Effect of weld thermal cycle on low temperature toughness of 09MnNiDR steel heat affected zone
-
摘要: 利用Gleeble-3800研究了焊接热循环对09MnNiDR钢焊接热影响区粗晶区(CGHAZ)和中间临界再热粗晶区(IRCGHAZ)低温韧性的影响. 结果表明,热输入为15 kJ/cm、层间温度为150 ℃时,CGHAZ组织形态为板条状马氏体+下贝氏体,下贝氏体的存在限制了马氏体的生长,提高了低温韧性,而IRCGHAZ继续保持了CGHAZ的组织. −70 ℃冲击试验中,IRCGHAZ相比于CGHAZ具有较好的低温冲击韧性,热输入为15 kJ/cm、层间温度为150 ℃时,冲击吸收能量最高为65 J. 根据热模拟结果,采用焊接热输入15 ~ 22 J/cm、层间温度为150 ℃的工艺参数对09MnNiDR钢进行焊接,−70 ℃冲击试验中热影响区冲击吸收能量值为101 J,冲击断口存在大量的等轴韧窝,具有较好的低温韧性;−70 ℃拉伸试验屈服强度为477 MPa、抗拉强度607 MPa、断后伸长率为28.5%,表现出较好的强度和塑性;硬度试验结果表明母材、焊缝和热影响区硬度依次增大,且没有软化现象.Abstract: The effect of welding heat cycle on low temperature toughness of the coarse-grained heat affected zone (CGHAZ) and inter-critically reheated coarse-grained heat affected zone (IRCGHAZ) of 09MnNiDR steel was studied by Gleeble-3800. The results show that when the heat input is 15 kJ/cm and the interpass temperature is 150 ℃, the microstructure of CGHAZ is lath martensite and lower bainite. The lower bainite restricts the growth of martensite and improves the low temperature toughness. While IRCGHAZ is continue to maintain the microstructure of CGHAZ. In the impact test at −70 ℃, IRCGHAZ has the better low-temperature impact toughness than CGHAZ. When the heat input is 15 kJ/cm and the interpass temperature is 150 ℃, the impact energy is the highest of 65 . According to the thermal simulation results, the 09MnNiDR steel was welded with the welding heat input of 15 ~22 J/cm and interpass temperature of 150 ℃, the impact energy of heat-affected zone is 101 J at −70 ℃, and the fracture morphology has a large number of isometric dimples, which has good low-temperature toughness. In the tensile test at −70 ℃, the yield strength is 477 MPa, the tensile strength is 607 MPa, and the elongation is 28.5%, showing the better strength and plasticity. Hardness test results show that the hardness of base metal, weld and heat affected zone increase successively, and there is no softening phenomenon.
-
Keywords:
- 09MnNiDR steel /
- thermal simulation /
- low-temperature toughness
-
0. 序言
近年来由于液化石油气(简称LPG)清洁环保、高能高效、成本经济等特点而备受各个行业的关注[1-2],对于贮存和运送LPG的低温储罐用量也逐年增加,LPG已成为道路运输部门能源组合的关键要素,关系着社会经济和环境效益.
09MnNiDR钢是国内目前−40 ~ −70 ℃工作环境中低温储罐制作的主要用钢,并以良好的低温韧性广泛应用于LPG储罐的建造中[3]. 由于受到制造工艺技术条件限制,仍会发生低温储罐焊接接头破坏事故,致使安全运行周期缩短. 为确保储罐安全可靠地运行,焊接接头需具有足够的低温韧性,因此准确评价焊接接头的低温韧性对保证结构的安全性至关重要[4]. 而焊接接头中,热影响区是性能最薄弱区域,对低温储罐的使用寿命起到重要的作用. 为了提高焊接热影响区低温韧性,获得强韧性较好的低碳马氏体和下贝氏体,通常采用焊前预热、控制热输入等措施[5].
由于HAZ的宽度一般只有几毫米,并且包括性能和组织不同的区域,因此对HAZ这些特定区域进行力学性能试验或焊接性试验是比较困难的[6]. 为使HAZ各区域放大,能够像大尺寸试样进行组织观察和性能试验,通常采用焊接热模拟技术.
采用焊接热模拟技术对09MnNiDR钢进行焊接热影响区模拟,利用焊接热模拟技术对热影响区“放大化”[7],进而分析经历热循环后,焊接热影响区组织和性能可能发生的变化及出现的问题[8],为制定合理的焊接工艺提供理论依据,指导实际生产.
1. 试验方法
试验材料为09MnNiDR钢,供货状态为正火,显微组织为铁素体+珠光体,如图1所示,化学成分及力学性能分别见表1和表2.
表 1 09MnNiDR的化学成分(质量分数,%)Table 1. Chemical composition of 09MnNiDR类别 C Si Mn S P Ni Nb Al 标准值 ≤ 0.12 0.15 ~ 0.5 1.2 ~ 1.6 ≤ 0.012 ≤ 0.025 0.3 ~ 0.8 ≤ 0.04 ≥ 0.02 实测值 0.09 0.39 1.42 0.009 0.012 0.46 0.012 0.048 表 2 09MnNiDR的力学性能Table 2. Mechanical properties of 09MnNiDR类别 热处理状态 屈服强度 Rp0.2/MPa 抗拉强度 Rm/MPa 断后伸长率 A(%) 冲击吸收能量 AKV/J(−70 ℃) 标准值 正火 ≥ 280 430 ~ 560 ≥ 23 ≥ 34 实测值 395 510 34.5 112 热模拟试验设备为Gleeble- 3800,热模拟试件尺寸为80 mm × 11 mm × 11 mm. 焊接热循环参数如表3所示,首先采用1 350 ℃焊接热循环峰值温度制备热影响区粗晶区(CGHAZ),随后采用750 ℃作为二次焊接热循环峰值温度对粗晶区进行二次热模拟,制备中间临界再热粗晶区(IRCGHAZ),热输入分别为15,22和30 kJ/cm,层间温度分别为100,125和150 ℃. 将热模拟后的试样加工成尺寸为55 mm × 10 mm × 10 mm的冲击标准试样,试样缺口轴线为板厚方向,进行低温冲击韧性(−70 ℃)试验,并分析其显微组织.
表 3 09MnNiDR钢热模拟试验参数Table 3. Thermal simulation parameters of 09MnNiDR steel编号 层间温度Tc/℃ 热输入E/(kJ·cm−1) 峰值温度Tm/℃ CGHAZ IRCGHAZ 1 100 15 1 350 1 350+750 2 100 30 3 150 15 4 150 30 5 125 22 以焊接热模拟为依据,进行实际焊接. 板材为300 mm × 200 mm × 25 mm规格的试板,焊前清理. 焊条选用低氢钠型W707Ni焊条,其化学成分见表4. 试验焊接参数见表5. 采用X形坡口(带钝边),坡口形式及焊接顺序如图2所示. 首先用断弧焊进行打底,其次利用小焊接热输入并且应用多层多道焊接方法,层间温度要控制在150 ℃左右. 考虑安全可靠性以及易操作两方面,设定其热处理规范为600 ℃ ± 20 ℃较为合理,如图3所示. 分别对焊接接头进行显微组织分析、−70 ℃低温冲击试验和拉伸试验以及焊接接头硬度试验.
表 4 W707Ni焊条熔敷金属化学成分(质量分数,%)Table 4. Chemical composition of W707Ni类别 C Si Mn S P Ni 成分范围 ≤ 0.12 ≤ 0.60 ≤ 1.25 ≤ 0.035 ≤ 0.035 2.00 ~ 2.75 实测值 0.048 0.26 0.86 0.012 0.008 2.56 表 5 09MnNiDR钢焊接参数Table 5. Welding parameters of 09MnNiDR steel道次 焊条直径d/mm 电流I/A 电压U/V 焊接速度 v/(cm·min−1) 焊接热输入 Q/(kJ·cm−1) 1 ~ 2 3.2 127 24 7.5 19.5 3 ~ 6 103 22 7 15.5 7 ~ 12 102 23 7 16.1 2. 试验结果及分析
2.1 热模拟组织与性能分析
2.1.1 CGHAZ的组织变化
经历单道次热循环模拟后,晶粒出现严重粗化现象,随着热输入E和层间温度Tc的改变,CGHAZ的组织形貌也发生相应的改变,见图4.
在相同层间温度下,当热输入E = 30 kJ/cm时,CGHAZ的组织形态会出现板条马氏体+上贝氏体的组合. 在连续冷却条件下,上贝氏体的增加导致低温韧性下降;当热输入为E = 22 kJ/cm时,显微组织为板条状马氏体+针状铁素体. 由于连锁结构的针状铁素体能够阻止裂纹的扩展,因此低温韧性提高;当热输入E = 15 kJ/cm时,其组织形态为板条状马氏体+下贝氏体. 下贝氏体的存在分割了原奥氏体晶粒,致使板条状马氏体有了更多的形核位置,限制了其自身的生长,提高了低温冲击韧性[9]. 因此,推荐热输入E范围15 ~ 22 kJ/cm,且尽量选择小的热输入.
热输入相同,层间温度不同,热模拟后CGHAZ的组织形态也不同. 当层间温度Tc = 100 ℃时,显微组织以M-A组元+上贝氏体为主,焊接热影响区有脆化倾向;当层间温度Tc = 125 ℃时,显微组织主要是板条状马氏体+针状铁素体;层间温度Tc = 150 ℃时,主要的组织是下贝氏体+板条马氏体,有利于提高低温韧性. 因此,在焊接09MnNiDR钢时要推荐的层间温度范围为125 ~ 150 ℃.
2.1.2 IRCGHAZ的组织变化
由于CGHAZ的组织由板条马氏体或贝氏体等非平衡相组成,而这些组织大多由奥氏体{111}1面产生切变而生成,并保持着母相的K-S的位相关系. 当经历二次热循环峰值温度时,为了降低相变阻力,奥氏体形核与结晶学有序组织在密排面和密排方向上保持平行. 这种有取向性形核的结果,造成了组织遗传现象[10]. 因此,IRCGHAZ继续保持了CGHAZ的组织.
2.1.3 性能变化
在一定热循环参数下,CGHAZ和IRCGHAZ的低温冲击吸收能量值有一定的差距,且IRCGHAZ的冲击吸收能量值高于CGHAZ的冲击吸收能量值,如表6所示. 当层间温度一定时,热输入越小冲击吸收能量值高,低温韧性显著提高. 而热输入相同时,层间温度越高,韧性越好. 主要是因为层间温度较高时,自回火作用增强,热影响区的硬度下降,而韧性得到了提高. 热输入增加,组织的晶粒尺寸增大,导致低温韧性降低. 而IRCGHAZ是经过二次热模拟后得到的,此过程相当于实际中的多层焊接. 当二次热循环峰值温度介于AC1 ~ AC3时,CGHAZ组织发生部分奥氏体化,使IRCGHAZ晶粒得到细化,冲击韧性提高. 因此,在实际焊接中推荐采用小的热输入、高的层间温度以及多层焊接.
表 6 热影响区(−70 ℃)冲击吸收能量Table 6. Impact energy of HAZ(−70 ℃)热输入E/(kJ·cm−1) 层间温度Tc/℃ 冲击吸收能量AKV/J CGHAZ ICCGHAZ 15 100 32.5 35.1 30 100 27.9 32.7 15 150 50.4 65.1 30 150 34.7 39.2 22 125 38.9 43.4 硬度试验结果表明(表7),层间温度不变,焊接热输入越小,热影响区的硬度值越低;热输入相同时,层间温度越高,热影响区的硬度值越高. 由于焊接热循环引起的组织强化,热影响区的硬度高于母材硬度. CGHAZ和IRCGHAZ的硬度基本相近,这是因为CGHAZ的组织主要以板条马氏体和贝氏体为主. 而IRCGHAZ只是小部分发生相变,晶粒大小和化学成分不均匀,由于组织遗传现象其组织基本不变. 由此得知,09MnNiDR钢焊接热影响区不会产生软化现象. 在保证低温韧性的前提下,宜采用较高的层间温度和较小的热输入进行焊接.
表 7 热影响区硬度值Table 7. Hardness of HAZ热输入E/(kJ·cm−1) 层间温度Tc/℃ 硬度H(HV) CGHAZ IRCGHAZ 15 100 192.9 187.4 30 100 223.9 214.7 15 150 207.4 197.0 30 150 230.5 223.2 22 125 217.6 198.9 2.2 焊接热影响组织与性能分析
2.2.1 显微组织
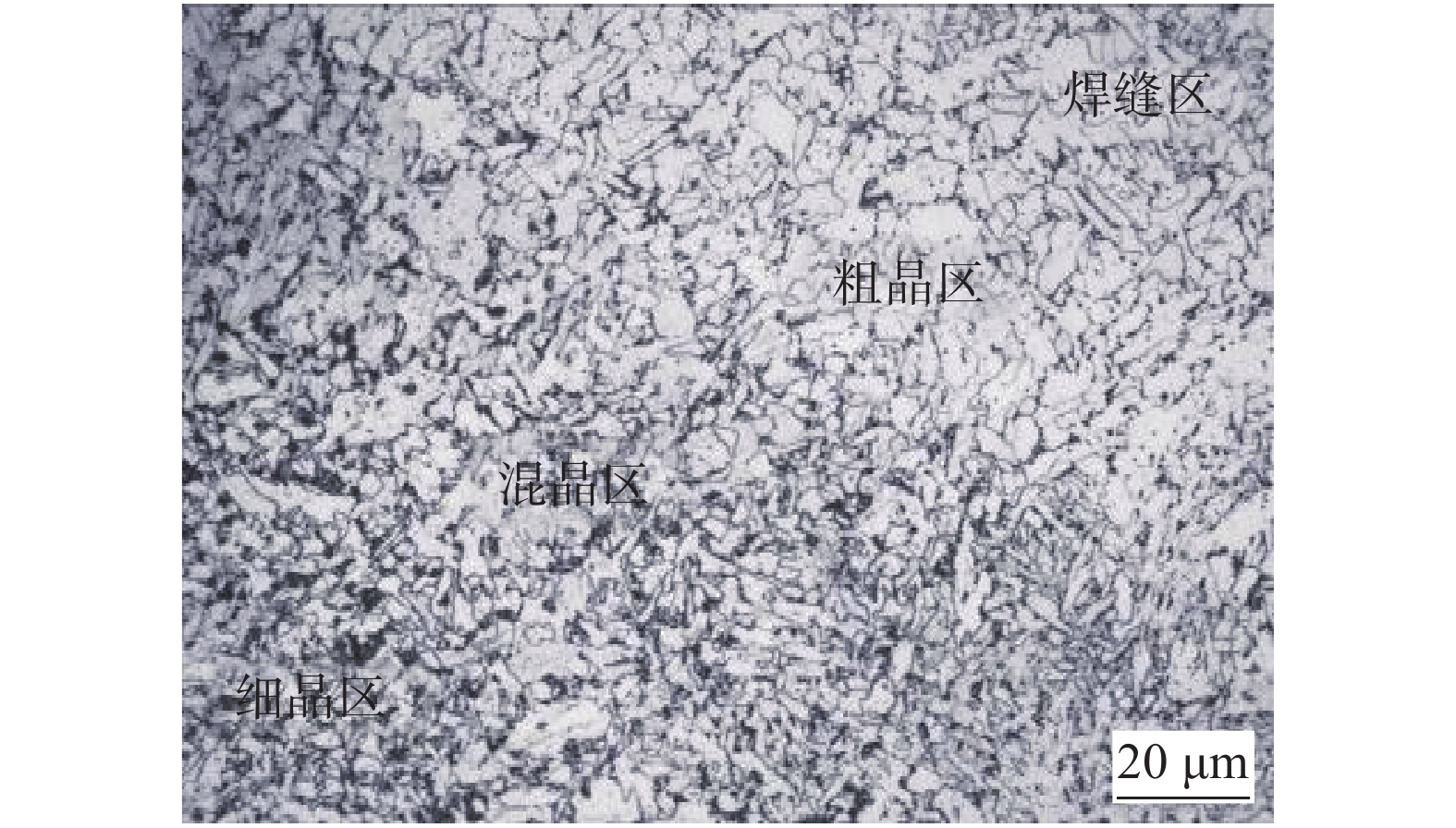
焊接热影响区组织如图5所示,其中细晶区组织为铁素体+珠光体,因为该区域被加热到Ac3以上,组织细小均匀,故其综合力学性能较好,是接头中性能最好的区域;混晶区室温组织为条状铁素体+针状铁素体+珠光体+块状铁素体,低温韧性低于细晶区但优于粗晶区;而粗晶区组织以铁素体+珠光体+粒状贝氏体为主. 此区晶粒粗大,联生结晶现象明显,晶粒生长形式呈长柱状. 粒状贝氏体硬度高,在载荷作用,相邻铁素体薄层中引发裂纹而使韧性下降. 所以粗晶区是单道焊热循环热影响区中性能薄弱区域. 采用的多层多道焊由于热输入不同可使焊缝晶粒变小,即减小了柱状晶长成的范围,达到晶粒细化的目的,增强了焊缝低温韧性.
2.2.2 焊接接头性能分析
焊缝区和热影响区在−70 ℃的低温冲击试验中冲击吸收能量平均值分别为176 和101 J(远高于国家标准规定的34 J),断面纤维率分别为52%和51%,在−70 ℃明显表现为韧性.
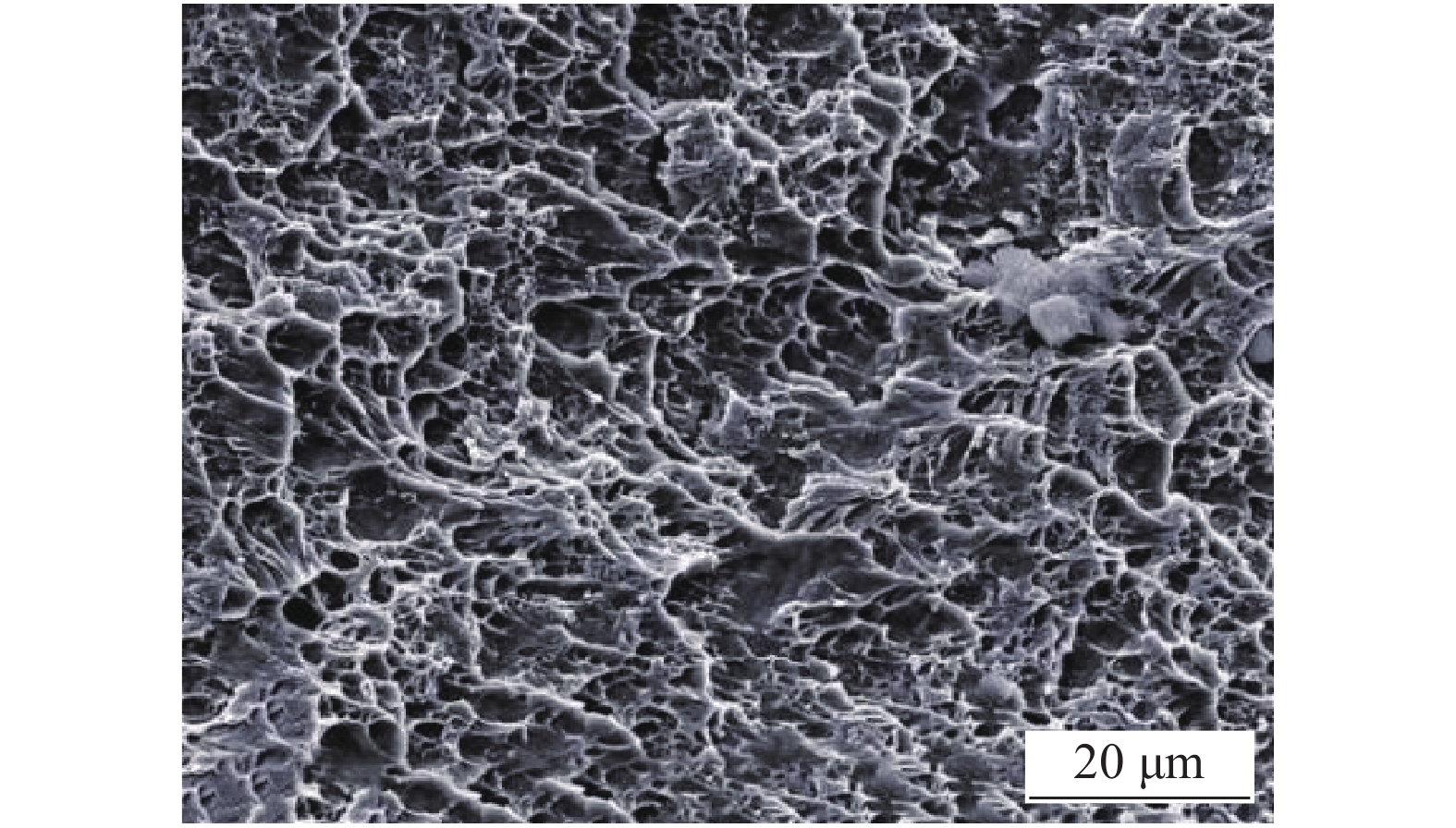
图6为焊缝区冲击试样在−70 ℃下的SEM形貌,从图中可以观察到断口形貌由撕裂韧窝和等轴韧窝组成,具有一定的韧性. 热影响区冲击断口可观察到大量的撕裂韧窝及少量的等轴韧窝,表现出解理断裂的特征,冲击韧性略低于焊缝区,如图7所示.
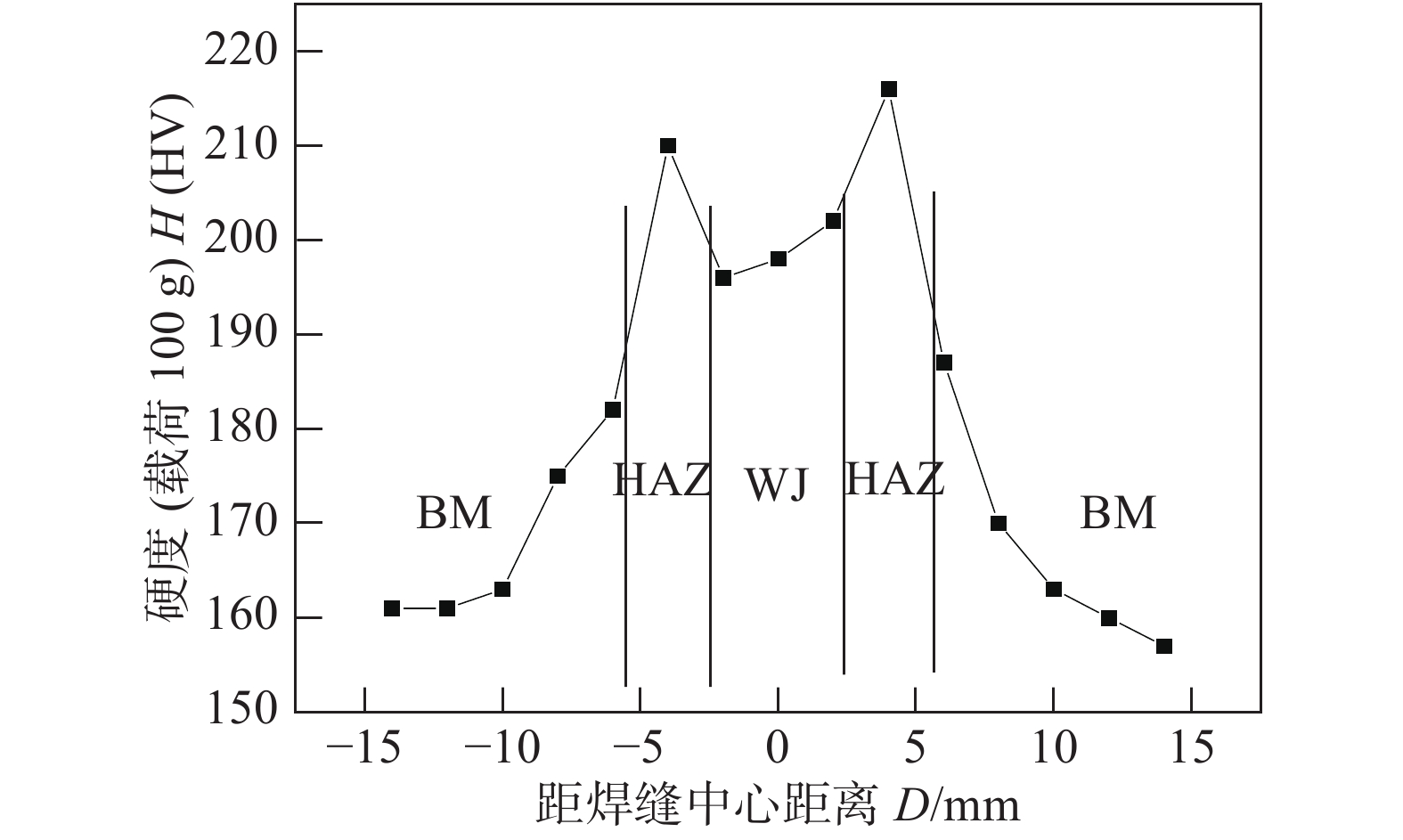
焊接接头硬度试验结果如图8所示,硬度值与距焊缝中心的位置呈“M”形. 母材、焊缝、热影响区的硬度值依次增大. 主要是由于热影响区组织中存在的粒状贝氏体具有着较高的硬度. 而焊缝显微组织中有侧板条状马氏体,不仅具有较高的强度,还具有良好的韧性.
焊接接头在−70 ℃低温拉伸试验结果见表8,09MnNiDR钢的抗拉强度、屈服强度和断后伸长率均高于表2中规定的标准值,且均断裂在母材处. 焊接接头的塑性和韧性优于母材,采用焊接工艺合理.
表 8 09MnNiDR钢(−70 ℃)拉伸试验结果Table 8. Result of tensile test for 09MnNiDR steel(−70 ℃)抗拉强度平均值Rm/MPa 屈服强度平均值Rp0.2/MPa 断后伸长率平均值A(%) 607 477 28.5 3. 结论
(1)经过不同焊接热循环参数焊接热模拟后CGHAZ组织类型主要为针状铁素体、贝氏体、板条状马氏体和珠光体. 由于组织遗传现象,IRCGHAZ继续保持了CGHAZ的组织. 采用焊接热输入15 ~ 22 J/cm,层间温度125 ~ 150 ℃,热影响区获得良好的低温韧性. IRCGHAZ区的低温韧性优于CGHAZ区的低温韧性,而硬度略低于CGHAZ区,但不会发生软化现象.
(2) 09MnNiDR钢采用焊接热输入15 ~ 22 J/cm、层间温度为150 ℃的工艺参数进行焊接,焊后焊缝的显微组织以铁素体为主,热影响区粗晶区为块状铁素体+珠光体+粒状贝氏体;−70 ℃低温冲击试验,热影响区的冲击韧性略低于焊缝的冲击韧性,但热影响的冲击吸收能量值远高于国家标准规定的34 J;−70 ℃低温拉伸试验结果表明焊接接头强度、塑性和韧性优于母材;硬度值与距焊缝中心的位置呈“M”形. 热影响区、焊缝、母材的硬度值依次增大.
-
表 1 09MnNiDR的化学成分(质量分数,%)
Table 1 Chemical composition of 09MnNiDR
类别 C Si Mn S P Ni Nb Al 标准值 ≤ 0.12 0.15 ~ 0.5 1.2 ~ 1.6 ≤ 0.012 ≤ 0.025 0.3 ~ 0.8 ≤ 0.04 ≥ 0.02 实测值 0.09 0.39 1.42 0.009 0.012 0.46 0.012 0.048 表 2 09MnNiDR的力学性能
Table 2 Mechanical properties of 09MnNiDR
类别 热处理状态 屈服强度 Rp0.2/MPa 抗拉强度 Rm/MPa 断后伸长率 A(%) 冲击吸收能量 AKV/J(−70 ℃) 标准值 正火 ≥ 280 430 ~ 560 ≥ 23 ≥ 34 实测值 395 510 34.5 112 表 3 09MnNiDR钢热模拟试验参数
Table 3 Thermal simulation parameters of 09MnNiDR steel
编号 层间温度Tc/℃ 热输入E/(kJ·cm−1) 峰值温度Tm/℃ CGHAZ IRCGHAZ 1 100 15 1 350 1 350+750 2 100 30 3 150 15 4 150 30 5 125 22 表 4 W707Ni焊条熔敷金属化学成分(质量分数,%)
Table 4 Chemical composition of W707Ni
类别 C Si Mn S P Ni 成分范围 ≤ 0.12 ≤ 0.60 ≤ 1.25 ≤ 0.035 ≤ 0.035 2.00 ~ 2.75 实测值 0.048 0.26 0.86 0.012 0.008 2.56 表 5 09MnNiDR钢焊接参数
Table 5 Welding parameters of 09MnNiDR steel
道次 焊条直径d/mm 电流I/A 电压U/V 焊接速度 v/(cm·min−1) 焊接热输入 Q/(kJ·cm−1) 1 ~ 2 3.2 127 24 7.5 19.5 3 ~ 6 103 22 7 15.5 7 ~ 12 102 23 7 16.1 表 6 热影响区(−70 ℃)冲击吸收能量
Table 6 Impact energy of HAZ(−70 ℃)
热输入E/(kJ·cm−1) 层间温度Tc/℃ 冲击吸收能量AKV/J CGHAZ ICCGHAZ 15 100 32.5 35.1 30 100 27.9 32.7 15 150 50.4 65.1 30 150 34.7 39.2 22 125 38.9 43.4 表 7 热影响区硬度值
Table 7 Hardness of HAZ
热输入E/(kJ·cm−1) 层间温度Tc/℃ 硬度H(HV) CGHAZ IRCGHAZ 15 100 192.9 187.4 30 100 223.9 214.7 15 150 207.4 197.0 30 150 230.5 223.2 22 125 217.6 198.9 表 8 09MnNiDR钢(−70 ℃)拉伸试验结果
Table 8 Result of tensile test for 09MnNiDR steel(−70 ℃)
抗拉强度平均值Rm/MPa 屈服强度平均值Rp0.2/MPa 断后伸长率平均值A(%) 607 477 28.5 -
[1] Laurencas Raslavičius, Artūras Keršys, Saulius Mockus, et al. Liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) as a medium-term option in the transition to sustainable fuels and transport[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2014, 32: 513 − 525. doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2014.01.052
[2] Fabbri G, Serra F, Paschero M, et al. Development of an innovative LPG system for ICE and extended range electric vehicles[C]//IEEE International Symposium on Industrial Electronics. New York: IEEE, 2013:1-6.
[3] 胡昕明, 高强, 乔馨, 等. 正火温度对09MnNiDR钢组织性能的影响[J]. 钢铁, 2011, 46(3): 71 − 74. Hu Xinming, Gao Qiang, Qiao Xin, et al. Effect of normalization temperature on microinstructure and mechanical properrties of 09MnNiDR plate steel[J]. Iron and Steel, 2011, 46(3): 71 − 74.
[4] 邓彩艳, 牛亚如, 王东坡, 等. 9Ni钢T&T焊接工艺低温韧性[J]. 焊接学报, 2018, 39(1): 109 − 113. Deng Caiyan, Niu Yaru, Wang Dongpo, et al. Low-temperature fracture toughness of welded joints for TOP-TIG welding on 9Ni steel[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2018, 39(1): 109 − 113.
[5] 刘璐, 王加友, 李大用, 等. 10Ni5CrMoV钢错位同步双面双弧焊接接头抗低温脆断性能[J]. 焊接学报, 2016, 37(8): 109 − 113. Liu Lu, Wang Jiayou, Li Dayong, et al. Low temperature brittle fracture resistance of asymmetrical synchronous double-sided arc jiont of 10Ni5CrMoV steel[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2016, 37(8): 109 − 113.
[6] 丁连征, 王锴, 孟庆森. SA38Gr.B钢焊接热影响区组织及性能的热模拟试验[J]. 焊接学报, 2014, 35(8): 91 − 94. Ding Lianzheng, Wang Kai, Meng Qingsen. Weldablity research on the the SA38Gr.B steel[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2014, 35(8): 91 − 94.
[7] 王西霞, 曲锦波, 杨汉. 09MnNiDR钢焊接临界粗晶区冲击脆断行为及焊后热处理工艺[J]. 钢铁研究学报, 2014, 26(4): 46 − 52. Wang Xixia, Qu Jinbo, Yang Han. Impact fracture behavior and post-welding heat treatment process of the intercritically reheated coarse-grained heat-affected zone of 09MnNiDR steel[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, 2014, 26(4): 46 − 52.
[8] Chen Jie, Zhan Xiaohong, Xia Ling, et al. Quantitative research on the heat affected zone of weave bead welding for Invar alloy[J]. China Welding, 2017, 26(2): 18 − 22.
[9] 严铿, 叶逢雨, 刘炜. 焊接热输入对F550Z钢焊接接头低温韧性的影响[J]. 焊接学报, 2014, 35(3): 93 − 96. Yan Keng, Ye Fengyu, Liu Wei. Effect of heat inputs on low temper- ature toughness of F550Z steel welding joints[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2014, 35(3): 93 − 96.
[10] 武强. 07MnNiCrMoVDR钢焊接热影响区性能的模拟研究[D]. 天津: 天津大学, 2007. -
期刊类型引用(4)
1. 朱梓坤,韩阳,张舟,张义,周龙早. Q690D低合金高强钢模拟焊接热影响区的组织和性能. 焊接. 2022(01): 26-33+40 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 朱梓坤,韩阳,张舟,张义,周龙早. Q690D低合金高强钢模拟焊接热影响区的组织和性能. 机械制造文摘(焊接分册). 2022(03): 12-19+36 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 李金梅,杨兆庆,梁小武,张建晓,雷万庆,曹睿. 热输入对09MnNiDR钢焊接热影响区粗晶区组织和韧性的影响. 机械工程材料. 2021(12): 72-77 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 徐鹏飞,赵作鹏,程红霞,肖福仁. X80管线钢焊接热模拟热影响区疲劳裂纹扩展行为的分析及预测. 金属热处理. 2020(12): 184-188 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(3)




 下载:
下载: