Microstructure and properties of Fe-Cr-C-B-W alloy by self-shielded flux-cored wire open-arc surfacing
-
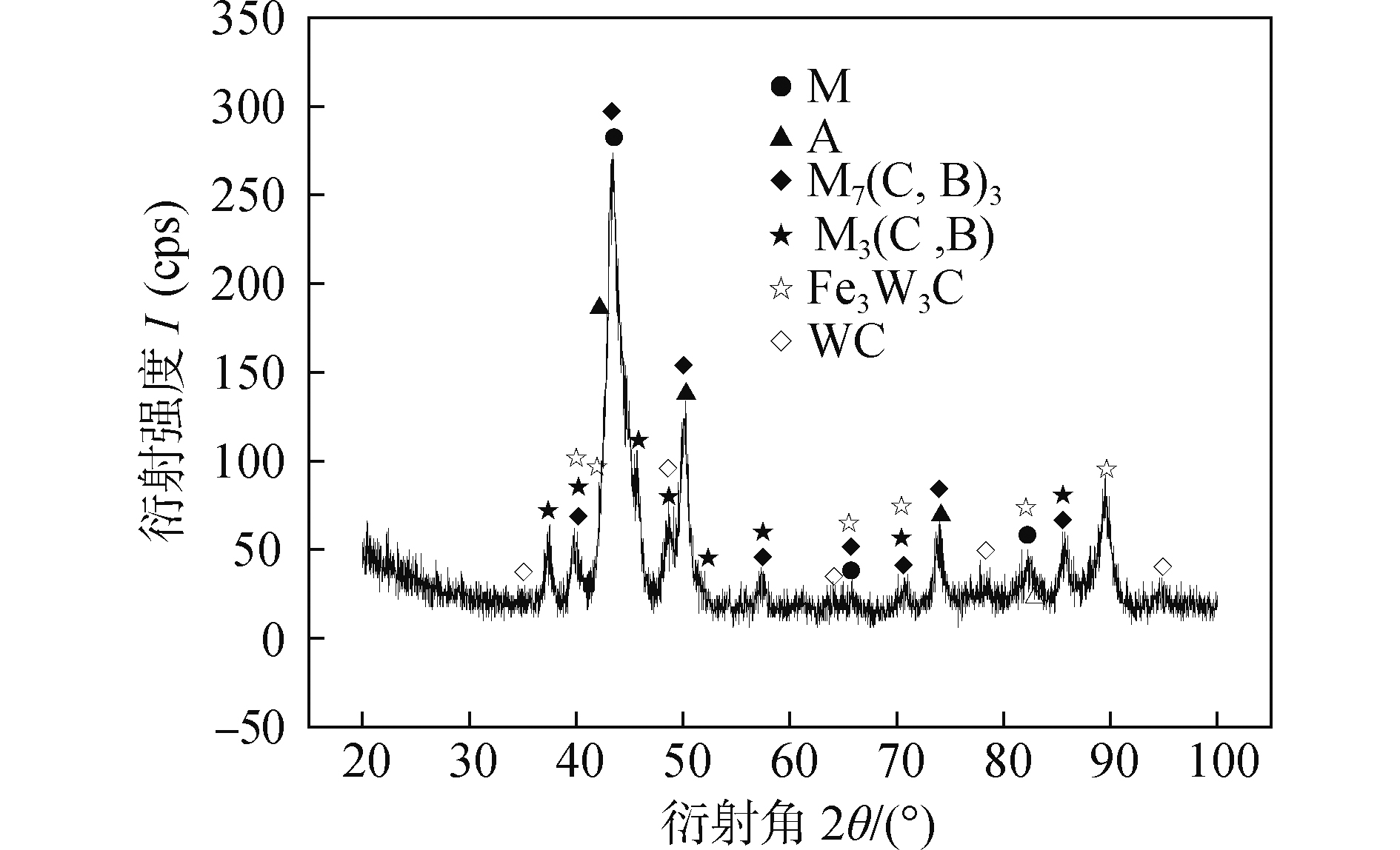
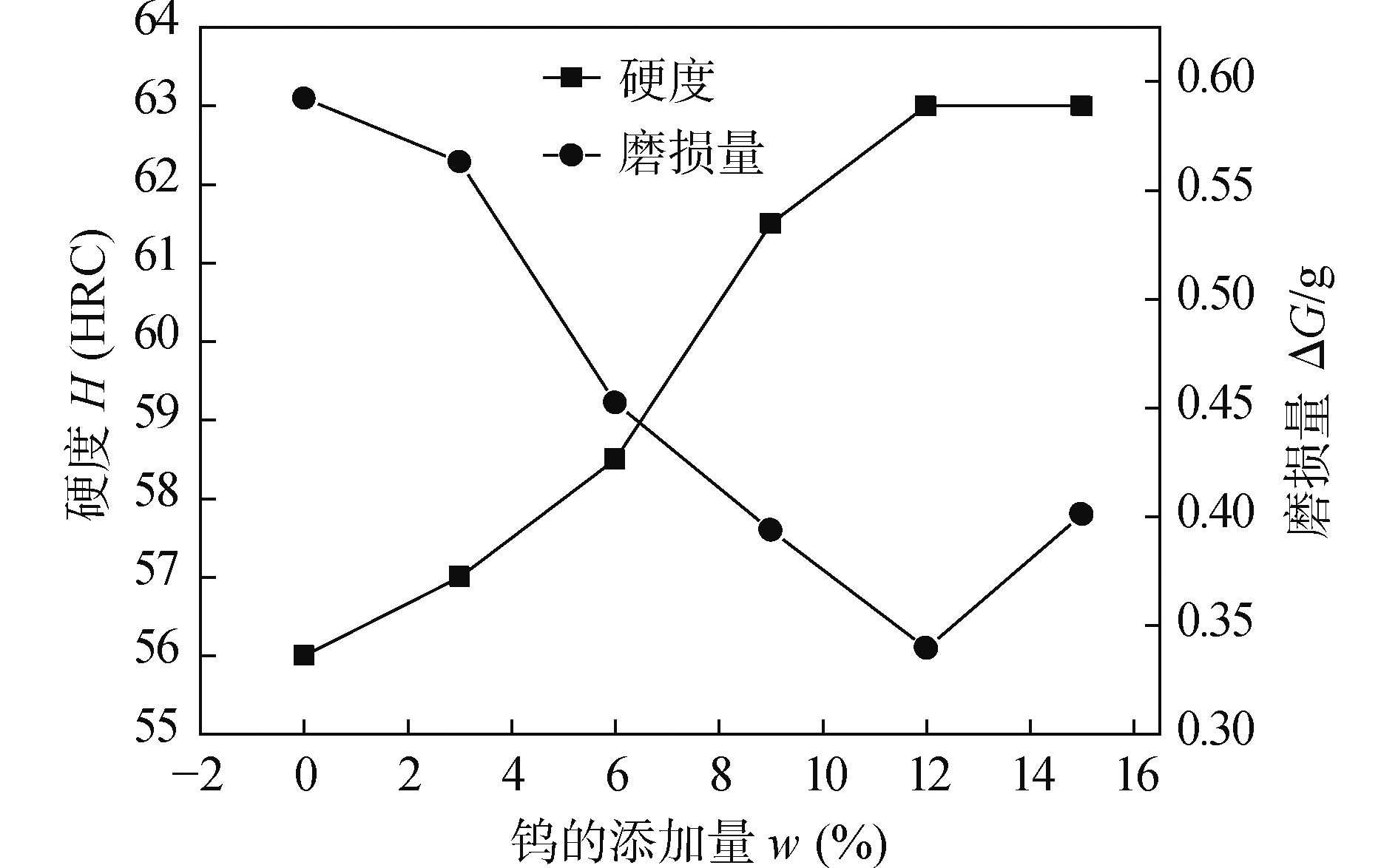
摘要: 采用自保护药芯焊丝明弧堆焊技术制备五组不同钨含量的Fe-Cr-C-B-W合金. 借助金相显微镜、扫描电子显微镜、X射线衍射仪、洛氏硬度计和磨损试验机分析堆焊合金的组织及性能. 结果表明,合金的显微组织由马氏体、残余奥氏体、M7(C,B)3,M3(C,B),Fe3W3C和WC组成. 大部分钨元素被迁移到晶界生成了比WC稳定性更好的Fe3W3C缺碳复合相,堆焊层中没有典型的初生WC硬质相颗粒生成. 随着钨添加量的增多,共晶硬质相M7(C,B)3,M3(C,B)和Fe3W3C随之增多,间距减小,呈连续网状均匀分布. 当钨的添加量为12%时,堆焊层的耐磨性达到最佳.
-
关键词:
- 自保护药芯焊丝 /
- 明弧堆焊 /
- Fe-Cr-C-B-W合金 /
- 组织及性能
Abstract: Five Fe-Cr-C-B-W alloy samples with different W contents were prepared by self-shielded flux cored wire arc surfacing technology. Microstructure and properties of surfacing alloys were analyzed by metallographic microscope, scanning electron microscope, X-ray diffractometer, Rockwell hardness tester and wear tester. The results show that the microstructure of the surfacing alloy consists of martensite, retained austenite, M7(C,B)3, M3(C,B), Fe3W3C and WC. Most of W is migrated to the grain boundary to produce Fe3W3C C deficiency composite phase which is more stable than the WC. There are no typical primary WC hard phase particles in the surfacing layer. With the increase of W content, the eutectic hard phase M7(C,B)3, M3(C,B) and Fe3W3C increase, and the spacing decreases. And they are continuous and evenly distributed. When the addition amount of W is 12%, the wear resistance of the surfacing layer is the best. -
0. 序言
奥氏体不锈钢复合板具有良好的焊接性和可加工性,广泛应用于石油和化工行业. 304/Q345R复合板主要以Q345R作为基体,在表面利用爆炸焊复合上304复层,不仅具有碳钢良好的焊接性能和高强度,而且还具有不锈钢的耐腐蚀、耐磨损、高导热等特性,同时大大节省成本[1]. 针对焊接的数值模拟过程,国内学者进行了大量研究,重庆大学的邓德安等人[2]开发了热-弹-塑性有限元方法计算了10 mm厚的多种坡口形式的304不锈钢对接接头的残余应力和焊接变形,试验证明该数值计算方法是可靠的. 中国石油大学(华东)的Jiang等人[3-4]采用中子衍射和有限元相结合的方法计算了304不锈钢复合钢板补焊过程中的残余应力,获得了沿厚度方向的残余应力分布. 丁肖等人[5]研究了304/Q345R复合板焊接接头的力学性能,发现复层侧硬度在焊接热影响区明显增大,进入焊缝区域硬度大幅下降;基层侧硬度值在热影响区略有上升. 奥氏体不锈钢与低合金钢焊接过程中,焊缝与相邻的热影响区元素含量差别很大,并且通常采用ERNiCr-7焊丝焊接SA508和316L金属,TIG焊接在焊缝生成树枝状晶状凝固组织,晶界存在M23C6碳化物,晶粒内部存在少量Ti(C, N)碳氮化合物与Al2MgO4化合物共生的双层结构夹杂物[6]. 然而由于奥氏体不锈钢复合板结构复杂,焊接过程中的热力学行为与微观组织之间的关系以及微观组织与焊后残余应力的分布规律并未明了,因此还需进一步研究.
基于弹塑性理论,以304/Q345R复合板为研究对象,采用试验和模拟相结合的方法研究焊接接头处的微观组织、温度场分布以及残余应力分布规律,讨论焊接温度场对复合板焊接接头微观组织和力学性能的影响,旨在为不锈钢/低合金钢等复合板的焊接工艺设计与优化提供理论依据.
1. 试验方法
1.1 试验材料
试验选用两块304/Q345R复合板,每块尺寸分别为200 mm × 100 mm × 8 mm,其中基层为Q345R,厚度为6 mm,复层为304不锈钢,厚度为2 mm,304与Q345R之间通过爆炸焊连接,为研究基层焊接对复层坡口的影响,在复层刨去宽为40 mm的倾斜焊道,坡口形式和焊道分布如图1所示,复合板的焊接采用V形坡口,坡口角度为60 °,基层依次焊接1,2两道,复层依次焊接3,4,5,6,7,8六道. 304/Q345R复合板的基层与复层化学成分见表1,试验选用ER50-6焊丝、J507和302焊条作为焊接材料,各焊接材料化学成分见表2.
表 1 Q345R和304不锈钢化学成分(质量分数,%)Table 1. Chemical compositions of Q345R steel and 304 stainless steel母材 C Si Mn P S Ni Cr Fe Q345R 0.20 0.247 0.604 ≤ 0.025 0.04 0.061 0.052 余量 304 0.07 0.345 1.091 ≤ 0.045 0.036 8.215 18.09 余量 表 2 焊接材料化学成分(质量分数,%)Table 2. Chemical compositions of the filler rods焊接材料 C Mn Si S P Ni Cr Mo Cu Fe ER50-6 0.105 0.163 0.975 0.013 0.015 0.016 — 0.06 — 余量 J507 0.12 1.60 0.75 0.035 0.040 0.30 0.20 0.30 — 余量 302 0.064 0.80 0.70 0.010 0.030 12.50 24.00 0.40 0.20 余量 为保证焊接接头的力学性能与焊缝的耐腐蚀性能,采用氩弧焊打底[7],Q345R基层与304复层均采用焊条电弧焊焊接. 由于经过爆炸焊和氩弧焊后,复合板的强度和硬度有所提高,但塑性减小,不利于之后的矫直及使用要求,因此一般要求通过热处理和超声波振动的方法来消除复合板的残余应力,及消除焊后的内应力,提高塑性. 焊接过程中主要控制焊接电压、电流和线速度,焊接参数见表3. 复层焊接采用直径为ϕ3.2 mm的小直径焊条、小电流、多道焊、浅熔深,有效地控制异种金属焊接间的元素稀释[8].
表 3 焊接工艺参数Table 3. Technological parameters of the welding process序号 焊接方法 焊层(道) 焊接电流I/A 电弧电压U/V 焊接时间t/s 冷却时间tc/s 焊条型号 直径ϕ/mm 1 氩弧焊 打底焊 146 22 — — ER50-6 3.2 2 焊条电弧焊 基层1 122 20 125 154 J507 3.2 3 焊条电弧焊 基层2 122 20 64 57 J507 3.2 4,5,6,7,8 焊条电弧焊 复层1,2,3,4,5 122 20 32 0 302 3.2 9 焊条电弧焊 复层6 122 20 50 冷却至室温 302 3.2 1.2 焊接热循环曲线测定
将3个热电偶分别焊接在如图2a所示的温度采集点上,用HPDJ-8125动态数据采集分析系统,采集焊接过程中的瞬态温度值. 按照拟定的焊接工艺进行焊接并采集数据. 能够测到各点位置的热循环曲线,现场测试图如图2b所示.
1.3 盲孔法测残余应力
采用HT21B型便携式数字残余应力检测仪对不同位置的残余应力进行测试,测量点的位置如图3中H,I,J所示. 利用盲孔法对焊接接头进行残余应力测试,用砂纸对测试区域进行打磨直至表面平整光滑,用棉球蘸取酒精擦拭测试区域,去除表面油脂和杂质,使用502胶将应变花固定在测试点区域,使用钻孔机对该点进行钻孔,钻孔直径ϕ2 mm,深约1.5 ~ 2 mm,记录显示器上的残余应力数值.
1.4 焊接接头微观组织表征
焊后使用机加工切割靠近焊缝几何中心位置且尺寸为10 mm × 10 mm × 8 mm的试样,进行金相制备,并利用王水对基层与复层的焊缝区域侵蚀[9],采用光学显微镜对焊接接头的不同区域进行微观组织观察,并使用电子探针对熔合线处的元素扩散进行分析.
1.5 焊接过程建模
1.5.1 三维建模与网格划分
为研究焊接过程中热循环曲线与焊接残余应力规律,采用三维有限元模型,如图4所示,建模时将整块板分为基层与复层两部分,由于基层与复层为整体建模,其交界处的热传递和应力会根据材料的热物理属性不同而发生传递,不考虑层间温度. 共划分20 763个单元结点,46 892个单元. 在模型网格划分过程中,对焊缝处网格采用加密处理,热影响区与距焊缝10 ~ 12 mm的区域内采用过渡网格,母材区采用稀疏网格.
1.5.2 材料热物理性能参数
304不锈钢/Q345R碳钢复合板基层与复层材料的热物理材料属性如图5所示.
1.5.3 热源模型
选用双椭球[10]分布热源作为数值模拟的热源模型,双椭球模型在板材上移动的体积热源分为前、后两部分. 前半球的解析表达式为
$$q\left( {x,y,{\textit{z}}} \right) = \frac{{6\sqrt 3 {f_{\rm{f}}}{q_0}}}{{ab{c_{\rm{f}}}{\text π} \sqrt {\text π} }}{\rm{exp}} \left( { - \frac{{3{{{x}}^2}}}{{{c_{\rm{f}}}^2}} - \frac{{3{{{y}}^2}}}{{{{{a}}^2}}} - \frac{{3{{\textit{z}}^2}}}{{{{{b}}^2}}}} \right)$$ (1) 后半球的解析表达式为
$$q\left( {x,y,{\textit{z}}} \right) = \frac{{6\sqrt 3 {f_{\rm{b}}}{q_0}}}{{ab{c_{\rm{b}}}{\text π} \sqrt {\text π} }}{\rm{exp}} \left( { - \frac{{3{x^2}}}{{{c_{\rm{b}}}^2}} - \frac{{3{y^2}}}{{{a^2}}} - \frac{{3{{\textit{z}}^2}}}{{{b^2}}}} \right)$$ (2) 式中:cf,cb,a,b均为双椭球热源分布参数;ff,fb分别为前、后半椭球体内能量分配系数,并且满足ff + fb等于2;q为焊接热输入功率.
1.5.4 边界条件
在焊接温度场中,主要由焊缝处的移动热源进行传热,故载荷为作用在焊缝的体热通量,其大小为1. 在焊接过程中,由于受焊缝处热源影响,整块焊件表面与周围环境进行传热,因此选取焊板的所有外表面为对流换热表面,设置焊接前初始温度为室温20 ℃. 热辐射和对流为焊接与环境进行热交换的主要方式,其中反射率为0.85,Stefan-Boltzmann常数为5.67 W/(m2·K4),对流传热系数为10 W/(m2·K).
在焊接应力场中,对复合板底面的四个顶点施加固定约束,限制其在x和y方向的位移.
2. 试验结果分析
2.1 焊接接头金相组织分析
图6所示为基层焊缝施焊后但复层未焊接前,复层坡口处的取样位置图,分别对图6中L,M,N 3个试样进行微观组织观察.
图7a,7b,7c中所示复层的微观组织分别与图6中L,M,N所对应. 利用截距法[11]测量晶粒尺寸得图7a中奥氏体晶粒大小为31.8 μm,图7b中奥氏体晶粒大小为36.4 μm,图7c中晶粒大小为40.2 μm. 图7a与图7b中奥氏体成分均匀且晶粒细小,而图7c中奥氏体成分较为稀疏且晶粒粗大. 由于图7a的取样位置距离焊道较近,受到的焊接热影响较大,由珠光体和铁素体转变而成的奥氏体会更加细小均匀,而图7c复层坡口位置距离焊道较远,受到焊接热影响相对较小.
如图6所示,分别在复合板R,S,T位置截取试样,其中R,S,T 3处的取样位置分别对应图8、图9和图10中的金相组织位置.
图8所示为304/Q345R复合板爆炸焊界面处的微观组织. 其中复层和基层之间经爆炸后的界面焊缝为波状[12]. 304复层与302焊条界面有熔合区,熔合区左右两侧分别为复层母材区和复层焊缝区,焊缝与母材组织均为奥氏体组织,但焊缝的奥氏体晶粒更加细小均匀. 波状边界的下方为Q345R基层组织,主要由铁素体和珠光体组成.
图9所示为复层焊缝处的金相组织,由图可知焊缝组织中奥氏体基体上和周围区域还分布着黑色蠕虫状δ铁素体. 在焊缝的凝固过程中,δ铁素体的存在会阻碍了奥氏体柱状晶粒的长大. 由于复层焊接过程中热输入较大,可能造成铁素体的含量较高,而铁素体的存在会在一定程度上提高焊接接头的耐腐蚀性能以及防止焊缝热裂纹的产生.
图10所示为复层焊缝和复层母材交界处的金相组织,焊缝与复层之间产生了一条由板条状和针状的铁素体组成的带状熔合区,熔合区左上方为焊缝组织,右下方为母材区域. 在熔合线附近,焊缝金属为柱状奥氏体晶粒,而且相比于其他区域晶粒更加细小. 通常,焊缝金属的奥氏体组织依附于半熔化的不锈钢复层表面开始结晶,图中可以看到304焊缝形成柱状晶粒,并且晶粒被细化,其原因可能为外层焊缝会熔化内层焊缝并在表面开始进行再结晶.
图11所示为304不锈钢对接时焊缝与母材区的金相组织,从图中可以看出,奥氏体主要呈带状分布,由于同种金属焊接时焊缝组织与过渡区域的成分与组织相差不大,两者之间并没有观察到明显的分界线.
2.2 温度场热循环曲线分析
为研究模拟过程中复合板的温度变化规律,选取模型中间横截面上3个检测点来观察温度随时间变化的热循环曲线. 该3个检测点分别位于复层第1道焊缝中心、复层第3道焊缝中心及复层第5道焊缝中心,所有点均位于焊缝截面的中心位置. 图12所示为各检测点的热循环曲线,由图可知,热源经过检测点时温度急剧升高,当热源经过之后,由于热源与检测点的距离逐渐变远,温度随着时间减小,直至其它焊道开始焊接时,温度再次升高.
为检验焊接温度场模拟的准确性,按照图2所示的测定位置,选取同样的3个点进行热电偶法试验测试,将模拟数据与热电偶法所测得的试验数据进行对比,对比结果如图13所示.
通过以上3组热循环曲线对比可以看出,模拟与试验结果能够较好的吻合,验证了建立模型的正确性与准确性,为残余应力场的模拟提供了基础.
2.3 热应力与残余应力分析
将温度场模型导入应力场中模拟得到焊接残余应力分布. 图14所示为复合板冯米塞斯(Von mises)应力分布云图,从图14a中可以看出,复合板残余应力主要集中在焊缝区,基层焊缝区的最大残余应力达到312 MPa,比复层焊缝区最大残余应力262 MPa略高,且残余应力的最大值基本集中在焊缝的两端. 从图14b中可以看出,由于304和Q345R两种材料的物理和化学性质的差异且模型采用一体建模,在焊接加热的过程中,异种材料的膨胀和冷却以及传热速率存在明显不同,在两种材料的交界处存在着应力不连续的情况.
3. 结论
(1) 304复合板焊接接头组织主要由奥氏体和铁素体组成. 复层熔合线附近的铁素体主要以板条状和针状形成带状过渡区域,而熔合线附近的奥氏体主要呈柱状晶粒分布,且平均晶粒尺寸相比于其他区域更加细小.
(2) 焊接接头的最大横向拉应力主要集中在熔合线附近,最大纵向拉应力出现在焊缝及热影响区,其值为283 MPa. 从焊缝、热影响区过渡到母材区,残余应力逐渐从最大值312 MPa降低到0 MPa,并趋于稳定.
(3) 复层在焊接过程中经过多次焊接,残余应力对基层板材产生了弯曲变形. 横向应力与纵向应力的模拟结果与盲孔法的测试结果较为吻合,证明了模型的正确性.
(4) 在焊接交界面处发现应力不连续现象,其原因可能为复层和基层材料力学性能差异造成,值得进一步研究. 另外,该现象建议可通过热处理或超声冲击进行改善.
-
表 1 不同钨添加量时堆焊层的化学成分(质量分数,%)
Table 1 Chemical compositions of surfacing layer with different W contents additions
钨添加量w(%) Cr C B W Fe 3 13.31 1.47 0.52 0.84 余量 6 13.55 1.52 0.51 1.71 余量 9 12.79 1.54 0.52 2.55 余量 12 12.94 1.51 0.55 3.47 余量 15 13.48 1.54 0.53 4.29 余量 -
[1] 张冀, 陈金梅, 冉申, 等. 碳化硅增强金属基复合材料的新型制备工艺[J]. 航空制造技术, 2014(6): 109 − 112. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-833X.2014.06.023 Zhang Ji, Chen Jinmei, Ran Shen, et al. New preparation technology of silicon carbide particles reinforced metal matrix composites[J]. Aeronautical Manufacturing Technology, 2014(6): 109 − 112. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-833X.2014.06.023
[2] Tang S L, Gao Y M, Li Y F. Recent developments in fabrication of ceramic particle reinforced iron matrix wear resistant surface composite using infiltration casting technology[J]. Ironmaking and Steelmaking, 2014, 41(8): 633 − 640. doi: 10.1179/1743281213Y.0000000175
[3] Ma Y P, Li X L, Wang C H, et al. Microstructure and impact wear resistance of Ti N reinforced high manganese steel matrix[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research International, 2012, 19(7): 60 − 65. doi: 10.1016/S1006-706X(12)60114-9
[4] 宗琳, 郭宁, 张晓玲. 原位合成(Ti, V)C增强铁基耐磨复合材料的研制[J]. 焊接学报, 2017, 38(8): 10 − 14. doi: 10.12073/j.hjxb.20150911001 Zong Lin, Guo Ning, Zhang Xiaoling. Investigation on wear resistance of in-situ (Ti, V)C reinforced Fe-based composite material[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2017, 38(8): 10 − 14. doi: 10.12073/j.hjxb.20150911001
[5] 刘政军, 勾健, 贾华, 等. Fe-Cr-C-B-Nb堆焊合金的显微组织和耐磨性[J]. 焊接学报, 2018, 39(3): 75 − 78. doi: 10.12073/j.hjxb.2018390072 Liu Zengjun, Gou Jian, Jia Hua, et al. Microstructure and wear resistance of Fe-Cr-C-B-Nb hardfacing alloy[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2018, 39(3): 75 − 78. doi: 10.12073/j.hjxb.2018390072
[6] Liu Z J, Su J G, Liu D, et al. Influence of magnetic field on microstructure and properties of Ni60 plasma surfacing layer[J]. China Welding, 2005, 14(2): 145 − 148.
[7] He Yanan, Song Qiang, Sun Kang, et al. Microstructure and properties of in-situ chromium carbide composite coating by laser cladding[J]. China Welding, 2018, 27(4): 10 − 17.
[8] 王智慧, 杨爱弟, 贺定勇, 等. 真空熔覆镍基合金涂层中碳化钨颗粒转变行为[J]. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2008, 37(10): 1869 − 1871. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-185X.2008.10.039 Wang Zhuhui, Yang Aidi, He Dingyong, et al. The transformation of WC in Ni-based alloy coating by vacuum melting[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2008, 37(10): 1869 − 1871. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-185X.2008.10.039
[9] 袁有录, 李铸国. 原位自生WC增强Fe基涂层的组织及干滑动摩擦磨损性能[J]. 材料工程, 2016, 44(5): 47 − 53. doi: 10.11868/j.issn.1001-4381.2016.05.008 Yuan Youlu, Li Zhuguo. Microstructure and dry sliding friction and wear properties of in-situ synthesized WC reinforced Fe-based coating[J]. Journal of Materials Engineering, 2016, 44(5): 47 − 53. doi: 10.11868/j.issn.1001-4381.2016.05.008
[10] 李震, 孙荣禄. 激光功率对Ni基WC熔覆层组织和性能的影响[J]. 金属热处理, 2016, 41(9): 107 − 110. Li Zhen, Sun Ronglu. Influence of laser power on microstructure and properties of Ni-based WC clad layer[J]. Heat Treatment of Metals, 2016, 41(9): 107 − 110.
[11] 徐卫仙, 张群莉, 姚建华. 热锻模激光熔覆Co基WC涂层的高温磨损性能研究[J]. 应用激光, 2013, 33(4): 370 − 375. doi: 10.3788/AL20133304.0370 Xu Weixian, Zhang Qunli, Yao Jianhua. Research on high-temperature wear resistance of laser cladding Co-based WC composite coating on hot-forging die[J]. Applied Laser, 2013, 33(4): 370 − 375. doi: 10.3788/AL20133304.0370
[12] 吴慧剑, 龚建勋, 刘江晴, 等. WC含量对明弧堆焊奥氏体合金显微组织及耐磨性的影响[J]. 粉末冶金材料科学与工程, 2016, 21(4): 562 − 568. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-0224.2016.04.008 Wu Huijian, Gong Jianxun, Liu Jiangqing, et al. Effects of WC content on the microstructure and abrasion wear of open arc hardfacing austenitic alloy[J]. Materials Science and Engineering of Powder Metallurgy, 2016, 21(4): 562 − 568. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-0224.2016.04.008
[13] Berndt A F. Binary phase diagrams[J]. Journal of Chemical Education, 2001, 46(46): 3733 − 3736.
-
期刊类型引用(8)
1. 曹宇堃,郭枭,徐锴,吕晓春,魏超. 新型镍基合金带极堆焊金属三维组织特征. 焊接. 2023(09): 24-29+39 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 陈佩寅,郝乾宇,徐锴,郭枭. 基于微观组织的镍基合金焊接热裂纹判据. 焊接. 2023(10): 6-12 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 张楚昊,赵壮,陆骏,柏连发,韩静. 基于边缘导向算子模板匹配的熔池轮廓提取方法. 焊接学报. 2022(02): 67-74+118 .  本站查看
本站查看
4. 余磊,曹睿. 镍基合金焊接裂纹研究现状. 金属学报. 2021(01): 16-28 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 李娟,李霄,李磊磊,马欢,乔佳轶,朱鹏龙. FM 52M熔敷金属微观组织及热裂纹敏感性分析. 焊管. 2021(02): 11-15 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 侯永涛,霍树斌,陈佩寅,徐锴,陈波,郭枭. 镍基合金焊接性的研究方法综述. 金属加工(热加工). 2021(08): 19-23 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 俞照辉,孙浈,杨涛,简海林,李青华. Inconel 690/S32101异种合金搭接接头的组织与性能. 焊接学报. 2021(10): 44-48+100 .  本站查看
本站查看
8. 霍树斌,侯永涛,郭枭,徐锴,陈波,杨再勋. Ta、Nb元素对ERNiCrFe-13焊丝熔敷金属组织与性能的影响. 电焊机. 2021(12): 12-15+126-127 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(2)




 下载:
下载: