}}} \right) = \sum\limits_{n = 0}^{N - 1} {\Delta {T_1}} \left( {t - \frac{{{n_i}}}{f},r,{\textit{z}} + {T_s}} \right)$$ (2) 式中:f为飞秒激光重复频率;∆T1为单个飞秒激光脉冲导致的温度变化. Ts为玻璃初始温度,可用室温代替. 进行线扫描时,公式变为
$$T\left( {t,r,{\textit{z}}} \right) = \sum\limits_{n = 0}^{N - 1} {\Delta {T_1}} \left( {t - \frac{{{n_i}}}{f},r - {n_i},\frac{v}{f},{\textit{z}}} \right) + {T_s}$$ (3) 式中:v为扫描速度.
图4为1 000 mm/s扫描速度下,激光能量为53%,60%峰值能量时熔石英表面加工点处的温度变化.图5为具有相同有效脉冲作用下的点加工温度计算结果. 结合两图可知,当激光扫描速度为1 000 mm/s时,53%,60%功率达到的峰值温度为2 087和2 914 ℃,相当于点加工时48%和54%的功率. 在热积累效应修正后可知,采用扫描速度1 000 mm/s、重复频率1 MHz进行连续微纳条纹加工的有效功率相当于25个有效脉冲数下以49% ~ 55%能量进行点加工.
对于高重频高速扫描时,仅仅将高速扫描时的有效脉冲数与单点扫描进行对应所得的结果将不再适用. 当激光打点时,每一个脉冲到来,该点都会获得最高的热量,直至第一个脉冲由于热扩散温度为0时,表面达到热积累最高温度. 对于线扫描,由于脉冲热源的高斯分布,当脉冲边缘到达某点时,该点处开始获得远低于中心的能量,随着脉冲数到该点越来越近,每个脉冲获得的热量增加,直到抵达该点时,才获得一次最高热量的热积累,随后脉冲继续作用,在远离过程中,之前积累的热量随着热扩散越来越低,当热积累小于热扩散时,该点处达到最高温度. 所以飞秒激光高速扫描想要实现与点加工相同的加工效果必须使用更高的功率才能实现. 这也是飞秒激光高速扫描得到的微纳周期性条纹为亚波长结构的原因.
2.3 多级微纳结构制备及表征
由上述分析可知,在保障微纳结构成形的前提下,较低的能量更易形成亚波长周期结构. 因此后续以1 000 mm/s扫描速度下 55%峰值功率进行大面积多级微纳结构制备. 一级纳米结构主要由槽内周期为 400 ~ 500 nm的周期性条纹组成;二级结构为蚀刻沟槽,槽宽12 μm,槽深5 μm;三级结构为沟槽阵列;图6为单向平行路径加工时不同加工间距下三维形貌及轮廓尺寸图. 当加工间距为10 μm时,线槽稍有重叠,只在线槽中心存在周期纳米级条纹,重叠区由于后续激光扫描对之前线槽产生重熔和等离子体溅射,形成了形状不规则的纳米块体. 当加工间距为30 μm与50 μm时,线槽间互不影响,线槽内为良好的周期性纳米条纹.
图7为不同加工间距90°正交扫描微纳结构形貌图. 由图可见,最终凹槽形貌由后续的交叉路径占主导作用. 当间距为10 μm时,交叉扫描并没有形成三级微纳结构,其微观形貌与相同间距的水平阵列扫描相似,这是由于阵列间距过小,后续交叉扫描对之前的沟槽重熔导致其擦除重写. 当阵列间距为 30 和50 μm时,依然是后续线槽深度较大,占主导地位,一级周期性微纳条纹结构成形稳定.
2.4 多级微纳结构润湿性表征
图8a为不同阵列间距对水润湿性的影响. 当阵列间距为10 μm时,水的润湿角由30°降为10°,当阵列间距为30 μm时,水的润湿角由29°降为5°,当阵列间距为50 μm时,润湿角仅降低3°.图8b为不同阵列间距对阵列高度Sa及界面扩展面积比Sdr的影响,由关系图可见阵列为30 μm时Sa最大,其水润湿性能最好. 对于间距10 μm与50 μm的平行沟槽,由于Sa较小,因而其对水的润湿性较差. 间距10 μm的沟槽Sa虽然要小于间距50 μm的沟槽,但其水润湿性却比后者要好,这说明多级微纳结构对水润湿性的影响不仅仅是由Sa决定的. 由图8b可以发现间距10 μm的界面扩展面积比达到了14.2%,远大于间距50 μm的 6.8%,所以间距10 μm对水的润湿性更好. 同时间距30 μm的沟槽Sdr也大于其它两者,润湿性能最好.
选择具有最优润湿性阵列间距为30 μm进行不同阵列方式三级微纳结构水润湿性研究. 由图9a可知,不同阵列方式水的润湿角都由未修饰时的30°降到了0°. 说明三级微纳结构能够有效提升熔石英的润湿性.图9b为不同阵列方式对Sa及Sdr的影响. 相较于二级微纳结构,两种沟槽交叉方式的Sa以及Sdr都大大增加,这是由于双向扫描形成的菱形以及矩形交叉处使表面复杂度大大增加. 两种三级微纳结构的Sa以及Sdr相差很小,90°正交阵列比45°倾斜阵列略大一点,这正是因为二者的尺寸差异,菱形微米柱的边长是矩形微米柱的
$\sqrt 2 $ 倍,因此正交微米柱单位面积数量更多,故而正交阵列的Sa及Sdr要比倾斜阵列的略大.将两种三级结构进行Wenzel粗糙度因子[15]计算,方程如下$$\cos {\theta _\omega } = R\left( {{\gamma ^{{\rm{sa}}}} - {\gamma ^{{\rm{sl}}}}} \right)$$ (4) $$R = \frac{{{S_{\rm{a}}}}}{{{S_{\rm{p}}}}}$$ (5) 式中:θω是平衡表观接触角,又称为Wenzel接触角;R为固体表面的粗糙度因子;γsa,γsl为固体-气体、固体-液体的界面张力;Sa为固/液界面实际接触面积;Sp为表观接触面积. 由于Wenzel模型假设液体始终填满表面上的凹槽结构,但是实际情况中,沟槽中液滴下会存有截留空气,一级微纳结构可以减少截留空气,但仍不能完全填满凹槽,故而用单条线槽水润湿实际接触面积增量Sl进行修正. 即
$${S_{\rm{l}}} = S_{{\rm{d}}r} - {S_{\rm{c}}}$$ (6) $$R = 1 + \frac{L}{d} \cdot \frac{{{S_{\rm{l}}}}}{{{S_{\rm{p}}}}}$$ (7) 式中:Sl为单条线槽实际接触面积增量;Sc为截留空气体积;L为加工面边长;d为阵列间距.
对于90°正交阵列,R符合式(8),即
$$R = 1 + \frac{{2\left( {L - a} \right)}}{d} \cdot \frac{{{S_{\rm{l}}}}}{{{S_{\rm{p}}}}}$$ (8) 式中:a为槽宽对于45°交叉阵列,其相交区边长为
$\sqrt 2 a$ . 因此符合式(9),即$$R = 1 + \frac{{2\left( {L - \sqrt 2 a} \right)}}{d} \cdot \frac{{{S_{\rm{l}}}}}{{{S_{\rm{p}}}}}$$ (9) 对比式(8)和式(9)可知,正交阵列的粗糙度因子大于倾斜阵列的粗糙度因子,所以正交阵列的润湿性更为优异.
图10为钎料650 ℃保温5 min后分别在未修饰以及三级微纳结构修饰后熔石英表面润湿角. 可以看出未修饰玻璃表面对钎料的润湿性较差,润湿角为52°,而钎料在三级微纳结构修饰后玻璃表面的润湿角为44°,润湿性得到明显提高. 值得说明的是由于钎料较多,保温时间较短,因而钎料铺展的面积较小,整体润湿角较大,但是,多级微纳结构相较未修饰玻璃表面,润湿角多降低了8°,有效说明多级微纳结构对钎料润湿的促进作用.
3. 结论
(1) 当飞秒激光重复频率1 MHz,扫描速度1 000 mm/s,55%峰值功率时成功在熔石英表面诱导出微纳周期性条纹结构,微纳条纹间距在400 ~ 500 nm之间,属于亚波长结构.
(2) 多级微纳结构能够有效改善熔石英的润湿性能,沟槽间距为30 μm的正交阵列润水润湿性最好,润湿角减小到0°.
(3) Bi2O3-50%B2O3钎料在修饰后熔石英表面的润湿性大幅提升. 相较于未修饰样品,具有多级微纳结构的熔石英在相同温度下润湿角降低了8°,有效改善了熔石英玻璃的钎焊能力.
-
表 1 堆焊工艺参数
Table 1 Hardfacing experiment parameters
电流I/A 电压U/V 焊丝伸出长度L/mm 焊接速度v/(mm·s−1) 层温T/℃ 焊后状态 极性 410 27 30 4.5 100 ~ 150以下 空冷 反接 表 2 堆焊合金的填粉率(质量分数,%)
Table 2 Powder addition ratios of hardfacing alloys
1号 2号 3号 4号 5号 30 33 38 42 45 表 3 高铬堆焊合金的微区化学成分(原子分数,%)
Table 3 Micro-area chemical composition in high chromium hardfacing alloys
能谱点 C Ti V Cr b1 20.78 — 0.52 7.32 b2 36.95 — 4.17 26.66 b3 20.89 9.13 8.33 26.44 g1 28.42 0.11 4.09 36.11 g2 14.66 0.13 0.57 10.39 g3 16.86 37.03 16.52 10.12 g4 22.32 0.22 2.75 25.00 -
[1] Correa E O, Alcantara N G, Tecco D G, et al. The relationship between the microstructure and abrasive resistance of a hardfacing alloy in the Fe-Cr-C-Nb-V system[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2007, 38(8): 1671 − 1780. doi: 10.1007/s11661-007-9220-8
[2] 魏建军, 潘健, 黄智泉, 等. 耐磨堆焊材料在我国水泥工业中的应用[J]. 中国表面工程, 2006, 19(3): 9 − 13. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1007-9289.2006.03.003 Wei Jianjun, Pan Jian, Huang Zhiquan, et al. The application of hardfacing material in Chinese cement industry[J]. China Surface Engineering, 2006, 19(3): 9 − 13. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1007-9289.2006.03.003
[3] Lin Yuchi, Chen Hanming, Chen Yongchwang. Microstructures and wear properties of various clad layers of the Fe-W-C-B-Cr system[J]. Surface & Coatings Technology, 2013, 236: 410 − 419.
[4] 刘跃, 张国赏, 魏世忠, 等. 堆焊工艺对高铬合金粉体堆焊层组织及耐磨性能的影响[J]. 机械工程材料, 2013, 37(8): 27 − 30. Liu Yue, Zhang Guoshang, Wei Shizhong, et al. Effects of surfacing technologies on microstructure and wear resistance of high chromium alloy powder surfacing layer[J]. Materials for Mechanical Engineering, 2013, 37(8): 27 − 30.
[5] 刘大双, 刘仁培, 邱悦. 无渣含铌自保护堆焊药芯焊丝的研制[J]. 焊接学报, 2012, 33(9): 73 − 76. Liu Dashuang, Liu Renpei, Qiu Yue. Development of slag-free self-shielded flux cored wire with niobium addition for hardfacing[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2012, 33(9): 73 − 76.
[6] Srikarun B, Muangjunburee P. The effect of iron-based hardfacing with chromium powder addition onto low carbon steel[J]. Materials Today: Proceedings, 2018, 5: 9272 − 9280. doi: 10.1016/j.matpr.2017.10.100
[7] 王智慧, 贺定勇, 张杰哲, 等. 用填粉式堆焊方法制造耐磨复合钢板[J]. 机械工程材料, 2001, 25(3): 25 − 27. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3738.2001.03.008 Wang Zhihui, He Dingyong, Zhang Jiezhe, et al. The development of wear resistant composite plate with powder adding welding method[J]. Materials for Mechanical Engineering, 2001, 25(3): 25 − 27. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3738.2001.03.008
[8] Zahiri R, Sundaramoorthy R, Lysz P, et al. Hardfacing using ferro-alloy powder mixtures by submerged arc welding[J]. Surface & Coatings Technology, 2014, 260: 220 − 229.
[9] Yüksel N, Sahin S. Wear behavior-hardness-microstructure relation of Fe-Cr-C and Fe-Cr-C-B based hardfacing alloys[J]. Materials and Design, 2014, 58: 491 − 498. doi: 10.1016/j.matdes.2014.02.032
[10] Coronado J. Effect of (Fe,Cr)7C3, carbide orientation on abrasion wear resistance and fracture toughness[J]. Wear, 2011, 270(3): 287 − 293.
[11] Günther K, Bergmann J P, Suchodoll D. Hot wire-assisted gas metal arc welding of hypereutectic FeCrC hardfacing alloys: microstructure and wear properties[J]. Surface & Coatings Technology, 2017, 334: 420 − 428.
[12] Li Meiyan, Wang Yong, Han Bin, et al. Microstructure and properties of high chrome steel roller after laser surface melting[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2009, 255: 7574 − 7579. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2009.04.030
[13] 龚建勋, 程诗尧, 姚惠文, 等. 以复合粉粒和实心焊丝为堆焊材料制备高硼合金的方法: 中国, 201811380791.X[P]. 2019-02-01. Gong Jianxun, Cheng Shiyao, Yao Huiwen. et al. A method forthe preparation of high boron hardfacing alloys with composite powder particles and solid wire: China, 201811380791.X[P]. 2019-02-01.
[14] Miná, Emerson Mendonça, Da Silva Y C, et al. Effect of dilution on the microstructure of AWS ERNiCrMo-14 alloy in overlay welding by the TIG process with cold wire feed[J]. Welding International, 2017, 32(2): 130 − 138.
[15] 龚建勋, 肖逸锋, 张清辉, 等. Fe-C-Cr-V高铬堆焊合金的M7C3型碳化物及其耐磨性[J]. 焊接学报, 2010, 31(1): 33 − 36. Gong Jianxun, Xiao Yifeng, Zhang Qinhui, et al. M7C3-type carbide and abrasion resistance of Fe-C-Cr-V high chromium hardfacing alloys[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2010, 31(1): 33 − 36.
-
期刊类型引用(2)
1. 刘鑫,刘紫微. 不同焊接特征对管线钢与法兰焊接接头疲劳寿命影响. 焊接. 2025(04): 91-96 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 王祉冰,王剑,张硕. 基于FAD图法的铁路货车车体断裂评估. 轨道交通装备与技术. 2024(05): 21-25 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(2)




 下载:
下载: