Effect mechanism of dilution on solidification crack in ENiCrFe-7 buffering layer of deposited metal
-
摘要: 采用ENiCrFe-7镍基焊材作为填充金属对Q345B钢进行焊接,在熔敷金属的隔离层中发现存在较大尺寸的微裂纹. 通过光学显微镜、扫描电子显微镜及能谱仪等手段,对隔离层内裂纹的分布、形态及裂纹内析出相等进行分析,并与不存在裂纹的熔敷金属区域进行对比. 结果表明,裂纹只存在于隔离层中,该区域中的稀释率较高,导致Fe含量较高;隔离层中富Nb析出物数量高于无裂纹的熔覆金属区域;裂纹表面呈现出典型的凝固裂纹形态,并存在大量富集Nb,S元素的析出相;焊接过程中,富Nb,S低熔点相析出是导致隔离层中形成凝固裂纹的主要原因.Abstract: Larger size microcracks were found in the buffering layer when ENiCrFe-7 nickel-based welding material is used as filler metal to weld Q345B steel. Adopting optical microscope, scanning electron microscope and energy spectrometer were used to analyse the distribution, morphology, and precipitation of cracks and compared results with the the area where no crack occurs. The results show that cracks are only distributed in the buffering layer which adjacent to the base material, and the dilution rate, Fe content, and number of Nb-rich precipitates in the crack occurrence area are higher than those in the area where no crack occurs; The crack is typical solidification crack and precipitation phases rich in Nb and S elements exist on the crack surface; The low melting point phase rich in Nb and S is the main cause of solidification cracking of buffering layer.
-
Keywords:
- 690 welding material /
- buffering layer /
- solidification crack /
- dilution /
- precipitates
-
0. 序言
焊接被喻为制造业的“裁缝”,在制造业中必不可少,高效焊接是焊接领域永恒的追求. 提高电弧穿透能力是提高焊接速度的一种有效途径[1-3]. 常规等离子弧焊接工艺不开坡口一次可焊透5 ~ 8 mm的钢板,可实现单面焊双面成形[3-4]. 然而当对更厚的工件进行焊接时,等离子弧穿孔过程中形成的小孔稳定性较差[5-6],电弧穿透能力不足[7-8],制约了其在工程领域中的应用.
为了提高等离子弧焊接电弧穿透能力,国内外研究学者开展了大量的研究工作. 武传松团队通过超声辅助等离子弧焊接工艺提高电弧穿透能力[9]. 陈树君课题组通过环境压力来改变电弧压力进而改变电弧穿透能力[10].Richardson团队通过在等离子弧焊接电弧周围增加径向气流,初步证实了径向气流可以增强电弧穿透能力[11]. 文中在前人的基础上研发了气流再压缩等离子弧焊接工艺,研究发现压缩气对喷嘴外部电弧的冷却作用是电弧收缩和电弧穿透能力提高的主要原因[12-15]. 基于前期研究,如果可以通过其它方式进一步冷却喷嘴外部电弧,就有可能进一步收缩电弧和提高电弧穿透能力. 金属粉末熔化会吸热,蒸发会吸热. 将金属粉末通过一定的角度和位置送入电弧弧柱中,金属粉末熔化吸热、蒸发吸热,是否能够压缩电弧和提高电弧穿透能力,这是一个值得研究的科学问题.
文中设计并搭建金属粉末再压缩等离子弧焊接试验平台,采集焊接过程电信号、视觉信号、弧光光谱信号等,并从焊缝成形、电弧电压、熔融金属过渡、弧光光谱等方面对比分析金属粉末再压缩等离子弧焊接和常规等离子弧焊接.
1. 金属粉末再压缩等离子弧焊接试验平台
试验平台主要包括等离子弧焊接电源及焊枪系统、机械控制系统、金属粉末供给系统、焊接过程电信号采集系统、视觉信号采集系统及电弧弧光光谱采集系统(图1).
在焊接电源及焊枪系统中,等离子弧焊接电源采用德国EWM Tetrix 422 DC plasma焊机,焊接电流输出范围为5 ~ 420 A. 焊枪是采用自主设计的金属粉末再压缩等离子弧焊枪.图2是金属粉末再压缩等离子弧焊枪结构示意图. 与常规等离子弧焊枪相比,该焊枪在保护气体通道和离子气体通道之间设计了金属粉末通道,该通道可将金属粉末送入等离子电弧中:一方面进入电弧的金属粉末在熔化和蒸发过程中会吸收电弧热量,起到冷却电弧的作用,迫使电弧收缩;另一方面蒸发后的金属蒸气会影响等离子体成分,改变等离子弧电流通道. 在上述的综合作用下,预期可以增加电弧穿透能力,实现对等离子弧的“再压缩”.
金属粉末供给系统主要由气瓶、气体质量流量控制器、送粉器、气管、焊枪等部分组成. 焊接过程电信号采集系统可实时采集焊接过程中的焊接电流、电弧电压信号. 视觉信号采集系统通过高速摄像机实时监测熔融金属过渡. 电弧弧光光谱采集系统主要包括等离子体光谱仪、光纤探头、光纤、计算机及其配套软件,光谱仪选用荷兰Avantes制造的等离子体光纤光谱仪.
2. 试验方法
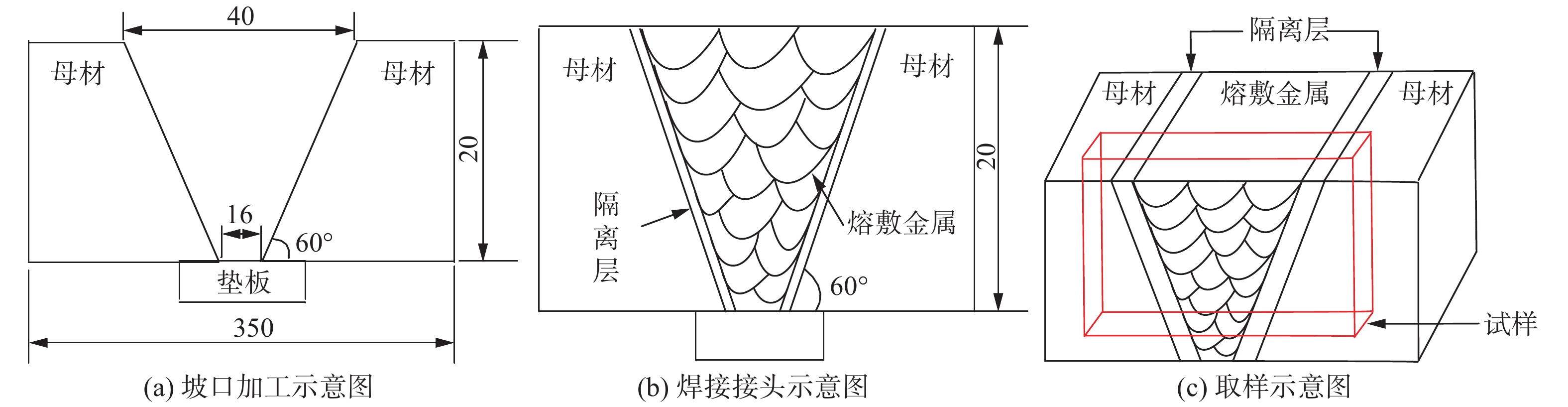
试验材料选用316L不锈钢板,尺寸为150 mm × 120 mm × 10 mm. 试验前,使用角磨机对钢板表面进行机械打磨,去除氧化膜,然后使用无水乙醇对表面进行清洗,去除油污,自然烘干. 选取两块试验钢板,分别进行金属粉末再压缩等离子弧焊接和常规等离子弧焊接. 焊枪喷嘴距离工件上表面的距离为5 mm,钨极选用铈钨极,钨极内缩量为5 mm,离子气体、保护气体选用纯度为99.99%的氩气. 其它主要焊接工艺参数如表1所示. 金属粉末为316L不锈钢粉末,粉末颗粒直径为120 ~ 150 μm. 与常规等离子弧焊接工艺相比,金属粉末再压缩等离子弧焊接工艺增加送粉量,其余焊接工艺参数相同.
表 1 焊接工艺参数Table 1. Welding parameter焊接工艺 焊接电流
I/A焊接速度
v/(mm·min−1)送粉速度
vs/(g·min−1)离子气流量
Q1/(L·min−1)保护气流量
Q2/(L·min−1)常规等离子弧焊接 195 96 0 3.1 20 金属粉末再压缩等离子弧焊接 195 96 1.15 3.1 20 在焊接试验过程中,实时采集金属粉末再压缩等离子弧焊接和常规等离子弧焊接过程的电信号、视觉信号、光谱信号. 焊接完成后,使用线切割设备在焊缝中间部分,沿着垂直于焊缝轴线方向截取试样,试样经清洗、打磨、抛光、腐蚀后,用体式显微镜观察焊缝截面形貌.
3. 结果分析
3.1 焊缝成形分析
图3a是常规等离子弧焊接焊缝截面形貌;图3b是金属粉末再压缩等离子弧焊接焊缝截面形貌. 常规等离子弧焊接工艺的焊缝熔深为8.0 mm,熔宽为13.42 mm,余高为0.95 mm;金属粉末再压缩等离子弧焊接工艺的焊缝熔深为9.29 mm,熔宽为11.77 mm,余高为1.16 mm. 可以看出,在相同电流195 A条件下,与常规等离子弧焊接相比,金属粉末再压缩等离子弧焊接焊缝熔深增加1.29 mm,熔宽减少1.65 mm,余高增加0.21 mm. 在相同电流条件下,与常规等离子弧焊接相比,金属粉末再压缩等离子弧焊接焊缝熔深增加、熔宽变窄. 这说明,相同电流条件下,金属粉末再压缩等离子弧焊接电弧穿透能力增强.
3.2 电信号分析
图4是采集的金属粉末再压缩等离子弧焊接和常规等离子弧焊接的电弧电压变化曲线. 计算得出,常规等离子弧焊接工艺的平均电压为29.68 V;金属粉末再压缩等离子弧焊接工艺平均电弧电压为30.31 V. 在相同电流195 A条件下,与常规等离子弧焊接相比,金属粉末再压缩等离子弧焊接电弧电压增加了0.63 V,电弧平均功率增加了122.85 W.从能量的角度分析,能量增加会改变焊缝成形. 能量增加,熔深和熔宽都有可能增加;然而金属粉末再压缩等离子弧焊接熔深增加、熔宽减小.
3.3 视觉信号分析
采用高速摄像机拍摄金属粉末再压缩等离子弧焊接金属粉末向熔池的过渡过程. 高速摄像机采集频率为2 000 Hz,曝光时间为8 μs.图5为焊接过程连续的3张熔融金属过渡照片. 从图中可见,电弧中间部分亮度最大,亮度沿着垂直于电弧轴线的方向逐渐递减. 电弧中间深色黑点为金属粉末熔化后形成的熔融金属. 若将熔融金属理想化为球形,经过计算得出,红色圈中的熔融金属直径大约为265 μm. 可见熔融金属非常细小. 与MIG焊接中的熔滴过渡不同,金属粉末再压缩等离子弧焊接熔融金属尺寸较小、过渡分布比较分散. 熔融金属对熔池会产生一定的冲击作用.
3.4 电弧弧光光谱分析
焊接电弧的物理本质是等离子体,金属粉末进入电弧后会吸收电弧热量,发生熔化、蒸发、电离等,随后参与电弧导电,改变电弧的电气特性. 基于搭建的电弧弧光光谱采集系统,对常规等离子弧焊接和金属粉末再压缩等离子弧焊接的电弧弧光信息进行采集,并根据美国国家标准局(National Institute of Standards and Technology,NIST)提供的原子辐射线谱资料进行标定.图6为采集的弧光光谱图片. 从采集的光谱数据可以看出,在波长为230 ~ 270 nm范围内:常规等离子弧焊接中主要是Fe和Cr的特征谱线,如图6a所示;金属粉末再压缩等离子弧焊接中主要是Fe,Cr和Ni的特征谱线,如图6c所示;与常规等离子弧焊接相比,金属粉末再压缩等离子弧焊接中Fe和Cr元素的特征谱线明显增多,说明金属粉末进入电弧后发生了一定程度的电离. 光谱数据表明,在波长为230 ~ 270 nm范围内,金属粉末再压缩等离子弧焊接电弧等离子体与常规等离子弧焊接电弧等离子体明显不同.
在波长为760 ~ 850 nm范围内,常规等离子弧焊接中主要是Ar的特征谱线,如图6b所示;金属粉末再压缩等离子弧焊接中也主要是Ar的特征谱线,如图6d所示. 为了更直观地对比分析在760 ~ 850 nm波长的两种焊接工艺的光谱,制作了此范围的光谱数据曲线(图7). 光谱数据表明,金属粉末再压缩等离子弧焊接电弧光谱各个特征谱线峰强度均比常规等离子弧焊接电弧光谱对应的特征谱线峰强度小. 金属粉末再压缩等离子弧焊接光谱与常规等离子弧焊接光谱存在差异,这种差异对焊接过程产生的影响有待进一步研究.
4. 结论
(1)在相同焊接电流条件下,与常规等离子弧焊接工艺相比,金属粉末再压缩等离子弧焊接焊缝熔深更深、熔宽更窄.
(2)在相同焊接电流195 A条件下,与常规等离子弧焊接工艺相比,金属粉末再压缩等离子弧焊接电弧电压升高0.63 V.
(3)金属粉末等离子弧焊接熔融金属尺寸细小、过渡较分散.
(4)在波长为230 ~ 270 nm范围内,与常规等离子弧焊接相比,金属粉末再压缩等离子弧焊接中Fe和Cr元素的特征谱线明显增多.
(5)仅对金属粉末再压缩等离子弧焊接新工艺开展了初步的研究,还需要对金属粉末再压缩等离子弧焊接机理进行深入系统研究.
-
图 5 凝固过程中组织形态演变示意图[12]
Figure 5. Schematic diagram of solidification
表 1 母材和焊材的主要成分(质量分数,%)
Table 1 Chemical composition of the base matel and welding material
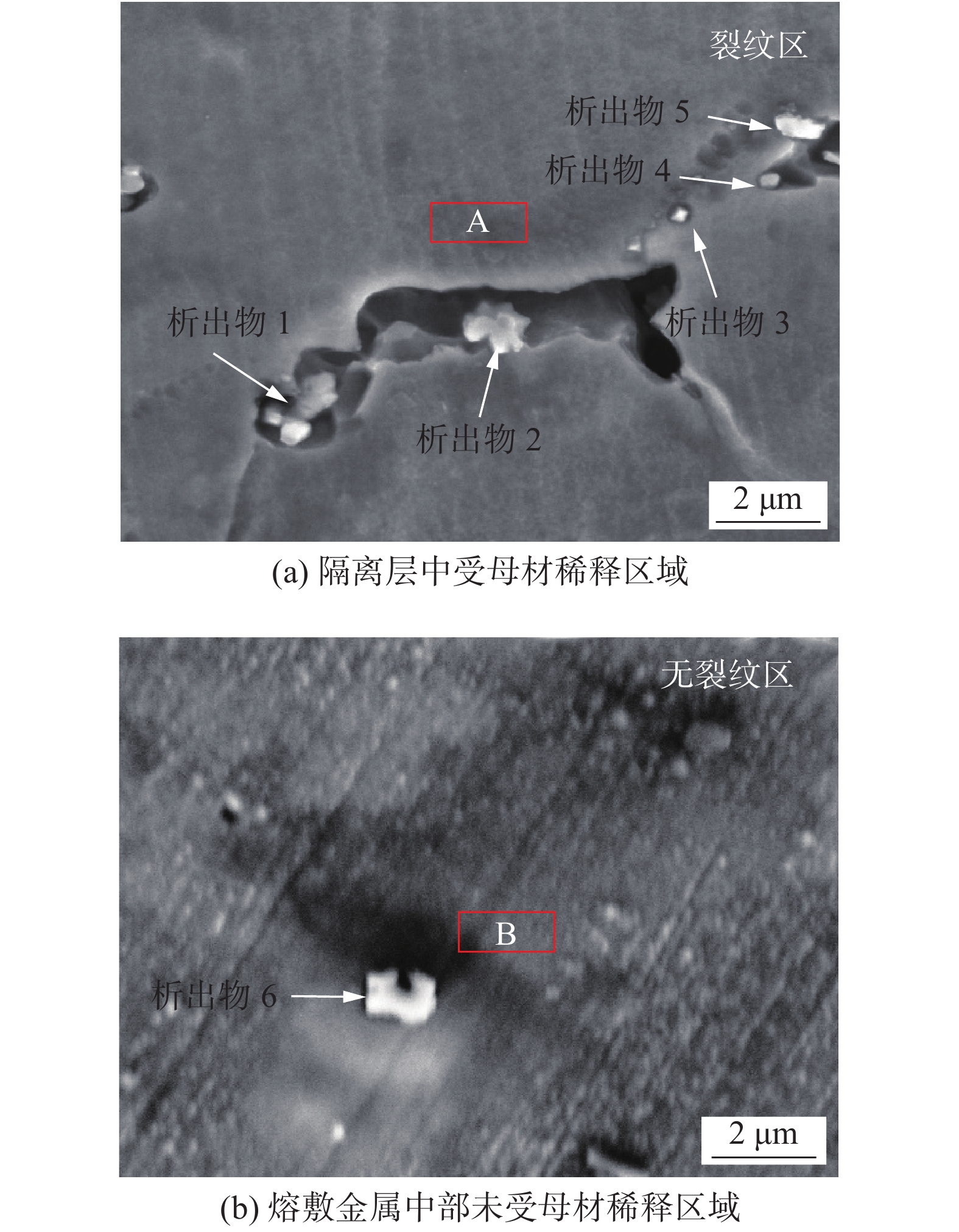
材料 Cr Mn S P Nb Ni Fe Q345B 0.300 1.700 0.035 0.035 0.070 0.500 96.000 ENiCrFe-7 29.500 3.800 0.009 0.006 1.750 56.800 8.300 表 2 图3各区域的成分分析(质量分数,%)及稀释率
Table 2 Chemical composition and dilution rate of different regions of weld in Fig. 3
位置 Si Nb Cr Mn Fe Ni 稀释率η(%) 有无裂纹 1 0.54 1.10 19.56 2.32 42.79 33.69 56 有 2 0.42 1.91 17.64 2.43 38.33 32.40 54 有 3 0.70 2.00 25.30 3.20 25.20 43.60 36 有 4 0.60 1.60 24.60 3.10 24.60 45.50 35 有 5 0.52 1.64 28.7 3.27 11.39 54.48 17 无 6 0.50 1.77 28.92 3.01 11.13 54.67 17 无 注:稀释率η的计算基于Fe和Ni的含量比值[11] 区域 Ni Cr Fe C Mn Nb S 1 3.30 3.90 2.40 18.70 2.40 63.90 5.40 2 9.50 7.00 6.90 25.70 2.20 46.10 2.60 3 9.10 6.30 5.30 22.70 2.40 51.90 2.30 4 15.90 11.20 9.00 16.50 1.70 43.80 1.90 5 19.30 12.70 10.60 19.70 1.70 36.20 1.60 6 6.60 6.90 6.00 12.90 1.90 64.40 1.30 A 28.54 15.30 34.66 18.48 1.44 0.70 0.75 B 52.50 27.30 8.60 5.50 3.10 1.50 0.30 -
[1] Li Xiaoquan, Hao Benxing, Chen Yixing, et al. The microscopic mechanical performance for nonuniform welded joint of nickel-based alloy with nanoindentation[J]. China Welding, 2019, 28(2): 29 − 34.
[2] 曹睿, 刘刚, 陈剑虹, 等. 镍基材料焊接中高温失塑裂纹DDC的生成机理及研究进展[J]. 焊接, 2018(7): 7 − 13,65. Cao Rui, Liu Gang, Chen Jianhong, et al. Formation mechanism and research progress of ductility dip cracking in welding of nickel-based materials[J]. Welding &Joining, 2018(7): 7 − 13,65.
[3] Yushchenko K, Savchenko V, Chervyakov N, et al. Comparative hot cracking evaluation of welded joints of alloy 690 using filler metals Inconel 52 and 52MSS[J]. Welding in the World, 2011, 55(9-10): 28 − 35. doi: 10.1007/BF03321317
[4] Ko G, Seo K M, Kim H J, et al. Characteristics of hot cracking in dissimilar joint of A690 overlay and stainless steel clad[J]. Welding in the World, 2017, 61(5): 945 − 953.
[5] Kadoi K, Shinozaki K. Effect of chemical composition on susceptibility to weld solidification cracking in austenitic weld metal[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2017, 48(12): 5860 − 5869. doi: 10.1007/s11661-017-4340-2
[6] Yang B I, Kim J T, Park K S, et al. Hot cracking behavior in inconel 690 overlay welds on Mn-Ni-Cr-Mo steel for pressure vessels [J].Journal of KWS, 2002, 20(2): 200–207.
[7] DuPont J N. Solidification of an alloy 625 weld overlay[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 1996, 27(11): 3612 − 3620. doi: 10.1007/BF02595452
[8] DuPont J N, Marder A R, Notis M R, et al. Solidification of Nb-bearing superalloys: Part II. Pseudoternary solidification surfaces [J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 1998, 29(11): 2797-2806.
[9] Banovic S W, Dupont J N, Marder A R. Dilution and microsegregation in dissimilar metal welds between super austenitic stainless steel and nickel base alloys[J]. Science and Technology of Welding and Joining, 2002, 7(6): 374 − 383. doi: 10.1179/136217102225006804
[10] Chu H A, Young M C, Chu H C, et al. Hot cracking susceptibility of Alloy 52M weld overlays onto CF8 stainless steel[J]. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 2013, 433(1-3): 419 − 423. doi: 10.1016/j.jnucmat.2012.10.041
[11] McCracken S L, Smith R E. Evaluation of filler metal 52M (ERNiCrFe-7A) hot cracking when welding on cast austenitic stainless steel base materials [C]//Proceedings of the ASME 2011 Pressure Vessels and Piping Conference Volume 6: Materials and Fabrication, Parts A and B. Baltimore, Maryland, USA: ASME, 2011: 407-420.
[12] Dupont J N, Robino C V, Marder A R. Modeling solute redistribution and microstructural development in fusion welds of Nb-bearing superalloys[J]. Acta Materialia, 1998, 46(13): 4781 − 4790. doi: 10.1016/S1359-6454(98)00123-2
[13] Chu H A, Young M C, Chu H C, et al. The effect of Nb and S segregation on the solidification cracking of alloy 52M weld overlay on CF8 stainless steel[J]. Journal of Nuclear Materials Engineering and Performance, 2014, 23(3): 967 − 974.
[14] 薄春雨, 杨玉亭, 丑树国, 等. 690镍基合金焊接结晶裂纹形成机理分析[J]. 焊接学报, 2007, 28(10): 69 − 72, 116-117. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-360x.2007.10.019 Bo Chunyu, Yang Yuting, Chou Shuguo, et al. Solidification cracking mechanism of 690 nickeil-based alloy surfacing metal[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2007, 28(10): 69 − 72, 116-117. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-360x.2007.10.019
-
期刊类型引用(3)
1. 潘睿志,林涛,李超,胡波. 基于深度学习的多尺寸汽车轮辋焊缝检测与定位系统研究. 光学精密工程. 2023(08): 1174-1187 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 刘岩,刘澳,张琳琳,杜安娜,刘兆真,贺春林. DP590镀锌双相钢CMT焊接接头气孔及锌层研究. 机械工程学报. 2023(16): 213-222 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 李文斌. 城市轨道交通车辆高强钢焊接用焊丝的选用方法. 焊接技术. 2022(03): 80-83 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)




 下载:
下载: