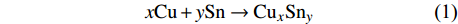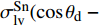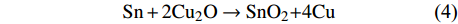Wetting behavior of Cu6Sn5 IMC by molten Sn
-
摘要: 利用改良座滴法研究了高真空条件下熔融纯Sn在350 ~ 450 ℃下分别与Cu6Sn5和T2纯铜的润湿行为. 结果表明,表面镀金的金属间化合物基板在各试验温度下的润湿性均优于纯铜基板;金属基板表面氧化膜对润湿性的影响不容忽视;离子溅射后表面形成的金膜可以作为一种改善润湿性及控制界面IMC厚度的有效方法;润湿性改善的机制为Sn与氧化膜的化学反应,界面析出IMC或者IMC的溶解过程并非限制铺展的主要因素;铺展过程表现出线性铺展规律,可用反应产物控制模型对其进行描述,计算得到Sn/Cu6Sn5和Sn/Cu两体系的铺展激活能分别为20.469 kJ/mol和22.270 kJ/mol.Abstract: Wetting behavior between the molten Sn and Cu6Sn5 and Cu under the temperature 350 ~ 450 ℃ was studied using the modified sessile drop method in the high vacuum. The results show that the IMCs substrates coated with a thin Au film have the better wettability than that of Sn/Cu system under the tested temperatures. The oxide film on the surface of metallic substrate is the key factor for wetting process. The thin passivation Au film on surface after ion-sputtering can be an effective method to improve the wettability and control the IMC thickness at interface. The mechanism of wettability improvement is the reaction between Sn and the oxide film. The precipitated IMC at interface or the melt process of IMC is not the main factor for spreading. All spreading dynamics show the near-linear variation, which can be described by the reaction-limited spreading model. The calculated wetting activation energies are 20.469 kJ/mol and 22.270 kJ/mol for Sn/Cu6Sn5 and Sn/Cu, respectively.
-
Keywords:
- intermetallic compounds(IMCs) /
- wettability /
- soldering
-
0. 序言
在电子封装领域,鉴于SnPb钎料中Pb对人体及环境的危害性,无铅钎料一直被倡导替代含铅钎料. 自2006年RoHS颁布以来,市场上流行各种无铅锡基钎料. 虽然无铅锡基钎料强度和抗蠕变性能优于传统Sn-Pb共晶钎料[1-3],但润湿性不足导致其使用条件较为苛刻. 故对于钎料的推广使用而言,如何改善润湿性首先要了解其相应的润湿机制[4-6].
Sn-Cu是典型的反应润湿体系,在采用Sn基钎料钎焊铜件的过程中,界面发生化学反应的同时常常伴有界面产物(Cu6Sn5,Cu3Sn IMCs)的析出. 其中IMCs的析出促进润湿的作用显而易见,然而体系最终的润湿性能否参照反应润湿控制(RPC)模型[7],即反应产物决定最终润湿性,还不得而知. Wedi等人[8]研究了SnPb/Cu体系的反应润湿,通过调控Pb的含量,来研究反应产物IMC对润湿性的影响,其认为一旦系统达到润湿平衡,即便是反应产物继续增加,接触角恒为定值,不再变化. 这似乎符合RPC模型的规律,然而即便在同样的润湿体系中存在相同的界面反应产物,被报道的接触角仍大相径庭[9]. 也曾有学者采用润湿平衡法研究了Sn基钎料与Sn-Cu IMCs的润湿行为,但鉴于此方法不能保证较好的真空状态且往往需要配合使用钎剂,不同活性强度的钎剂造成润湿性数据的差异显著,例如Wang等人[10]报道富锡钎料与Cu和Cu6Sn5/Cu3Sn/Cu展现出相接近的润湿时间,而文献[11]报道纯锡与Cu6Sn5不润湿. 综上,在金属与金属的润湿体系中,界面析出的IMC与润湿性的耦合关系仍不明确.
通过选取Sn/Cu和Sn/Cu6Sn5润湿行为与界面微观结构为主要研究对象,探究界面IMC对润湿性的作用,并揭示其中的润湿机制. 研究结果有望加深对钎焊过程中基本物理现象的认识.
1. 试验方法
试验所用的材料为99.99%的纯锡和尺寸为20 mm × 20 mm × 1 mm的T2纯Cu. IMC基板通过热浸镀的方法获得. 具体工艺为在400 ℃、高真空的环境下,将T2铜板浸泡于熔融的Sn液中浸镀2 h,并在300 ℃下保温约336 h后,机械打磨去除浸镀后基板表面的残存锡,再用4%的硝酸酒精溶液进行腐蚀,进一步去除IMC层上残留的锡. 所制得的IMC基板经表面抛光后,采用离子溅射仪(HM-ETD-2000C,中国)在真空下条件下镀金. 基板的表面状态采用X射线光电子能谱仪(XPS, Thermo ESCALAB 250, USA)进行表征.
润湿试验在高真空(~ 10−4 Pa)环境中进行. 当润湿温度、真空度稳定后,由外部磁力推进杆将待融锡粒推置Al2O3滴落管开口处,并使其落至基板表面.为获取熔滴在基板表面润湿的清晰轮廓,采用650 nm波长的激光作为背光源,在相机镜头前配以此波长的滤光片来过滤炉内杂光,待融锡粒完全融化(即t = 0 s,t为熔滴在基板表面等温润湿的时间),采用高分辨相机记录整个润湿铺展过程,对所获得图像信息利用数据分析终端计算接触角和接触半径.
润湿试验后,选取典型样品,将其沿横截面切开并抛光,用配备能谱仪(EDS)的FEG 450扫描电子显微镜(SEM,Quanta Feg-450,荷兰)对界面三相线、微观结构及化学组分进行分析.
2. 试验结果
图1为IMC基板纵截面的微观结构. IMC基板以Cu为基体,表面由两层连续的IMC层构成. 在润湿试验中与液相直接接触的Cu6Sn5层平均厚度约45 μm,底下Cu3Sn层约22 μm. 由于金属/金属润湿体系中的润湿性对基板表面初始状态十分敏感,润湿试验前基板表面的原始状态由XPS表征,如图2所示. 图2a和2b分别为电荷校正后的Cu2p和Au4f的特征峰,分别对应于Cu基板(上部分黑线)和离子溅射后的IMC基板. 对于Cu基板,由于Cu2O和金属铜的结合能很接近,并不能直接通过Cu2p(Cu2p1/2和Cu2p3/2) 峰将其区分,但微弱的卫星峰(如图2a中黑色虚线矩形标记)表明基板表面呈氧化状态(即有Cu2O膜). 图2b中显示,由于Au4f区域具有良好的分离自旋轨道组分约为3.7 eV,表明IMC上的Au处于金属态,且Au薄膜的厚度约为10 nm,在Au薄膜下并未检测到Cu或Sn的氧化物.
图3为锡在铜基板表面及IMC基板表面润湿过程中接触角及归一化半径随时间变化的关系. 从图中可以看出接触角跟半径都随时间呈单调变化,其中各个温度下,锡在IMC表面上的润湿性明显好于锡在铜表面的润湿性. 温度对Sn/IMCs的初始接触角有显著的影响,而对平衡接触角则影响不大;温度对Sn/Cu的初始接触角及平衡接触角的影响均不明显. 从归一化半径与时间的关系(图2b),不难发现,3个试验温度下,Sn/IMCs的铺展速率均分别大于Sn/Cu的铺展速率,且前者在最低试验温度350 ℃时的铺展速率比后者最高试验温度450 ℃还要大得多.
润湿试验后,选取典型试样,对其横截面用SEM进行观察,如图4所示. 图4a ~ 4b和图4c ~ 4d分别对应于400 ℃时Sn/Cu和Sn/IMCs的界面形貌. 图4a,4c对应三相线附近的位置,图4b,4d对应界面中心的位置. Sn/Cu和Sn/IMCs两者的界面产物都分为上下两层,EDS结果表明上层为Cu6Sn5,下层为Cu3Sn,且其平均厚度已在图中标记. 两个体系中Cu3Sn均厚于Cu6Sn5,且就IMC层的总厚度而言,Sn/Cu体系界面中心处与三相线附近处无明显差异,Sn/IMCs体系界面中心处却略厚于三相线附近处. 尽管Sn/IMCs具有更好的润湿性,但润湿试验前后界面IMC层的厚度变化并不显著,试验前IMC层的总厚度为67 μm,试验后界面中心处IMC层厚68.5 μm,三相线附近IMC层厚58.8 μm,这小范围的厚度变化说明了界面存在IMC的溶解,具体表现为Cu3Sn的增厚和Cu6Sn5的变薄.
3. 分析与讨论
按照反应产物决定润湿理论(RPC理论)[8],界面产物决定润湿性及润湿行为. 在Sn/Cu体系中,倘若考虑到如下界面反应发生
$$ x{\rm{Cu}} + y{\rm{Sn}} \to {\rm{C}}{{\rm{u}}_x}{\rm{S}}{{\rm{n}}_y} $$ (1) Yost等人[12]认为单位长度内体系的自由能可由下式描述
$$\frac{{{\rm{d}}G}}{{{\rm{d}}r}} = 2{\text{π}} r[\varepsilon + \sigma _{\rm{lv}}^{\rm{S_n}}(\cos {\theta _{\rm{d}}} - \cos {\theta _{\rm{e}}})]$$ (2) 式中:r为瞬时接触半径;
$\sigma _{\rm{lv}}^{\rm{S_n}}$ 为Sn熔滴的表面张力;θd为Sn熔滴的瞬时接触角;θe为Sn熔滴的平衡接触角;ε为反应中过剩自由能产生的铺展驱动力,其值等于ρCulCuΔG/(xMCu);ΔG为CuxSny的吉布斯形成自由能,Cu6Sn5和Cu3Sn的ΔG分别为−7 747.65 − 0.371 T (J/mol)[12]和−11 318.4 + 3.1 T (J/mol)[13];ρCu为Cu的密度;lCu为反应层的厚度;MCu为Cu的摩尔质量.基于上式,体系的铺展驱动力约为−3.3 × 103~ − 5.3 × 103 J/m2,与式(2)中表面张力引起的非平衡驱动力,即$\sigma _{\rm{lv}}^{\rm{Sn}}(\cos {\theta _{\rm{d}}}\;- \cos {\theta _{\rm{e}}})$ 相比(约为1 J/m2),界面反应可能成为铺展的驱动力.按照文献[14-15]报道,界面先析出相为Cu6Sn5,倘若铺展的行为由界面反应产物Cu6Sn5的析出决定,那么Cu6Sn5的析出率或形核速率应与铺展速率相当. Cu6Sn5的析出速率可以估算为[16-17]
$$J = {J_0}\exp \left[ - \frac{{16{\text{π}} \sigma _{\rm{sl}}^3}}{{3kT{{(\Delta {G_{\rm{v}}})}^2}}}\left(\frac{{{{\cos }^3}{\theta _{\rm{n}}} - 3\cos {\theta _{\rm{n}}} + 2}}{4}\right)\right]$$ (3) 式中:J0为表面形核的频率因子(约为1031 ± 1 /m2·s);σsl为固液界面张力(约为0.05 ~ 0.15 J/m2)[18-19];k为玻尔兹曼常数;θn为形核与固相形成的接触角(约为23o)[20];ΔGv为形核驱动力(约为245 ~ 1 043 J/mol)[18]. 假设形成1 μm厚的Cu6Sn5层,形成的Cu6Sn5层扩展速率将在105 m/s数量级,相比于三相线移动速率(~ 10−6 m/s), 显然不受控于Cu6Sn5的析出.
按照整个动力学过程受限于其中最慢的一个环节,假设三相线附近先发生如下反应
$$ {\rm{Sn + 2C}}{{\rm{u}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{O}} \to {\rm{Sn}}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{ + 4Cu}} $$ (4) $$ {\rm{5Sn + 6Cu}} \to {\rm{C}}{{\rm{u}}_{\rm{6}}}{\rm{S}}{{\rm{n}}_{\rm{5}}} $$ (5) 那么整个铺展过程有可能受限于反应(4)的动力学过程. 从图3b中的Rd/R0-t曲线也可以看出近线性铺展的特征与反应控制铺展的特征相似. 值得注意的是IMC的润湿性对气氛中的氧十分敏感,即使表面存在非常薄的金膜,金膜随着加热过程中会固溶于IMC中,进而形成(Cu, Au)6Sn5. 其中IMC基板润湿试验后的表面经XPS检测,发现了Cu2O的氧化峰印证了上述事实. 这就导致限制Sn/Cu和Sn/IMCs两个体系铺展的因素十分接近,即受控于反应(4). 其中ln1/te与1/T的Arrhenius曲线关系(te为达到铺展平衡所需的时间)如图5所示,可推导得到润湿激活能分别为22.270 kJ/mol和20.469 kJ/mol,两者相近的激活能表明铺展可能受限于同一机制. 反应(4)的反应吉布斯自由能如果按照表面相反应理论估算,其值为体相反应自由能的1/4,那么也可以推导出铺展激活能与反应式(4)表面相反应的吉布斯自由能接近. 表明整个铺展过程受限于反应(4)的动力学过程.
4. 结论
(1) 在试验温度下,Sn在Cu6Sn5表面的润湿性要好于Sn/Cu体系,导致润湿性差异的主要原因来自于基板表面的氧化膜的影响,故RPC模型不能用来预测此体系中的润湿性.
(2) Sn/Cu和Sn/IMCs的润湿过程受限于锡与表面氧化膜的反应而非界面析出的金属间化合物,铺展激活能为分别为22.270 kJ/mol和20.469 kJ/mol.
-
-
[1] Cornelius B, Treivish S, Rosenthal Y, et al. The phenomenon of tin pest: a review[J]. Microelectronics Reliability, 2017, 79: 175 − 192. doi: 10.1016/j.microrel.2017.10.030
[2] 王慧, 薛松柏, 陈文学, 等. Ag, Al, Ga对Sn-9Zn无铅钎料润湿性能的影响[J]. 焊接学报, 2007, 28(8): 33 − 36. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-360x.2007.08.009 Wang Hui, Xue Songbai, Chen Wenxue, et al. Effect of Ag, Al, Ga addition on wettability of Sn-9Zn lead-free solder[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2007, 28(8): 33 − 36. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-360x.2007.08.009
[3] Cheng S, Huang C M, Pecht M. A review of lead-free solders for electronics applications[J]. Microelectronics Reliability, 2017, 75: 77 − 95. doi: 10.1016/j.microrel.2017.06.016
[4] Kang Yuqing, Shen Haoran, Fu Yang, et al. Microstructure evolution and mechanical properties of the Sip/Zn-Al composite joints by ultrasonic-assisted soldering in air[J]. China Welding, 2018, 17(2): 39 − 44.
[5] 张亮, Tu K N, 孙磊, 等. Sn-0.3Ag-0.7Cu-xSb无铅钎料润湿性[J]. 焊接学报, 2015, 36(1): 59 − 62. Zhang Liang, Tu K N, Sun Lei, et al. Wettability of Sn-0.3Ag-0.7Cu-xSb lead-free solders[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2015, 36(1): 59 − 62.
[6] 曾承宗, 林巧力, 曹睿, 等. 冷金属过渡下熔融铝合金在钢板上润湿铺展的数值模拟[J]. 焊接学报, 2017, 38(3): 61 − 65. Zeng Chengzong, Lin Qiaoli, Cao Rui, et al. Simulation of spreading of molten Al alloy on Q235 steel under the cold metal transfer condition[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2017, 38(3): 61 − 65.
[7] Eustathopoulos N, Nicholas M G, Drevet B. Wettability at high temperatures[M]. Oxford: Elsevier, 1999.
[8] Wedi A, Baither D, Schmitz G. Contact angle and reactive wetting in the SnPb/Cu system[J]. Scripta Materialia, 2011, 64(7): 689 − 692. doi: 10.1016/j.scriptamat.2010.12.026
[9] Satyanarayana, Prabhu K N. Study of reactive wetting of Sn-0.7Cu and Sn-0.3Ag-0.7Cu lead free solders during solidification on nickel coated Al substrates[J]. International Journal of Chemical, Molecular, Nuclear, Materials and Metallurgical Engineering, 2013, 7: 25 − 28.
[10] Wang H, Gao F, Ma X, et al. Reactive wetting of solders on Cu and Cu6Sn5/Cu3Sn/Cu substrates using wetting balance[J]. Scripta Materialia, 2006, 55(9): 823 − 826. doi: 10.1016/j.scriptamat.2006.07.017
[11] Hosking M, Yost F G. The mechanics of solder alloy wetting and spreading [M]. New York: Springer Science & Business Media, 2012.
[12] Yost F G, Romig A D. Thermodynamics of wetting by liquid metals[M]. Pittsburgh: Materials Research Society, 1988.
[13] Sobiech M, Krüger C, Welzel U, et al. Phase formation at the Sn/Cu interface during room temperature aging: Microstructural evolution, whiskering, and interface thermodynamics[J]. Journal of Materials Research, 2011, 26(12): 1482 − 1493. doi: 10.1557/jmr.2011.162
[14] Salleh M A A M, Mcdonald S D, Yasuda H, et al. Rapid Cu6Sn5 growth at liquid Sn/solid Cu interfaces[J]. Scripta Materialia, 2015, 100: 17 − 20. doi: 10.1016/j.scriptamat.2014.11.039
[15] Huang M L, Yang F, Zhao N, et al. In situ study on dissolution and growth mechanism of interfacial Cu6Sn5 in wetting reaction[J]. Materials Letters, 2015, 139: 42 − 45. doi: 10.1016/j.matlet.2014.10.041
[16] Volmer M, Weber A. Keimbildung in übersättigten Gebilden[J]. Zeitschrift für physikalische Chemie, 1926, 119(1): 277 − 301.
[17] Bondy A. The spreading of liquid metals on solid surfaces[J]. Chemical Reviews, 1953(2): 417 − 458.
[18] Bader S, Gust W, Hieber H. Rapid formation of intermetallic compounds interdiffusion in the Cu-Sn and Ni-Sn systems[J]. Acta Metallurgica Et Materialia, 1995, 43(1): 329 − 337.
[19] Jena A K, Chaturvedi M C. Phase transformation in materials[M]. New Jersey: Prentice Hall, 1992.
[20] Gagliano R A, Ghosh G, Fine M E. Nucleation kinetics of Cu6Sn5 by reaction of molten tin with a copper substrate[J]. Journal of Electronic Materials, 2002, 31(11): 1195 − 1202. doi: 10.1007/s11664-002-0010-1
-
期刊类型引用(1)
1. 朱明涛,孟云娜,凡亚丽,卢晨,侯雨珊,倪锋. 粉末烧结Cu-C-SnO_2多孔材料摩擦磨损特性研究. 粉末冶金工业. 2022(01): 36-44 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)




 下载:
下载: