Microstructure and mechanical properties of CMT + P welding process on G115 steel
-
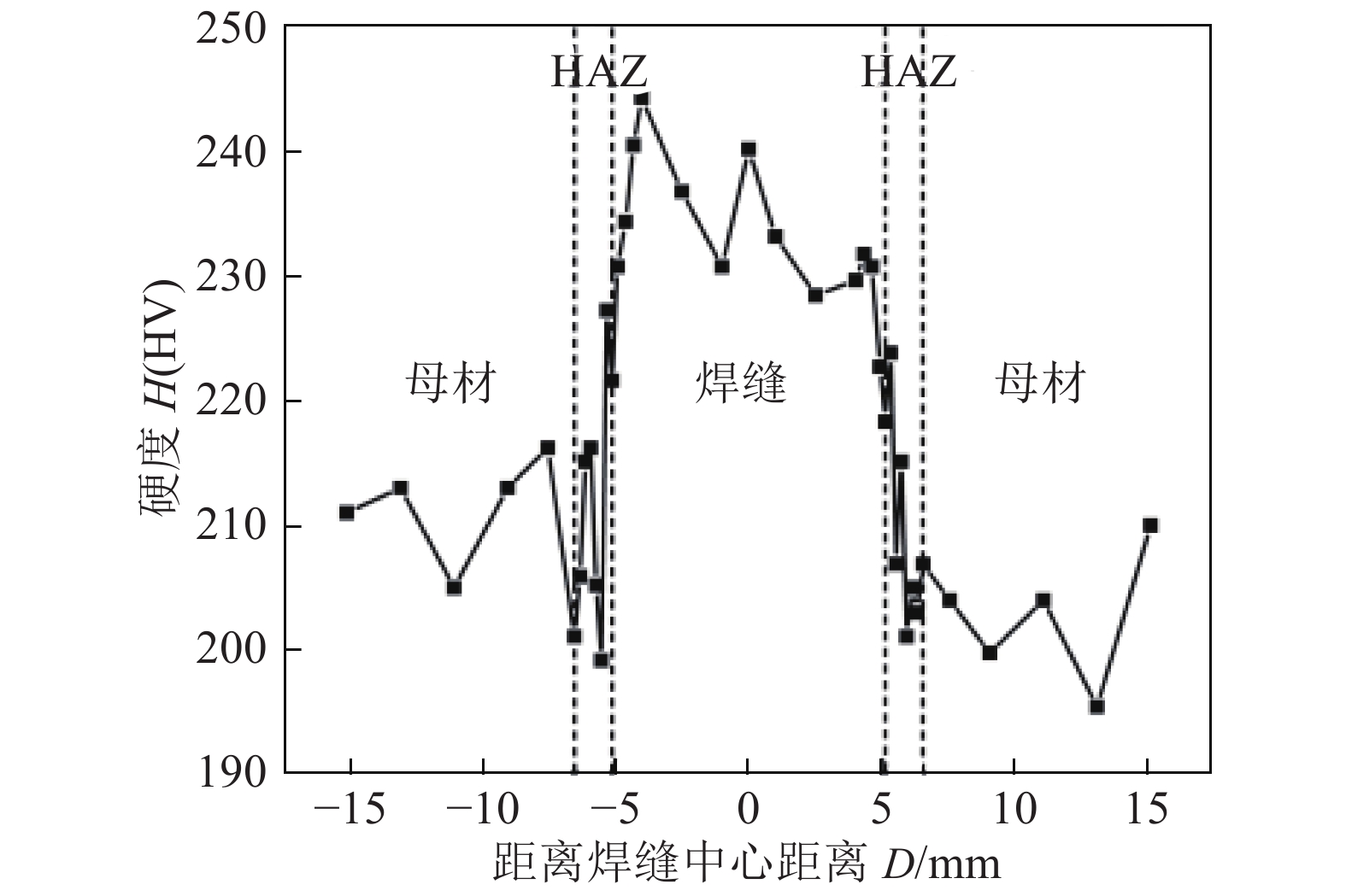
摘要: 基于冷金属过渡加脉冲(CMT + P)的焊接方法,研究了新型回火马氏体耐热钢G115的焊接性以及焊接接头组织和性能. 结果表明,焊接接头经热处理后为回火马氏体组织,焊缝晶粒呈现出等轴晶和柱状晶两种不同的形貌,而焊接热影响区和母材晶粒均为等轴晶. 与焊条电弧焊(SMAW)相比,CMT + P焊接方法有效降低了热输入,大幅度减小了热影响区宽度,提高了焊接接头的拉伸性能和热影响区冲击韧性,焊接接头焊缝冲击韧性略有降低. 焊接接头的室温和高温拉伸断裂机理均为韧性断裂,室温拉伸断口的韧窝内存在一定量的析出相.
-
关键词:
- 新型回火马氏体耐热钢 /
- 微观组织 /
- 力学性能 /
- 冷金属过渡
Abstract: Based on cold metal transfer + pulse welding (CMT + P) welding method, the weldability of G115, a novel tempered martensitic heat resisting steel, microstructures and mechanical properties of welding joint were studied. The results showed that the microstructure of the welding joint was tempered martensite after welding and heat treatment. Two different grains were found in the weld metal, while both the weld heat affected zone and the base metal were equiaxed grains. Compared with manual arc welding (SMAW), CMT + P welding method reduces the heat input effectively, diminishing the size of the heat-affected area prominently, improving the tensile performance of the welded joint and the impact toughness of the heat-affected area, weakening the impact toughness of the welded joint slightly. The tensile fracture mechanism of welded joints at room and high temperature is ductile fracture. A certain amount of precipitate exists in the dimples of tensile fracture at room temperature. -
-
表 1 焊接工艺参数
Table 1 Welding parameters
编号 热输入E/(kJ·cm−1) 送丝速度v1/(m·min−1) 焊接速度v2/(mm·s−1) 脉冲比 焊枪摆动幅度A/mm 摆动停留时间t/s 1 5.7 4.5 4 ~ 5 1∶10 无 无 2 5.7 4.5 4 ~ 5 1∶10 0.5 0.1 3 7.7 5 ~ 5.5 5 1∶15 1 0.2 -
[1] Liu Z, Xie X. The Chinese 700 ℃ A-USC development program[M]. Materials for Ultra-Supercritical and Advanced Ultra-Supercritical Power Plants, 2017.
[2] 李海昭, 梁军, 周超, 等. 正火温度对G115钢组织及室温强度的影响[J]. 金属热处理, 2018, 39(1): 71 − 76. Li Haizhao, Liang Jun, Zhou Chao, et al. Effect of normalizing temperature on microstructure and room temperature strength of G115 steel[J]. Heat Treatment of Metals, 2018, 39(1): 71 − 76.
[3] Xiao B, Xu L, Zhao L, et al. Tensile mechanical properties, constitutive equations, and fracture mechanisms of a novel 9% chromium tempered martensitic steel at elevated temperatures[J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2017, 690: 104 − 119. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2017.02.099
[4] Zhao L, Jing H, Xu L, et al. Analysis of creep crack growth behavior of P92 steel welded joint by experiment and numerical simulation[J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2012, 558: 119 − 128. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2012.07.094
[5] 徐忠峰, 王淦刚, 鲁立, 等. 焊后热处理对P92钢焊接接头显微组织和力学性能的影响[J]. 金属热处理, 2019, 44(1): 148 − 151. Xu Zhongfeng, Wang Gangang, Lu Li, et al. Effect of post-weld heat treatment on microstructure and mechanical properties of P92 steel welded joint[J]. Heat Treatment of Metals, 2019, 44(1): 148 − 151.
[6] 乔亚霞, 武英利, 徐连勇. 9% ~ 12%Cr高等级耐热钢的IV型开裂研究进展[J]. 中国电力, 2008(5): 33 − 36. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9649.2008.05.007 Qiao Yaxia, Wu Yingli, Xu Lianyong, et al. Research progress on Type IV cracking of 9% ~ 12%Cr high-grade heat-resisting steel[J]. Electric Power, 2008(5): 33 − 36. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9649.2008.05.007
[7] Zhao L, Jing H, Xu L, et al. Experimental study on creep damage evolution process of Type IV cracking in 9Cr0.5Mo1.8WVNb steel welded joint[J]. Engineering Failure Analysis, 2012, 19: 22 − 31. doi: 10.1016/j.engfailanal.2011.09.003
[8] 黄瀚川, 徐连勇, 荆洪阳, 等. SAF2507超级双相不锈钢CMT + P熔滴过渡特性[J]. 焊接学报, 2019, 40(10): 127 − 136. Huang Hanchuan, Xu Lianyong, Jin Hongyang, et al. Study on droplet transfer of CMT + P welding process in SAF2507 super duplex stainless steel[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2019, 40(10): 127 − 136.
[9] Ge J, Wang K, Zhang D, et al. Microstructure characteristics and mechanical properties of steel stud to Al alloy by CMT welding-brazing process[J]. China Welding, 2016, 25(1): 49 − 56.
[10] 陈庆宏, 吕小青, 徐连勇, 等. P92钢的CMT + P焊接接头组织性能[J]. 焊接学报, 2018, 39(12): 110 − 114. doi: 10.12073/j.hjxb.2018390308 Chen Qinghong, Lü Xiaoqing, Xu Lianyong, et al. Microstructure and properties of CMT + P welded joints of P92 steel[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2018, 39(12): 110 − 114. doi: 10.12073/j.hjxb.2018390308
-
期刊类型引用(16)
1. 张竟文,余黎明,刘晨曦,丁然,刘永长. 高Cr马氏体耐热钢的协同强化机制及形变热处理应用. 金属学报. 2024(06): 713-730 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 陈卫,刘斌,张琪飞,张震,李忠华,毕家伟. CMT+P焊接行为及其AE特征频率. 焊接学报. 2024(06): 89-96 .  本站查看
本站查看
3. 江骏东,马庆爽,陈乐利,罗锐,李会军,高秋志. G115钢模拟热影响区界面组织演变研究. 材料工程. 2024(11): 91-106 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 马志宝,郭新芳,姜海峰,蔡文河,杜双明,张学星,董树青,万夫伟. G115钢TIPTIG焊接接头组织与性能研究. 锅炉技术. 2024(06): 51-55 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 徐连勇,王成,杨连河,赵雷,荆洪阳,韩永典. P110套管内壁CMT/P堆焊Inconel 625合金的组织及性能研究. 机械工程学报. 2023(14): 159-168 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 刘岩,刘澳,张琳琳,杜安娜,刘兆真,贺春林. DP590镀锌双相钢CMT焊接接头气孔及锌层研究. 机械工程学报. 2023(16): 213-222 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 郄默繁,何长树,李送斌,尹玉环,封小松. 电弧增材制造Al-Zn-Mg-Cu合金组织与性能的研究. 航天制造技术. 2023(05): 28-33 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 黄靖,严靖博,易大伟,李斌,杨征. 高参数燃煤机组用高温材料焊接研究进展. 材料导报. 2023(S2): 375-382 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 何焕生,余黎明,刘晨曦,李会军,高秋志,刘永长. 新一代马氏体耐热钢G115的研究进展. 金属学报. 2022(03): 311-323 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 赵雷,冯国才,徐连勇,韩永典,荆洪阳. 新型马氏体耐热钢蠕变-疲劳性能与寿命预测. 焊接学报. 2022(05): 1-7+113 .  本站查看
本站查看
11. 郭新芳,崔凤友,范宏举,万夫伟,陈澜文,刘鹏,冯雪雁. 大口径厚壁G115耐热钢管TIG+SMAW工艺及性能分析. 电焊机. 2022(08): 101-107 .  百度学术
百度学术
12. 刘岩,刘晓昂,张琳琳,杜安娜,刘兆真,贺春林. DP590镀锌双相钢CMT焊接接头显微组织及力学性能. 焊接. 2022(07): 34-39 .  百度学术
百度学术
13. 张志强,白玉洁,徐连勇,韩永典,荆洪阳. UNS S32750超级双相不锈钢的CMT+P焊接工艺. 材料热处理学报. 2022(11): 197-206 .  百度学术
百度学术
14. 肖晖,马风辉. 9%Cr马氏体耐热钢C9MVW和5Co1焊条的研制. 机械制造文摘(焊接分册). 2022(06): 34-39 .  百度学术
百度学术
15. 张群兵,张建勋,魏文澜. 10%Cr耐热钢/镍基合金焊接接头高温疲劳性能. 焊接. 2021(05): 25-28+64 .  百度学术
百度学术
16. 寇荣魁,朱加雷,焦向东,童佟,李丛伟. 预热温度对U75V激光熔覆成形性能的影响. 焊接. 2021(10): 29-33+62 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(6)




 下载:
下载: