Microstructure to properties of coarse grained heat affected zone in deposited weld metal of metal cored wire E120C-K4
-
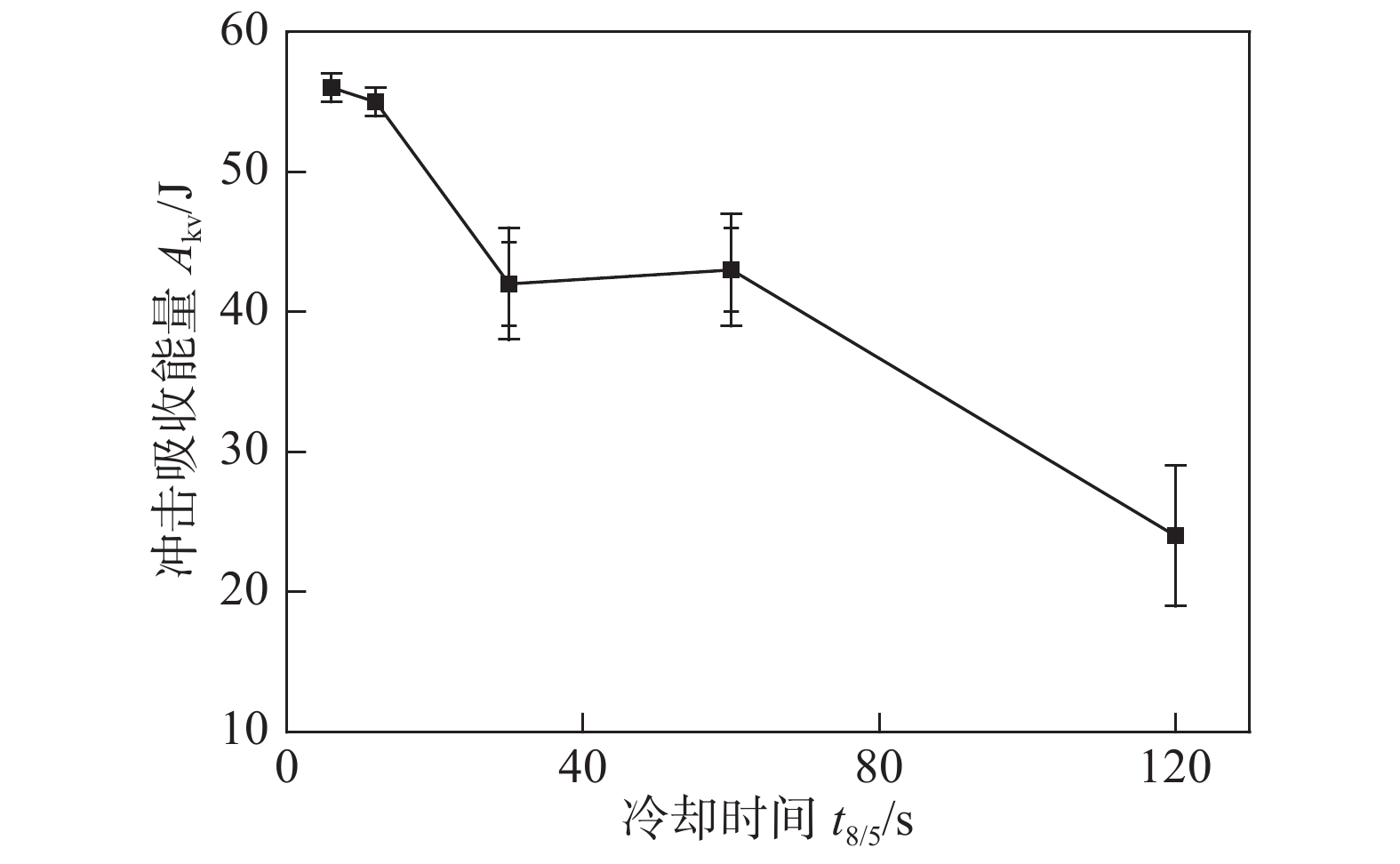
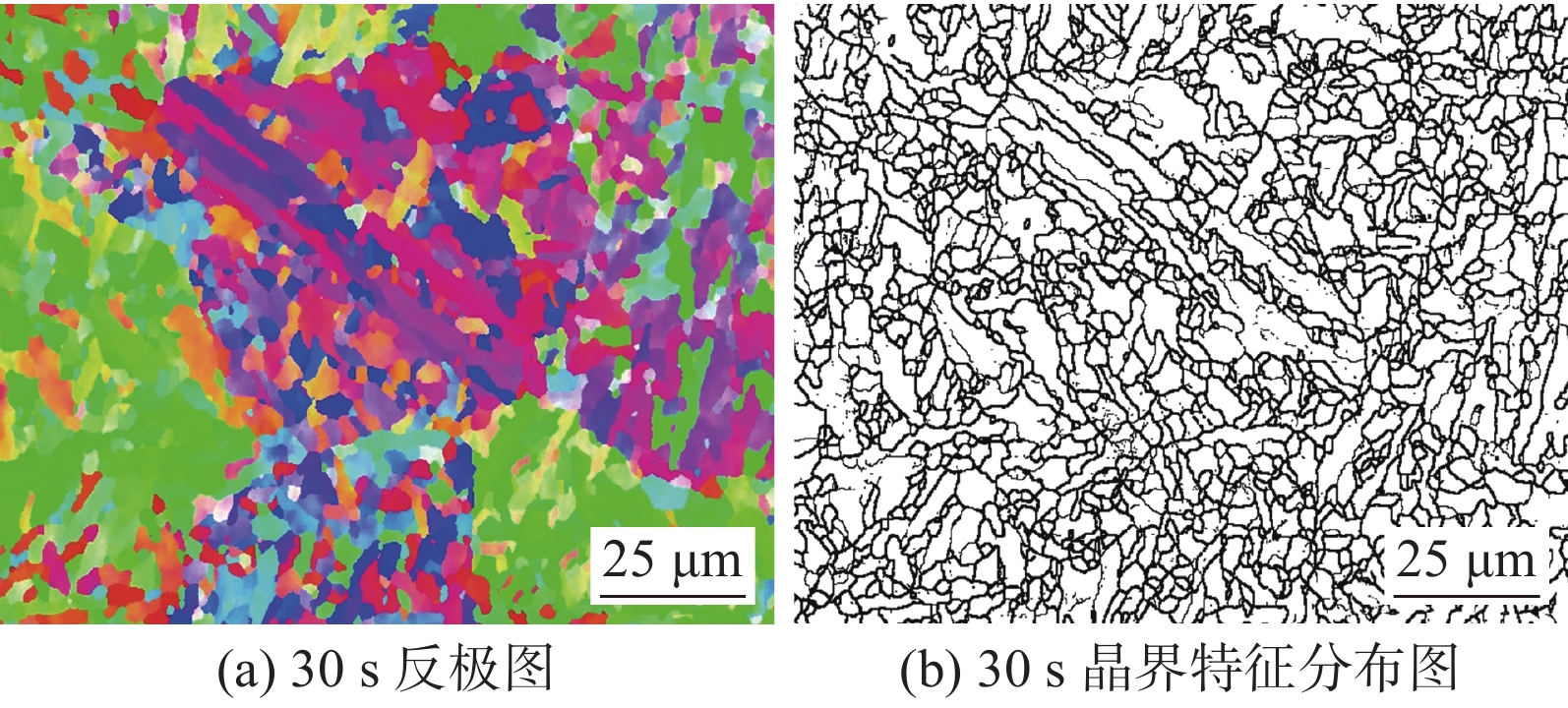
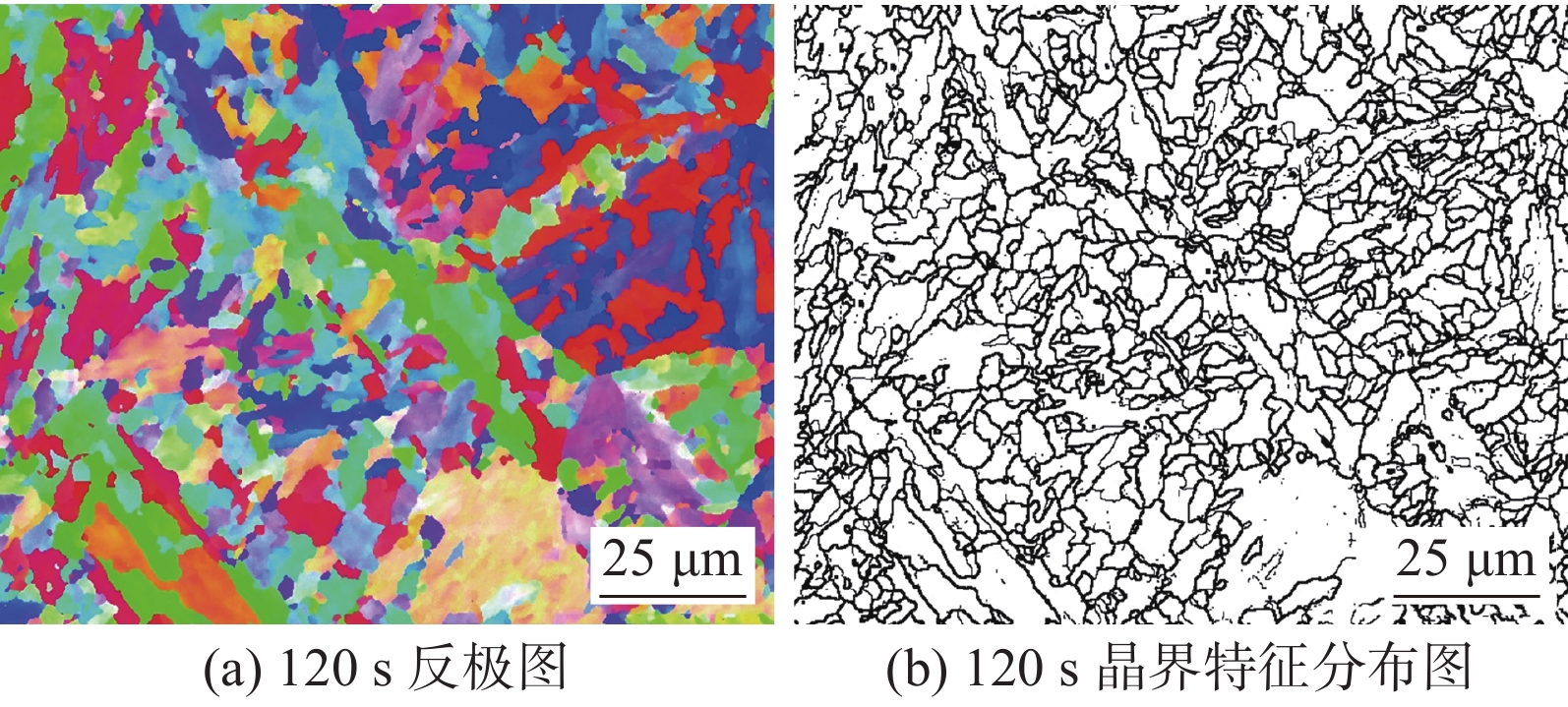
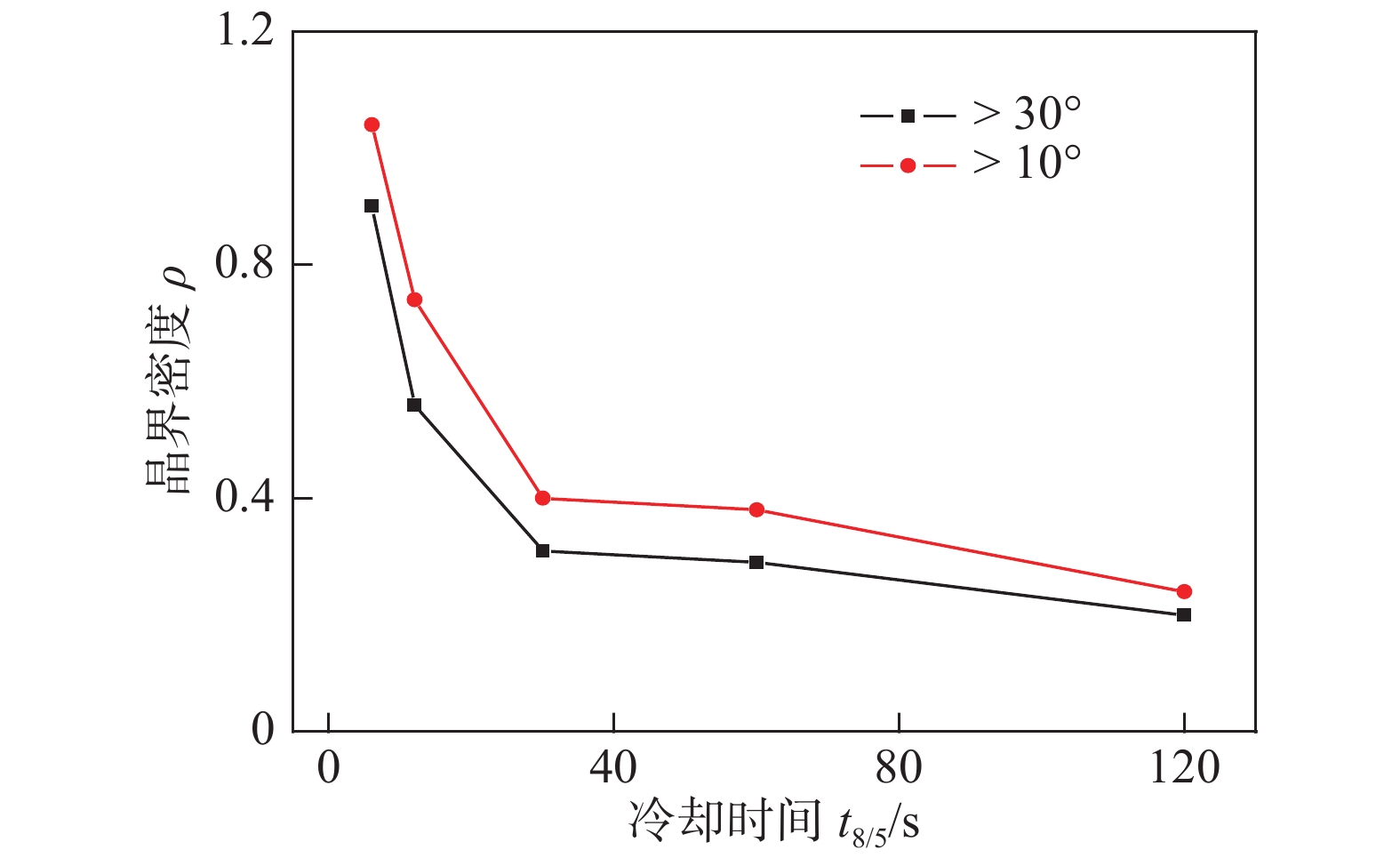
摘要: 采用焊接热模拟通过改变冷却时间(t8/5),研究了金属芯焊丝E120C-K4多道焊熔敷金属模拟粗晶区(CGHAZ)显微组织对冲击韧性的影响规律. 结果表明,当t8/5为6 ~ 12 s时,CGHAZ显微组织由蜕化上贝氏体、粒状贝氏体和针状铁素体组成,奥氏体晶粒内部形成复相分割结构,冲击韧性最好. 而当t8/5为30 ~ 120 s时CGHAZ显微组织主要由粒状贝氏体和针状铁素体组成,冲击韧性下降. t8/5为120 s时,冲击韧性最差,–40 ℃冲击吸收能量仅为24 J. t8/5为6 ~ 12 s时韧性改善的关键是形成复相分割微观结构;晶粒细小;单位距离上大角度晶界数量多.
-
关键词:
- 焊接热模拟 /
- 800 ~ 500 °C冷却时间 /
- 粗晶区;显微组织 /
- 冲击韧性
Abstract: The effect of microstructure as a function of welding cooling time (t8/5) from 800 °C to 500 °C on the impact toughness of coarse grained heat affected zone (CGHAZ) of deposited metal of metal cored wire E120C-K4 was investigated by welding thermal simulation. The results showed that the microstructure of CGHAZ was mainly composed of degenerate upper bainite (DUB) granular bainite (GB) and Acicular ferrite(AF) at t8/5 from 6 s to 12 s, forming the interlace multiphase microstructure, then the optimal impact toughness was obtained. The microstructure of CGHAZ formed with granular bainite (GB) and Acicular ferrite(AF) and the impact toughness decreased when t8/5 from 30 s to 120 s. The absorbed energy of CGHAZ was only 24 J at −40 °C at t8/5 of 120 s, the worst impact toughness. The key of improving impact toughness at t8/5 from 6 s to 12 s was: ① forming the interlace multiphase microstructure; ② refining grains; ③ more high-angle grain boundaries per unit distance. -
-
表 1 焊接试验工艺参数
Table 1 Parameters of welding
电流I/A 电压U/V 气体流量Q/(L·mm−1) 保护气体 焊接速度v/(cm·min–1) 道间温度T/℃ 预热温度T/℃ 焊丝伸出长度L/mm 200 ~ 220 28 ~ 30 20 10%CO2 + 90%Ar 28 ~ 30 150 ~ 160 150 16 表 2 E120C-K4焊丝化学成分(质量分数,%)
Table 2 Chemical composition of E120C-K4 wire
C Mn Si Cr Mo Ni P S 0.04 1.793 0.597 0.514 0.519 2.226 0.011 0.008 6 表 3 E120C-K4焊丝力学性能
Table 3 Mechanical properties of E120C-K4 wire
屈服强度
ReL/ MPa抗拉强度
Rm/ MPa断后伸长率
A(%)–40 ℃冲击吸收能量
Akv/ J815 907 16.3 70 表 4 粗晶区热模拟参数
Table 4 Thermal simulation parameters for coarse-grained regions
加热速度
ωH /(℃·s−1)预热温度
T/℃峰值温度
Tmax/℃峰值温度停
留时间tH/s冷却时间
t8/5/s150 150 1 350 5 6 150 150 1 350 5 12 150 150 1 350 5 30 150 150 1 350 5 60 150 150 1 350 5 120 -
[1] Zhang T, Li Z, Young F, et al. Global progress on welding consumables for HSLA steel[J]. Transactions of the Iron & Steel Institute of Japan, 2014, 54(7): 1472 − 1484.
[2] 周灿丰, 焦向东, 陈家庆, 等. 海底管道J形铺设焊接技术[J]. 焊接, 2019(8): 21 − 24. Zhou Canfeng, Jiao Xiangdong, Chen Jiaqing, et al. Sub-sea pipeline J-lay welding technology[J]. Welding & Joing, 2019(8): 21 − 24.
[3] Mohrbacher H. Combined effects of nb and b microalloying in molybdenum based ultra low carbon bainitic (ULCB) steels[J]. Journal of Iron & Steel Research, 2011(S1): 785 − 791.
[4] 张元杰, 彭 云, 马成勇, 等. Q890高强钢焊接淬硬倾向和冷裂纹敏感性[J]. 焊接学报, 2013, 34(6): 53 − 56. Zhang Yuanjie, Peng Yun, Ma Chengyong, et al. Harden quenching tendency and cold cracking susceptibility of Q890 steel during welding[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2013, 34(6): 53 − 56.
[5] Zhang T, Li Z, Ma S, et al. High strength steel (600–900 MPa) deposited metals: microstructure and mechanical properties[J]. Science & Technology of Welding & Joining, 2016, 21(3): 1 − 8.
[6] Liu C, Bhole S D. Challenges and developments in pipeline weldability and mechanical properties[J]. Science & Technology of Welding & Joining, 2013, 18(2): 169 − 181.
[7] 张灵芝, 徐学利, 李 光, 等. X100管线钢埋弧焊缝焊接热影响区组织性能研究[J]. 热加工工艺, 2014(17): 37 − 40. Zhang Lingzhi, Xu Xueli, Li Guang, et al. Microstructure and properties of welding heat affected zone of X100 pipeline steel submerged arc weld[J]. Hot Working Technology, 2014(17): 37 − 40.
[8] Bhadeshia H K D H, Bainite in steels. 2nd Ed. [M]. London: Institute of Materials, 2001.
[9] Keehan E, Karlsson L, Bhadeshia H K D H, et al. Electron backscattering diffraction study of coalesced bainite in high strength steel weld metals[J]. Materials Science and Technology, 2008, 24(10): 1183 − 1188. doi: 10.1179/174328407X226572
[10] 安同邦, 田志凌, 单际国, 等. 保护气对1000 MPa级熔敷金属组织及力学性能的影响[J]. 金属学报, 2015, 51(12): 1489 − 1499. doi: 10.11900/0412.1961.2015.00294 An Tongbang, Tian Zhiling, Shan Jiguo, et al. Effect of shielding gas on micrpstructure and performance of 1000 MPa grade deposited metals[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2015, 51(12): 1489 − 1499. doi: 10.11900/0412.1961.2015.00294
[11] 王惜宝. 材料加工物理[M]. 天津: 天津大学出版社, 2011. [12] 戴起勋. 金属材料学[M]. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2005. [13] 张文钺. 焊接冶金学:基本原理[M]. 北京: 机械工业出版社, 2004. [14] Casalino G, Campanelli S L, Ludovico A D. Laser-arc hybrid welding of wrought to selective laser molten stainless steel[J]. International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2013, 68(1–4): 209 − 216. doi: 10.1007/s00170-012-4721-z
[15] Lan L, Qiu C, Zhao D, et al. Microstructural characteristics and toughness of the simulated coarse grained heat affected zone of high strength low carbon bainitic steel[J]. Materials Science & Engineering A, 2011, 529(1): 192 − 200.
[16] Lambert A, Garat X, Sturel T, et al. Application of acoustic emission to the study of cleavage fracture mechanism in a HSLA steel[J]. Scripta Materialia, 2000, 43(2): 161 − 166. doi: 10.1016/S1359-6462(00)00386-9
[17] Lambert-Perlade A, Gourgues A F, Pineau A. Austenite to bainite phase transformation in the heat-affected zone of a high strength low alloy steel[J]. Acta Materialia, 2004, 52(8): 2337 − 2348. doi: 10.1016/j.actamat.2004.01.025
-
期刊类型引用(0)
其他类型引用(6)




 下载:
下载: