Effect of V content and tempering treatment on microstructure and mechanical properties of the high strength steel TIG weld metal
-
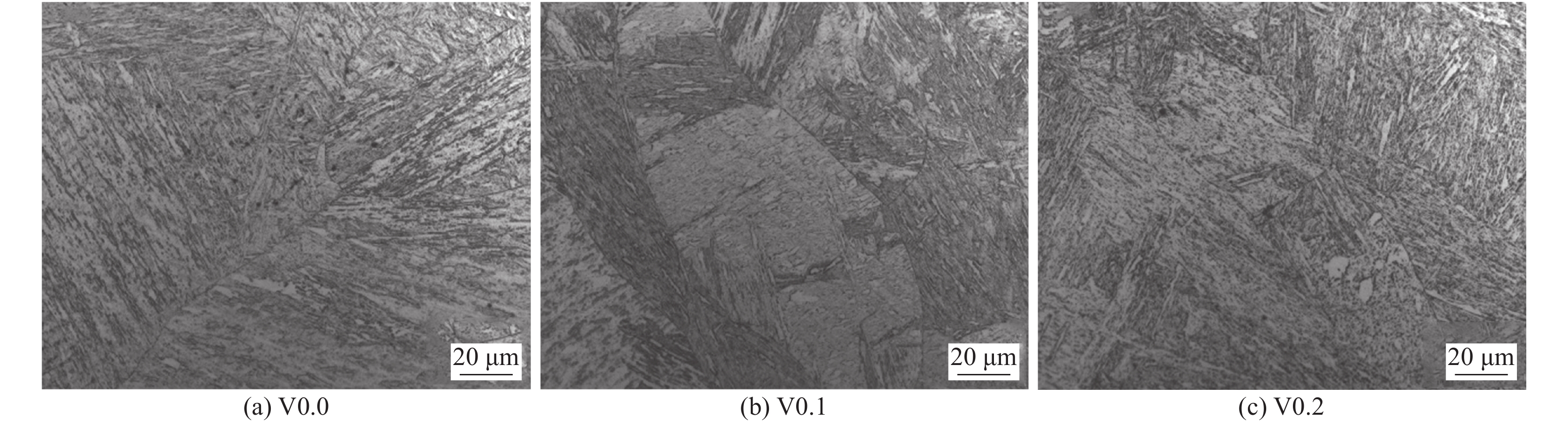
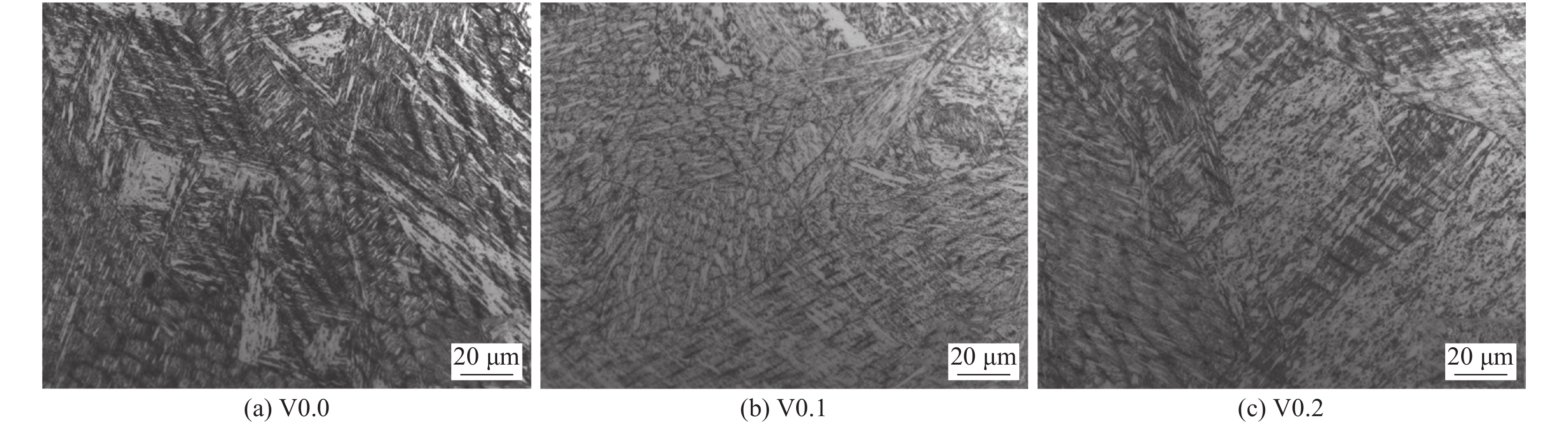
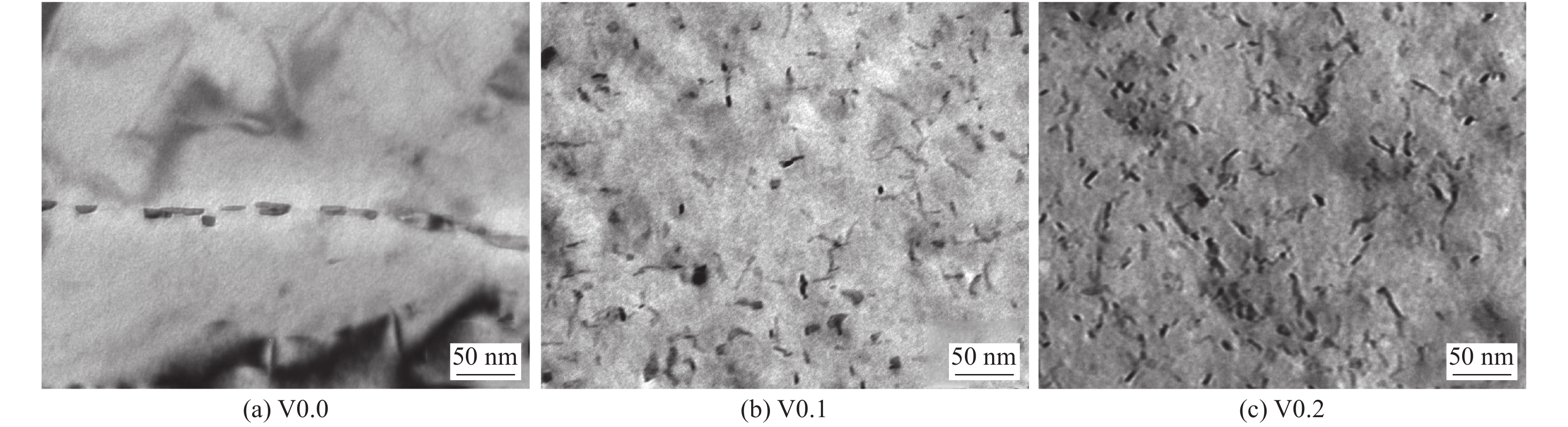
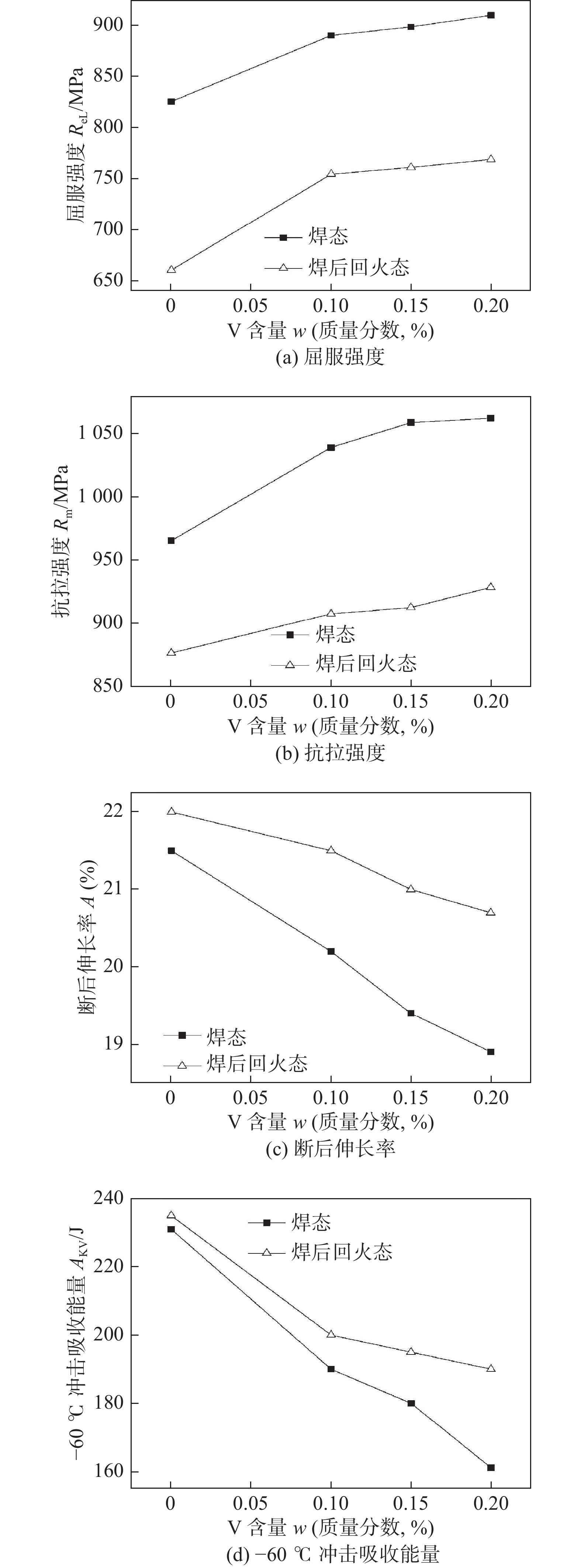
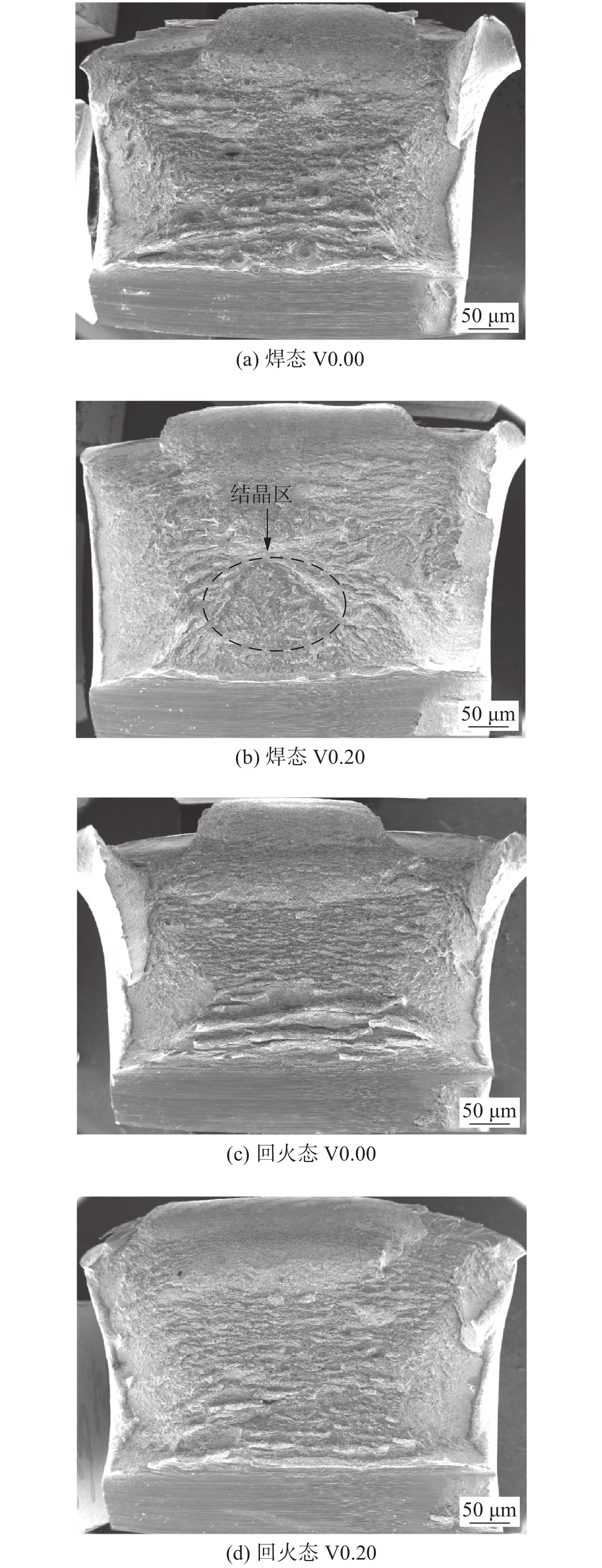
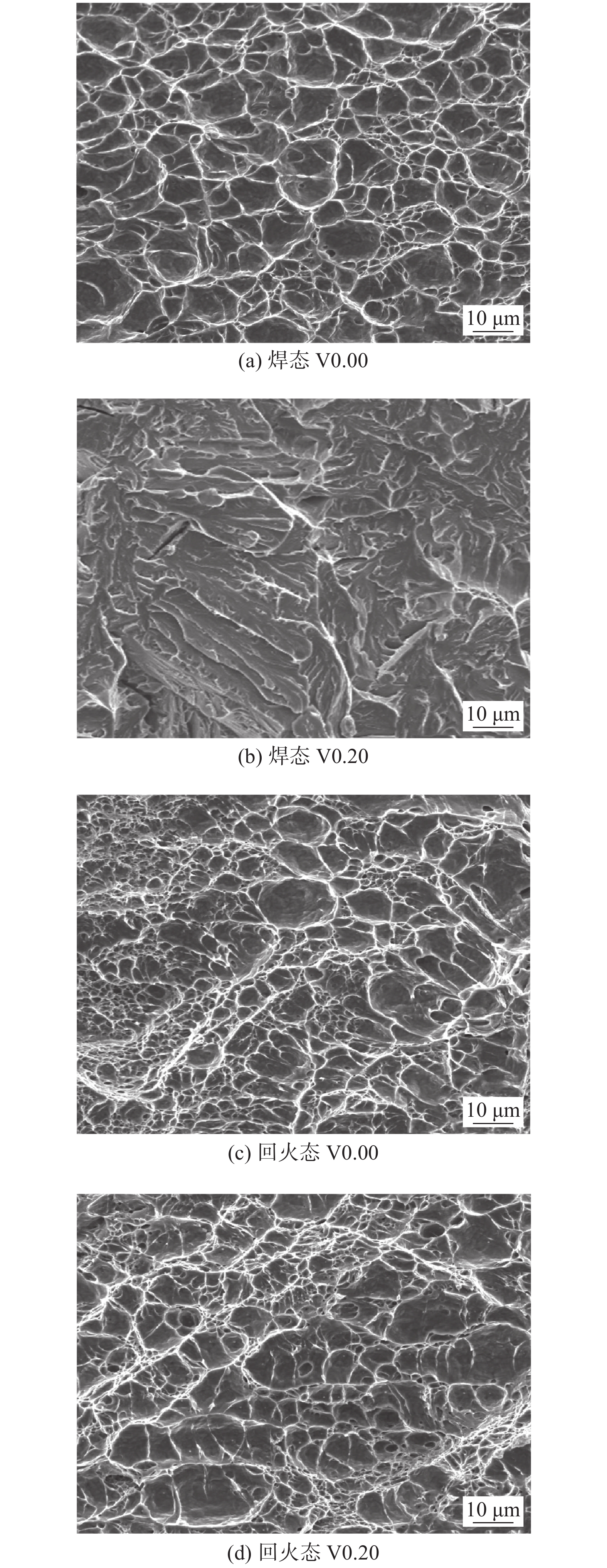
摘要: 采用四种不同V含量焊丝对高强钢板进行钨极氩弧焊试验,焊后对熔敷金属进行640 ℃保温2 h的回火处理. 研究了V含量和回火处理对熔敷金属微观组织及力学性能的影响. 结果表明,焊态及焊后回火态条件下,随着V含量的增加,熔敷金属强度升高,延伸率和冲击功降低,经回火处理后,不含V熔敷金属内晶界处析出M2C碳化物,而含V熔敷金属内析出弥散分布的VC析出相,焊后回火过程中位错回复引起基体软化的作用高于M2C及VC的析出强化作用,导致回火后强度降低,断后伸长率冲击吸收能量升高. 细小VC具有阻碍位错运动的作用,导致回火后含V熔敷金属仍保留较高的位错密度. 实际应用中应根据熔敷金属性能要求合理选择V含量及焊后回火工艺.Abstract: Four kinds of welding wires with different V contents were used to weld the high strength steel plates by tungsten inert gas welding method. After welding, the weld metals of different welding wires were tempered at 640 ℃ for 2 h. The effects of V content and tempering treatment on microstructure and mechanical properties of weld metal were studied. The results show that for the as-welded and as-tempered weld metals, with the increase of V content, the strength increases and the elongation and impact energy decrease. Furthermore, after tempering treatment, M2C carbide precipitated at the grain boundary of the V-free weld metal, while VC precipitated in V-bearing weld metals. During the post weld tempering process, the effect of dislocation recovery on matrix softening is stronger than precipitation strengthening of M2C and VC. Therefore, under the combined effects of the two factors, the tempering treatment decreases the strength and improves the elongation and impact energy. The dispersed VC precipitates have the effect of hindering dislocation movement, which causes that the V-bearing weld metal retains high dislocation density after tempering. In practical application, V content and post weld tempering process should be selected reasonably according to the performance requirements of weld metal.
-
Keywords:
- high strength steel /
- weld metal /
- post weld heat treatment /
- microstructure /
- mechanical property
-
0. 序言
增减材复合加工技术是一种将增材制造与减材制造相结合的新技术[1-2].增材制造利用计算机生成的三维模型,并针对模型生成数控代码,最终实现三维实体零件的加工,减材制造则是对成形零件进行铣削.在同一台设备上完成增减材加工,可以提高制造精度和生产效率,尽管增减材复合制造的优势已经被广泛认可,但其仍有很多技术难题有待解决.增材制造过程中构件内部产生复杂的内应力,在后续铣削减材中,随着材料的不断去除会导致构件残余应力的部分释放和再分布[3],并引起构件二次变形[4]. 因此,构件的最终成形精度不仅取决于增材过程中的应力累积及宏观变形,而且与减材过程中的应力释放与再分布有重要的关系.
在增材制造中,热力耦合有限元分析是理解和揭示零件在增材制造过程中瞬态热/力学行为的主要手段[5-7].DING 等人[8]使用了三维热弹性塑性瞬态模型和基于高级稳态热分析的模型,有效的加快了计算时间,并且稳态热模型能够有效的模拟构件的温度及应力场;DENLINGER等人[9]研究了通过增材制造工艺构建的大型零件的变形抑制技术,用简单的有限元模拟验证了变形抑制策略的有效性;SUN 等人[10]通过数值模拟分析了铝合金电弧增材中残余应力的分布特征,得到了电弧增材多层沉积后零件上残余应力分布的规律;HUANG 等人[11]以壁结构和管结构两种典型结构为例,建立了增材制造热力耦合模型,研究了两种典型结构残余应力的分布特征.大量文献表明,顺序耦合求解在减少计算量的同时并没有损失太多的计算精度[12-13],因此目前研究人员均以顺序耦合[14-15]的方式求解增材制造的热力耦合问题.
在传统的减材制造中,随着材料的去除,会引起零件初始残余应力的释放和再分布,目前针对增减材复合制造过程的模拟仿真较少.SALONITIS 等人[16]进行了激光熔覆增材成形复合减材制造的变形—应力联合数值仿真,发现减材只能修正部分变形,这是因为有较大初始残余应力的存在;赵宇辉等人[17]利用数值模拟探究了增减材复合制造过程中减材工艺的介入时机对工件表面的应力状态的影响;SUNNY 等人[18]研究了定向沉积的薄壁结构加工中,以不同刀具路径加工,零件上的残余应力和变形存在差异,并且初始残余应力对后续铣削加工产生的残余应力和变形会产生影响;WEBER等人[19]研究了整体铝块零件在铣削成薄壁零件的过程中,初始体积内的残余应力和铣削后诱导的残余应力对零件变形的影响; LANDWEHR等人[20]通过一种新的加工变形预测方法研究航空薄壁零件上加工时的残余应力引起的变形,演示了薄壁零件的变形预测.以上大部分文献研究了铣削对残余应力以及变形的影响,但是对于增减材复合加工制造中残余应力及变形的产生演变以及再分布没有过多的阐明.
增减材复合制造构件的最终成形精度不仅取决于增材过程中非均匀温度场导致的变形和应力累积,而且和减材过程中的应力释放与二次变形有重要的关系.当前增减材构件的变形研究尚处于起步阶段,变形控制主要依靠试验经验,热—力学过程基础研究不足.文中通过建立电弧增减材复合制造的仿真模型和联合模拟方法,研究增减材复合制造中的应力与变形的演变规律,为构件的精度控制提供参考.
1. 增减材复合制造有限元模型
1.1 增材制造模拟
文中主要研究增减材过程的应力与变形演变规律,对该过程进行了合理简化,忽略了电弧增材表面可能出现的凹凸不平的现象. 焊接残余应力的产生归因于焊接热源引起的温度分布不均匀[21],热源模型决定了热量的输入密度和分布方式.采用电弧增材常用的双椭球热源模型,即
$$ {{q}_1}{{(x,y,z) = }}\frac{{6\sqrt {3\eta P{f_1}} }}{{\text{π} \sqrt {\text{π} {a_1}bc} }}\exp \left( { - 3\frac{{{x^2}}}{{{a_1}^2}} - 3\frac{{{y^2}}}{{{b^2}}} - 3\frac{{{z^2}}}{{{c^2}}}} \right),x \geqslant 0 $$ (1) $$ {{q}_2}{(x,y,z) = }\frac{{6\sqrt {3\eta P{f_2}} }}{{\text{π} \sqrt {\text{π} {a_2}bc} }}\exp \left( { - 3\frac{{{x^2}}}{{{a_2}^2}} - 3\frac{{{y^2}}}{{{b^2}}} - 3\frac{{{z^2}}}{{{c^2}}}} \right),x \geqslant 0 $$ (2) $$ {f}_{1} + {f}_{2} = 2.0 $$ (3) 式中: $ {q}_{1},{q}_{2} $为前半部分和后半部分椭球热流密度;P为功率;$ \eta $为吸收率;$ \eta P $为有效功率;$ {f}_{1},{f}_{2} $为热量在前后两部分之间的比例;a,b,c为双椭球的形状参数.
电弧增材数值模拟计算过程中涉及的材料热性能参数主要包括密度、热传导系数、比热容等系数. 在该模型中,同时考虑对流和辐射两种方式分析工件与外界环境之间的热交换. 对流换热由牛顿定律描述,而辐射换热由斯蒂芬玻尔兹曼定律描述,即
$$ {q}_{{\mathrm{c}}}\text{ = }{-h}_{{\mathrm{c}}}\left({T}_{{\mathrm{S}}}-{T}_{0}\right) $$ (4) $$ {q}_{{\mathrm{r}}} = -\varepsilon \sigma \left({{T}_{{\mathrm{S}}}}^{4}-{{T}_{0}}^{4}\right) $$ (5) 式中:$ {q}_{{\mathrm{c}}} $为对流散热系数;$ {{h}}_{{\mathrm{c}}} $为对流换热系数;$ {q}_{{\mathrm{r}}} $为辐射散热;$ \varepsilon $为发射率;$ \sigma $为斯蒂芬玻尔兹曼常数;$ {T}_{{\mathrm{S}}} $为指定边界温度;$ {T}_{0} $为环境温度.
在电弧增材过程中,总应力是多种应力相互叠加的结果. 首先,由弹性应变、热应变、塑性应变及相变导致的应变等构成总应变;其次,根据广义的胡克定律,成形制件所承受的等效应力由这几种应变对应的分应力叠加而成,应力和变形遵循热弹塑性理论,总应变为
$$ {\varepsilon }_{{\mathrm{total}}} = {\varepsilon }_{{\mathrm{e}}} + {\varepsilon }_{{\mathrm{p}}} + {\varepsilon }_{{\mathrm{t}}} $$ (6) 式中:$ {\varepsilon }_{{\mathrm{total}}} $为总变形;$ {\varepsilon }_{{\mathrm{e}}} $为弹性应变;$ {\varepsilon }_{{\mathrm{p}}} $为塑性应变;$ {\varepsilon }_{{\mathrm{t}}} $为热变形.
模拟时考虑了材料的各项性能受温度变化的影响,热物理参数见表1[22].
表 1 6061铝合金材料参数Table 1. Material properties of 6061 aluminum alloy温度
T/K比热容
c/(J·kg−1·℃−1)传导率
λ/(W·m−1·℃−1)膨胀系数
aj/10−5 K−1弹性系数
E/GPa塑性系数
R/MPa293 728 176 2.22 71 300 373 795 180 2.38 65 284 573 963 188 2.53 49 100 773 1290 198 2.69 40 30 973 1580 200 3.02 28 10 使用ABAQUS模拟多道多层电弧增材制造工艺,在ABAQUS软件中创建有限元模型,增材部分尺寸为100 mm × 20 mm × 6 mm,基材部分的尺寸为200 mm × 100 mm × 6 mm,增材部分和基材材料同为6061铝合金,模型如图1所示.
为了保证数值模拟过程的准确性,实际增材过程中,成形件外表面主要通过与空气热辐射、对流换热和与基板热传导接触进行散热.设置对流传热系数为50 W/(m2·K)[23],辐射换热系数为0.4.为了防止电弧增材过程中由于热积累过大导致基板变形,在增材基板四周通过向压板施加载荷从而限制基板z轴方向变形,故设置约束上,在基板4个角施加了z轴上的约束以及xOy面的转动约束,考虑到实际情况基板总是与装夹处相连,故设置基板底面的z轴上的位移约束.
1.2 铣削减材过程模拟
材料本构模型是金属切削仿真技术中的核心要素之一.本构模型的精确性对金属切削仿真的精度有重要影响,文中选用Johnson-Cook模型(简称 J-C 模型),综合考虑了材料成形过程中的应变率、应变等各种因素对流动应力的影响,建立了应变强化、应变率强化与温度软化的函数,J-C 模型可用于大变形、大应变率条件下的材料变形计算.6061铝合金的Johnson-Cook参数见表2[24].
表 2 6061铝合金J-C模型参数Table 2. Johnson-Cook plasticity model parameters for 6061 alumimum alloy屈服强度
Rel/MPa硬化模量
ε/MPaC n m $ {\varepsilon }_{0} $ 熔点
TC/K室温
T/K324 114 0.0128 0.42 1.34 1 893 293 在材料切削加工过程中,应力、应变以及温度的变化发生区域主要集中在切屑与坯料的分离阶段,在这一过程中有着非常复杂的物理、化学变化过程.因此,合理选择材料的分离准则表征切屑的分离过程是仿真结果正确性的直接影响因素.选用的J-C damage模型是物理分离准则中应用最为广泛的损伤模型. 6061铝合金的Johnson-Cook失效模型参数见表3[24].
表 3 6061铝合金J-C失效模型参数Table 3. Johnson-Cook damage model parameters for 6061 aluminum alloy$ {d}_{1} $ $ {d}_{2} $ $ {d}_{3} $ $ {d}_{4} $ $ {d}_{5} $ $ {\varepsilon }_{0} $ 熔点TC/K 室温T/K −0.77 1.45 −0.47 0 1.6 1 893 293 减材刀具采用与试验相同的钨钢圆柱三头铣刀,直径为10 mm,刀具定义为刚体,在铣刀中轴线上选一点建立参考点,将刀具与参考点进行耦合,在边界条件中定义刀具的加工参数,切削速度5 m/s,转速
3000 r/min.刀具与被铣削工件接触选用表面与表面接触,为了降低计算量,指定两对接触面,即沉积层与刀具的接触及沉积层与自身的接触. 文中采用库伦摩擦定律描述铝合金切削模型中的摩擦行为,在切削加工仿真中正向摩擦选用罚函数,摩擦系数为0.2[24].零件及刀具的网格划分如图2所示.在薄壁零件铣削加工过程中,将刀具考虑为刚体,将零件与刀具进行刚性约束,通过设置参考点实现刚性连接.研究增减材一体化模拟仿真模型,将增材制造后的残余应力映射到铣削的几何模型中,作为铣削模拟仿真的初始条件,之后进行铣削加工过程的模拟.通过对刀具旋转运动以及进给运动进行定义并且进行相应约束,同时对边界条件进行定义,并对整个铣削过程进行定义和约束.2. 试验验证
2.1 试验设备
试验装置包括KUKA KR210型号机器人搭配弗尼斯CMT Advanced焊机组成的电弧增材制造系统,机器人其负载重量为210 kg,重复定位精度为0.05 mm.铣削减材装置为KUKA KR500机器人,负载重量为500 kg,重复定位精度为0.05 mm,该机器人末端配备ES779高速铣削头,最高转速为
22000 r/min.铣削时采用钨钢材料的三头铣刀,刀具全长100 mm,刀片长45 mm,直径12 mm,螺旋角55°.2.2 温度的比较
试验前对试验和模拟仿真的温度结果进行了比较,图3(b)中所示A点与B点为提取温度循环曲线的位置.由图3(c)和图3(d)中可以看出,试验中测得的温度循环曲线与模拟仿真中提取的温度循环曲线较为吻合,可以说明,有限元模型可以较好地反映模型中的温度场分布.
2.3 应力的比较
在电弧增材制造时,由于温度不均匀分布的影响,导致沉积层的成形不均匀,在沉积层表面较为凹凸不平,不易测量应力.因此在文中选择了铣削后沉积层上较为平整的区域进行应力的测量,如图4(c)所示,选择Path3路径上进行试验和模拟仿真应力的对比.采用X射线衍射的方法对沉积层侧面选择的5个点进行测量.为了计算几个点位的应力分量,选择了−2.5° ~ 43.5°的phi角,采用311衍射晶面对峰位进行测定,使用了1 mm的Cr靶材探测直径,在139°处的衍射角为2θ,在这些条件下对应力进行测量,X射线仪(X’Pert Pro MPD)由荷兰帕纳科公司制造.
图5将试验结果与仿真结果在横向和纵向残余应力分布上进行了比较,图5中的5个点对应仿真中Path3上的5个位置.可以看出,预测的纵向残余应力分布以及横向残余应力分布形状和大小与试验结果吻合良好.
3. 结果与讨论
3.1 增材过程应力演变规律
在沉积过程中,纵向残余应力的演化过程如图6所示,在每一层沉积进行到达中点时,由于该处的单元未被激活,所以该位置的应力数值为零.沉积到达中点后,单元被激活,由于此时热源移动到此处,该位置的单元对应实际增材过程中的熔化过程,而在熔化时,对应的有限元单元中也没有应力的产生,所以应力也为零.当热源离开中点继续移动,熔化的区域开始凝固,凝固的区域开始产生应力并逐渐增大,在这一层沉积结束与下一层沉积开始之前,该区域的应力达到最大值.在初始时刻,零件上的纵向应力主要为拉应力,且分布在沉积层的中间,如图6(a)所示.在沉积了五层之后,沉积层下方的应力从拉应力变成压应力,尤其是熔池下方的区域,压应力较大,如图6(b)所示.最后一层沉积时,沉积层中间区域以拉应力为主,上方出现压应力,这是由于沉积到第十层时,由于热输入不断累积,应力逐渐增大,沉积层上层区域的变形量增大,出现了压缩应变,从而产生了较大的压应力,如图6(c)所示.沉积结束冷却时,沉积层中间区域压应力大的区域压应力逐渐恢复成拉应力,整体沉积层的纵向应力分布又以拉应力为主,而在两侧区域依然保留了压应力区域.结束冷却后,薄壁零件在基板交接处的应力较大,尤其是在两端位置处,并且在沉积层上,中间区域的残余应力较大而两侧的残余应力较小,如图6(d)所示.
3.2 铣削过程应力演化
为探究铣削过程中残余应力的演化规律以及铣削后产生的二次变形,在数值模拟的结果中分别提取某条路径上残余应力以及变形的数值进行分析,文中选取应力与变形变化较大的路径进行分析,Path1为提取二次变形的路径,Path2为提取纵向残余应力的路径,Path3为试验验证时所提取应力数据的路径,如图4(c)所示.
图7为薄壁零件铣削过程的纵向应力演变过程.随着铣削过程的进一步进行,可以看出在铣削过程中,随着进给运动的不断进行,薄壁零件上多余的材料被去除,同时图中可以发现在铣削减材过程中增材过程产生的残余应力出现重新分布.增材制造结束后,薄壁零件在基板交接处的应力较大,尤其是在两端位置处,并且在沉积层上,中间区域的残余应力较大而两侧的残余应力较小,如图7(a)所示.当高速旋转的铣刀接近工件时,铣刀前方的拉应力逐渐减小,而且与铣削刚开始的时候相比较,左边应力集中的情况不再明显,如图7(b)和图7(c)所示,这是由于随着铣削过程的进行,铣削实际上可以为零件施加部分压应力,抵消部分之前产生的残余拉应力.如图7(d)所示,最终在零件中间与基板交界的位置产生较大的残余拉应力,但是与初始状态相比,零件表面的高残余应力区域的残余应力明显减小了很多.
图8为薄壁零件铣削过程在特定路径下的纵向应力曲线,可以看到,在铣削加工之前,纵向残余应力在两侧的值较低,而越接近中心区域靠拢纵向残余应力的值越高,呈现出一个中间高两边低的分布态势.而在铣削过程中,随着切削刃进入加工零件,可以看到铣削前方的纵向应力略有减小,而且在铣削后方的区域纵向残余应力有明显的减小.在铣削完成后,该路径上整体的纵向残余应力减小,最大值从240 MPa降低到40 MPa左右.纵向残余应力整体的分布态势在图8中可以看出也有了明显的改变.因此,铣削过程中,增材制造薄壁零件内部残余应力是逐渐释放且重新分配的过程,并且整体上降低了零件内部的残余应力.
3.3 铣削过程变形演变规律
图9为铣削过程中增材零件的变形演变过程.由于薄壁零件的刚度较低,变形较大,而刀具的刚度较高,变形很小,因此在分析过程中忽略刀具的变形.铣削加工过程中,薄壁零件在x、y、z(纵向、横向、法向)方向都会产生一定的变形.模拟中发现薄壁零件的加工变形主要发生在y方向,x、y方向的加工变形在铣削加工过程中,随着刀具与工件的接触,在开始接触时位置处应力较为集中导致接触的位置变形较大,如图9(b)所示,同时释放的薄壁零件本身的内应力,因此在两侧变形量较大,而加工中间部位由于应力集中现象不再明显,因此变形量较小,见图9(c).同时随着刀具的高速转动,残余应力出现再分布现象,也导致薄壁零件出现在两端变形量较大的情况,如图9(d)所示 .图10为铣削减材过程沿着所取路径y方向变形的演化曲线,可以看到在铣削过程中,进刀的位置变形量最大,可以达到0.15 mm,随着铣削减材过程的结束,在这个表面上刀具经过的区域整体出现了变形,产生变形的原因部分归因于加工过程中刀具施加的切削力和产生的切削热,另一方面,铣削加工结束后,原有的增材制造过程中积累的内应力得以释放,导致应力重新分布,进而引发了零件的变形.
4. 结论
(1) 建立了增减材一体化的仿真模型,采用了预定义场的方式实现了两个工艺温度场和应力场的衔接,实现了增减材复合加工的数值模拟计算.
(2) 增材制造后薄壁零件在基板交接处的应力较大,尤其是在两端位置,并且在沉积层上中间区域的残余应力较大,而两侧的残余应力较小.
(3) 由于铣刀切削力和切削热的联合作用,铣削过程中沉积层上残余应力是一个不断释放和再分布的过程.铣削后整体残余应力减小,峰值从240 MPa降低到40 MPa左右.铣削完之后残余应力分布有明显的改变,分布更为均匀.
(4) 铣削中在沉积层上产生变形,沉积层中部和下部变形较小,变形主要集中在沉积层上部区域,在上部区域铣削过程中变形值可以达到0.15 mm.
-
表 1 母材及焊材化学成分(质量分数,%)
Table 1 Chemical compositions of base metal and welding wires
材料 C Si Mn Ni Cr Mo V 母材 0.15 0.30 1.40 4.20 0.80 0.60 <0.01 焊丝V0.00 0.03 0.40 1.20 5.50 1.00 0.70 <0.01 焊丝V0.10 0.03 0.40 1.20 5.50 1.00 0.70 0.10 焊丝V0.15 0.03 0.40 1.20 5.50 1.00 0.70 0.15 焊丝V0.20 0.03 0.40 1.20 5.50 1.00 0.70 0.20 表 2 微应变及位错密度
Table 2 Microstrain and austenite volume fraction
熔敷金属 微应变e 位错密度ρ/nm−2 焊态V0.00 0.24 13.30 焊态V0.20 0.30 20.80 回火态V0.00 0.17 7.10 回火态V0.20 0.24 12.90 -
[1] 文明月, 董文超, 庞辉勇, 等. 一种Fe-Cr-Ni-Mo高强钢焊接热影响区的显微组织与冲击韧性研究[J]. 金属学报, 2018, 54(4): 501 − 511. Wen Mingyue, Dong Wenchao, Pang Huiyong, et al. Microstructure and Impact toughness of welding heat-affected zones of a Fe-Cr-Ni-Mo high strength steel[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2018, 54(4): 501 − 511.
[2] 王长军, 梁剑雄, 刘振宝, 等. 亚稳奥氏体对低温海工用钢力学性能的影响与机理[J]. 金属学报, 2016, 52(4): 385 − 393. doi: 10.11900/0412.1961.2015.00312 Wang Changjun, Liang Jianxiong, Liu Zhenbao, et al. Effect of metastable austenite on mechanical property and mechanism in cryogenic steel applied in oceaneering[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2016, 52(4): 385 − 393. doi: 10.11900/0412.1961.2015.00312
[3] Zhou Yanlei, Jia Tao, Zhang Xiangjun, et al. Microstructure and toughness of the CGHAZ of an offshore platform steel[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2015, 219: 314 − 320. doi: 10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2014.12.017
[4] 张熹, 张楠, 刘宏, 等. 母材熔合作用对EQ51海工钢焊缝组织及韧性的影响[J]. 焊接学报, 2016, 37(12): 125 − 128. Zhang Xi, Zhang Nan, Liu Hong, et al. Fusion effect on weld joint microstructure and toughness of EQ51 ocean engineering steel[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2016, 37(12): 125 − 128.
[5] Li Hongliang, Liu Duo, Tang Dongyan, et al. Microstructure and mechanical properties of E36 steel joint welded by underwater wet welding[J]. China Welding, 2016, 25(1): 30 − 35.
[6] Haslberger P, Holly S, Ernst W, et al. Microstructure and mechanical properties of high-strength steel welding consumables with a minimum yield strength of 1100 MPa[J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2018, 53(9): 6968 − 6979. doi: 10.1007/s10853-018-2042-9
[7] Holly S, Haslberger P, Zügner D, et al. Development of high-strength welding consumables using calculations and microstructural characterisation[J]. Welding in the World, 2018, 62(3): 451 − 458. doi: 10.1007/s40194-018-0562-1
[8] Ju Yulin, Goodall Aimee, Strangwood Martin, et al. Characterisation of precipitation and carbide coarsening in low carbon low alloy Q & T steels during the early stages of tempering[J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2018, 738: 174 − 189. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2018.09.044
[9] Williamson G K, Smallman R E. Dislocation densities in some annealed and cold-worked metals from measurements on the X-ray debye-scherrer spectrum[J]. Philosophical Magazine, 1956, 1(1): 34 − 46. doi: 10.1080/14786435608238074
[10] Yan Jiacheng, Xu Hongwei, Zuo Xiaowei, et al. Strategies for strengthening-ductility and hierarchical co-precipitation in multicomponent nano-precipitated steels by Cu partitioning[J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2019, 739: 225 − 234. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2018.10.036
[11] Xu S S, Zhao Y, Chen D, et al. Nanoscale precipitation and its influence on strengthening mechanisms in an ultra-high strength low-carbon steel[J]. International Journal of Plasticity, 2019, 113: 99 − 110. doi: 10.1016/j.ijplas.2018.09.009



 下载:
下载: