Microstructure and microhardness analysis of laser welded dissimilar steel
-
摘要: 采用激光摆动焊接方法焊接异种钢,利用JMATPro软件计算了母材3Cr13,VG10的平衡相图,通过XRD,SEM,EPMA等技术分别对焊缝、熔合区、热影响区的相组成和显微组织进行了分析,测定了焊接接头的显微硬度分布. 试验结果表明,焊缝主要为α相和碳化物M7C3;从熔合线到焊缝中心,组织由平面晶逐渐变为胞状晶、胞状树枝晶、树枝状晶、柱状晶、等轴晶. 焊缝组织存在显微偏析,其中C,Cr元素在晶界富集,Fe元素在晶内富集,同时在晶界处有条棒状的M7C3析出. 熔合线附近的母材处有C迁移现象,其中3Cr13侧母材处有类针状马氏体组织产生,VG10侧熔合区存在非对流混合区,在该位置有块状、岛状组织嵌入母材,且在该组织上有片层状的碳化物生成. 熔合线两侧的母材硬度值最大,焊缝区硬度变化较小,热影响区硬度随着远离焊缝中心距离的增加而逐渐减少.Abstract: After welding dissimilar steel by laser swing welding, the equilibrium phase diagrams of base 3Cr13 and VG10 were calculated by JMATPro software, and the phase composition and microstructure of weld, fusion zone and heat affected zone were analyzed by XRD, SEM, EPMA and other techniques. in addition, the microhardness distribution of welded joints was determined. The results show that the weld is mainly composed of phases and carbides M7C3, and from the fusion line to the weld center, the structure changes from plane crystal to cellular crystal, cellular dendrite, columnar crystal, dendritic crystal and equiaxed crystal. The microstructure of the weld exists micro-segregation, in which C and Cr elements are enriched at the grain boundary, Fe elements are enriched within the grains, and bar-like M7C3 precipitates at the grain boundaries. There is a C migration phenomenon at the base material of the fusion line near. Among them, acicular martensitic structure is generated on the 3Cr13 side, and the unmixed zone exists in the fusion zone on the VG10 side. At this position, the massive, island tissue is embedded in the base Material, and there are lamellar carbides on the structure. The hardness of the base metal on both sides of the fusion line is the largest, and the hardness of the weld zone changes little. The hardness of the heat affected zone decreases with the increase of the distance away from the weld center.
-
Keywords:
- laser welding /
- dissimilar steel /
- microstructure /
- microhardness
-
0. 序言
不同成分的材料具有不同的使用性能,将异种材料焊接在一起,组合后的构件可以充分发挥良好的综合性能,同时节约生产成本. 其中,异种钢材的焊接已经在天然气、石油化工、发电工程、核工业等领域得到了广泛的应用[1-5]. 激光焊接技术是20世纪中期发展起来的一种高精密焊接技术,它具有高能量密度、可聚焦、深穿透、高效率、高精度、适应性强等优点而受到越来越多的重视. 激光焊接已被公认为最具吸引力的焊接技术之一,并已被应用于各种金属的焊接[6-7].
VG10钢具有优良的强度、耐腐蚀、耐磨损等性能,通常被用于制作高性能的刀具[8]. 3Cr13不锈钢是传统的厨刀制作材料,锋利度和耐磨性很难满足高性能刀具的要求[9]. 通过激光焊接技术将高性能刀具材料VG10焊接在普通刀具材料3Cr13上作为刃口,这种方法不仅提高了刀具性能,同时极大的降低了刀具生产成本.
采用激光焊接VG10与3Cr13,测试分析了焊缝组织形态变化、焊缝区元素分布及焊接接头显微硬度变化,以期为该异种钢的激光焊接组合应用提供一定的理论与数据支撑.
1. 试验方法
用摆动激光焊接的方式将VG10不锈钢刀条焊接在3Cr13的刀体上,刀体与刀条厚度均为2.8 mm. 其中3Cr13和VG10母材成分分别如表1和表2所示.试验采用德国TRUDISK 4002碟片激光器,波长1 030 nm、输出功率80 ~ 4 000 W. 使用日本FANUC R-30iB Mate焊接机器人控制激光焊接头的移动. 焊接前将两种母材对接部位用砂纸打磨干净,同时用酒精擦拭,去除油污. 通过前期试验,得到较好的激光摆动焊接工艺参数,如表3所示.
表 1 3Cr13的化学成分(质量分数,%)Table 1. Chemical composition of 3Cr13C Si Mn Cr Ni S P Fe 0.29 0.37 0.37 13.8 0.12 0.01 0.02 余量 表 2 VG10的化学成分(质量分数,%)Table 2. Chemical composition of VG10C Si Co Mo Mn V Cr Ni S P Fe 0.98 0.41 1.1 0.98 0.41 0.28 14.92 0.32 < 0.01 0.02 余量 表 3 激光焊接工艺参数Table 3. Parameters of laser welding激光功率P/W 焊接速度v/(mm·s−1) 离焦量△f/mm 保护气流量Q/(L·min−1) 摆动频率f/Hz 摆动幅度A/mm 3 750 43 + 2 20 200 0.3 垂直焊缝将焊接接头部位加工成长和宽都为10 mm的金相试样,利用Axio Scope A1光学显微镜、QUANTAFE 450扫描电子显微镜分析焊缝组织及成分. 使用EPMA-1600电子探针分析仪对焊接接头部分区域进行线分析. 将焊接试样沿焊缝中部切开,采用X射线衍射仪对焊缝区进行相分析. 运用HDX-1000型显微硬度计测量焊接接头显微硬度分布情况,加载载荷为1.96 N,加载时间为10 s. 沿焊缝截面方向由焊缝中部向焊缝两侧母材进行测量,每隔0.05 mm测量一个点,直至母材区域硬度值不再变化.
JMATPro软件拥有强大的热力学计算能力,在热力学平衡相图的计算中应用较广[10-11]. 试验采用JMATPro软件计算两种母材平衡相与温度的关系,为后期试验结果分析提供参考.
2. 结果与分析
2.1 JMATPro相图模拟
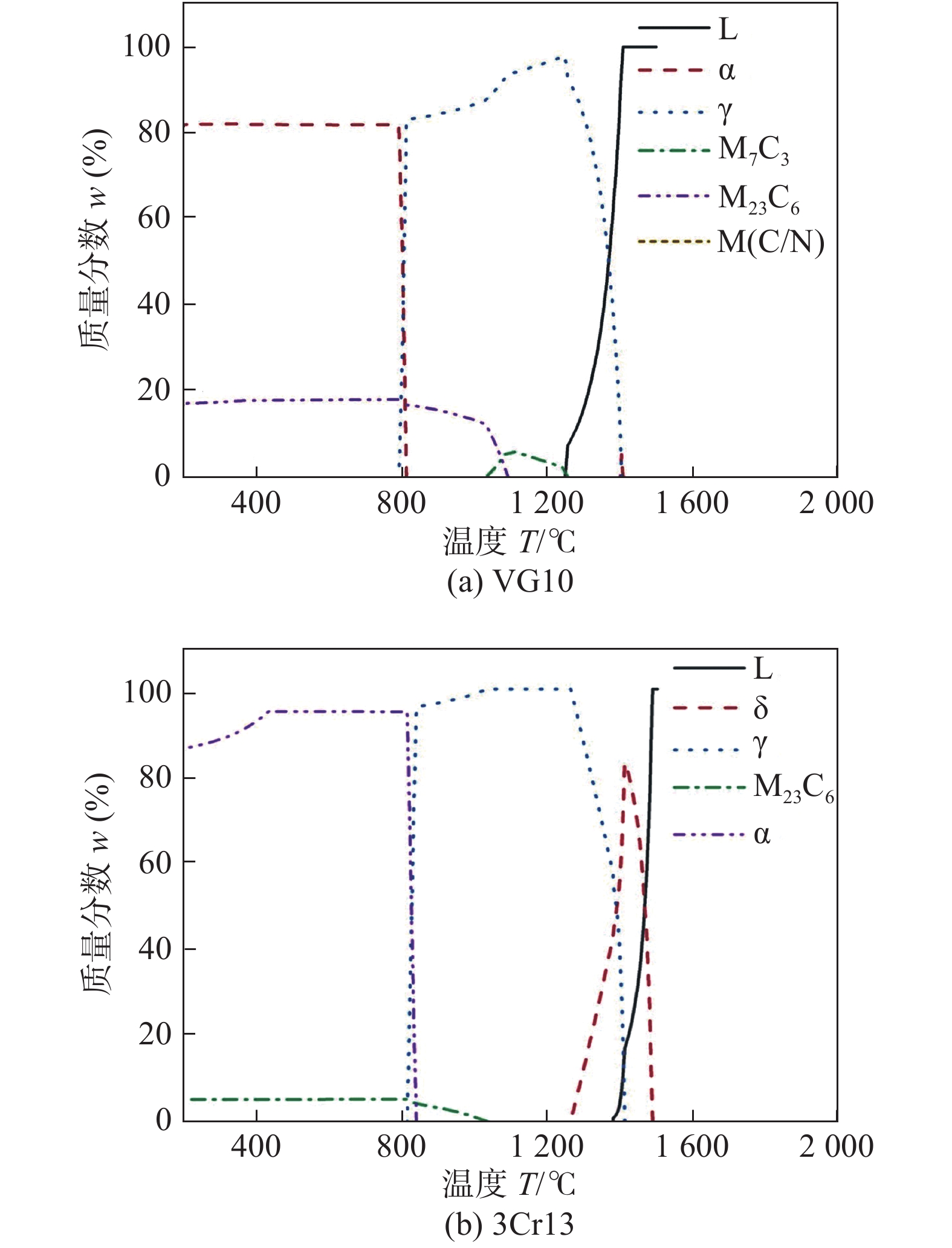
利用JMATPro7.0软件计算两种母材的平衡相与温度的关系图,设定温度区间为200 ~ 1 500 ℃,步长为5. 计算结果如图1所示. 其中图1a为VG10母材,图1b为3Cr13母材.
计算结果显示,VG10在1 405 ℃以上全为液相,温度降低到1 405 ℃以下时开始从液相中结晶出奥氏体γ相,随着温度的降低,γ相含量逐渐增加,当温度为1 245 ℃时全为固相,γ相含量达到最大,碳化物M7C3开始析出. 1 091 ℃时在γ相中开始析出碳化物M23C6,同时碳化物M7C3开始溶解,1 036 ℃时溶解完成. 温度达到812 ℃,γ相开始转化为铁素体α相. 室温下VG10钢为α相、M23C6以及少量的M(C/N). 3Cr13在1 470 ℃开始从液相中结晶出δ相,随着温度的降低,δ相含量逐渐增加,当温度降至1 389 ℃时,δ相和剩余液相开始转变为奥氏体γ相,在830 ℃时,α相开始形成,温度继续下降,在755 ℃时,γ相完全转化为α相. 温度降低的过程中还有其它相产生,在1 060 ℃时,从γ相中析出M23C6,其含量在γ相完全转化为α相后基本保持不变.
2.2 焊接接头组织分析
2.2.1 XRD试验
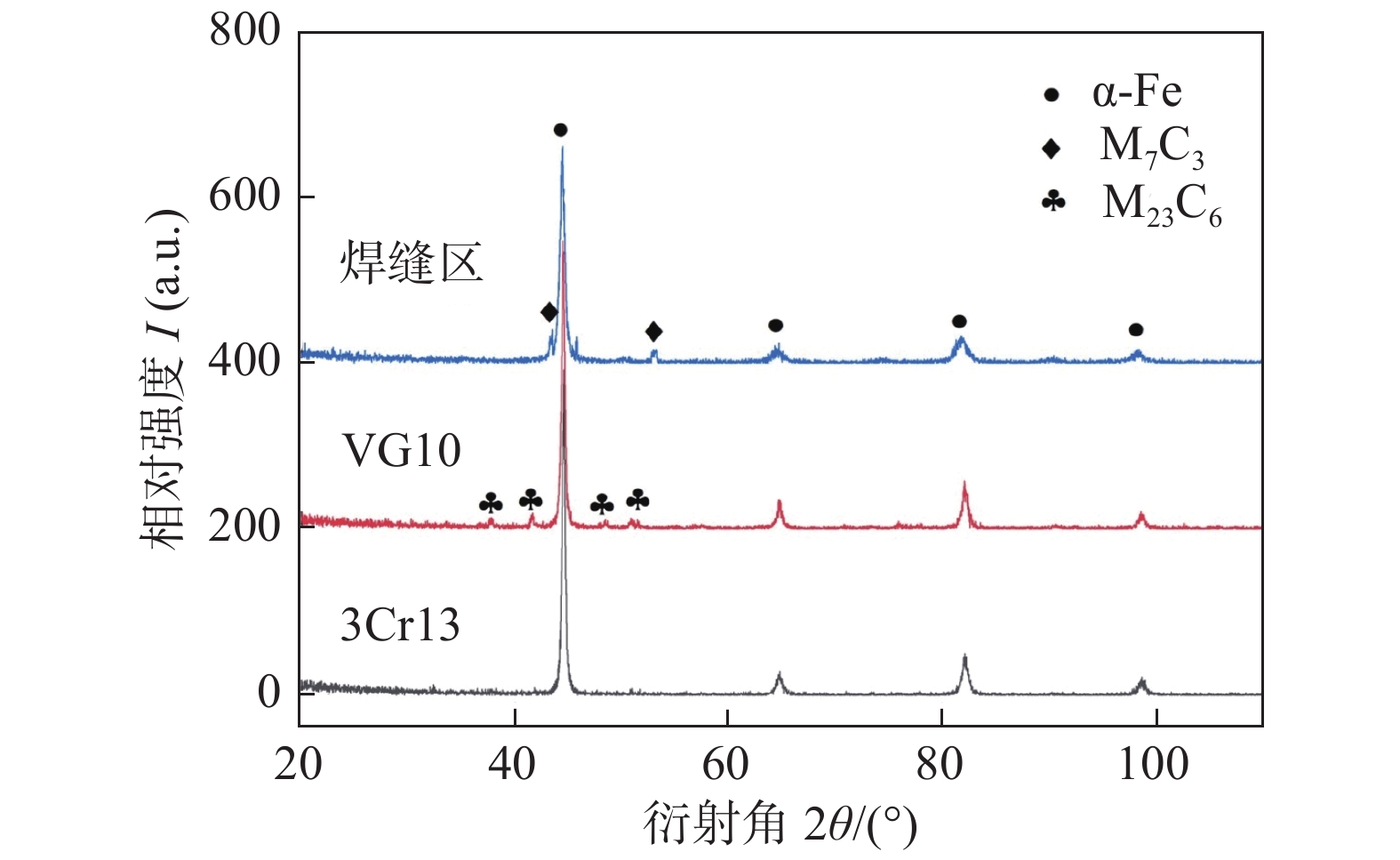
图2所示分别为VG10,3Cr13母材及焊缝区域的XRD试验结果. 母材基体相为α-Fe,其中VG10有M23C6衍射峰出现,但在3Cr13母材中并未检测出. 焊接后的焊缝区域基体相为α-Fe,同时有M7C3的衍射峰出现.
通过JMATPro计算结果发现,M7C3在温度下降时会逐渐转化为更稳定的M23C6. 焊缝区是由两个母材熔化混合后形成,因此在焊缝凝固过程中,在元素化学成分上有条件生成M7C3. 而激光能量密度高,焊接速度快,焊缝熔池凝固时间极短. 因此在实际过程中,M7C3转变为M23C6的条件难以达到,故在焊缝中检测出M7C3,而未检测到M23C6. 母材的平衡相与温度的关系图中,两个母材在凝固终了都有M23C6出现,在XRD图谱中只在VG10中有的M23C6,在3Cr13中未检测到. M23C6的形成需要较多的C及Cr元素,因此在碳含量约为1%的VG10中更容易达到这一条件,而含量越高,越容易检测出,3Cr13中碳元素含量较低,数量较少,难以检测.
2.2.2 焊缝组织形态
图3所示为焊缝组织形态照片. 图3a,3e分别为VG10侧和3Cr13侧焊缝组织. 在VG10侧及3Cr13侧焊缝熔合线位置有联生生长的平面晶,并且随着向焊缝中心伸展逐渐变为胞状晶、胞状树枝晶、柱状晶. 图3b为焊缝中部中心位置组织,其主要为柱状晶、树枝状晶. 图3c为焊缝顶部中心位置组织,该位置有大量的等轴晶存在. 而焊缝底部中心位置主要为树枝状晶,如图3d所示.
在焊缝中,位置不同液固前沿的成分过冷的程度的不同,由此形成了不同焊缝结晶形态[12]. 在整个激光作用形成的熔池结构中,成分过冷程度由两个母材侧表面沿着熔池结构体中心向后端面逐步递增. 当成分过冷由小变大时,焊缝结晶形态会从平面结晶形态逐渐转化为胞状晶、胞状树枝晶、树枝状晶、柱状晶以及等轴晶.
在图3a,3e中可以清楚的看到熔合线两侧为在半熔态的母材晶体表面上生长的平面晶,而随着向焊缝中心的深入,平面晶向胞状晶、胞状树枝晶、柱状晶、等轴晶逐渐转变. 焊缝上表面熔池接触空气以及保护气体,此外焊缝上表面有少量下陷,因此,还可以通过母材两侧金属进行散热,散热比焊缝中部位的速度更快,使得整体凝固速率高于焊缝中部中心部位. 这样,在相同的温度梯度下,由于焊缝上表面的凝固速率更快,成分过冷更大. 从图3b中可以看到,焊缝顶部中心部位拥有更多的等轴晶粒. 焊缝底部表面有少量下凸,这样大部分底部焊缝金属与空气接触,而向焊缝两侧母材金属的散热减少,使得散热速率减慢,在相同的温度梯度下,成分过冷较小. 在图3d中多为树枝状晶. 而焊缝中部介于顶部和底部之间,有较多的柱状晶.
2.2.3 显微偏析及晶界析出物
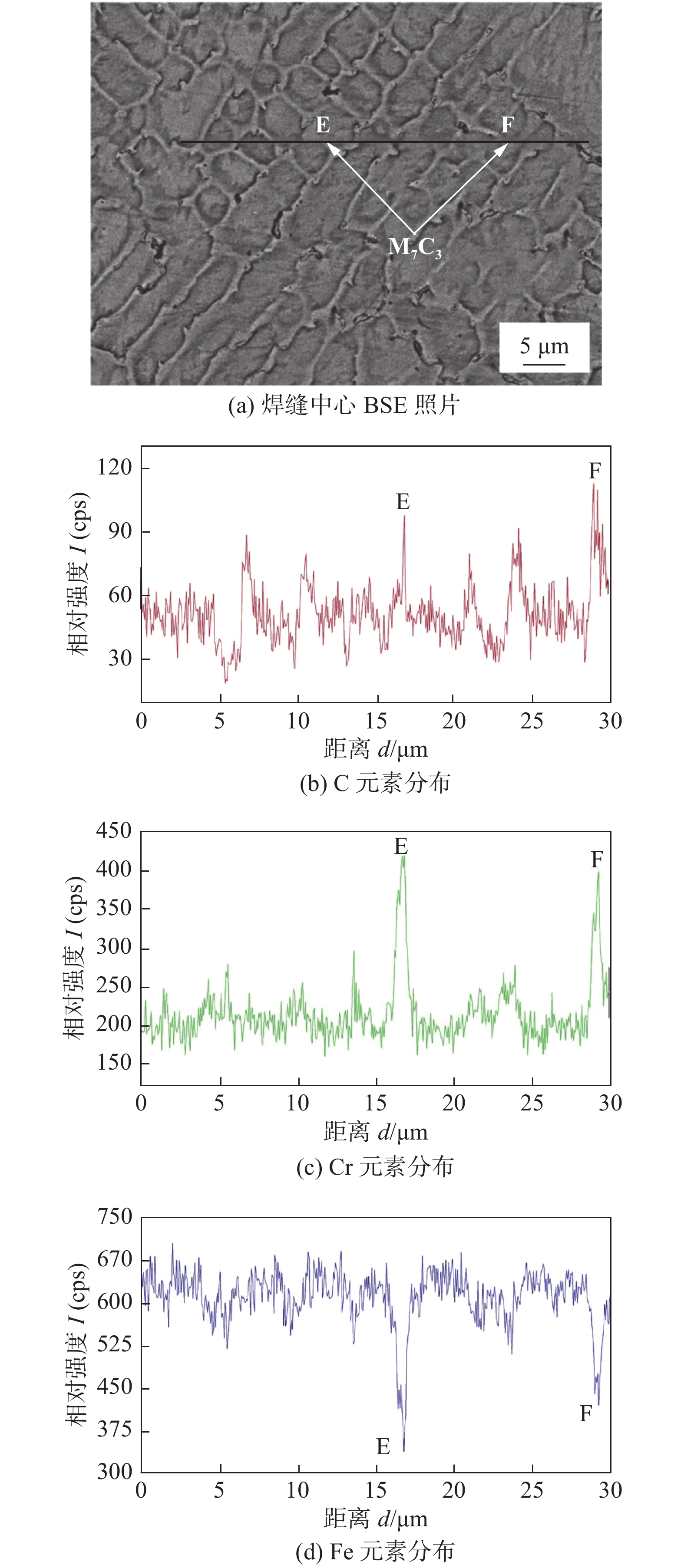
图4所示为焊缝中心组织EDS线分析试验结果. 其中,图4a是焊缝中心部位的背散射(BSE)照片,黑色线段表示EDS线分析位置,图4b,4c,4d分别为C,Cr,Fe元素线分布结果. 图4a中箭头所指的E,F处为条棒状析出物位置. 从图4a中可以看到焊缝部位为胞状树枝晶,其中晶界与晶内颜色深度有差异.
黑色线段为EDS线分析位置,由结果可知,C,Cr元素在晶界附近富集明显,而Fe元素在晶内较多. 同时在E,F所指条棒状析出物上,C,Cr元素富集更加明显,Fe元素含量大量减少. 结合XRD结果分析,认为该条棒状析出物为M7C3. 激光焊接过程中,高能的激光束照射金属,使金属熔化形成液态,当激光束远离焊缝位置时,焊缝金属开始凝固结晶. 在凝固过程中,当温度降低到结晶温度后,液相中开始形成晶核,并同时通过液固界面向液相中排出多余的溶质原子. 这样,先结晶的晶内溶质原子较少,而后结晶的晶界溶质原子较多[11],因此晶界部位存在较多的杂质原子. 此外晶界处也是晶格缺陷较多的地方. Cr元素富集于胞状树枝晶的枝晶间为负偏析元素,而Fe元素富集于晶内为正偏析元素[12]. 在激光的作用下熔化凝固时,由于固态相变,该合金从面心立方的γ相转变为室温下的α相,由于γ相的溶碳量远大于α相,这样使得C元素排出晶内,同时Cr元素为强碳化物形成元素,它们在枝晶间偏析也会加剧C元素在枝晶间的聚集,因而在晶界部位更容易产生碳化物M7C3. 制备金相试样过程中,通常使用酸性溶液对试样进行腐蚀. 由于晶界部位为杂质元素及晶体缺陷富集区,较易腐蚀,而碳化物耐腐性高,不易腐蚀,因此可以在晶界部位观察到条、棒状析出相.
2.2.4 熔合区及热影响区组织形态
图5所示为焊缝两侧熔合区及热影响区组织形貌图,其中图5a为3Cr13侧组织形貌. 可以看到3Cr13侧的熔合线清晰,但熔合区与热影响区的差别较小难以区分. 图5b为图5a的局部区域放大图. 在图5b中可观察到熔合线附近的母材为淬火状态下的类针状马氏体组织. 图5c为VG10侧的组织形貌,其熔合线弯曲,同时可以看到熔合区与热影响区有明确的分界线,熔合区大小为30 µm左右,从图5c的局部放大图5d中可以看到熔合区中有非对流混合区,该区域为未充分与焊缝金属混合的母材,在该位置有块状、岛状组织嵌入母材[13],如A所指. 该组织上存在连片分布的片层状的共晶碳化物,碳化物形态如图5e所示.
2.2.5 焊接接头元素分布
图6所示为电子探针分析结果. 图6a是焊缝中部的宏观照片,红线表示EPMA线分析位置. 图6b,6c,6d图分别为C,Cr,Fe元素在红线位置的线分布结果. 从图中可以看出,C元素在熔合线附近聚集,含量有所增加. Cr元素的分布变化相对较平缓,但在VG10侧的熔合线附近母材位置有峰值出现. Fe元素含量从VG10侧向3Cr13侧呈逐渐增加的趋势,但分布相对平稳.
根据EPMA试验结果,C在焊缝两侧熔合线附近的母材部位发生了聚集,即发生了C迁移现象,在钢铁材料中,C在固相中的化学位高于在液相中的化学位[14],C元素易于从母材的熔合区向焊缝区扩散迁移,但由于激光焊接热量集中,热输入小、冷却速度快. 使得C元素从母材往液态焊缝中扩散时只在熔合线附近聚集,而不能扩散到更远处的焊缝中去. 因此C元素只在熔合线附近的母材位置含量增加.
液态焊缝的化学成分为两种母材成分的混合,由于母材VG10中含有更多的合金元素, 混合后的焊缝成分相对于3Cr13母材拥有更多的合金元素和更高的含量. 而Mo,Mn,V等合金元素可促使C元素的迁移[12]. 因此在熔合区3Cr13侧的C元素聚集被加强. 在图5b中观察到在3Cr13侧的熔合线附近的母材为类针状马氏体组织,在焊接过程中熔合线附近区域的母材温度较高,在该部分的金属相当于经历了淬火处理. 3Cr13马氏体不锈钢在淬火后一般为板条马氏体,但由于C元素在该位置的扩散、迁移,使得板条马氏体转变为高碳的类针状马氏体. 在焊接过程中熔池内部为湍流区,而边界区域为层流区,在熔池流动方式以及填充金属与母材成分差异造成了在非对流混合区有嵌入母材的块状、岛状组织的产生. 在该组织上有片层状的共晶碳化物生成,激光焊接熔池较小,在非对流混合区形成后,在较短时间内将凝固结晶. 在凝固过程中,先结晶的γ相通过固液界面向液相排出多余的合金元素,由于凝固时间较短,因此合金元素不能扩散均匀. 形成共晶碳化物后,前段液相部分因为合金元素消耗,成分达到γ相,又开始析出γ相,这样重复结晶过程直到液相完全转化完全固相. 而在随后的冷却过程中γ相转变为α相,最后形成了片层状的碳化物[15]. VG10侧母材的C含量有迁移、聚集现象. 使得该部分的C元素含量进一步的增加,进而导致了共晶碳化物的形核数量增加,进一步的促进了共晶碳化物的形成[16]. 结合前面软件模拟结果及焊缝XRD分析,该共晶碳化物为M7C3. 此外VG10侧共晶碳化的出现使得Cr元素在该区域的分布有波动.
2.3 焊接接头硬度分布
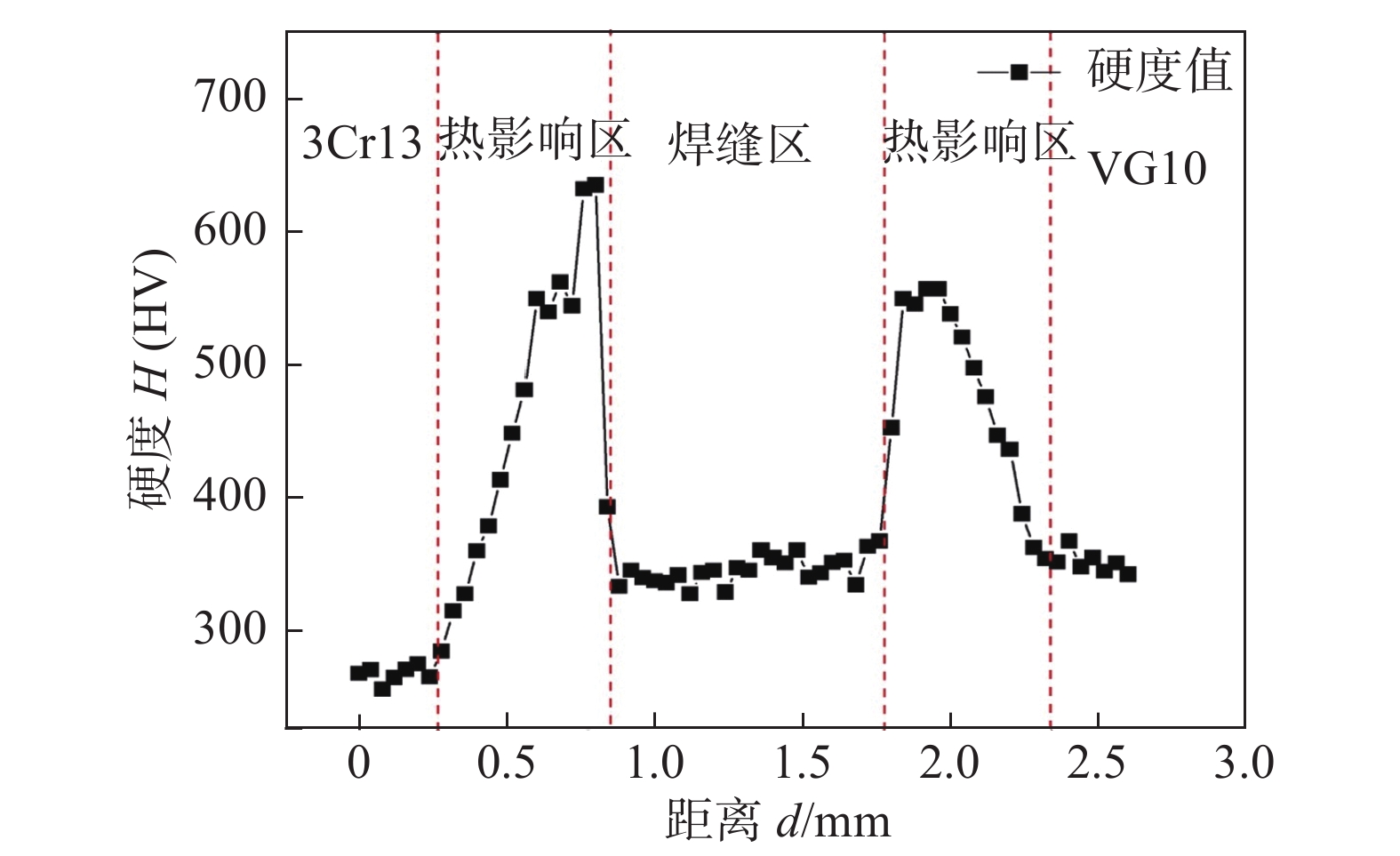
图7所示为焊接接头的硬度分布. 焊缝区硬度变化较小、分布均匀约为355 HV;3Cr13侧及VG10侧热影响区硬度值陡增,并且靠近熔合线附近硬度值最大,其中3Cr13侧为635 HV,VG10侧为553 HV. VG10母材区域硬度值略微高于3Cr13母材.
VG10母材中的含碳量更高,母材硬度高于3Cr13. 而焊缝区为两种母材成分的混合,含碳量应介于两种母材之间,但由于焊缝金属冷却较快,使得整个焊缝的晶粒较为细小,细晶强化的作用使得其硬度有部分提升,焊缝区域的硬度与母材VG10相差较小. 在熔合线附近的母材部分,硬度值有明显的提升,同时在熔合区附近硬度值最高. 在前文中通过组织分析,3Cr13侧熔合线附近母材部分有类针状马氏体出现,该部位的硬度值最大. 而VG10侧的熔合区出现共晶碳化物因此该部分的硬度也有明显的升高. 两侧的热影响区随着与焊缝距离的增加而逐步的减小,这是因为热影响区与焊缝中心的距离不同受到的温度的影响不同,使得热影响区晶粒大小发生变化. 同时,在温度的影响下,C在α相中的固溶量不同,以及析出碳化物的数量不相同,因此,在显微硬度的数值上也有不同的变化.
3. 结论
(1) 通过JMATPro软件模拟了3Cr13及VG10的平衡相与温度的关系图,平衡条件下VG10,3Cr13凝固终了,其基体相为α相,同时有碳化物M23C6存在,此外VG10中还有少量的M(C/N).
(2) 分析焊缝组织发现,焊缝晶粒有元素偏析,且在晶界部位有条棒状的析出物,通过XRD及EDS试验,确定该析出物为M7C3.
(3) 焊缝两侧熔合线附近母材处有C迁移现象,由于C元素的迁移使得该位置处C含量上升,3Cr13侧出现类针状马氏体组织,VG10侧存在非对流混合区,并且在该部分区域有块状、岛状组织出现,且在该部分组织上有共晶碳化物M7C3形成.
(4) 通过硬度试验发现熔合线附近的母材硬度上升较大,同时热影响区硬度随着与焊缝中心的距离的增加而逐渐减小. VG10母材侧的硬度高于3Cr13母材的.
-
表 1 3Cr13的化学成分(质量分数,%)
Table 1 Chemical composition of 3Cr13
C Si Mn Cr Ni S P Fe 0.29 0.37 0.37 13.8 0.12 0.01 0.02 余量 表 2 VG10的化学成分(质量分数,%)
Table 2 Chemical composition of VG10
C Si Co Mo Mn V Cr Ni S P Fe 0.98 0.41 1.1 0.98 0.41 0.28 14.92 0.32 < 0.01 0.02 余量 表 3 激光焊接工艺参数
Table 3 Parameters of laser welding
激光功率P/W 焊接速度v/(mm·s−1) 离焦量△f/mm 保护气流量Q/(L·min−1) 摆动频率f/Hz 摆动幅度A/mm 3 750 43 + 2 20 200 0.3 -
[1] Mittal R, Sidhu B S. Microstructures and mechanical properties of dissimilar T91/347H steel weldments[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2015, 220: 76 − 86. doi: 10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2015.01.008
[2] 王瑞, 石玗, 李广, 等. 镍对铜/不锈钢GTAW接头导电性及腐蚀性能的影响[J]. 焊接学报, 2019, 40(12): 53 − 58. Wang Rui, Shi Yu, Li Guang, et al. Effect of nickel on conductivity and corrosion of copper/stainless steel GTAW joints[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2019, 40(12): 53 − 58.
[3] Liu Liming, Zhou Yanbin. Mechanism analysis of free formation of backing weld by the pulsed MAG-TIG double arc tandem welding[J]. China Welding, 2019, 28(4): 8 − 15.
[4] Liu G L, Yang S W, Han W T, et al. Microstructural evolution of dissimilar welded joints between reduced-activation ferritic-martensitic steel and 316L stainless steel during the post weld heat treatment[J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2018, 722: 182 − 196. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2018.03.035
[5] 刘桐, 杨立军, 邱文聪, 等. 304不锈钢激光深熔焊元素蒸发及焊缝合金含量变化[J]. 焊接学报, 2018, 39(2): 8 − 12. Liu Tong, Yang Lijun, Qiu Wencong, et al. Vaporization and composition change of 304 stainless steel during keyhole mode laser welding[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2018, 39(2): 8 − 12.
[6] 母晓红, 牛旭, 惠文. 激光焊的原理及其应用研究[J]. 科技创新导报, 2009(8): 5 − 6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-098X.2009.08.004 Mu Xiaohong, Niu Xu, Hui Wen. Principle and application of laser welding[J]. Science and Technology Innovation Herald, 2009(8): 5 − 6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-098X.2009.08.004
[7] He Yannan, Song Qiang, Sun Kang, et al. Microstructure and properties of in-situ chromium carbide composite coating by laser cladding[J]. China Welding, 2018, 27(4): 10 − 17.
[8] 宗攀, 张覃轶, 孙伟, 等. 热处理工艺对大马士革VG10钢组织和性能的影响[J]. 金属热处理, 2018(11): 117 − 122. Zong Pan, Zhang Qinyi, Sun Wei, et al. Effect of heat treatment process on microstructure and mechanical properties of Damascus VG10 steel[J]. Heat treatment of metals, 2018(11): 117 − 122.
[9] 尹燕, 栗子林, 许广伟, 等. 3Cr13厨刀碟片激光同轴送粉熔覆层的显微硬度与组织[J]. 焊接学报, 2016, 37(10): 86 − 87. Yin Yan, Li Zilin, Xu Guangwei, et al. Microhardness and microstructure of laser cladding layer on 3Cr13 kitchen knife by disc laser coaxial powder[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2016, 37(10): 86 − 87.
[10] 徐仰涛, 沙岐振. 基于JMatPro软件对不同B含量下Co-8.8Al-9.8W合金析出相的热力学模拟计算[J]. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2016, 45(9): 2332 − 2336. Xu Yangtao, Sha Qizhen. Thermodynamic simulation calculation of Co-8.8A1-9.8W alloy with different B contents based on JMatPro software[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2016, 45(9): 2332 − 2336.
[11] 王鲁, 杨钢, 刘正东, 等. 基于Thermo-Calc和JMatPro模拟计算的新型镍基合金设计[J]. 材料热处理学报, 2017, 38(4): 193 − 199. Wang Lu, Yang Gang, Liu Zhengdong, et al. Design of a new Ni-base alloy based on simulated calculation on Thermo-Calc & JMatPro[J]. Transaction of Materials and Heat Treatment, 2017, 38(4): 193 − 199.
[12] 黄继华. 焊接冶金原理[M]. 北京: 机械工业出版社, 2015. Huang Jihua. Principle of welding metalluryy[M]. Beijing: China Machine Press, 2015.
[13] 魏翔云, 张玉生. 碳含量对Fe-30Ni-20Cr-6Mo铸造合金元素偏析和耐蚀性的影响[J]. 腐蚀科学与防护技术, 1996(3): 210 − 213. Wei Xiangyun, Zhang Yusheng. Effect of carbon content on element segregation and corrosion-resistance of cast alloy fe-30Ni-20Cr-6Mo[J]. Corrosion Science and Protection Technology, 1996(3): 210 − 213.
[14] 潘春旭. 异种钢及异种金属焊接显微结构特征及其转变机理[M]. 北京: 人民交通出版社, 2000. Pan Chunxu. Microstructure characteristics and transformation mechonism of dissimilar sreels and metals[M]. Beijing: China Communications Press, 2000.
[15] Wieczerzak K, Bala P, Stepien M, et al. Formation of eutectic carbides in Fe-Cr-Mo-C alloy during non-equilibrium crystallization[J]. Materials & Design, 2016, 94(3): 61 − 68.
[16] Chang C M, Lin C M, Hsieh C C, et al. Effect of carbon content on microstructural characteristics of the hypereutectic Fe-Cr-C claddings[J]. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 2009, 117(1): 257 − 261. doi: 10.1016/j.matchemphys.2009.05.052
-
期刊类型引用(2)
1. 栗振鑫,蔡创,余杰,陈梓琳,熊发帅,汤坪,陈辉. 激光摆动对TC4钛合金窄间隙焊接接头组织性能的影响. 中国激光. 2025(08): 77-86 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 郭克星. 铝合金激光焊接技术研究进展. 热处理. 2024(06): 1-7 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(2)



 下载:
下载: